Abstract
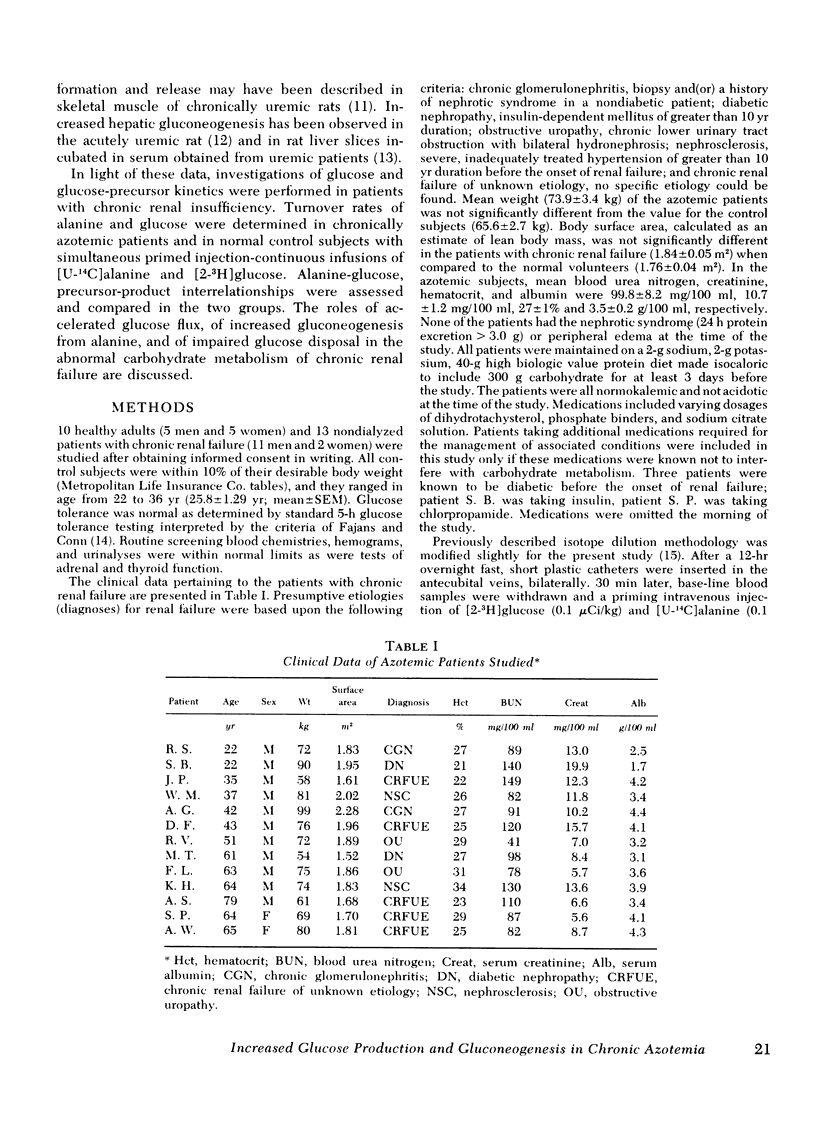
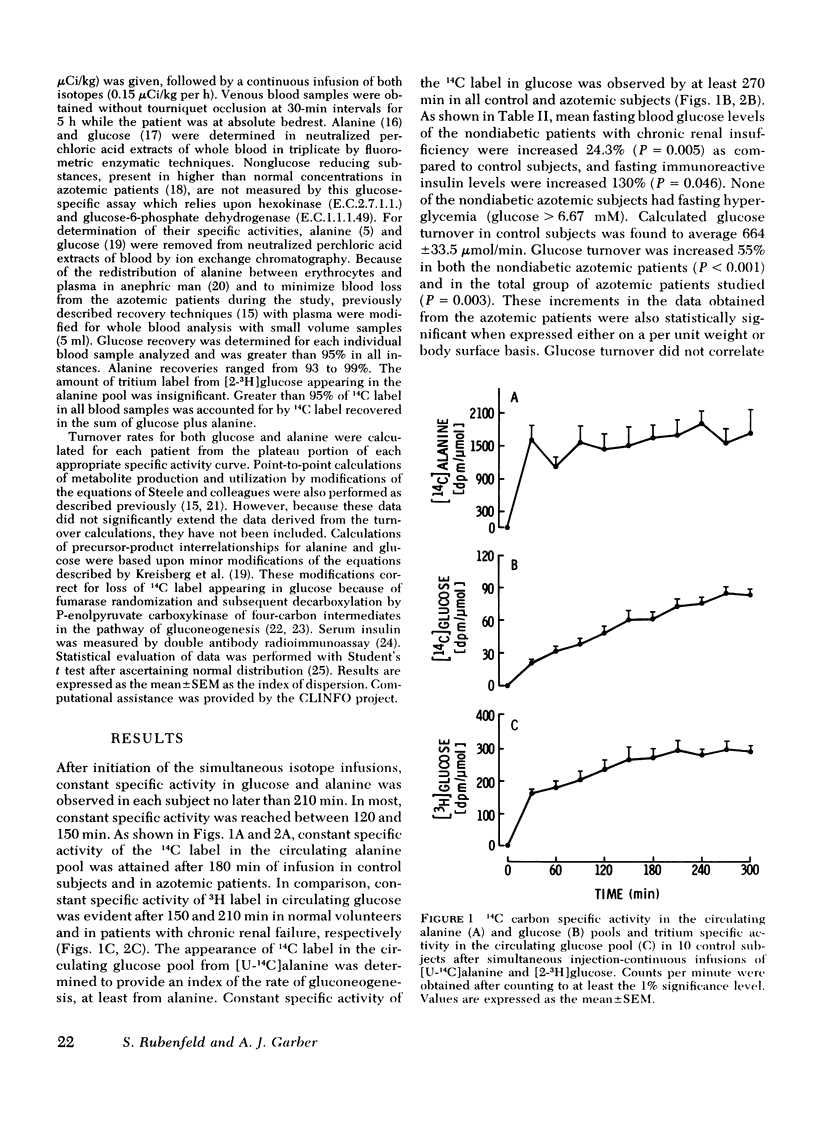
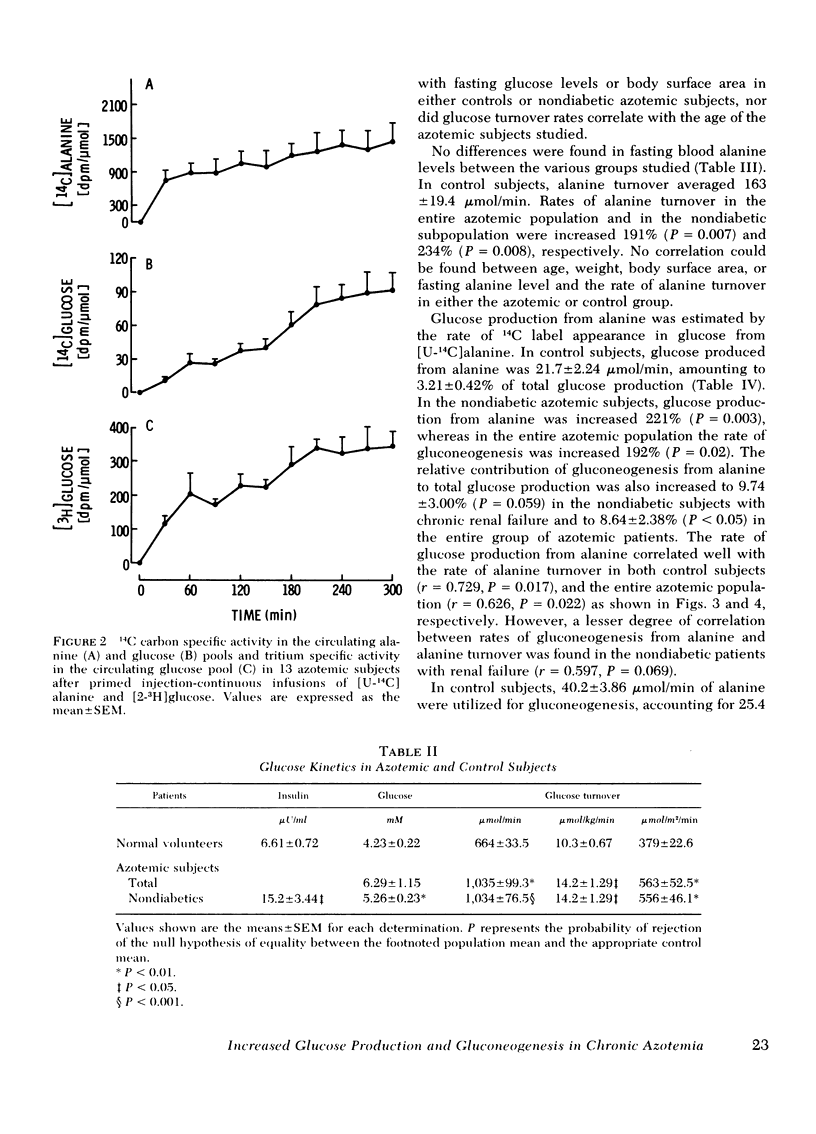
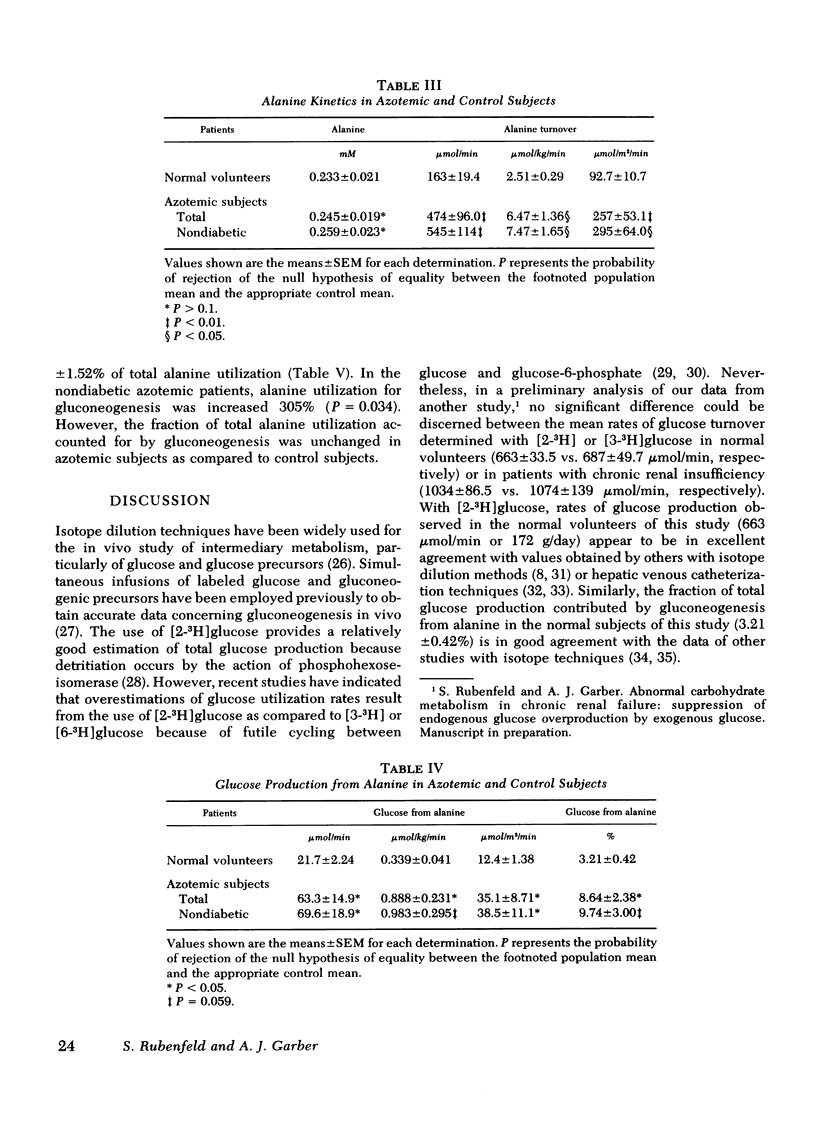
To delineate the potential role of disordered glucose and glucose-precursor kinetics in the abnormal carbohydrate metabolism of chronic renal failure, alanine and glucose production and utilization and gluconeogenesis from alanine were studied in patients with chronic compensated renal insufficiency and in normal volunteers. With simultaneous primed injection-continuous infusions of radiolabeled alanine and glucose, rates of metabolite turnover and precursor-product interrelationships were calculated from the plateau portion of the appropriate specific activity curves. All subjects were studied in the postabsorption state. In 13 patients with chronic renal failure (creatinine = 10.7±1.2 mg/100 ml; mean±SEM), glucose turnover was found to be 1,035±99.3 μmol/min. This rate was increased 56% (P = 0.003) over that observed in control subjects (664±33.5 μmol/min). Alanine turnover was 474±96.0 μmol/min in azotemic patients. This rate was 191% greater (P = 0.007) than the rate determined in control subjects (163±19.4 μmol/min). Gluconeogenesis from alanine and the percent of glucose production contributed by gluconeogenesis from alanine were increased in patients with chronic renal failure (192% and 169%, respectively) as compared to controls (P < 0.05 for each). Alanine utilization for gluconeogenesis was increased from 40.2±3.86 μmol/min in control subjects to 143±39.0 μmol/min in azotemic patients (P < 0.05). The percent of alanine utilization accounted for by gluconeogenesis was not altered in chronic renal insufficiency. In nondiabetic azotemic subjects, mean fasting glucose and immunoreactive insulin levels were increased 24.3% (P = 0.005) and 130% (P = 0.046), respectively.
These results in patients with chronic renal failure demonstrate (a) increased glucose production and utilization, (b) increased gluconeogenesis from alanine, (c) increased alanine production and utilization, and (d) a relative impairment to glucose disposal. We conclude that chronic azotemia is characterized by increased rates of glucose and glucose precursor flux and by a relative impairment to glucose disposal. These findings may suggest an underlying hepatic and peripheral insensitivity to the metabolic action of insulin in patients with chronic renal insufficiency.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amend W. J., Jr, Steinberg S. M., Lowrie E. G., Lazarus J. M., Soeldner J. S., Hampers C. L., Merrill J. P. The influence of serum calcium and parathyroid hormone upon glucose metabolism in uremia. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Sep;86(3):435–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen H. F., Moorhouse J. A. Glucose turnover and disposal in maturity-onset diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3033–3045. doi: 10.1172/JCI107502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canterbury J. M., Levy G., Ruiz E., Reiss E. Parathyroid hormone activation of adenylate cyclase in liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Nov;147(2):366–370. doi: 10.3181/00379727-147-38343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerletty J. M., Engbring N. H. Azotemia and glucose intolerance. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jun;66(6):1097–1108. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-66-6-1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson J. L., Liljenquist J. E., Lacy W. W., Jennings A. S., Cherrington A. D. Gluconeogenesis: methodological approaches in vivo. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):229–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson J. L., Liljenquist J. E., Sinclair-Smith B. C., Lacy W. W. Gluconeogenesis from alanine in normal postabsorptive man. Intrahepatic stimulatory effect of glucagon. Diabetes. 1975 Jun;24(6):574–584. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.6.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Andres R., Edgar P., Walker W. G. Carbohydrate metabolism in uremia: a review. Medicine (Baltimore) 1973 Sep;52(5):469–481. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197309000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzúrik R., Niederland T. R., Cernácek P. Carbohydrate metabolism by rat liver slices incubated in serum obtained from uraemic patients. Clin Sci. 1969 Oct;37(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAJANS S. S., CONN J. W. The early recognition of diabetes mellitus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:208–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Pozefsky T., Marliss E., Cahill G. F., Jr Alanine: key role in gluconeogenesis. Science. 1970 Feb 13;167(3920):1003–1004. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3920.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell M., Larsen P. R., Field J. B. Spontaneous hypoglycemia associated with chronic renal failure. Diabetes. 1973 Jul;22(7):493–498. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.7.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich J., Schölmerich J., Hoppe-Seyler G., Maier K. P., Talke H., Schollmeyer P., Gerok W. The effect of acute uraemia on gluconeogenesis in isolated perfused rat livers. Eur J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec 5;4(6):453–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb00419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulks R. M., Li J. B., Goldberg A. L. Effects of insulin, glucose, and amino acids on protein turnover in rat diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):290–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganda O. P., Aoki T. T., Soeldner J. S., Morrison R. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Hormone-fuel concentrations in anephric subjects. Effect of hemodialysis (with special reference to amino acids). J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1403–1411. doi: 10.1172/JCI108409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. J., Bier D. M., Cryer P. E., Pagliara A. S. Hypoglycemia in compensated chronic renal insufficiency. Substrate limitation of gluconeogenesis. Diabetes. 1974 Dec;23(12):982–986. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.12.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. J., Cryer P. E., Santiago J. V., Haymond M. W., Pagliara A. S., Kipnis D. M. The role of adrenergic mechanisms in the substrate and hormonal response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):7–15. doi: 10.1172/JCI108460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. W., Garber A. J. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. I. Its role in gluconeogenesis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Oct;25(10):1010–1021. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.10.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. S., Johnson C., Lebovitz H. E. Carbohydrate metabolism in uremia. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Jan;68(1):63–74. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Rannels D. E., Munger B. L., Morgan H. E. Insulin in the regulation of protein turnover in heart and skeletal muscle. Fed Proc. 1974 Apr;33(4):1098–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl I. E., Pagliara A. S., Kipnis D. M. A microfluorometric enzymatic assay for the determination of alanine and pyruvate in plasma and tissues. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Sep;80(3):434–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Dunn A., Chenoweth M., Golden S. Determination of synthesis, recycling and body mass of glucose in rats and rabbits in vivo 3H-and 14C-labelled glucose. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;142(1):171–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1420171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Dunn A. Glucose-2-t as a tracer for glucose metabolism. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):1–5. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Rostami H., Dunn A. Evaluation of glucose turnover, body mass and recycling with reversible and irreversible tracers. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;142(1):161–170. doi: 10.1042/bj1420161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg R. A., Siegal A. M., Owen W. C. Glucose-lactate interrelationships: effect of ethanol. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):175–185. doi: 10.1172/JCI106471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrie E. G., Soeldner J. S., Hampers C. L., Merrill J. P. Glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in uremic, prediabetic, and normal subjects. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Oct;76(4):603–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxley M. A., Bell N. H., Wagle S. R., Allen D. O., Ashmore J. Parathyroid hormone stimulation of glucose and urea production in isolated liver cells. Am J Physiol. 1974 Nov;227(5):1058–1061. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.5.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKOFF G. T., THOMAS C. L., NEWTON J. D., SELLMAN J. C., TYLER F. H. Mechanism of impaired glucose tolerance in uremia and experimental hyperazotemia. Diabetes. 1958 Sep-Oct;7(5):375–383. doi: 10.2337/diab.7.5.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagliara A. S., Kari I. E., De Vivo D. C., Feigin R. D., Kipnis D. M. Hypoalaninemia: a concomitant of ketotic hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1440–1449. doi: 10.1172/JCI106940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P., Bortz W. M. Turnover and oxidation of plasma glucose in lean and obese humans. Metabolism. 1969 Jul;18(7):570–584. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUNYAN J. W., Jr, HURWITZ D., ROBBINS S. L. Effect of Kimmelstiel-Wilson syndrome on insulin requirements in diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1955 Mar 10;252(10):388–391. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195503102521004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle G. L. The use of isotope turnover techniques in the study of carbohydrate metabolism in man. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Nov;5(3):783–804. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(76)80051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Bastl C., Finkelstein F. O., Fisher M., Black H., Hendler R., Felig P. Influence of uremia and hemodialysis on the turnover and metabolic effects of glucagon. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):722–731. doi: 10.1172/JCI108330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman V., Felig P. Glucagon and insulin binding to liver membranes in a partially nephrectomized uremic rat model. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):224–232. doi: 10.1172/JCI108759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Spitz I. M., Rubenstein A. H., Bersohn I., Abrahams C., Lowy C. Carbohydrate metabolism in renal disease. Q J Med. 1970 Apr;39(154):201–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R., Rostami H., Altszuler N. A two-compartment calculator for the dog glucose pool in the nonsteady state. Fed Proc. 1974 Jul;33(7):1869–1876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Felig P., Ahlborg G., Jorfeldt L. Glucose metabolism during leg exercise in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2715–2725. doi: 10.1172/JCI106772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Felig P., Cerasi E., Luft R. Splanchnic and peripheral glucose and amino acid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1870–1878. doi: 10.1172/JCI106989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Felig P., Cerasi E., Luft R. Splanchnic and peripheral glucose and amino acid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1870–1878. doi: 10.1172/JCI106989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Felig P., Hagenfeldt L. Effect of protein ingestion on splanchnic and leg metabolism in normal man and in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):987–999. doi: 10.1172/JCI108375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Paetkau V., Lardy H. A. Paths of carbon in gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis. 3. The role and regulation of mitochondrial processes involved in supplying precursors of phosphoenolpyruvate. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 10;241(11):2523–2532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt F. B., Jr Uremia and insulin response. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Nov;126(5):865–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



