Abstract
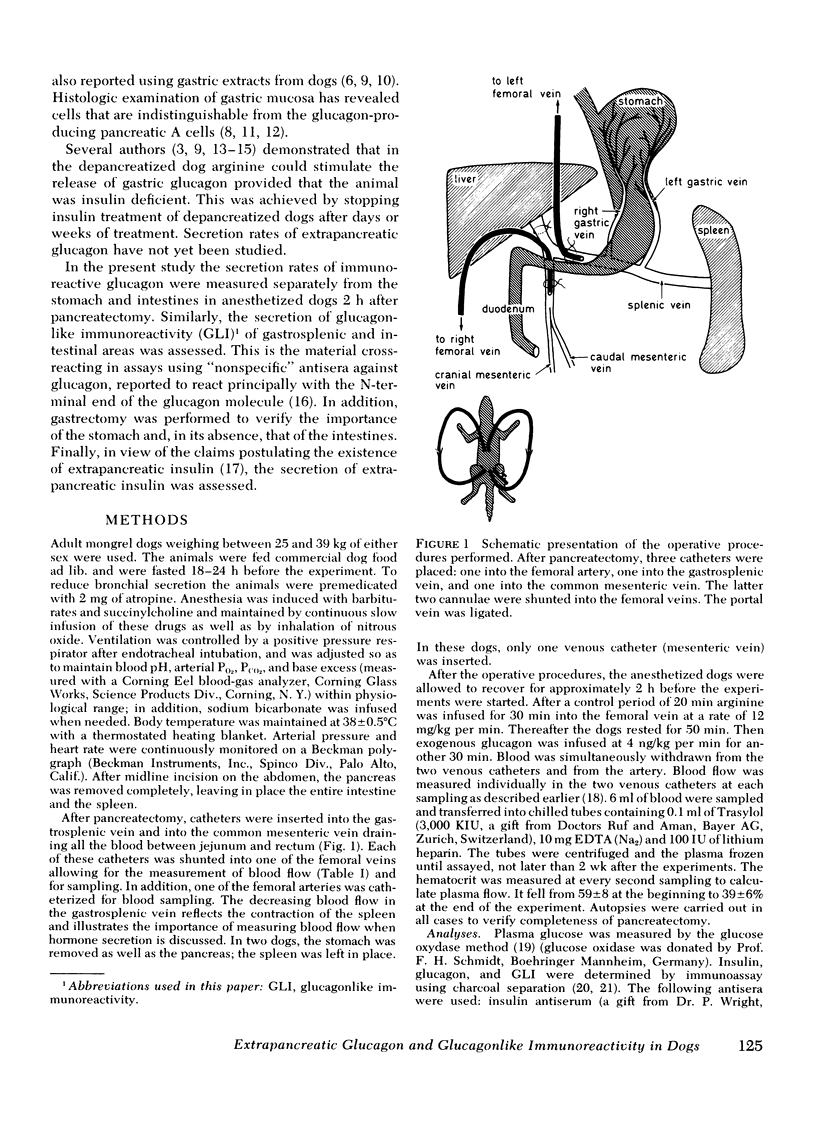
The anatomical sites and the rates of extrapancreatic secretion of glucagon and of glucagon-like immunoreactivity (GLI) were assessed in dogs 2 h after pancreatectomy by catheterization of the gastrosplenic and mesenteric veins.
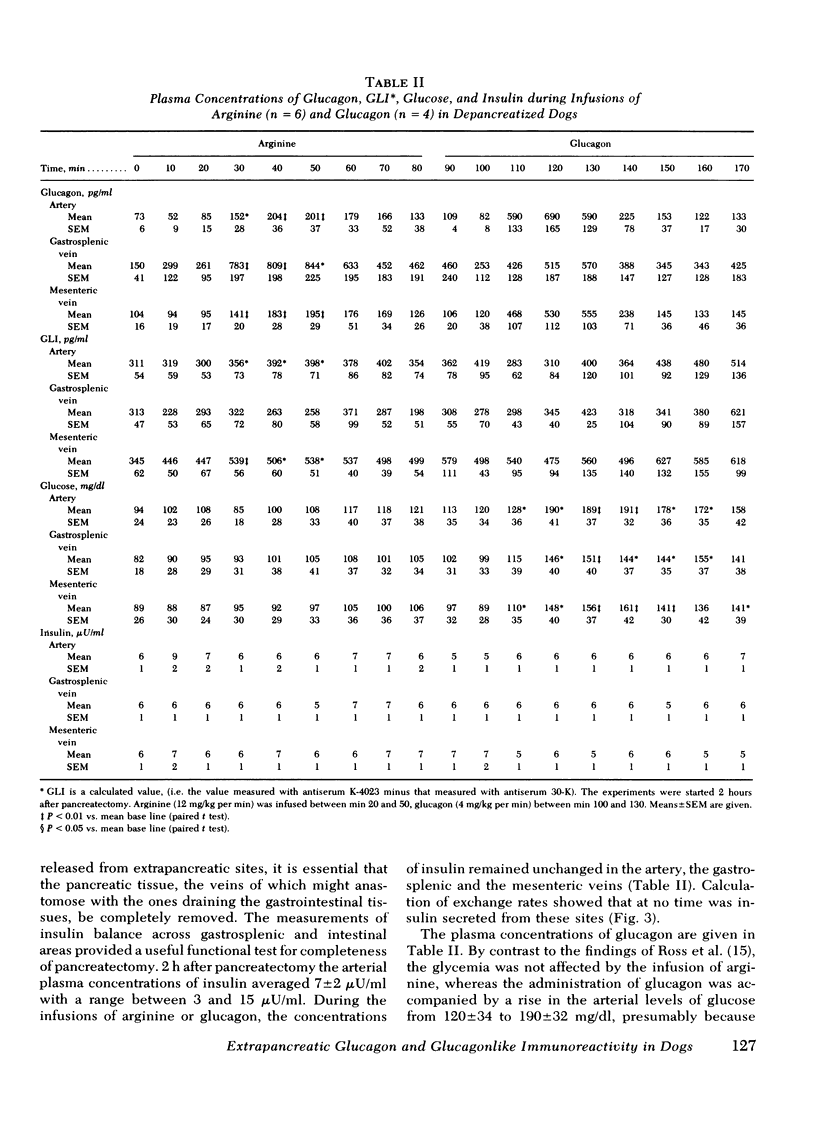
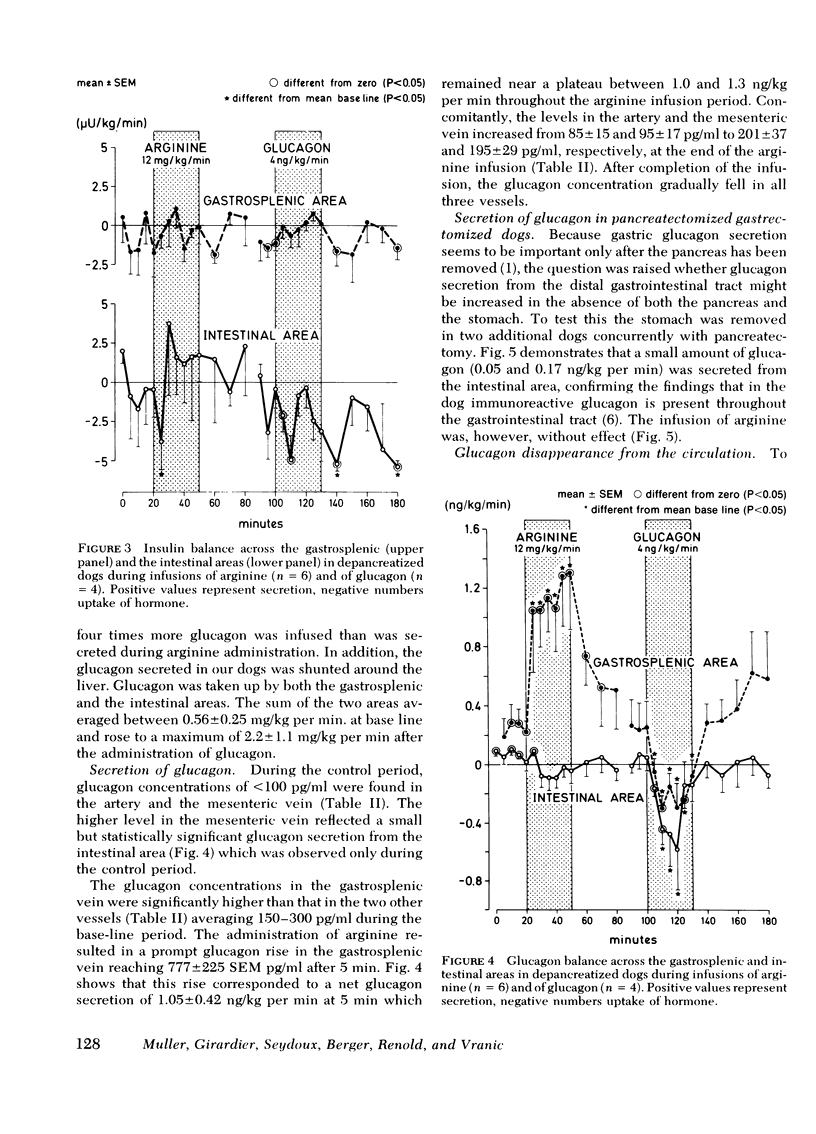
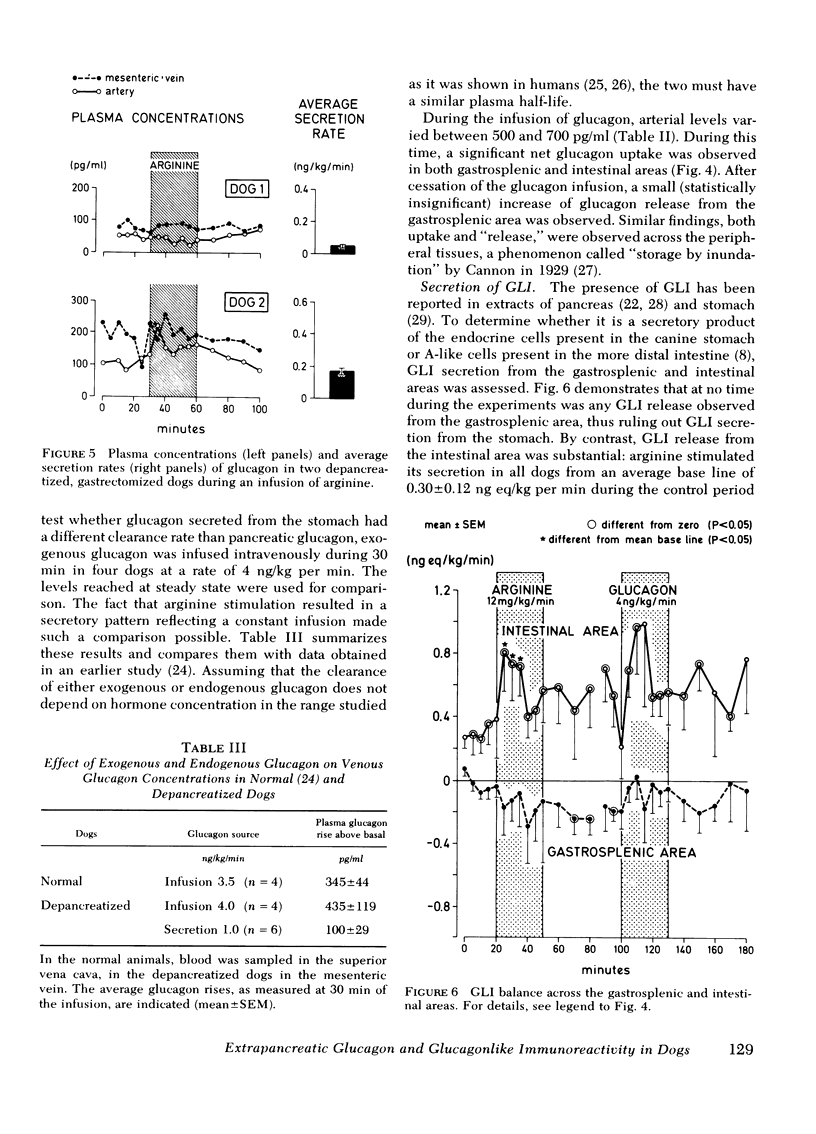
Glucagon release from the gastrosplenic area approximated one-fourth that of a normal pancreas and rose from 0.25 to 1.0 ng/kg per min during arginine stimulation. Intestinal glucagon secretion was small and did not respond to arginine, suggesting that the stomach is the only important extrapancreatic source of glucagon.
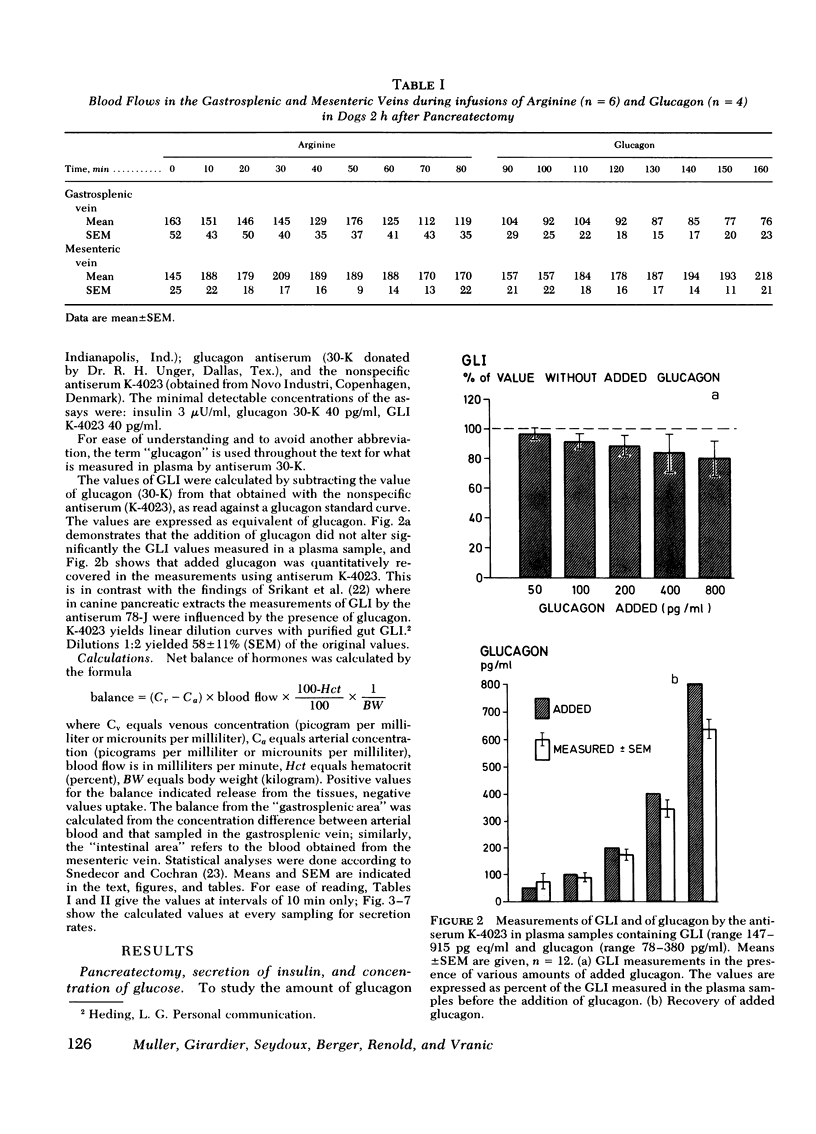
Glucagon concentrations attained by gastrosplenic secretion were in close proportion to those obtained during the administration of exogenous glucagon, indicating similar clearance rates of extrapancreatic and pancreatic glucagon, approximating 10 ml/kg per min.
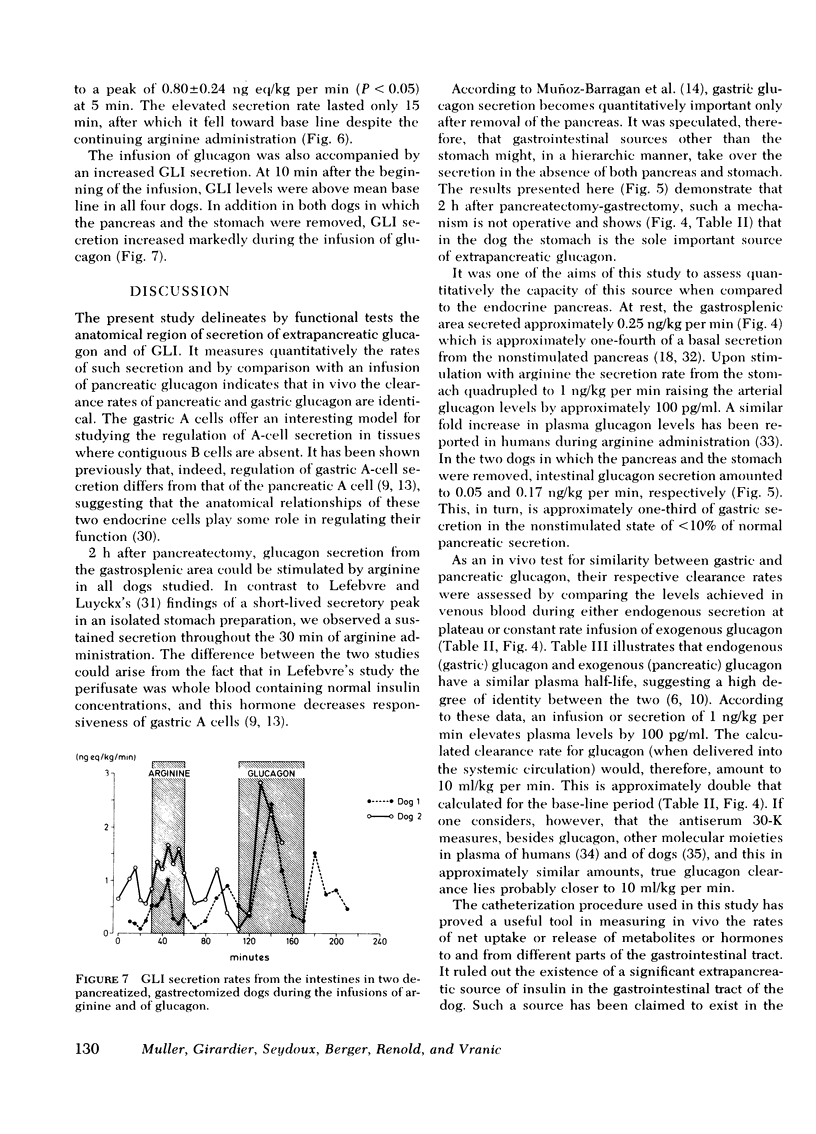
GLI secretion (0.3 ng eq/kg per min) was limited to the intestinal area and was transiently stimulated by arginine and exogenous glucagon. Base-line GLI clearance approximated 1 ml/kg per min. No insulin secretion could be detected. Gastrointestinal glucose uptake rose from 0.56 to 2.2 mg/kg per min after glucagon administration suggesting that as much as 10% of total glucose production can be taken up by the gastrointestinal tract.
In two dogs both the stomach and pancreas were removed. Intestinal glucagon release remained small and did not increase during arginine administration. By contrast, GLI release was stimulated by both arginine and exogenous glucagon.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alford F. P., Bloom S. R., Nabarro J. D. Glucagon metabolism in man, studies on the metabolic clearance rate and the plasma acute disappearance time of glucagon in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 May;42(5):830–838. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-5-830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assan R., Slusher N. Structure-function and structure-immunoreactivity relationships of the glucagon molecule and related synthetic peptides. Diabetes. 1972 Aug;21(8):843–855. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.8.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baetens D., Rufener C., Srikant B. C., Dobbs R., Unger R., Orci L. Identification of glucagon-producing cells (A cells) in dog gastric mucosa. J Cell Biol. 1976 May;69(2):455–464. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.2.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazquez E., Muñoz-Barragan L., Patton G. S., Orci L., Dobbs R. E., Unger R. H. Gastric A-cell function in insulin-deprived depancreatized dogs. Endocrinology. 1976 Nov;99(5):1182–1188. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-5-1182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M., Sherwin R. S., Hendler R., Felig P. Kinetics of glucagon in man: effects of starvation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1735–1739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Brandenburg D., Wollmer A. Receptor-binding assay of chemically modified insulins. Comparison with in vitro and in vivo bioassays. Diabetologia. 1974 Feb;10(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00421406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardier L., Seydoux J., Campfield L. A. Control of A and B cells in vivo by sympathetic nervous input and selective hyper or hypoglycemia in dog pancreas. J Physiol (Paris) 1976 Nov;72(6):801–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst J. J. Extraction, gel filtration pattern, and receptor binding of porcine gastrointestinal glucagon-like immunoreactivity. Diabetologia. 1977 Apr;13(2):159–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00745145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühl C., Jensen S. L., Nielsen O. V. Porcine gastric insulin. Endocrinology. 1976 Dec;99(6):1667–1670. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-6-1667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Holst J., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Distribution and properties of glucagon immunoreactivity in the digestive tract of various mammals: an immunohistochemical and immunochemical study. Histochemistry. 1975 Sep 29;44(4):281–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00490364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefèbvre P. J., Luyckx A. S. Factors controlling gastric-glucagon release. J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;59(4):716–722. doi: 10.1172/JCI108690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Girardier L., Seydoux J., Wollheim C. B., Kanazawa Y., Orci L., Renold A. E., Porte D., Jr Glucagon release induced by pancreatic nerve stimulation in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1246–1259. doi: 10.1172/JCI107292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashiter K., Harding P. E., Chou M., Mashiter G. D., Stout J., Diamond D., Field J. B. Persistent pancreatic glucagon but not insulin response to arginine in pancreatectomized dogs. Endocrinology. 1975 Mar;96(3):678–693. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-3-678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Foà P. P. Plasma glucose, insulin, pancreatic, and enteroglucagon levels in normal and depancreatized dogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Oct;147(1):97–102. doi: 10.3181/00379727-147-38288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita S., Doi K., Yip C. C., Vranic M. Measurement and partial characterization of immunoreactive glucagon in gastrointestinal tissues of dogs. Diabetes. 1976 Nov;25(11):1018–1025. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.11.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. A., Aoki T. T., Egdahl R. H., Cahill G. F., Jr Effects of exogenous glucagon and epinephrine in physiological amounts on the blood levels of free fatty acids and glycerol in dogs. Diabetologia. 1977 Jan;13(1):55–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00996328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Barragan L., Blazquez E., Patton G. S., Dobbs R. E., Unger R. H. Gastric A-cell function in normal dogs. Am J Physiol. 1976 Oct;231(4):1057–1061. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.4.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osaka M., Sasagawa T., Fujita T. Endocrine cells in human jejunum and ileum: an electron microscope study of biopsy materials. Arch Histol Jpn. 1973 Mar;35(3):235–248. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.35.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigopoulou D., Valverde I., Marco J., Faloona G., Unger R. H. Large glucagon immunoreactivity in extracts of pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 10;245(3):496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Rubalcava B., Baetens D., Blazquez E., Srikant C. B., Orci L., Unger R. H. Identification of glucagon in the gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):135–145. doi: 10.1172/JCI108062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikant C. B., McCorkle K., Unger R. H. Properties of immunoreactive glucagon fractions of canine stomach and pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1847–1851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikant C. B., Unger R. H. Evidence for the presence of glucagon-like immunoreactivity (GLI) in the pancreas. Endocrinology. 1976 Dec;99(6):1655–1658. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-6-1655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundby F., Jacobsen H., Moody A. J. Purification and characterization of a protein from porcine gut with glucagon-like immunoreactivity. Horm Metab Res. 1976 Sep;8(5):366–371. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Aguilar-Parada E., Müller W. A., Eisentraut A. M. Studies of pancreatic alpha cell function in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI106297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. The Banting Memorial Lecture 1975. Diabetes and the alpha cell. Diabetes. 1976 Feb;25(2):136–151. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.2.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde I., Dobbs R., Unger R. H. Heterogeneity of plasma glucagon immunoreactivity in normal, depancreatized, and alloxan-diabetic dogs. Metabolism. 1975 Sep;24(9):1021–1028. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vranic M., Engerman R., Doi K., Morita S., Yip C. C. Extrapancreatic glucagon in the dog. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11 Suppl 1):1469–1473. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vranic M., Pek S., Kawamori R. Increased "glucagon immunoreactivity" in plasma of totally depancreatized dogs. Diabetes. 1974 Nov;23(11):905–912. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.11.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C., Knowlton S. D., Martin D. B. High molecular weight glucagon-like immunoreactivity in plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Feb;40(2):296–302. doi: 10.1210/jcem-40-2-296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


