Abstract
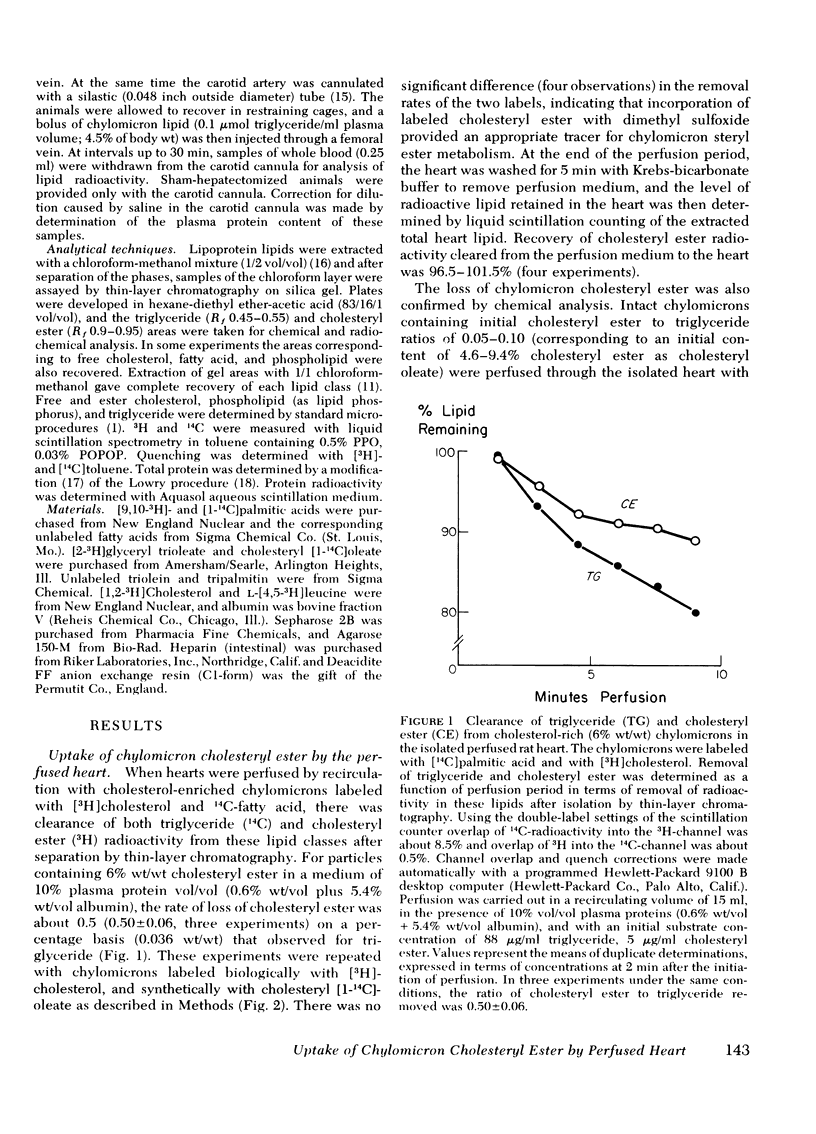
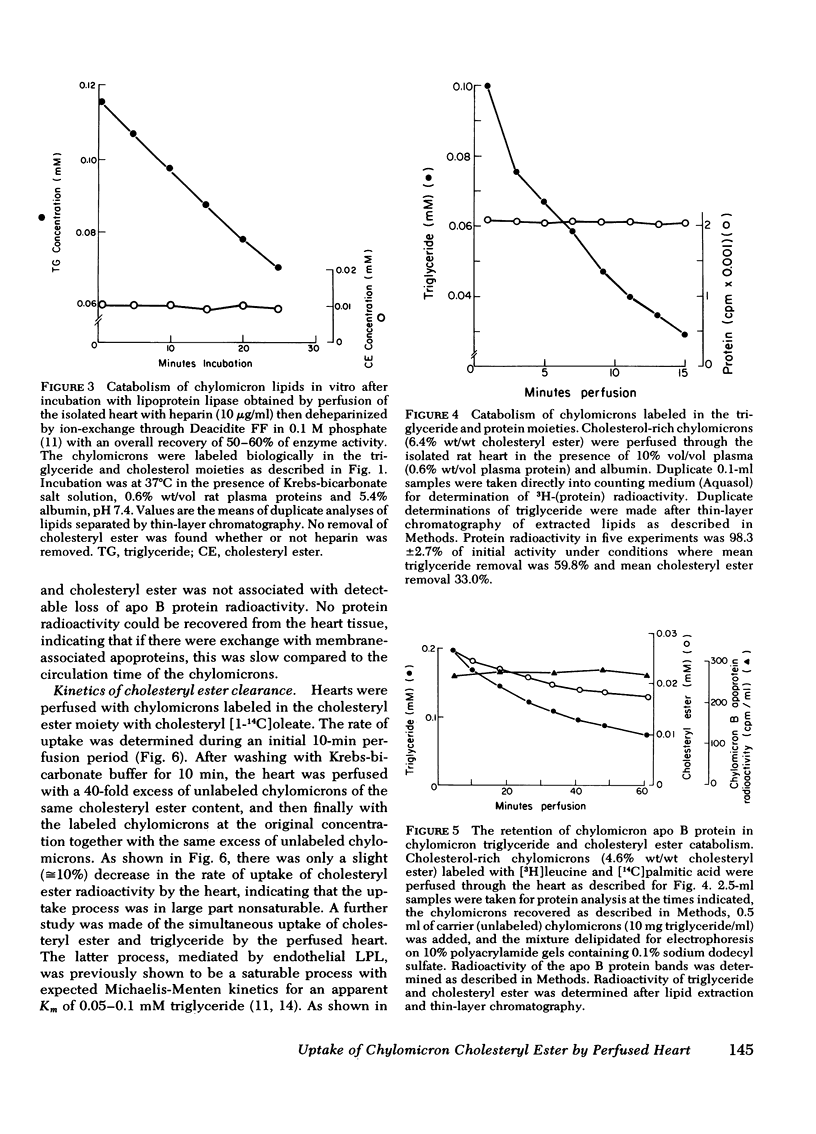
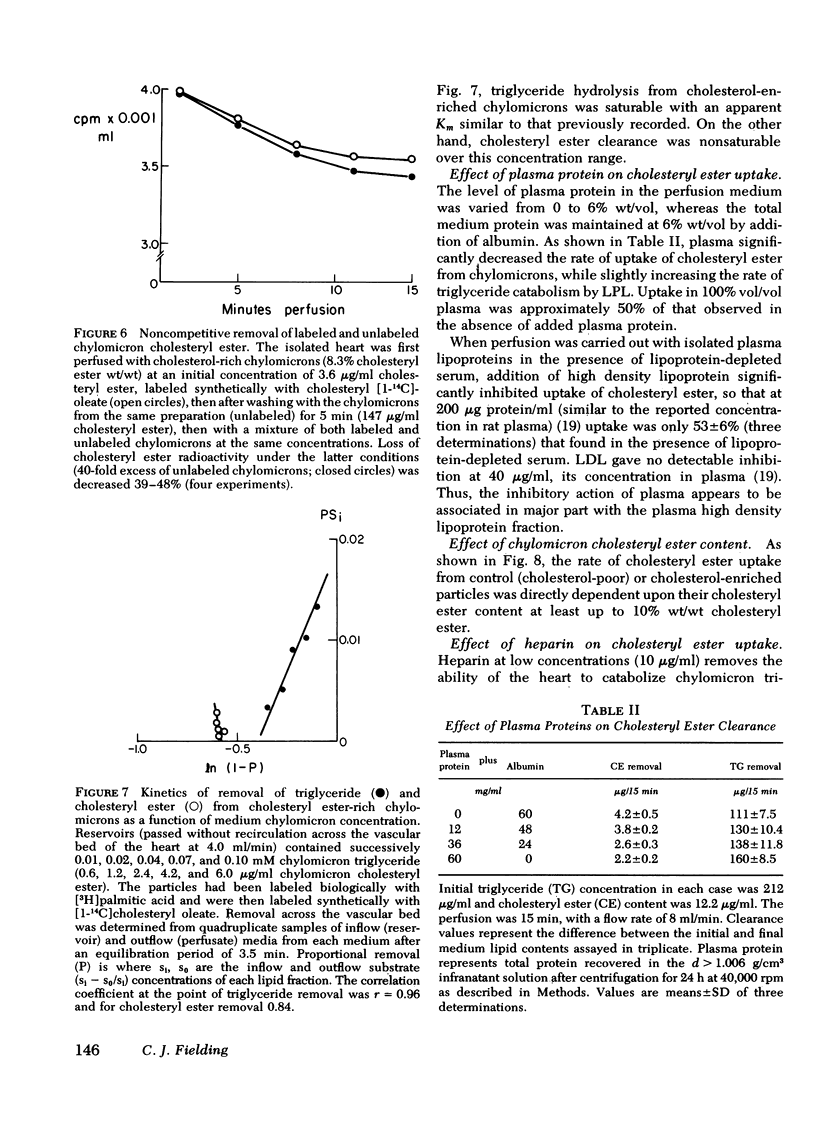
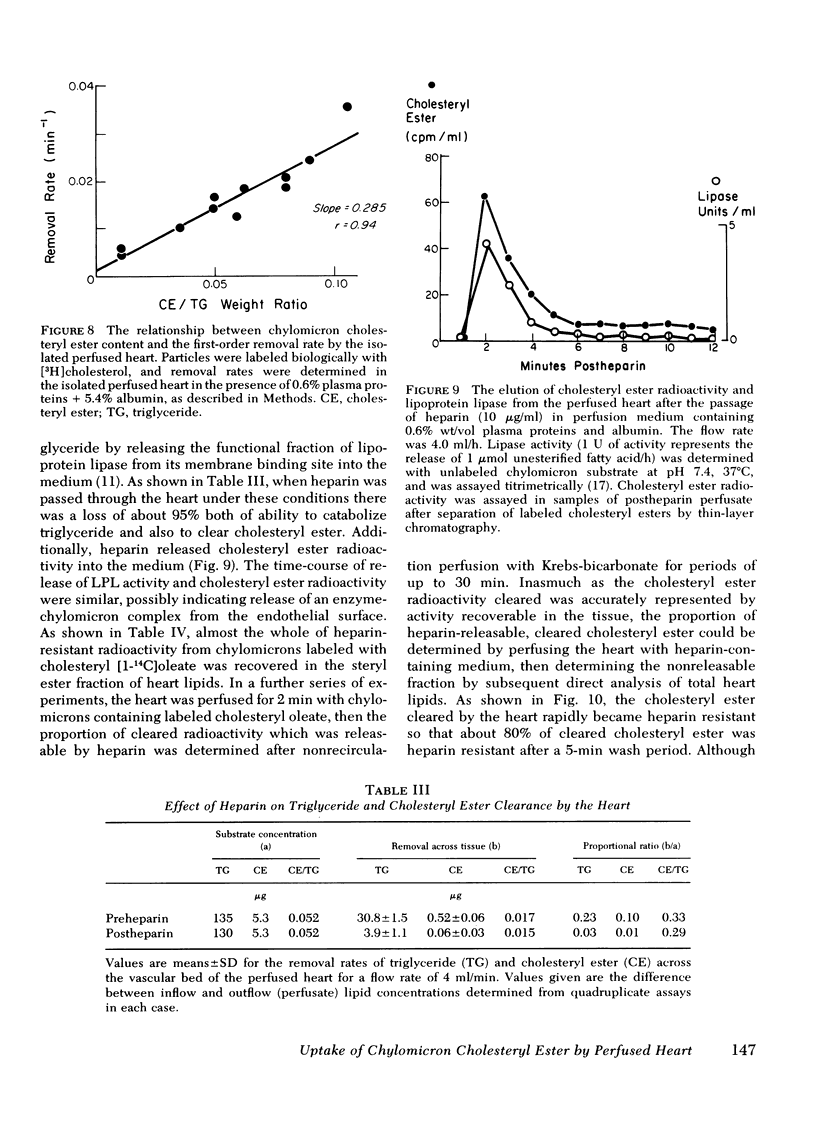
The rate of uptake of cholesteryl ester from chylomicrons has been determined with the isolated perfused rat heart and both intact and functionally hepatectomized rats. Uptake was found to be proportional to the cholesteryl ester content of the particles. Transfer of cholesteryl ester to other lipoprotein classes of the plasma was negligible under these conditions, and loss of cholesteryl ester from the medium was associated with quantitative recovery in the vascular bed. The uptake mechanism was nonsaturable and independent of the lipoprotein lipase binding site. Compared with receptor-dependent uptake of low density lipoprotein cholesteryl ester by heart endothelium, the chylomicron pathway appears to provide a major proportion of cholesteryl ester cleared from the plasma. Uptake was initially heparin dependent, and cleared lipid was released by 10 microgram/ml of heparin; however, lipid taken up rapidly became heparin resistant and was then hydrolyzed slowly with production of unesterified fatty acid. These results are discussed in the context of the possible role of cholesterol-rich chylomicron remnant lipoproteins in atherogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman E. N., Havel R. J., Wolfe B. M., Bohmer T. Quantitative studies of the metabolism of chylomicron triglycerides and cholesterol by liver and extrahepatic tissues of sheep and dogs. J Clin Invest. 1971 Sep;50(9):1831–1839. doi: 10.1172/JCI106674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bersot T. P., Mahley R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Interaction of swine lipoproteins with the low density lipoprotein receptor in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2395–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Dana S. E., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-dependent hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters contained in plasma low density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2925–2929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan B. A., Schwartz C. J. Increased endothelial cell turnover in areas of in vivo Evans Blue uptake in the pig aorta. Atherosclerosis. 1973 May-Jun;17(3):401–417. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(73)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Schurr D. Phospholipid removal during degradation of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein in vitro. J Lipid Res. 1976 Nov;17(6):578–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Higgins J. M. Lipoprotein lipase: comparative properties of the membrane-supported and solubilized enzyme species. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4324–4330. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J. Lipoprotein lipase: evidence for high- and low-affinity enzyme sites. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):879–884. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J. Purification of lipoprotein lipase from rat post-heparin plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 27;178(3):499–507. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding P. E., Shore V. G., Fielding C. J. Lipoprotein lipase. Isolation and characterization of a second enzyme species from postheparin plasma. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1896–1900. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Release of low density lipoprotein from its cell surface receptor by sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Binding and degradation of low density lipoproteins by cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5153–5162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazzard W. R., Bierman E. L. Delayed clearance of chylomicron remnants following vitamin-A-containing oral fat loads in broad-beta disease (type III hyperlipoproteinemia). Metabolism. 1976 Jul;25(7):777–801. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazzard W. R., Porte D., Jr, Bierman E. L. Abnormal lipid composition of chylomicrons in broad-beta disease (type 3hyperlipoproteinemia). J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1853–1858. doi: 10.1172/JCI106403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. M., Fielding C. J. Lipoprotein lipase. Mechanism of formation of triglyceride-rich remnant particles from very low density lipoproteins and chylomicrons. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2288–2293. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasser N. L., Roheim P. S., Edelstein D., Eder H. A. Serum lipoproteins of normal and cholesterol-fed rats. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jan;14(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Hughes F. B., Isselbacher K. J. Very low density lipoproteins in intestinal lymph: role in triglyceride and cholesterol transport during fat absorption. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2367–2373. doi: 10.1172/JCI106203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPOVIC V., POPOVIC P. Permanent cannulation of aorta and vena cava in rats and ground squirrels. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Jul;15:727–728. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Formation of cholesteryl ester-rich particulate lipid during metabolism of chylomicrons. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):465–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichl D., Simons L. A., Myant N. B., Pflug J. J., Mills G. L. The lipids and lipoproteins of human peripheral lymph, with observations on the transport of cholesterol from plasma and tissues into lymph. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Sep;45(3):313–329. doi: 10.1042/cs0450313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Egelrud T. Hydrolysis of chylomicron phosphatidylcholine in vitro by lipoprotein lipase, phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 22;431(3):538–549. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Fielding P. E., Fielding C. J., Gospodarowicz D. Role of contact inhibition in the regulation of receptor-mediated uptake of low density lipoprotein in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):356–360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. B., Carew T. E., Steinberg D. Uptake and degradation of low density lipoprotein by swine arterial smoot muscle cells with inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 26;424(3):404–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilversmit D. B. A proposal linking atherogenesis to the interaction of endothelial lipoprotein lipase with triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. Circ Res. 1973 Dec;33(6):633–638. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.6.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


