Abstract
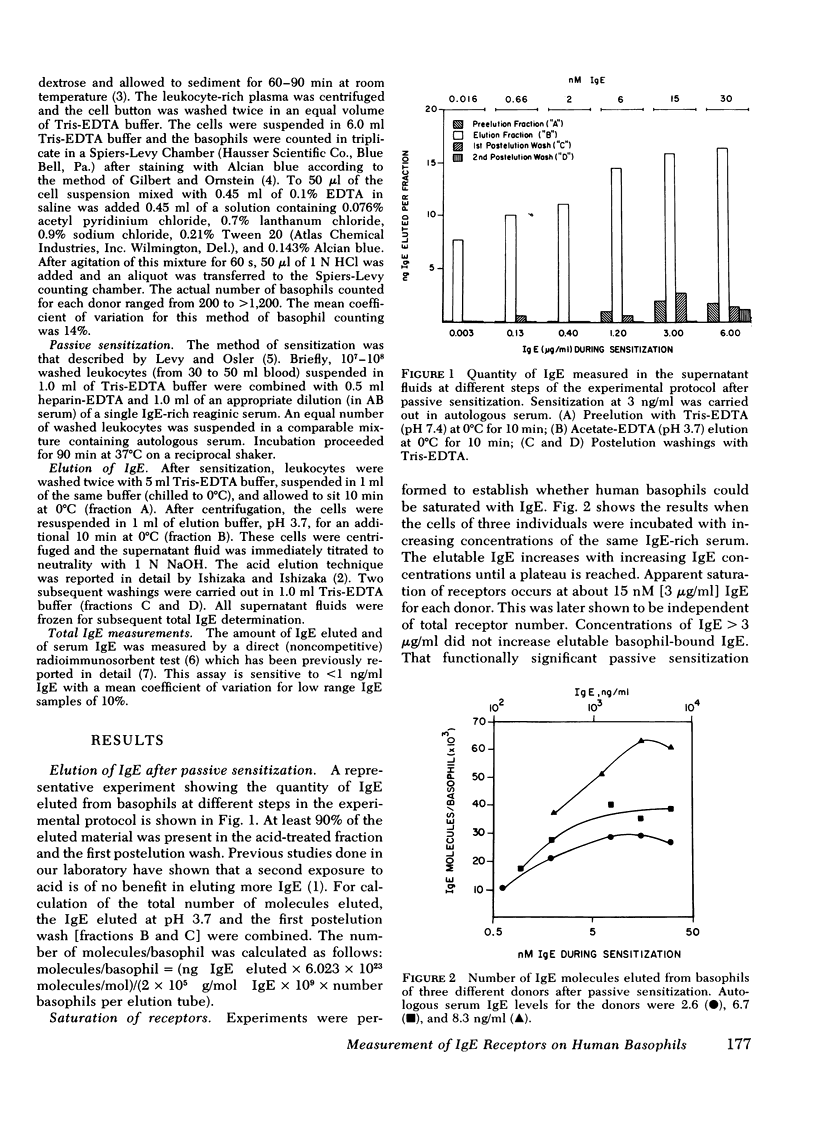
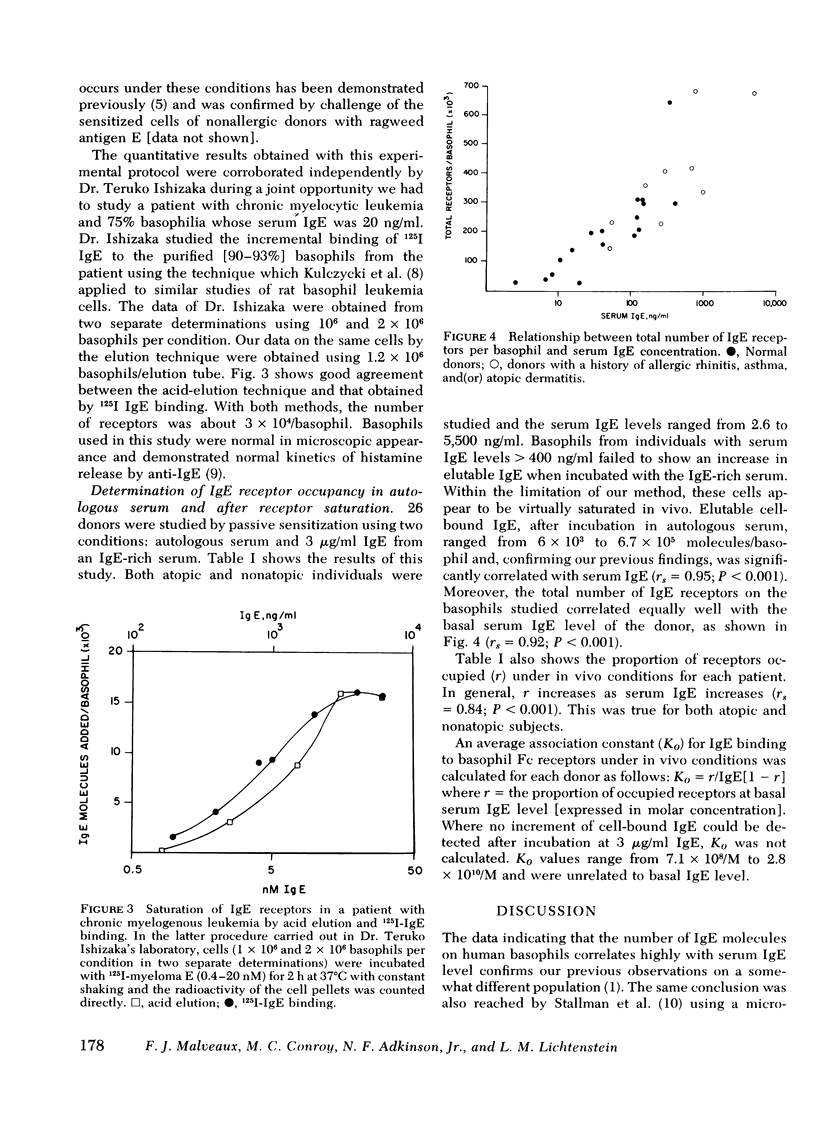
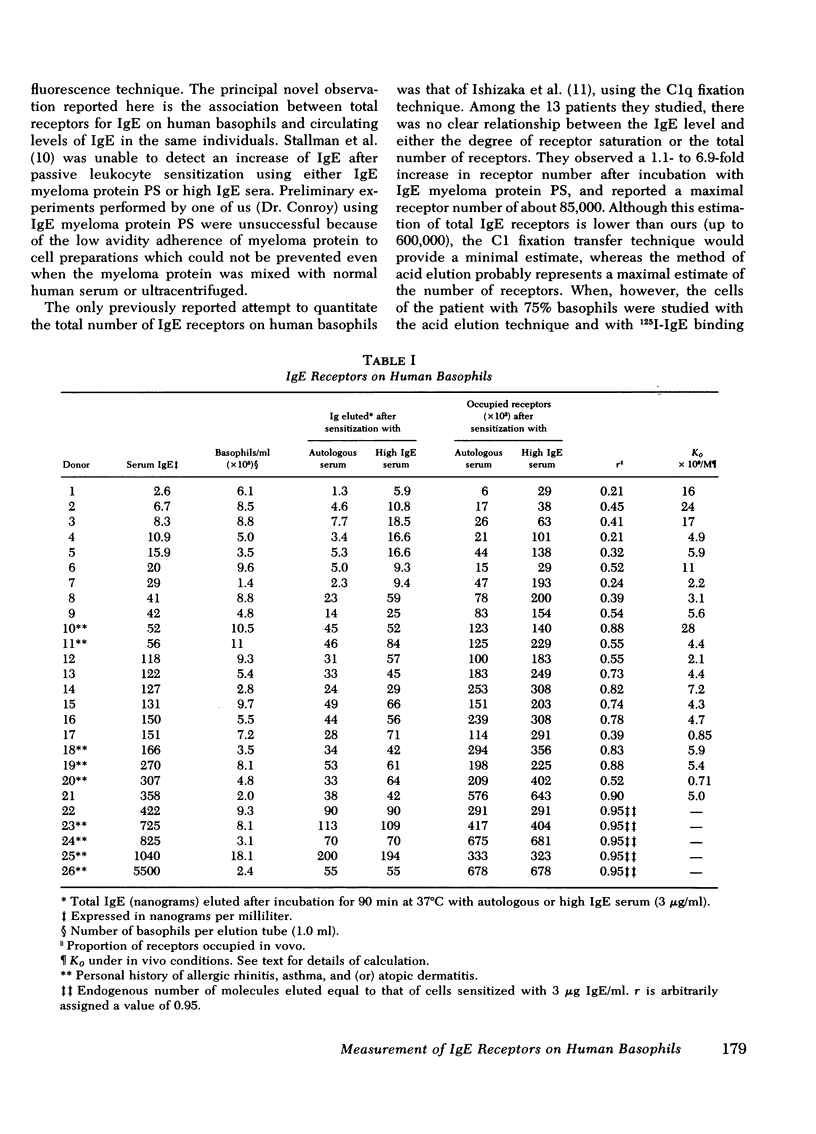
As reported previously, and confirmed here in 26 donors, the serum IgE level (2.6-5,500 ng/ml) correlates well (rs = 0.95, P less than 0.001) with the in vivo number of IgE molecules/basophil (6,000-600,000). The total number of IgE receptors/basophil was monitored by incubating them with an IgE-rich serum (15 microgram/ml), quantitatively stripping IgE from the cells at pH 3.7, and measuring eluted IgE by a direct radioimmunosorbent test. Saturation of receptors for each donor was achieved with 15 nM IgE (3 microgram/ml). The proportion of receptors occupied in vivo correlated with the serum IgE (rs = 0.84, P less than 0.001) whereas the average association constant of the receptors was independent of serum IgE and ranged from 7.1 X 10(8)/M to 2.8 X 10(10)/M, averaging 7.7 X 10(9)/M. Unexpectedly, the total number of IgE receptors/basophil was closely related to the serum IgE level. (rs = 0.92, P less than 0.001). Thus, either there is genetic association between serum IgE and the number of basophil IgE receptors, or, more likely, the receptor number is modulated by the serum IgE concentration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conroy M. C., Adkinson N. F., Jr, lichtenstein L. M. Measurement of IgE on human basophils: relation to serum IgE and anti-IgE-induced histamine release. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1317–1321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Metzger H. Some physical chemical aspects of receptor-ligand interactions. Immunol Commun. 1976;5(5):417–436. doi: 10.3109/08820137609033858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert H. S., Ornstein L. Basophil counting with a new staining method using alcian blue. Blood. 1975 Aug;46(2):279–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Molina A., Spiegelberg H. L. A subpopulation of normal human peripheral B lymphcytes that bind IgE. J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;59(4):616–624. doi: 10.1172/JCI108679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isersky C., Metzger H., Buell D. N. Cell cycle-associated changes in receptors for IgE during growth and differentiation of a rat basophilic leukemia cell line. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1147–1162. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Tomioka H., Ishizaka T. Mechanisms of passive sensitization. I. Presence of IgE and IgG molecules on human leukocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1459–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K. Mechanisms of passive sensitization. IV. Dissociation of IgE molecules from basophil receptors at acid pH. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1078–1084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Soto C. S., Ishizaka K. Mechanisms of passive sensitization. 3. Number of IgE molecules and their receptor sites on human basophil granulocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):500–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Megyesi K., Bar R. S., Eastman R. C., Flier J. S. Receptors for peptide hormones. New insights into the pathophysiology of disease states in man. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Feb;86(2):205–219. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Membrane receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):261–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki A., Jr, Isersky C., Metzger H. The interaction of IgE with rat basophilic leukemia cells. I. Evidence for specific binding of IgE. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):600–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki A., Jr, Metzger H. The interaction of IgE with rat basophilic leukemia cells. II. Quantitative aspects of the binding reaction. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1676–1695. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN L. M., OSLER A. G. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISMS OF HYPERSENSITIVITY PHENOMENA. IX. HISTAMINE RELEASE FROM HUMAN LEUKOCYTES BY RAGWEED POLLEN ANTIGEN. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:507–530. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Sharp G. W., Haber E. Specific binding of -adrenergic catecholamines to a subcellular fraction from cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):342–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. A., Osler A. G. Studies on the mechanisms of hypersensitivity phenomena. XIV. Passive sensitization in vitro of human leukocytes to ragweed pollen antigen. J Immunol. 1966 Aug;97(2):203–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein L. M., Sobotka A. K., Malveaux F. J., Gillespie E. IgE-induced changes in human basophil cyclic AMP levels. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1978;56(5):473–478. doi: 10.1159/000232059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G., Newman S. A., Metzger H. Assay and partial characterization of the solubilized cell surface receptor for immunoglobulin E. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):704–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soli A. H., Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin receptor deficiency in genetic and acquired obesity. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):769–780. doi: 10.1172/JCI108155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallman P. J., Aalberse R. C., Brühl P. C., van Elven E. H. Experiments on the passive sensitization of human basophils, using quantitative immunofluorescence microscopy. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;54(4):364–373. doi: 10.1159/000231849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallman P. J., Aalberse R. C. Estimation of basophil-bound IgE by quantitative immunofluorescence microscopy. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;54(1):9–18. doi: 10.1159/000231803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsson A. V., Hintz R. L. Insulin receptors in the newborn. Increase in receptor affinity and number. N Engl J Med. 1977 Oct 27;297(17):908–912. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197710272971704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


