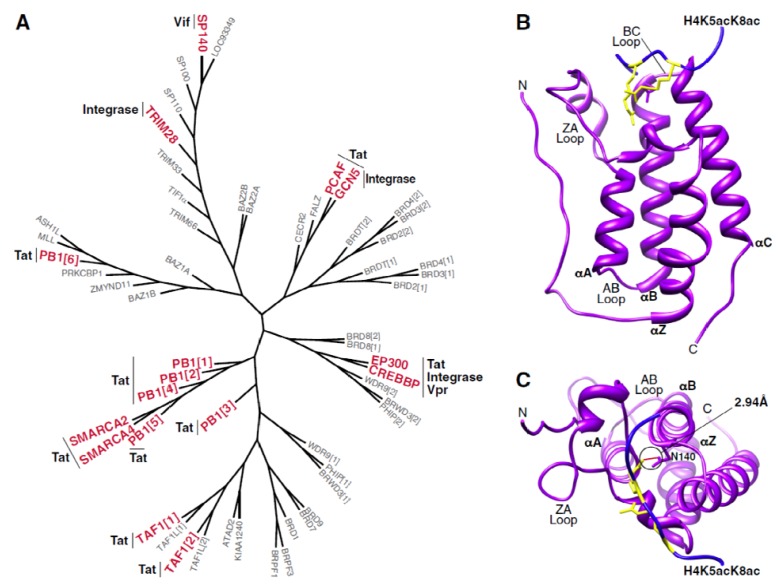
Figure 1.
The human bromodomain family. (A) Phylogenetic tree of 57 human bromodomains. Those bromodomain-containing proteins that have been shown to interact with HIV proteins are denoted in red with the corresponding viral factor indicated alongside. Phylogenetic trees were generated using Seaview v4.4.1 with individual bromodomain sequences obtained from [23]. (B) Structure of the first bromodomain of BRD4 (purple) in complex with a diacetylated histone peptide (blue). Histone acetyllysine residues are shown in yellow. Structural representations in (B,C) were rendered using Chimera (UCSF) with PDB: 3UVW (C) Top view of interaction between first bromodomain of BRD4 and a diacetylated histone peptide. The hydrogen bond between the canonical bromodomain asparagine residue (N140 in BRD4) and the histone acetyllysine residue is shown in red with an estimated length of 2.94A.