Abstract
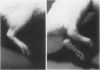
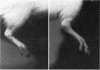
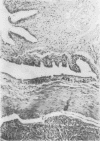
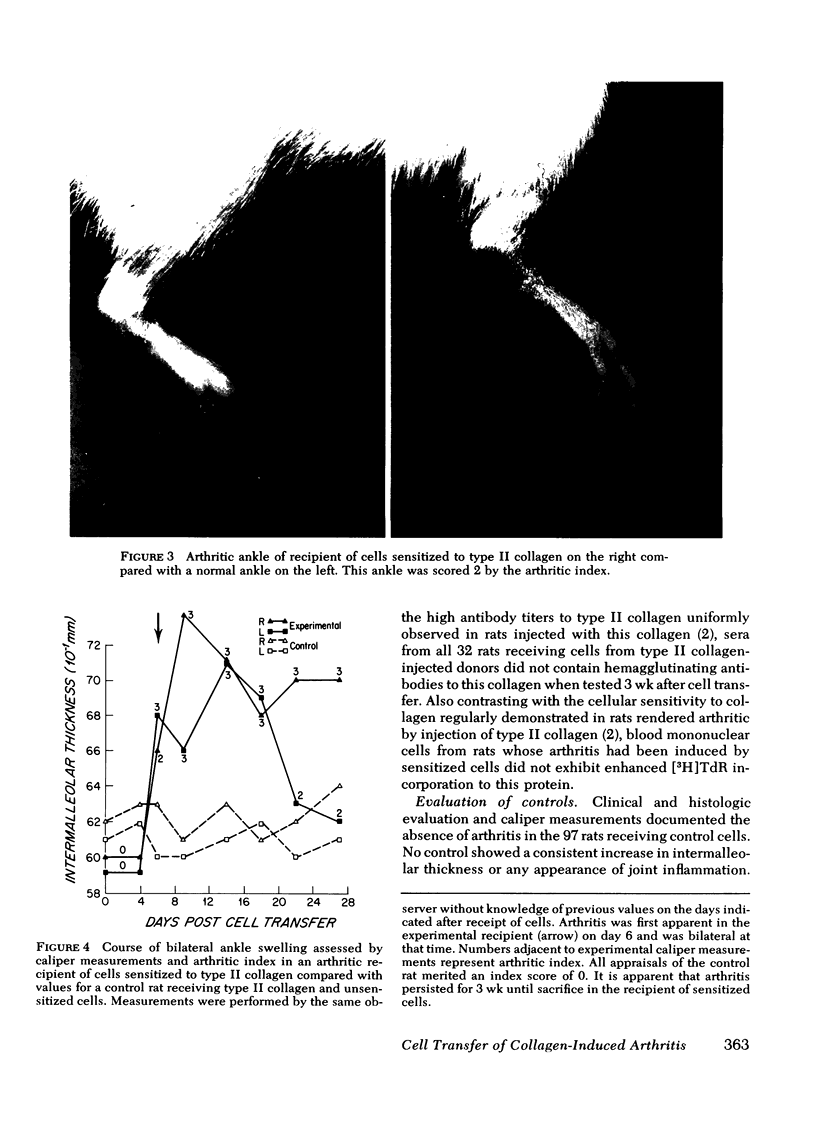
To investigate the role of immunologic hypersensitivity to collagen in the causation of type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats, passive transfer experiments were performed. Wistar/Lewis rats used in these experiments were demonstrated to be histocompatible by prolonged skin graft survival and mixed lymphocyte cultures. Popliteal lymph node weight assays excluded a potential for graft-vs.-host reactivity in this strain. 9 of 32 naive rats developed arthritis after intravenous receipt of pooled spleen and lymph node cells from donors that had been injected intradermally with type II collagen emulsified in incomplete Freund's adjuvant. This passively transferred synovitis was evident clinically as well as histologically. In control cell transfer experiments involving a total of 97 recipients, transfer of arthritis was shown to require viable cells sensitized to type II collagen. These controls included 17 rats receiving cells from unimmunized donors, 20 recipients of cells from donors injected with incomplete Freund's adjuvant alone, and 24 recipients of cells from rats injected with type I collagen in adjuvant. Deliberate addition of solubilized type II collagen to unsensitized cells at the time of transfer or injection of heat-killed sensitized cells also did not cause arthritis in a total of 36 recipients. These latter two control groups indicate that disease transfer was not the result of antigen carry-over. Intravenous injection of sera from arthritic donors was incapable of passively transferring clinical or histologic synovitis in 30 recipients. Thus, these studies directly implicate immunologic sensitivity to the cartilage type of collagen in the etiology of this autoimmune disease.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BILLINGHAM R. E., DEFENDIV, SILVERS W. K., STEINMULLER D. Quantitative studies on the induction of tolerance of skin homografts and on runt disease in neonatal rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Feb;28:365–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford W. L., Burr W., Simonsen M. A lymph node weight assay for the graft-versus-host activity of rat lymphoid cells. Transplantation. 1970 Sep;10(3):258–266. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197009000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn E., Timpl R., Miller E. J. The production of specific antibodies to native collagens with the chain compositions, (alpha1(I))3, (alpha1(II))3, and (alpha1(I))2alpha 2. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):421–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsenmayer T. F., Smith G. N., Jr, Hay E. D. Synthesis of two collagen types by embryonic chick corneal epithelium in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):39–43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Isolation and characterization of a collagen from chick cartilage containing three identical alpha chains. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1652–1659. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. N., Jr, Linsenmayer T. F., Newsome D. A. Synthesis of type II collagen in vitro by embryonic chick neural retina tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4420–4423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Autoimmunity to type II collagen an experimental model of arthritis. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):857–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Townes A. S., Kang A. H., David J. R. Humoral and cellular sensitivity to collagen in type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):89–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI108929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung K. S., Leong C., McCarty T. Pathogenesis of experimental allergic orchitis. III. T lymphocyte requirement in local adoptive transfer by peritoneal exudate cells. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1774–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung K. S., Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of experimental allergic orchitis. II. The role of antibody. J Immunol. 1971 Jun;106(6):1463–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B. Quantitative studies on the mixed lymphocyte interaction in rats. I. Conditions and parameters of response. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):625–654. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]