Abstract
The relative contributions of impaired insulin secretion and of tissue insensitivity to insulin to the carbohydrate intolerance of uremia were investigated in 10 chronically uremic subjects. Two types of glucose-clamp experiments were performed in each patient before and after 10 wk of thrice weekly hemodialysis. In both types the blood glucose concentration was maintained at a constant level by the periodic adjustment of a variable glucose infusion with a negative feedback formula.
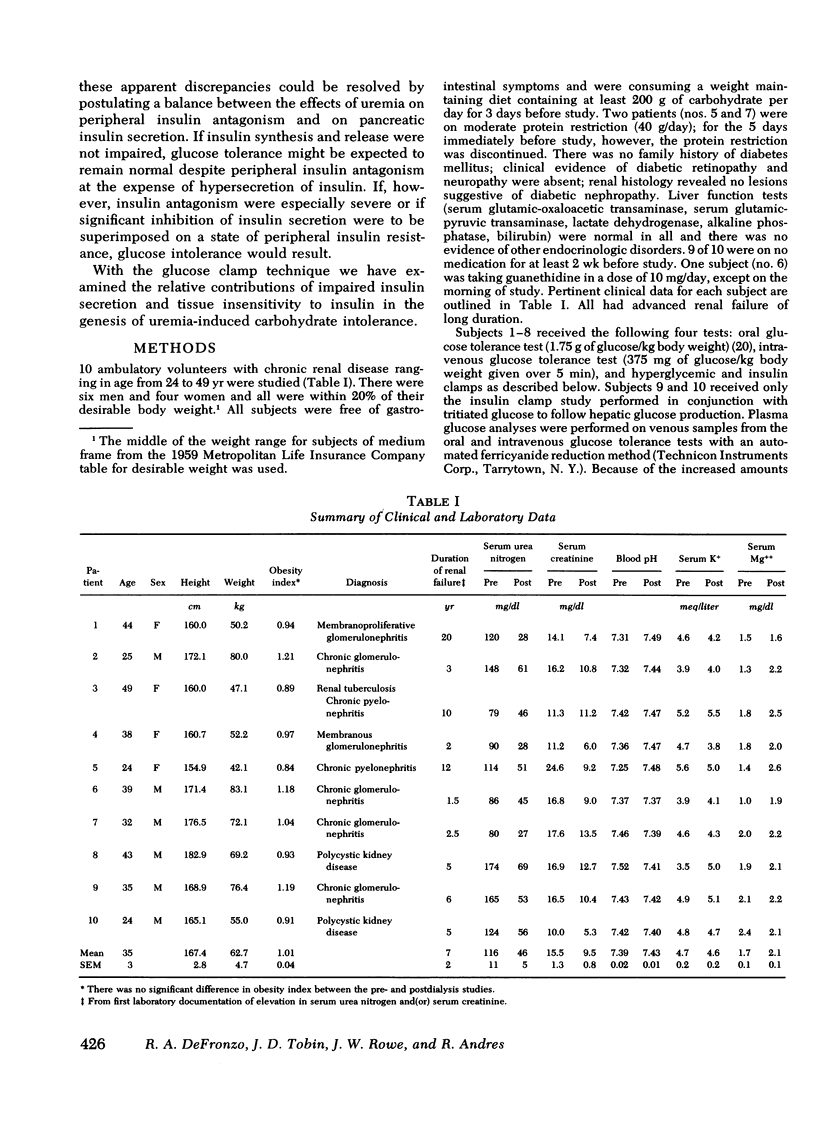
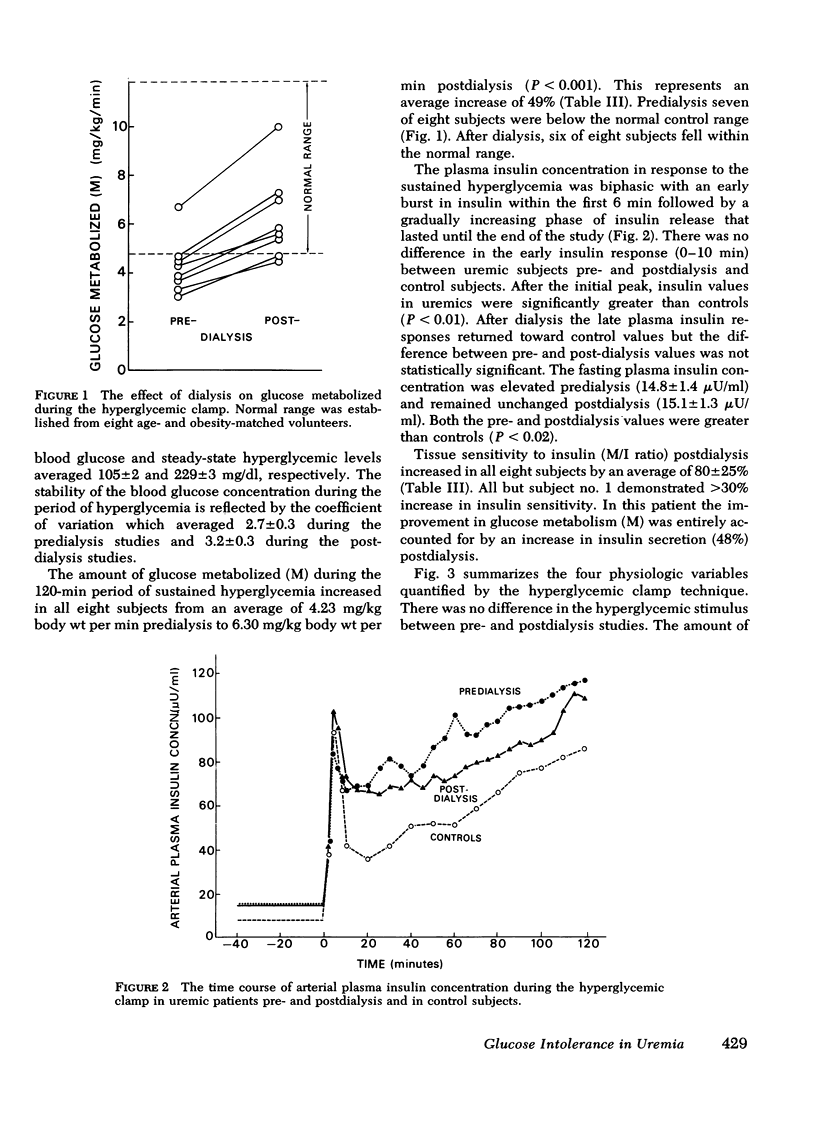
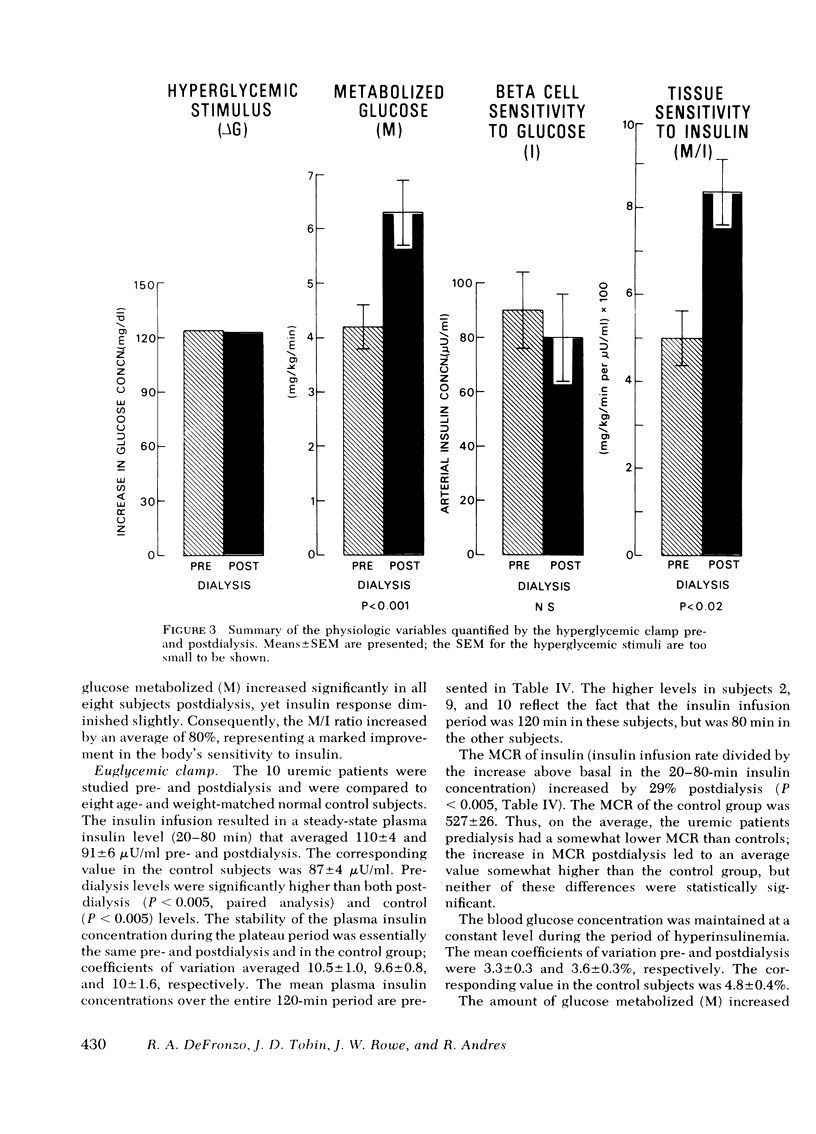
Hyperglycemic clamp. The blood glucose concentration was acutely raised and maintained 125 mg/dl above basal levels for 2 h. Since the glucose concentration was held constant, the glucose infusion rate is an index of glucose metabolism (M). After dialysis M increased in all patients from an average of 4.23 to 6.30 mg/kg body wt per min (P < 0.001). The plasma insulin responses (I) both pre- and postdialysis were biphasic with an early burst within the first 2-5 min, followed by a phase of gradually increasing insulin concentration. After dialysis the plasma insulin response diminished slightly. Consequently, the M/I ratio, an index of tissue sensitivity to endogenous insulin, increased postdialysis in all subjects by an average of 92% (P < 0.01).
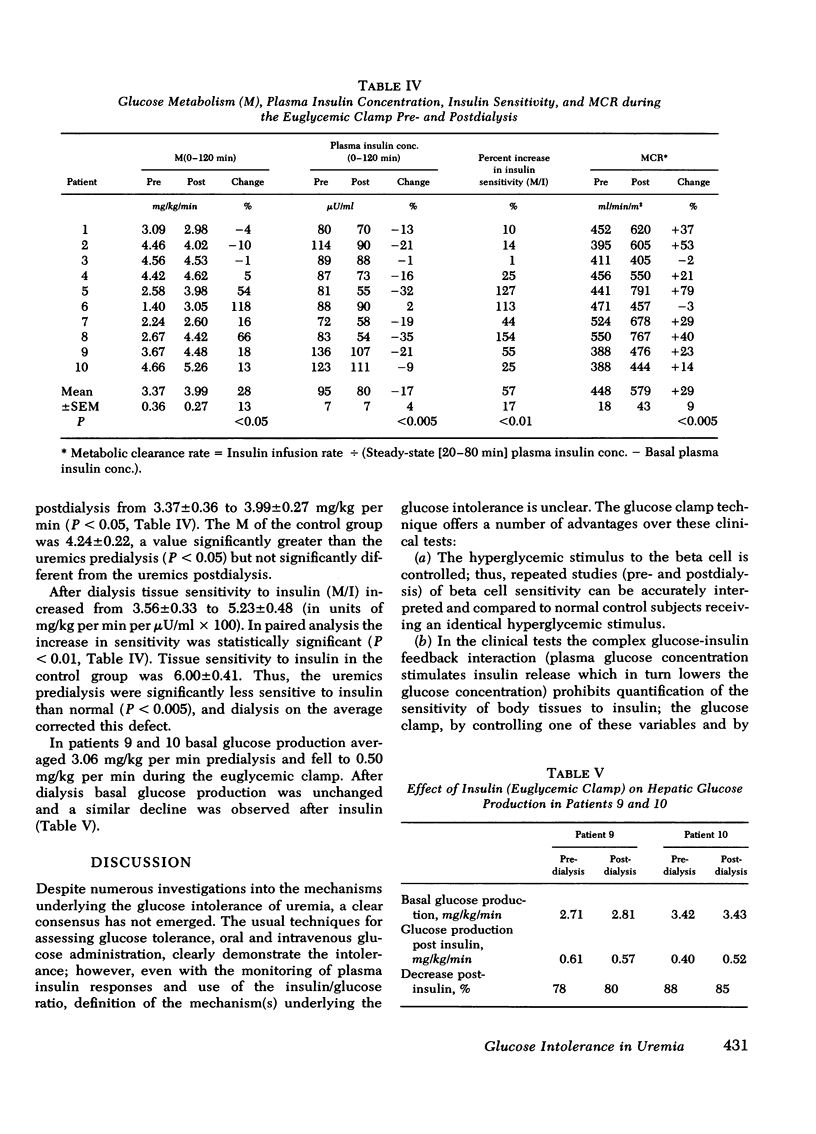
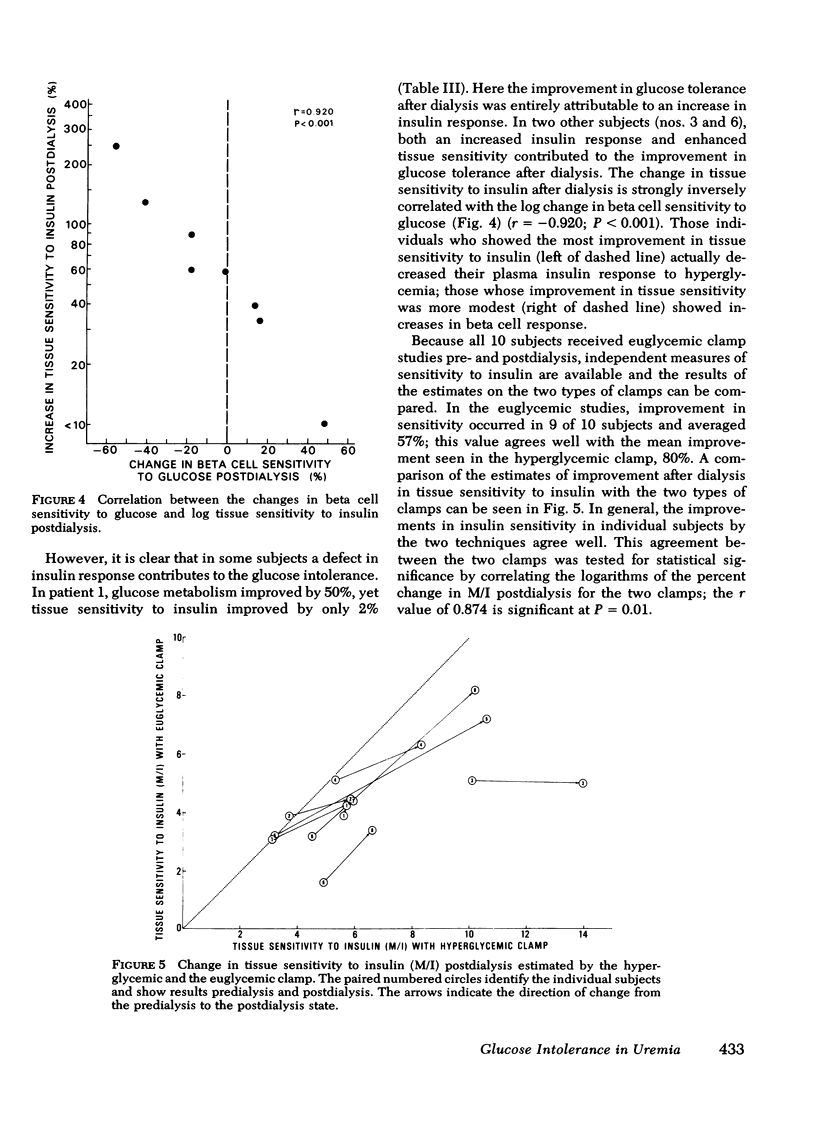
Euglycemic clamp. The plasma insulin concentration was acutely raised and maintained by a primecontinuous insulin infusion. The blood glucose concentration was held constant at the basal level by a variable glucose infusion as above. M/I again is a measure of tissue sensitivity to insulin (exogenous) and increased in all patients postdialysis by an average of 57% (P < 0.01). In two patients hepatic glucose production was measured with tritiated glucose during the euglycemic clamp and declined by 84% predialysis. A similar decrease (82%) was observed postdialysis. Thus, both the hyperglycemic and euglycemic clamp techniques demonstrated tissue insensitivity to insulin to be the dominant carbohydrate defect in uremia. The surprising apparent lack of consistency in the change in beta cell response postdialysis is explained by the strong inverse correlation between beta cell sensitivity to glucose and tissue sensitivity to insulin (r = -0.920; P < 0.001). Those individuals who showed the most striking improvement in tissue sensitivity to insulin actually decreased their serum insulin response to hyperglycemia; those whose improvement in tissue sensitivity was more modest showed increases in beta cell responses.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres R. Aging and diabetes. Med Clin North Am. 1971 Jul;55(4):835–846. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32479-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilbrey G. L., Faloona G. R., White M. G., Knochel J. P. Hyperglucagonemia of renal failure. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):841–847. doi: 10.1172/JCI107624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Nelson N. C. Portal vein insulin concentrations in diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1971 May;20(5):286–288. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.5.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs J. D., Buchanan K. D., Luke R. G., McKiddie M. T. Role of insulin in glucose intolerance in uraemia. Lancet. 1967 Mar 4;1(7488):462–464. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E. An analogue computer model for the insulin response to glucose infusion. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 May;55(1):163–183. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0550163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerletty J. M., Engbring N. H. Azotemia and glucose intolerance. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jun;66(6):1097–1108. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-66-6-1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain M. J., Stimmler L. The renal handling of insulin. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jun;46(6):911–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI105597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. D., Horowitz H. I. Carbohydrate metabolism in uremia: inhibition of phosphate release. Am J Clin Nutr. 1968 May;21(5):407–413. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/21.5.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan J. S., Hetenyi G., Jr Glucoregulatory responses in normal and diabetic dogs recorded by a new tracer method. Metabolism. 1971 Apr;20(4):360–372. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Dynamics of insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1968 Sep;83(3):572–584. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Andres R., Edgar P., Walker W. G. Carbohydrate metabolism in uremia: a review. Medicine (Baltimore) 1973 Sep;52(5):469–481. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197309000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez A. R., Khurana R. C., Jung Y., Livstone E., Wolinsky A., Sinclair C., Danowski T. S. Enhanced response to tolbutamide in uremia. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1972 May-Jun;9(3):373–386. doi: 10.1007/BF01564560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M. A threshold distribution hypothesis for packet storage of insulin and its mathematical modeling. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2047–2059. doi: 10.1172/JCI107011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampers C. L., Lowrie E. G., Soeldner J. S., Merrill J. P. The effect of uremia upon glucose metabolism. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Nov;126(5):870–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampers C. L., Soeldner J. S., Doak P. B., Merrill J. P. Effect of chronic renal failure and hemodialysis on carbohydrate metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1719–1731. doi: 10.1172/JCI105478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampers C. L., Soeldner J. S., Gleason R. E., Bailey G. L., Diamond J. A., Merrill J. P. Insulin-glucose relationships in uremia. Am J Clin Nutr. 1968 May;21(5):414–422. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/21.5.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. S., Johnson C., Lebovitz H. E. Carbohydrate metabolism in uremia. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Jan;68(1):63–74. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrie E. G., Soeldner J. S., Hampers C. L., Merrill J. P. Glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in uremic, prediabetic, and normal subjects. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Oct;76(4):603–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADISON L. L., COMBES B., UNGER R. H., KAPLAN N. The relationship between the mechanism of action of the sulfonylureas and the secretion of insulin into the portal circulation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Mar 30;74(3):548–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb39579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov H., Christensen N. J. Growth hormone in uremia. I. Plasma growth hormone, insulin and glucagon after oral and intravenous glucose in uremic subjects. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Feb;27(1):51–60. doi: 10.3109/00365517109080189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKOFF G. T., THOMAS C. L., NEWTON J. D., SELLMAN J. C., TYLER F. H. Mechanism of impaired glucose tolerance in uremia and experimental hyperazotemia. Diabetes. 1958 Sep-Oct;7(5):375–383. doi: 10.2337/diab.7.5.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Pupo A. A. Insulin responses to glucose: evidence for a two pool system in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2309–2319. doi: 10.1172/JCI106197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J., Norwich K. H., Vranic M. Measurement and validation of nonsteady turnover rates with applications to the inulin and glucose systems. Fed Proc. 1974 Jul;33(7):1855–1864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaan N. A., Freeman R. M. Growth hormone levels in severe renal failure. Metabolism. 1970 Feb;19(2):102–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Bastl C., Finkelstein F. O., Fisher M., Black H., Hendler R., Felig P. Influence of uremia and hemodialysis on the turnover and metabolic effects of glucagon. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):722–731. doi: 10.1172/JCI108330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Hendler R., DeFronzo R., Wahren J., Felic P. Glucose homeostasis during prolonged suppression of glucagon and insulin secretion by somatostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):348–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Kramer K. J., Tobin J. D., Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Berman M., Andres R. A model of the kinetics of insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1481–1492. doi: 10.1172/JCI107697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitz I. M., Rubenstein A. H., Bersohn I., Abrahams C., Lowy C. Carbohydrate metabolism in renal disease. Q J Med. 1970 Apr;39(154):201–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEUSCHER A. BEURTEILUNG DER BLUTZUCKERWERTE UND DER GLUKOSETOLERANZ BEI URAEMIE. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1964 Jan 18;94:69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEUSCHER A., FANKHAUSER S., KUFFER F. R. [Studies on carbohydrate metabolism in renal insufficiency]. Klin Wochenschr. 1963 Jul 15;41:706–715. doi: 10.1007/BF01478416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchobroutky G., Rosselin G., Assan R., Derot M. Glucose intolerance in uraemia. II. Plasma growth hormone and glucagon values. Diabetologia. 1969 Feb;5(1):25–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01212215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESTERVELT F. B., Jr, SCHREINER G. E. The carbohydrate intolerance of uremic patients. Ann Intern Med. 1962 Aug;57:266–276. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-57-2-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILDBERGER H. L., RICKETTS H. T., REGUT L. Degradation of insulin by tissue extracts of normal and nephrotic rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jan;112:168–170. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-27982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt F. B. Insulin effect in uremia. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Jul;74(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt F. B., Jr Abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in uremia. Am J Clin Nutr. 1968 May;21(5):423–425. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/21.5.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt F. B., Jr Uremia and insulin response. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Nov;126(5):865–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. D., Lowy C., Fraser T. R., Spitz I. M., Rubenstein A. H., Bersohn I. Serum-growth hormone and glucose intolerance in renal failure. Lancet. 1968 Oct 12;2(7572):798–801. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92456-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


