Abstract
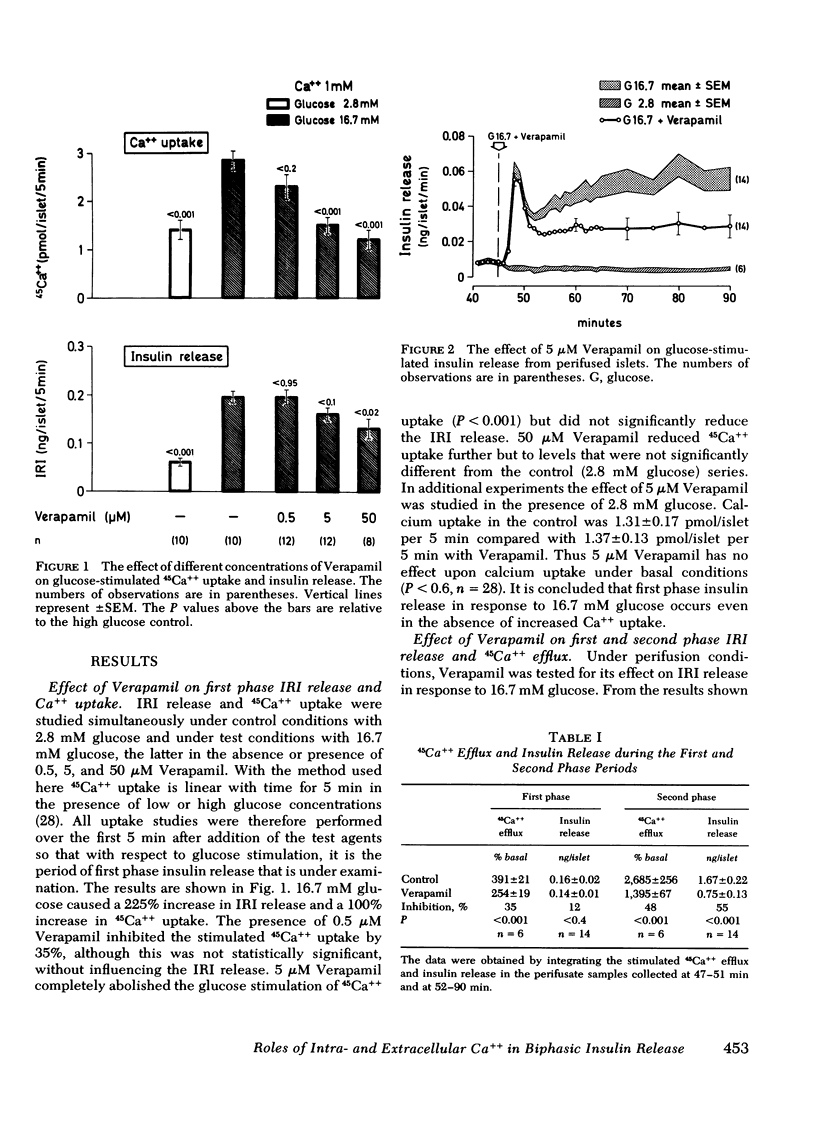
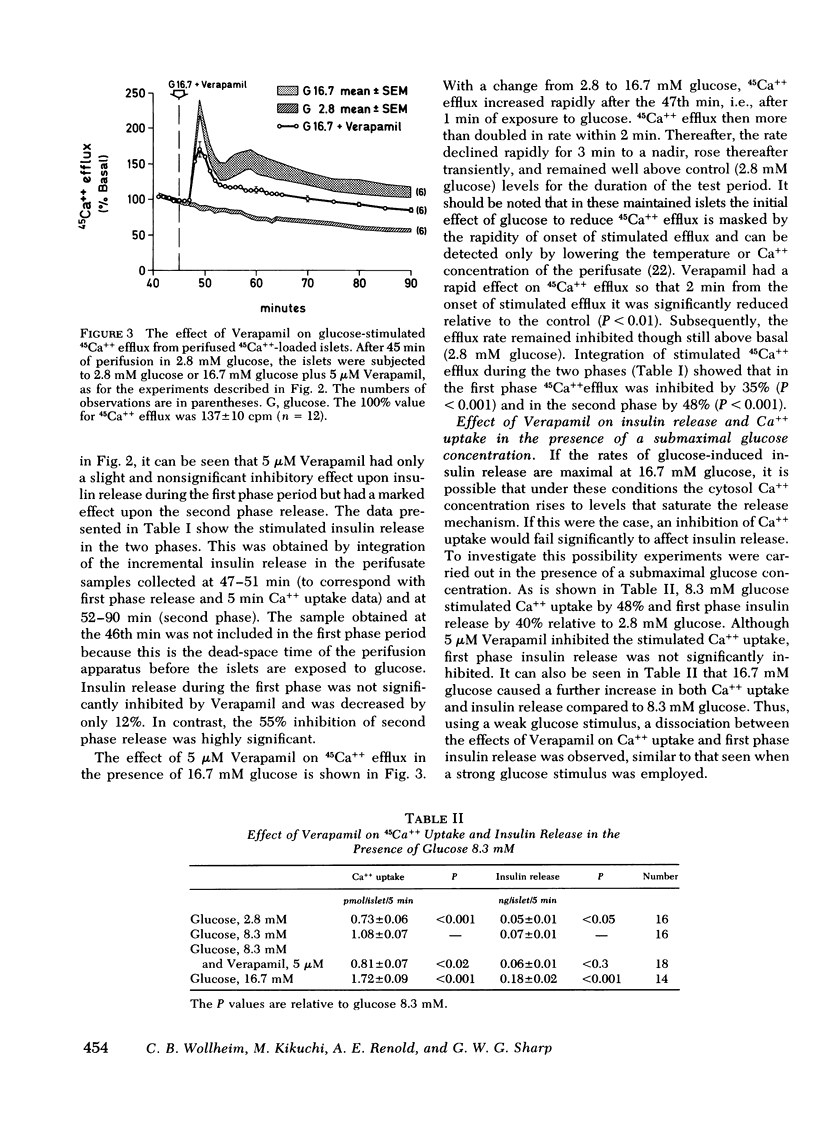
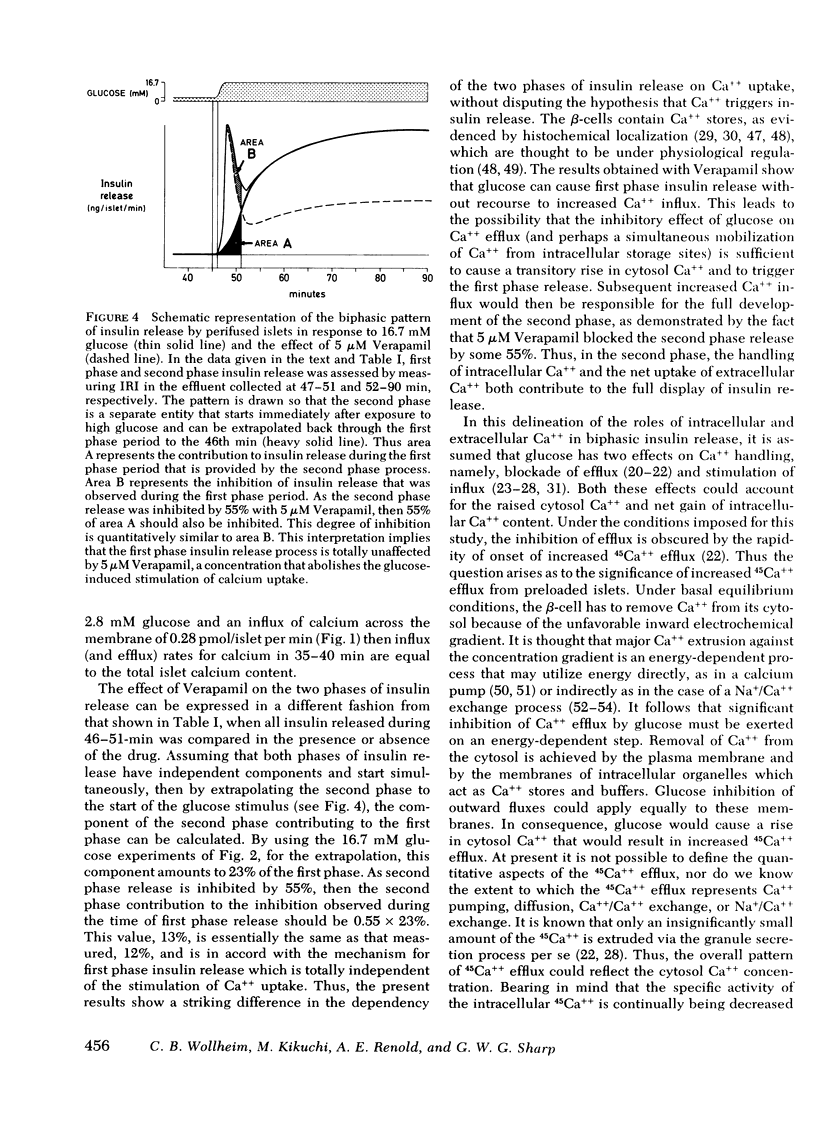
Verapamil, an agent known rapidly to block calcium uptake into islets of Langerhans, has been used to study the roles of intra- and extracellular calcium in the two phases of glucose-induced insulin release. Rates of calcium uptake and insulin release during the first phase were measured simultaneously over 5 min in rat islets after maintenance in tissue culture for 2 days. Rates of 45Ca++ efflux and insulin release during the first and second phases were also measured simultaneously under perifusion conditions. For this, islets were loaded with 45Ca++ during the entire maintenance period to complete isotopic equilibrium. Under static incubation conditions 5 μM Verapamil had no effect upon Ca++ uptake or insulin release in the presence of 2.8 mM glucose. By contrast, glucose-stimulated calcium influx was totally abolished without there being any significant effect upon first phase insulin release. Thus first phase insulin release is independent of increased uptake of extracellular calcium. The lack of effect of 5 μM Verapamil blockade on first phase insulin release was confirmed, under perifusion conditions, and was in marked contrast to the observed 55% inhibition of second phase release. 45Ca++ efflux was inhibited during both phases of the insulin release response.
The results show that increased calcium uptake in response to glucose is not involved in the mechanism of first phase insulin release but is required for the full development and maintenance of the second phase release. It seems possible that intracellular calcium is the major regulatory control for first phase insulin release and that intracellular calcium and increased uptake of extracellular calcium contribute almost equally to the second phase of glucose-induced release.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby J. P., Speake R. N. Insulin and glucagon secretion from isolated islets of Langerhans. The effects of calcium ionophores. Biochem J. 1975 Jul;150(1):89–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Nelson N. C. Portal vein insulin concentrations in diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1971 May;20(5):286–288. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.5.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. The interrelationship between sodium and calcium fluxes across cell membranes. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1974;70:33–82. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowiecki L., Freinkel N. Relationship between efflux of ionic calcium and phosphorus during excitation of pancreatic islets with glucose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 4;436(1):190–198. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R., Efendic S. Decreased sensitivity of the pancreatic beta cells to glucose in prediabetic and diabetic subjects. A glucose dose-response study. Diabetes. 1972 Apr;21(4):224–234. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.4.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. The plasma insulin response to glucose infusion in healthy subjects and in diabetes mellitus. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Jun;55(2):278–304. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0550278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles M. A., Lawecki J., Pictet R., Grodsky G. M. Insulin secretion. Interrelationships of glucose, cyclic adenosine 3:5-monophosphate, and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6134–6140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Dynamics of insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1968 Sep;83(3):572–584. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devis G., Somers G., Malaisse W. J. Stimulation of insulin release by calcium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 17;67(2):525–529. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90843-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donatsch P., Lowe D. A., Richardson B. P., Taylor P. The functional significance of sodium channels in pancreatic beta-cell membranes. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):357–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eto S., Wood J. M., Hutchins M., Fleischer N. Pituitary 45 Ca ion uptake and release of ACTH, GH, and TSH: effect of verapamil. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jun;226(6):1315–1320. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.6.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleckenstein A., Grün G., Tritthart H., Byon K. Uterus-Relaxation durch hochaktive Ca plus,plus-antagonistische Hemmstoffe der elektro-mechanischen Koppelung wie Isoptin (Verapamil, Iproveratril), Substanz D 600 und Segontin (Prenylamin). Versuche am isolierten Uterus virgineller Ratten. Klin Wochenschr. 1971 Jan;49(1):32–41. doi: 10.1007/BF01494064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formby B., Capito K., Egeberg J., Hedeskov C. J. Ca-activated ATPase activity in subcellular fractions of mouse pancreatic islets. Am J Physiol. 1976 Feb;230(2):441–448. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.2.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Osterlind K., Vinten J., Gammeltoft S. A procedure for measurement of distribution spaces in isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 24;286(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M. A threshold distribution hypothesis for packet storage of insulin and its mathematical modeling. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2047–2059. doi: 10.1172/JCI107011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Bennett L. L. Cation requirements for insulin secretion in the isolated perfused pancreas. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):910–913. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. J., Berent C. Calcium ion-induced uptakes and transormations of substrates in liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):645–652. doi: 10.1042/bj1150645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Calcium and secretion: distinction between two pools of glucose-sensitive calcium in pancreatic islets. Science. 1976 Dec 24;194(4272):1421–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.795030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Calcium uptake by pancreatic -cells as measured with the aid of 45 Ca and mannitol- 3 H. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1795–1801. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Effects of glucose on 45Ca2+ uptake by pancreatic islets as studied with the lanthanum method. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(3):639–656. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Evidence for mediated transport of glucose in mammalian pancreatic -cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 6;241(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Transport of -aminoisobutyric acid in mammalian pancretic -cells. Diabetologia. 1971 Aug;7(4):256–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01211878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B. Stimulation of insulin release after raising extracellular calcium. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Lambert A. E. Cobalt inhibition of insulin secretion and calcium uptake by isolated rat islets. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1669–1677. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman L., Sato T., Hales C. N. The electron microscopic localization of cations to pancreatic islets of Langerhans and their possible tole in insulin secretion. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Feb;42(3):298–311. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Montague W., Tyhurst M. Calcium distribution in islets of Langerhans: a study of calcium concentrations and of calcium accumulation in B cell organelles. J Cell Sci. 1975 Nov;19(2):395–409. doi: 10.1242/jcs.19.2.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl R. C., Zawalich W. S., Ferrendelli J. A., Matschinsky F. M. The role of Ca-2+ and cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in insulin release induced in vitro by the divalent cation ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4575–4579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi M., Rabinovitch A., Blackard W. G., Renold A. E. Perifusion of pancreas fragments. A system for the study of dynamic aspects of insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1974 Jun;23(6):550–559. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.6.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi M., Wollheim C. B., Cuendet G. S., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Studies on the dual effects of glucose on 45Ca++ efflux from isolated rat islets. Endocrinology. 1978 May;102(5):1339–1349. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-5-1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Howell S. L., Young D. A., Fink C. J. New hypothesis of insulin secretion. Nature. 1968 Sep 14;219(5159):1177–1179. doi: 10.1038/2191177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. 3. Uptake of 45 calcium by isolated islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1971 Jan;88(1):72–80. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-1-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Brisson G. R., Baird L. E. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. X. Effect of glucose on 45 Ca efflux from perifused islets. Am J Physiol. 1973 Feb;224(2):389–394. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.2.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Devis G., Pipeleers D. G., Somers G. Calcium-antagonists and islet function. IV. Effect of D600. Diabetologia. 1976 Mar;12(1):77–81. doi: 10.1007/BF01221969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Herchuelz A., Levy J., Sener A. Calcium antagonists and islet function--III. The possible site of action of verapamil. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Apr 15;26(8):735–740. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Van Obberghen E., Devis G., Somers G., Ravazzola M. Dynamics of insulin release and microtubular-microfilamentous system. V. A model for the phasic release of insulin. Eur J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;4(5):313–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb00409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. D., Hales C. N. The role of calcium and magnesium in insulin secretion from rabbit pancreas studied in vitro. Diabetologia. 1967 Mar;3(1):47–49. doi: 10.1007/BF01269910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naber S. P., McDaniel M. L., Lacy P. E. The effect of glucose on the acute uptake and efflux of calcium-45 in isolated rat islets. Endocrinology. 1977 Sep;101(3):686–693. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-3-686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayler W. G., Szeto J. Effect of verapamil on contractility, oxygen utilization, and calcium exchangeability in mammalian heart muscle. Cardiovasc Res. 1972 Mar;6(2):120–128. doi: 10.1093/cvr/6.2.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S., Matschinsky F. M., Lacy P. E., Conant S. Electrophysiological evidence for the autoregulation of beta-cell secretion by insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 27;497(2):408–414. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90198-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Pupo A. A. Insulin responses to glucose: evidence for a two pool system in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2309–2319. doi: 10.1172/JCI106197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch A., Gutzeit A., Kikuchi M., Cerasi E., Renold A. E. Defective early phase insulin release in perifused isolated pancreatic islets of spiny mice (Acomys cahirinus). Diabetologia. 1975 Oct;11(5):457–465. doi: 10.1007/BF00429916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravazzola M., Malaisse-Lagae F., Amherdt M., Perrelet A., Malaisse W. J., Orci L. Patterns of calcium localization in pancreatic endocrine cells. J Cell Sci. 1976 Jun;21(1):107–117. doi: 10.1242/jcs.21.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. T., Thorn N. A. Calcium and stimulus-secretion coupling in the neurohypophysis. II. Effects of lanthanum, a verapamil analogue (D600) and prenylamine on 45-calcium transport and vasopressin release in isolated rat neurohypophyses. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1974 Jul;76(3):471–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J., Rossi G. L. (Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ )-activated membrane ATPases in human red cells and their possible relations to cation transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer H. J., Klöppel G. The significance of calcium in insulin secretion. Ultrastructural studies on identification and localization of calcium in activated and inactivated B cells of mice. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1974;362(3):231–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00432197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehilin J. Calcium uptake by subcellular fractions of pancreatic islets. Effects of nucleotides and theophylline. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):63–69. doi: 10.1042/bj1560063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer H. S., Allen E. W., Herron A. L., Jr, Brennan M. T. Insulin secretion in response to glycemic stimulus: relation of delayed initial release to carbohydrate intolerance in mild diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Mar;46(3):323–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI105534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. G., Benedetti A., Grodsky G. M., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Early phase of insulin release. Diabetes. 1968 Nov;17(11):684–692. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.11.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Trueheart P. A., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Calcium-induced insulin release in monolayer culture of the endocrine pancreas. Studies with ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1354–1360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Kikuchi M., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Somatostatin- and epinephrine-induced modifications of 45Ca++ fluxes and insulin release in rat pancreatic islets maintained in tissue culture. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1165–1173. doi: 10.1172/JCI108869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


