Abstract
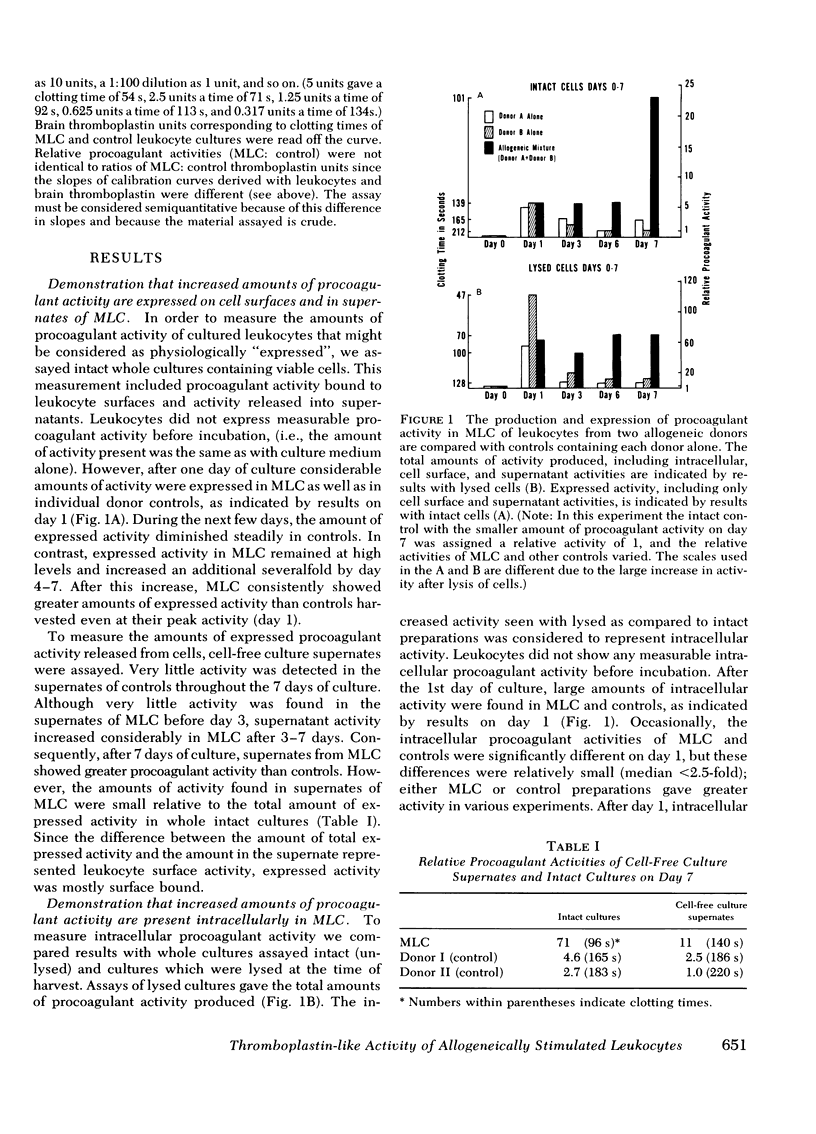
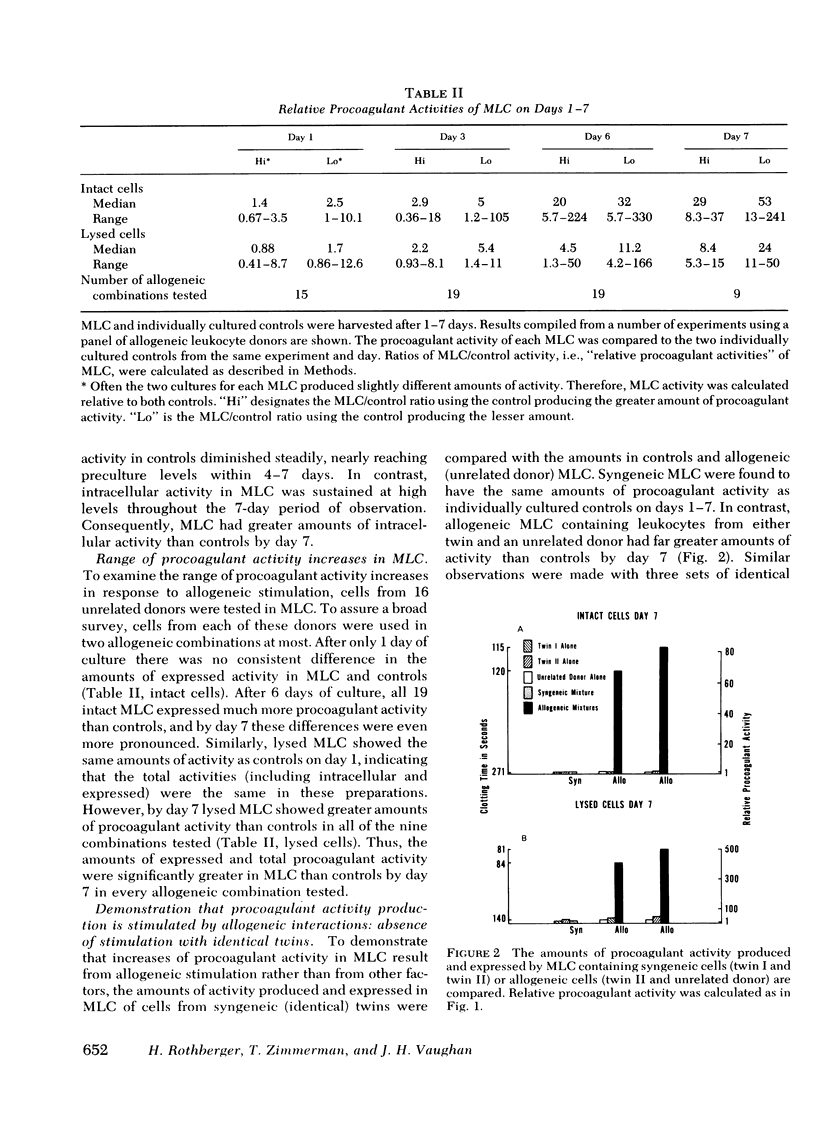
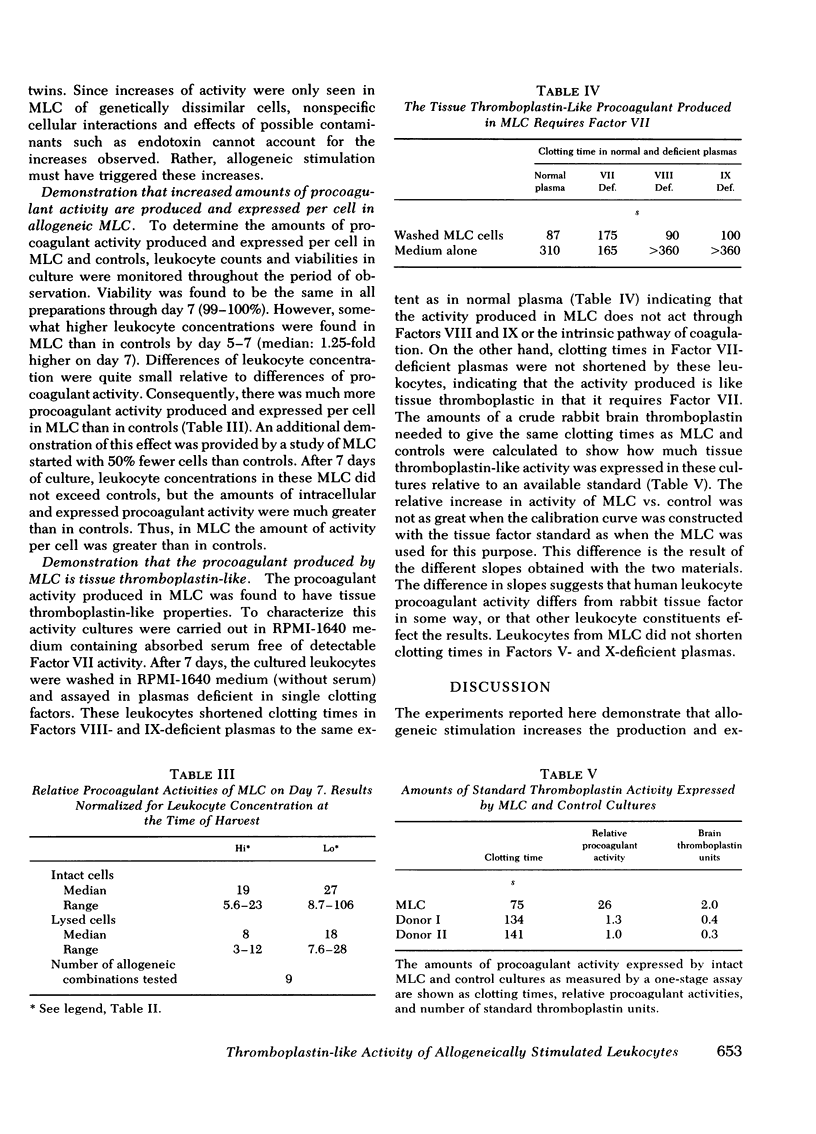
Intravascular coagulation, thrombosis, and fibrin deposition often produce tissue damage in allogeneic inflammatory reactions such as allograft rejection. The mechanisms which initiate blood clotting in these reactions are poorly understood. We find that allogeneic stimulation of human leukocytes in vitro increases production and expression of tissue thromboplastin-like activity. In our experiments mixed leukocyte cultures (MLC) of cells from allogeneic (unrelated) donors produced and expressed more procoagulant activity than control cultures of cells from each donor alone. After 7 days, allogeneic MLC had 5- to 50-fold more total procoagulant activity than controls, as shown by assaying lysed whole cultures. Additionally, allogeneic MLC had 8- to 240-fold more procoagulant activity expressed on leukocyte surfaces and in culture supernates than controls after 7 days, as shown by assaying intact whole cultures and cell-free supernates. These increases were largely accounted for by gains in the amounts of procoagulant activity produced and expressed per cell in MLC as compared to controls. Controls and MLC produced and expressed considerable amounts of procoagulant activity during the 1st day of culture, and there were no differential effects of allogeneic stimulation on day 1. However, after day 1, the total amount of procoagulant activity produced and the amount expressed declined steadily in controls, nearly reaching preculture levels by day 7. In contrast, the total amount of procoagulant activity in allogeneic MLC remained high, and the amount of activity expressed on cell surfaces and in supernates increased severalfold by day 7. MLC of syngeneic (identical twin) cells produced and expressed the same amount of activity as controls over a 7-day period, whereas MLC of cells from each twin and an allogeneic donor produced and expressed more activity than controls (at least 9- and 35-fold more, respectively). Thus, increases of procoagulant activity production and expression were found only in MLC of genetically dissimilar cells. Therefore, these increases must have resulted from allogeneic stimulation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach F. H., Rood J. J. The major histocompatibility complex--genetics and biology (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 14;295(16):872–878. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610142951606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun W. E., Merrill J. P. Urine fibrinogen fragments in human renal allografts. A possible mechanism of renal injury. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jun 20;278(25):1366–1371. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196806202782503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch G. J., Braun W. E., Carpenter C. B., Corson J. M., Galvanek E. R., Reynolds E. S., Merrill J. P., Dammin G. J. Intravascular coagulation (IVC) in human renal allograft rejection. Transplant Proc. 1969 Mar;1(1):267–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch G. J., Reynolds E. S., Galvanek E. G., Braun W. E., Dammin G. J. Human renal allografts. The role of vascular injury in early graft failure. Medicine (Baltimore) 1971 Jan;50(1):29–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. B., d'Apice A. J., Abbas A. K. The role of antibodies in the rejection and enhancement of organ allografts.?7318. Adv Immunol. 1976;22:1–65. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60547-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronlund M., Hardin J., Burton J., Lee L., Haber E., Bloch K. J. Fibrinopeptide A in plasma of normal subjects and patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):142–151. doi: 10.1172/JCI108443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski A. J., Dupont B., Hansen J. A., Safai B., Pahwa S., Good R. A. Human immunodeficiency disease: impairment of cellular interactions leading to abnormal mediator production in mixed lymphocyte culture reaction. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):858–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanyerezi B. R., Lwanga S. K., Block K. J. Fibrinogen degradation products in serum and urine of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Relation to renal disease and pathogenetic mechanism. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Mar-Apr;14(2):267–275. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid-Smith P. Coagulation and renal disease. Kidney Int. 1972 Oct;2(4):183–190. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kociba G. J., Loeb W. F., Wall R. L. Development of procoagulant (tissue thromboplastin) activity in cultured leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 May;79(5):778–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. J., Granger G. A. Relationship of lymphotoxin secretion and DNA synthesis in the human mixed lymphocytes reaction in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1975 May;17(1):192–201. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. G., Goldstein R., Cummings G., Lange K. Stimulation of human leukocyte thromboplastic activity by endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):145–148. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi S. L., Aptekar R. G., Steinberg A. D., Gralnick H. R., Decker J. L. Urinary fibrin split products in lupus nephritis. Correlation with other parameters of renal disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Mar-Apr;17(2):158–164. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. Biological control of factor VII. Thromb Haemost. 1976 Feb 29;35(1):96–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemetz J. Coagulant activity of leukocytes. Tissue factor activity. J Clin Invest. 1972 Feb;51(2):307–313. doi: 10.1172/JCI106815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemetz J., Fani K. Role of leukocytes in blood coagulation and the generalized Shwartzman reaction. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 25;232(34):247–248. doi: 10.1038/newbio232247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemetz J., Marcus A. J. The stimulatory effect of platelets and platelet membranes on the procoagulant activity of leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1437–1443. doi: 10.1172/JCI107891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter K. A., Dossetor J. B., Marchioro T. L., Peart W. S., Rendall J. M., Starzl T. E., Terasaki P. I. Human renal transplants. I. Glomerular changes. Lab Invest. 1967 Jan;16(1):153–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles F. R., Hardin J. A., Pitlick F. A., Hoyer L. W., Conrad M. E. Tissue factor activity in lymphocyte cultures from normal individuals and patients with hemophilia A. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1427–1434. doi: 10.1172/JCI107316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles F. R., Levin J., Hardin J. A., Barr C. F., Conrad M. E., Jr Tissue factor generation by human mononuclear cells: effects of endotoxin and dissociation of tissue factor generation from mitogenic response. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Apr;89(4):792–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivers R. P., Hathaway W. E., Weston W. L. The endotoxin-induced coagulant activity of human monocytes. Br J Haematol. 1975 Jul;30(3):311–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberger H., Zimmerman T. S., Spiegelberg H. L., Vaughan J. H. Leukocyte procoagulant activity: enhancement of production in vitro by IgG and antigen-antibody complexes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):549–557. doi: 10.1172/JCI108670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. T., Jr, Hill G. S., Zmijewski C. M. The pathology of renal homograft rejection. A review. Am J Pathol. 1976 Dec;85(3):773–804. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli P., McCluskey R. T. The pathogenetic role of the coagulation process in glomerular diseases of immunologic origin. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1971;1:47–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeldis S. M., Nemerson Y., Pitlick F. A., Lentz T. L. Tissue factor (thromboplastin): localization to plasma membranes by peroxidase-conjugated antibodies. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):766–768. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Fierer J., Rothberger H. Blood coagulation and the inflammatory response. Semin Hematol. 1977 Oct;14(4):391–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. The immunopathology of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):265–336. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


