Abstract
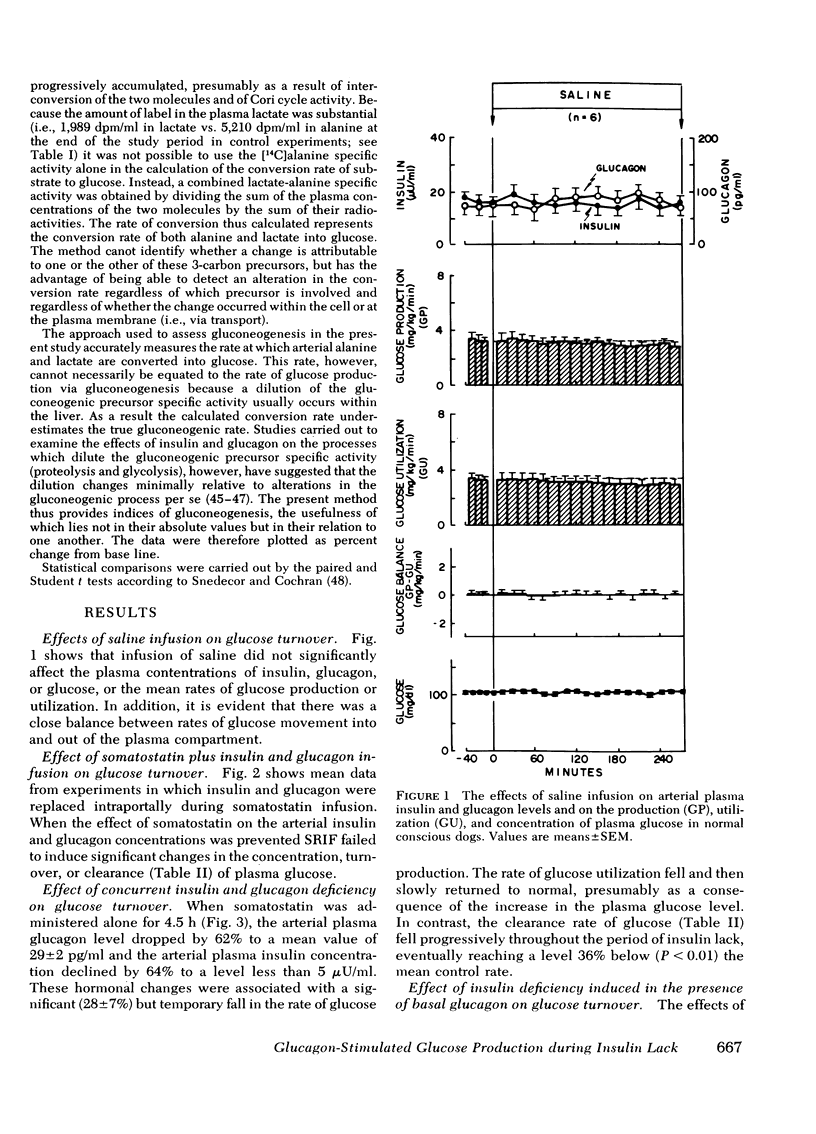
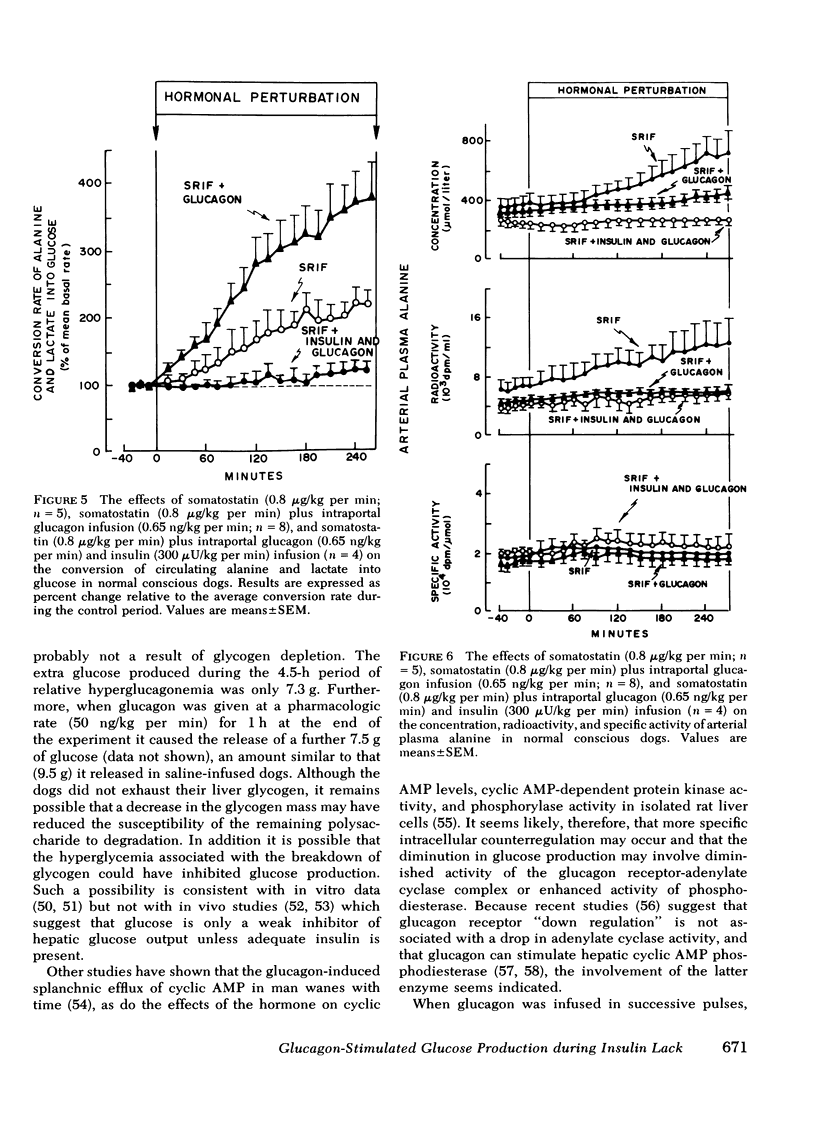
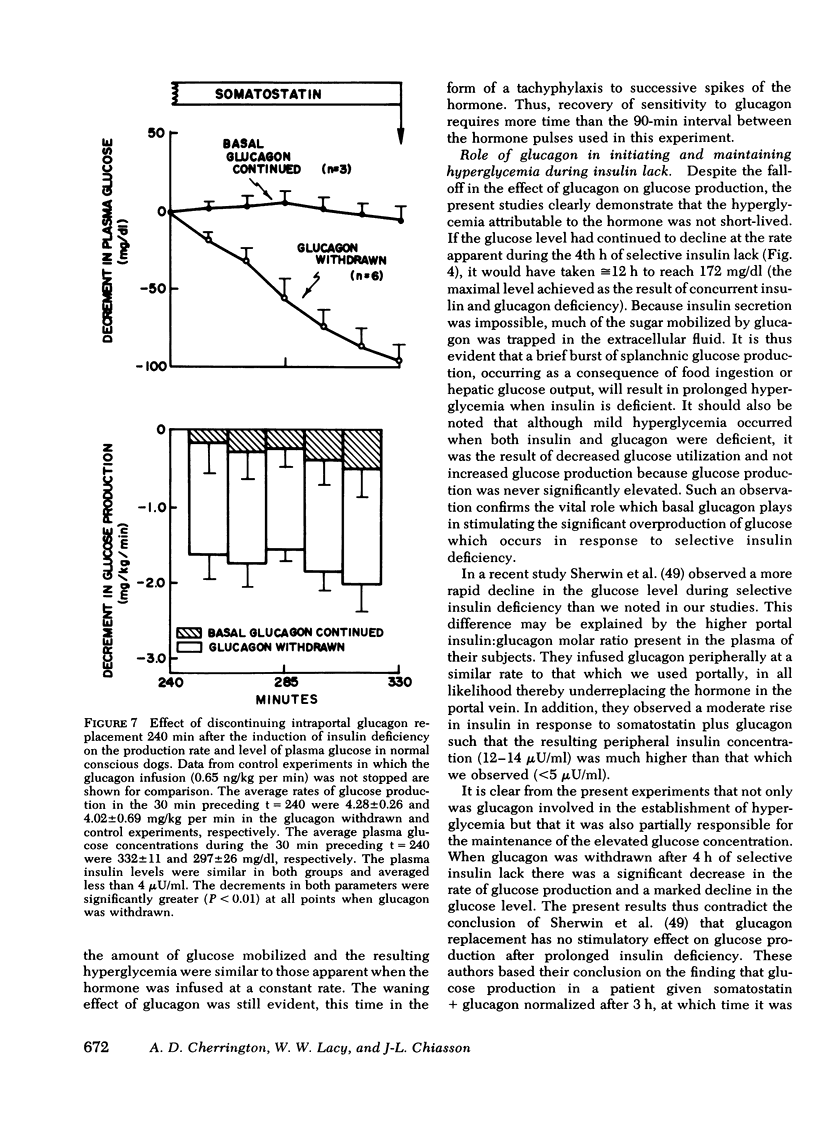
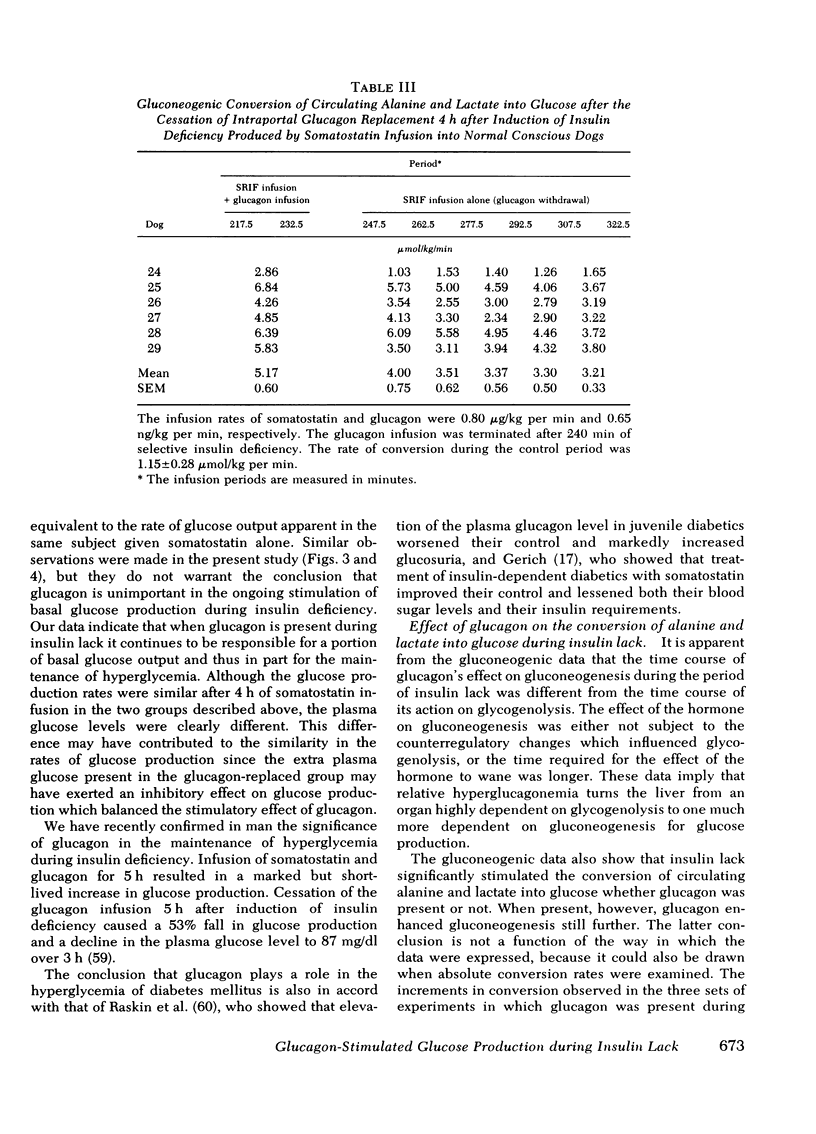
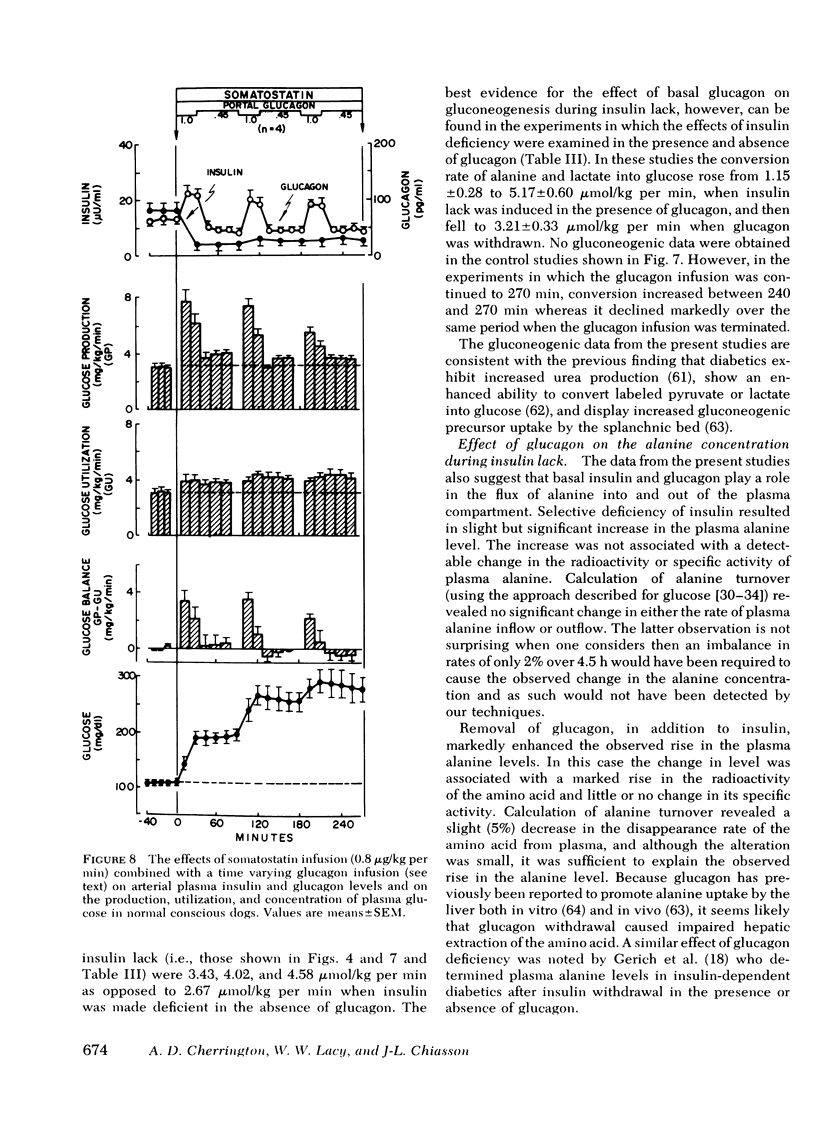
The aim of the present experiments was to determine the effects of basal glucagon on glucose production after induction of prolonged insulin lack in normal conscious dogs fasted overnight. A selective deficiency of insulin or a combined deficiency of both pancreatic hormones was created by infusing somatostatin alone or in combination with an intraportal replacement infusion of glucagon. Glucose production (GP) was measured by a primed constant infusion of [3H-3]glucose, and gluconeogenesis (GNG) was assessed by determining the conversion rate of circulating [14C]alanine and [14C]lactate into [14C]glucose. When insulin deficiency was induced in the presence of basal glucagon the latter hormone caused GP to double and then to decline so that after 4 h it had returned to the conrol rate. The conversion of alanine and lactate into glucose, on the other hand, increased throughout the period of insulin lack. Withdrawal of glucagon after GP had normalized resulted in a 40% fall in GP, a 37% decrease in GNG, and a marked decrease in the plasma glucose concentration. Induction of insulin deficiency in the absence of basal glucagon resulted in an initial (30%) drop in GP followed by a restoration of normal GP after 2--3 h and moderately enhanced glucose formation from alanine and lactate. It can be concluded that (a) the effect of relative hyperglucagonemia on GP is short-lived; (b) the waning of the effect of glucagon is attributable solely to a diminution of glycogenolysis because GNG remains stimulated; (c) basal glucagon markedly enhances the GNG stimulation apparent after induction of insulin deficiency; and (d) basal glucagon worsens the hyperglycemia pursuant on the induction of insulin deficiency both by triggering an initial overproduction of glucose and by maintaining the basal production rate thereafter.
Full text
PDF


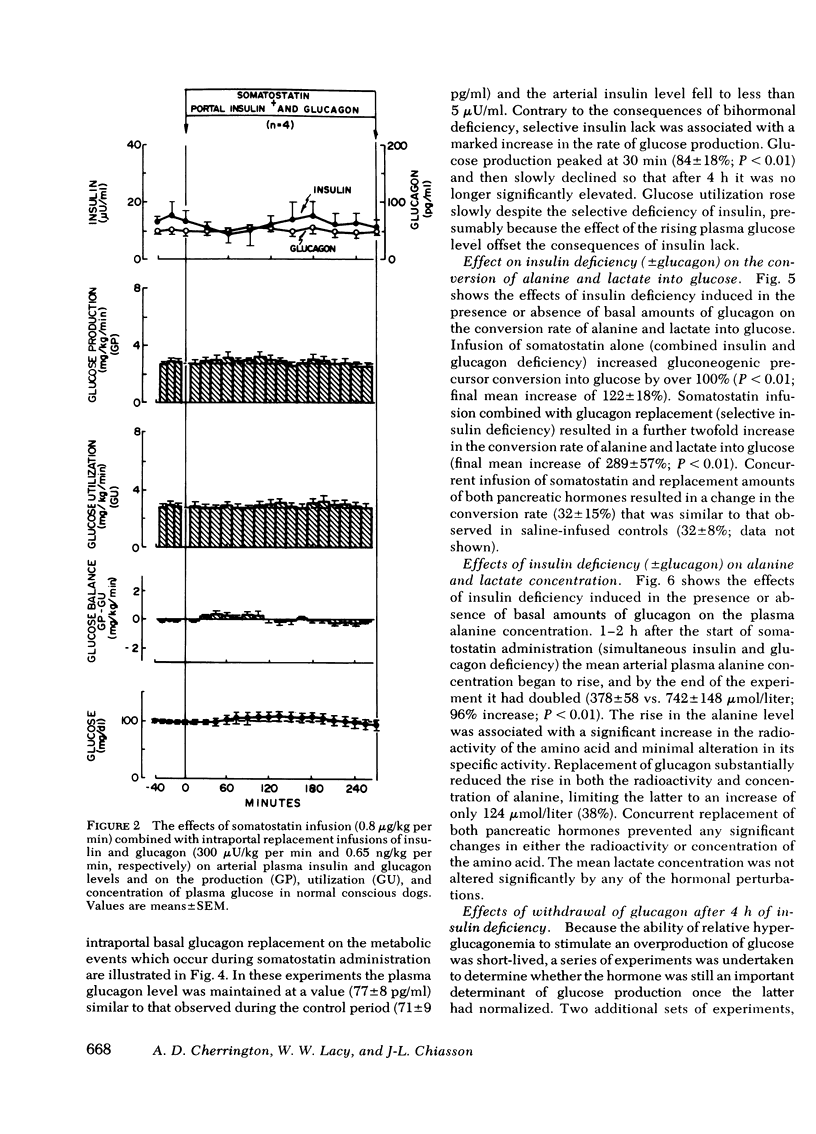
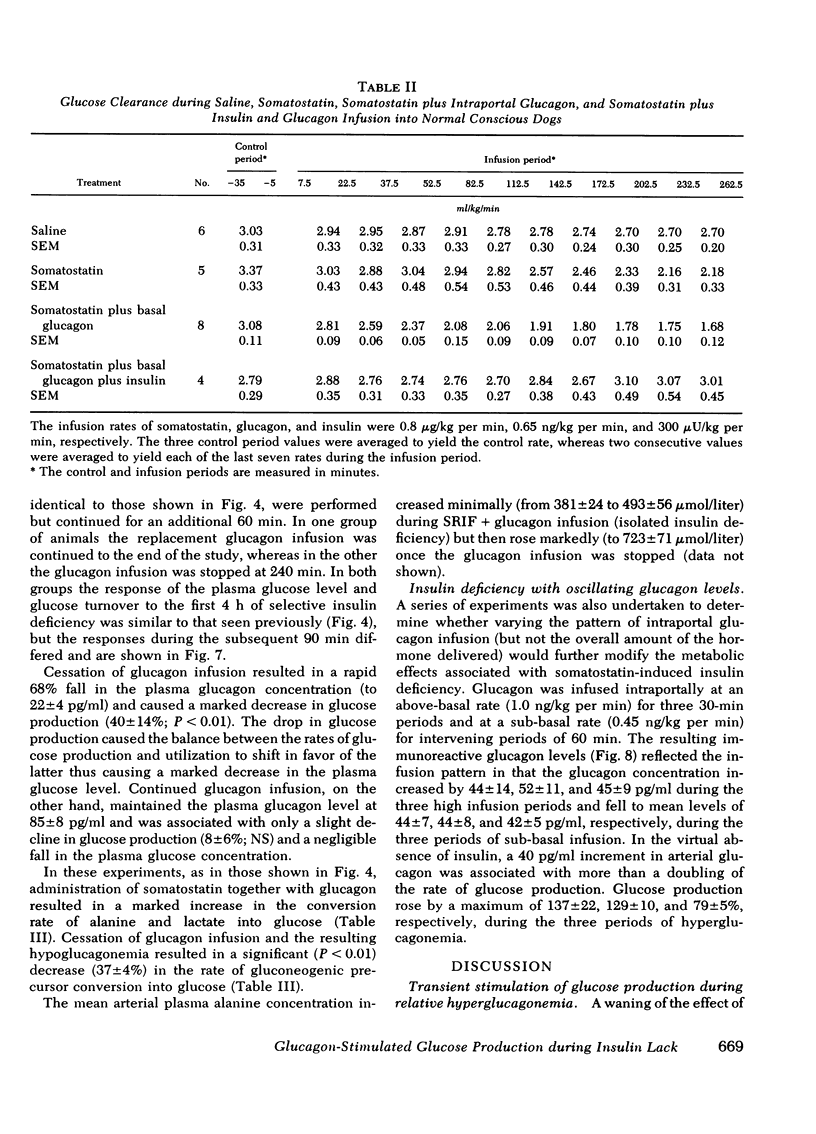
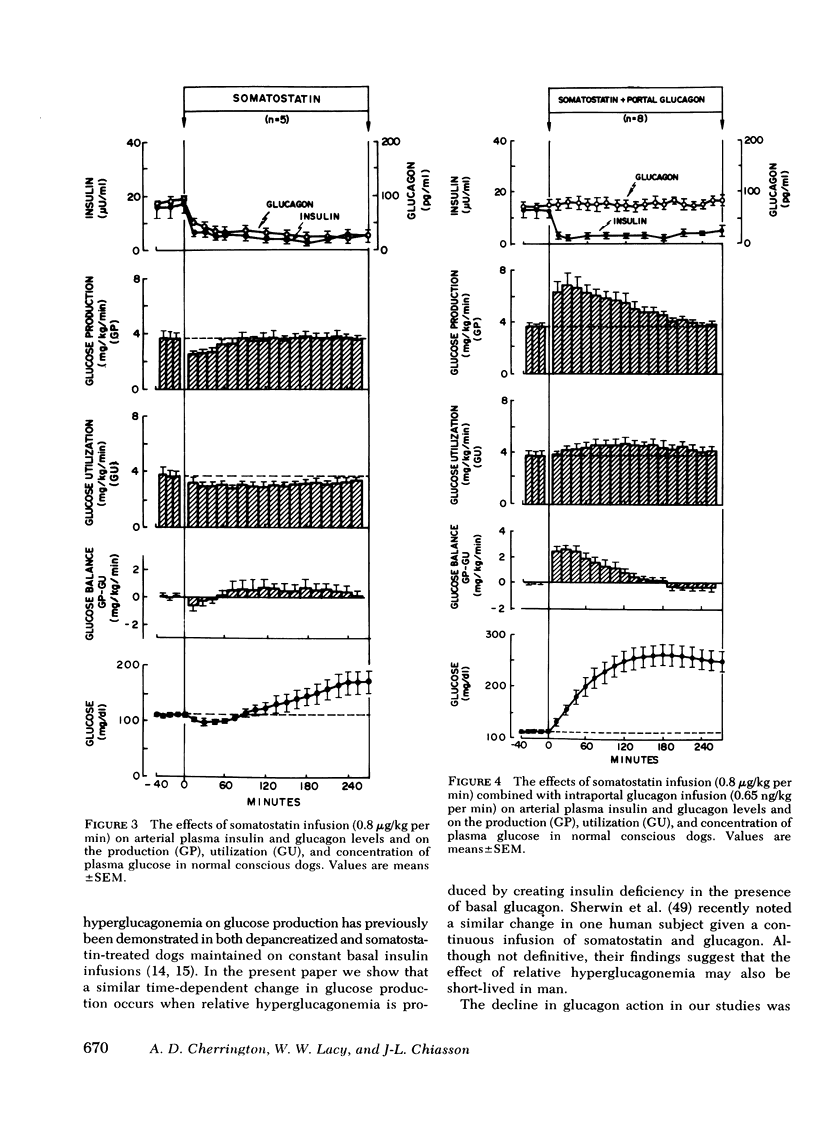



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilar-Parada E., Eisentraut A. M., Unger R. H. Pancreatic glucagon secretion in normal and diabetic subjects. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Jun;257(6):415–419. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196906000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan E. H., Sneyd J. G. An effect of glucagon on 3', 5'-cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase activity in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):594–601. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altszuler N., Barkai A., Bjerknes C., Gottlieb B., Steele R. Glucose turnover values in the dog obtained with various species of labeled glucose. Am J Physiol. 1975 Dec;229(6):1662–1667. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.6.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altszuler N., Gottlieb B., Hampshire J. Interaction of somatostatin, glucagon, and insulin on hepatic glucose output in the normal dog. Diabetes. 1976 Feb;25(2):116–121. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.2.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayuso-Parrilla M. S., Martín-Requero A., Pérez-Días J., Parrilla R. Role of glucagon on the control of hepatic protein synthesis and degradation in the rat in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7785–7790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes A. J., Bloom S. R. Pancreatectomised man: A model for diabetes without glucagon. Lancet. 1976 Jan 31;1(7953):219–221. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomboy J. D., Jr, Lewis S. B., Lacy W. W., Sinclair-Smith B. C., Liljenquist J. E. Transient stimulatory effect of sustained hyperglucagonemia on splanchnic glucose production in normal and diabetic man. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):177–174. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy P. K., Bloom W. L., Whitner V. S., Farrar B. W. STUDIES OF THE ROLE OF THE LIVER IN HUMAN CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM BY THE VENOUS CATHETER TECHNIC. II. PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC KETOSIS, BEFORE AND AFTER THE ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN. J Clin Invest. 1949 Sep;28(5 Pt 2):1126–1133. doi: 10.1172/JCI102146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucolo R. J., Bergman R. N., Marsh D. J., Yates F. E. Dynamics of glucose autoregulation in the isolated, blood-perfused canine liver. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jul;227(1):209–217. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.1.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Caldwell M. D., Dietz M. R., Exton J. H., Crofford O. B. The effect of somatostatin on glucose uptake and production by rat tissues in vitro. Diabetes. 1977 Aug;26(8):740–748. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.8.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Chiasson J. L., Liljenquist J. E., Jennings A. S., Keller U., Lacy W. W. The role of insulin and glucagon in the regulation of basal glucose production in the postabsorptive dog. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1407–1418. doi: 10.1172/JCI108596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Exton J. H. Studies on the role of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in the actions of glucagon and catecholamines on liver glycogen metabolism. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11 Suppl 1):1351–1354. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Kawamori R., Pek S., Vranic M. Arginine infusion in dogs. Model for the roles of insulin and glucagon in regulating glucose turnover and free fatty acid levels. Diabetes. 1974 Oct;23(10):805–815. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.10.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Vranic M. Effect of arginine on glucose turnover and plasma free fatty acids in normal dogs. Diabetes. 1973 Jul;22(7):537–543. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.7.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Vranic M. Effect of interaction between insulin and glucagon on glucose turnover and FFA concentration in normal and depancreatized dogs. Metabolism. 1974 Aug;23(8):729–744. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A., Vranic M., Fono P., Kovacevic N. Effect of glucagon on glucose turnover and plasma free fatty acids in depancreatized dogs maintained on matched insulin infusions. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1972 Oct;50(10):946–954. doi: 10.1139/y72-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson J. L., Liljenquist J. E., Lacy W. W., Jennings A. S., Cherrington A. D. Gluconeogenesis: methodological approaches in vivo. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):229–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson J. L., Liljenquist J. E., Sinclair-Smith B. C., Lacy W. W. Gluconeogenesis from alanine in normal postabsorptive man. Intrahepatic stimulatory effect of glucagon. Diabetes. 1975 Jun;24(6):574–584. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.6.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chideckel E. W., Palmer J., Koerker D. J., Ensinck J., Davidson M. B., Goodner C. J. Somatostatin blockade of acute and chronic stimuli of the endocrine pancreas and the consequences of this blockade on glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):754–762. doi: 10.1172/JCI107986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan J. S., Hetenyi G., Jr Glucoregulatory responses in normal and diabetic dogs recorded by a new tracer method. Metabolism. 1971 Apr;20(4):360–372. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE MEUTTER R. C., SHREEVE W. W. Conversion of DL-lactate-2-C14 or -3-C14 or pyruvate-2-C14 to blood glucose in humans: effects of diabetes, insulin, tolbutamide, and glucose load. J Clin Invest. 1963 Apr;42:525–533. doi: 10.1172/JCI104741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEBODO R. C., STEELE R., ALTSZULER N., DUNN A., BISHOP J. S. ON THE HORMONAL REGULATION OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM; STUDIES WITH C14 GLUCOSE. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1963;19:445–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn A., Katz J., Golden S., Chenoweth M. Estimation of glucose turnover and recycling in rabbits using various [3H, 14C]glucose labels. Am J Physiol. 1976 Apr;230(4):1159–1162. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.4.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Park C. R. Control of gluconeogenesis in liver. I. General features of gluconeogenesis in the perfused livers of rats. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2622–2636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P. The glucose-alanine cycle. Metabolism. 1973 Feb;22(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J., Hendler R. Influence of physiologic hyperglucagonemia on basal and insulin-inhibited splanchnic glucose output in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):761–765. doi: 10.1172/JCI108523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J., Sherwin R., Hendler R. Insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin in normal physiology and diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1976 Dec;25(12):1091–1099. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.12.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Bier D. M., Schneider V., Tsalikian E., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Prevention of human diabetic ketoacidosis by somatostatin. Evidence for an essential role of glucagon. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 8;292(19):985–989. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505082921901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Karam J. H., Schneider V., Forsham P. H. Abnormal pancreatic glucagon secretion and postprandial hyperglycemia in diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 1975 Oct 13;234(2):159–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E. Metabolic effects of long-term somatostatin infusion in man. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11 Suppl 1):1505–1507. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinsmann W. H., Hern E. P., Lynch A. Intrinsic regulation of glucose output by rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):698–703. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R., Gerich J. E. Somatostatin: physiological and clinical significance. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:379–388. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.27.020176.002115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall S. E., Goebel R., Barnes I., Hetenyi G., Jr, Berman M. The turnover and conversion to glucose of alanine in newborn and grown dogs. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):239–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwata K., Hetenyi G., Jr, Vranic M. Effect of D-glucose or D-ribose on the turnover of glucose in pancreatectomized dogs maintained on a matched intraportal infusion of insulin. Diabetes. 1969 Dec;18(12):820–827. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.12.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings A. S., Cherrington A. D., Liljenquist J. E., Keller U., Lacy W. W., Chiasson J. L. The roles of insulin and glucagon in the regulation of gluconeogenesis in the postabsorptive dog. Diabetes. 1977 Sep;26(9):847–856. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.9.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Dunn A. Glucose-2-t as a tracer for glucose metabolism. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):1–5. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller U., Chiasson J. L., Liljenquist J. E., Cherrington A. D., Jennings A. S., Crofford O. S. The roles of insulin, glucagon, and free fatty acids in the regulation of ketogenesis in dogs. Diabetes. 1977 Nov;26(11):1040–1051. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.11.1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg R. A., Pennington L. F., Boshell B. R. Lactate turnover and gluconeogenesis in normal and obese humans. Effect of starvation. Diabetes. 1970 Jan;19(1):53–63. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljenquist J. E., Bomboy J. D., Lewis S. B., Sinclair-Smith B. C., Felts P. W., Lacy W. W., Crofford O. B., Liddle G. W. Effects of glucagon on lipolysis and ketogenesis in normal and diabetic men. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):190–197. doi: 10.1172/JCI107537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljenquist J. E., Mueller G. L., Cherrington A. D., Keller U., Chiasson J-L, Perry J. M., Lacy W. W., Rabinowitz D. Evidence for an important role of glucagon in the regulation of hepatic glucose production in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):369–374. doi: 10.1172/JCI108649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallette L. E., Exton J. H., Park Effects of glucagon on amino acid transport and utilization in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5724–5728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimore G. E., Mondon C. E. Inhibition by insulin of valine turnover in liver. Evidence for a general control of proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2375–2383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. R., Wagle S. R. Studies on the inhibition of insulin release, glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis by somatostatin in the rat islets of langerhans and isolated hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):772–777. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90466-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J., Norwich K. H., Vranic M. Experimental validation of measurements of glucose turnover in nonsteady state. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):E84–E93. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.1.E84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J., Norwich K. H., Vranic M. Measurement and validation of nonsteady turnover rates with applications to the inulin and glucose systems. Fed Proc. 1974 Jul;33(7):1855–1864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskin P., Unger R. H. Effects of exogenous hyperglucagonemia in insulin-treated diabetics. Diabetes. 1977 Nov;26(11):1034–1039. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.11.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks H., Waligora K., Matthews J., Pimstone B. Inhibition by somatostatin of glucagon-induced glucose release from the isolated perfused rat liver. Endocrinology. 1977 Dec;101(6):1751–1759. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-6-1751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai H., Dobbs R. E., Unger R. H. The role of glucagon in the pathogenesis of the endogenous hyperglycemia of diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1975 Nov;24(11):1287–1297. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Fisher M., Hendler R., Felig P. Hyperglucagonemia and blood glucose regulation in normal, obese and diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 26;294(9):455–461. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602262940901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Tamborlane W., Hendler R., Saccá L., DeFronzo R. A., Felig P. Influence of glucagon replacement on the hyperglycemic and hyperketonemic response to prolonged somatostatin infusion in normal man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Nov;45(5):1104–1107. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-5-1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Aydin I., Nakabayashi H., Srikant C. B., Raskin P. The effects of glucagon administration to nondiabetics and diabetics. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11 Suppl 1):1523–1526. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Ohneda A., Aguilar-Parada E., Eisentraut A. M. The role of aminogenic glucagon secretion in blood glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):810–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI106039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. The Banting Memorial Lecture 1975. Diabetes and the alpha cell. Diabetes. 1976 Feb;25(2):136–151. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.2.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva M. L., Hedo J. A., Marco J. Plasma glucagon immunoreactivity in a totally pancreatectomized patient. Diabetologia. 1976 Dec;12(6):613–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01220639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vranic M., Kawamori R., Pek S., Kovacevic N., Wrenshall G. A. The essentiality of insulin and the role of glucagon in regulating glucose utilization and production during strenuous exercise in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):245–255. doi: 10.1172/JCI108275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL J. S., STEELE R., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Effect of insulin on utilization and production of circulating glucose. Am J Physiol. 1957 Apr;189(1):43–50. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.189.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Efendić S., Luft R., Hagenfeldt L., Björkman O., Felig P. Influence of somatostatin on splanchnic glucose metabolism in postabsorptive and 60-hour fasted humans. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):299–307. doi: 10.1172/JCI108641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Felig P., Cerasi E., Luft R. Splanchnic and peripheral glucose and amino acid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1870–1878. doi: 10.1172/JCI106989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



