Abstract
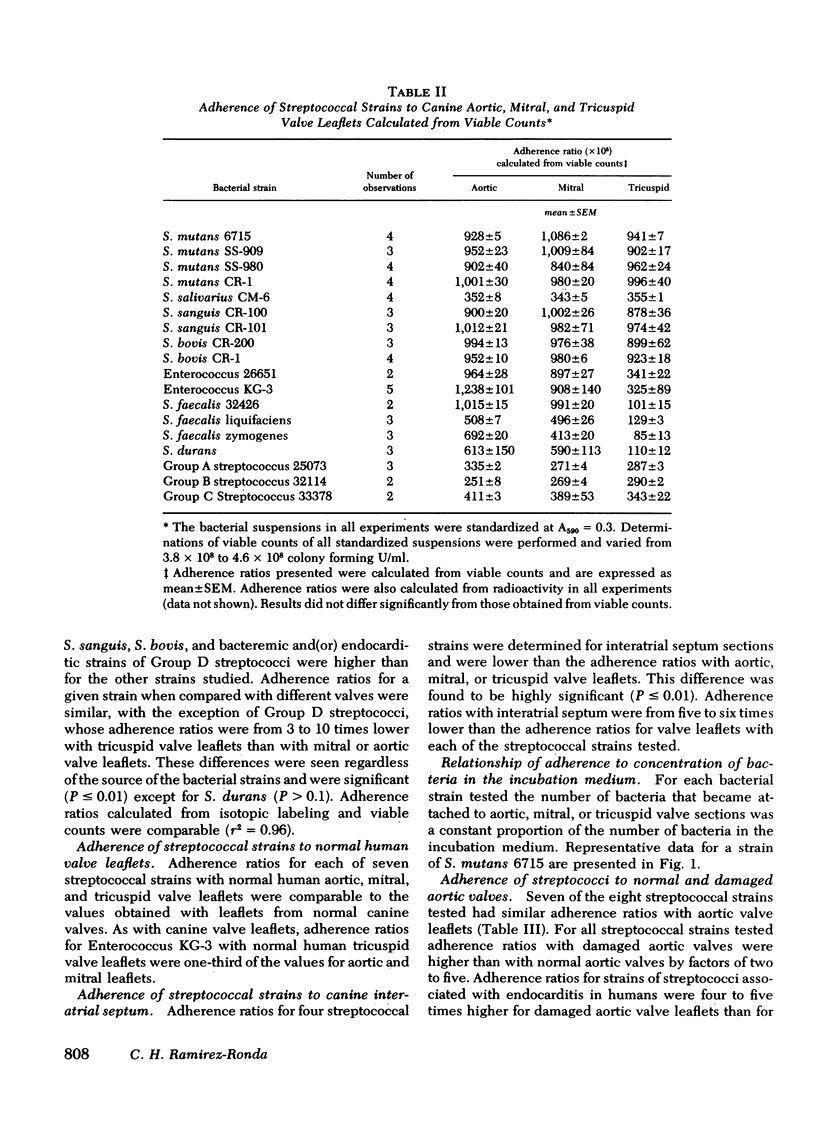
The adherence of 18 strains of streptococci to sections of normal canine and human aortic, mitral, and tricuspid valves and to canine interatrial septum was compared in an in vitro system. Quantitative measurements of adherence ratios were performed by two independent methods. Adherence ratios for Streptococcus mutans, S. sanguis, S. bovis, and Group D streptococci were higher (0.0058-0.0101) than for the other streptococcal strains studied (0.0025-0.0041). With the exception of Group D streptococci, adherence ratios for each bacterial strain were similar with the aortic, mitral, and tricuspid valve sections. Adherence ratios with normal human and canine valve leaflets were similar, but adherence ratios with interatrial septum were lower than with normal valve sections.
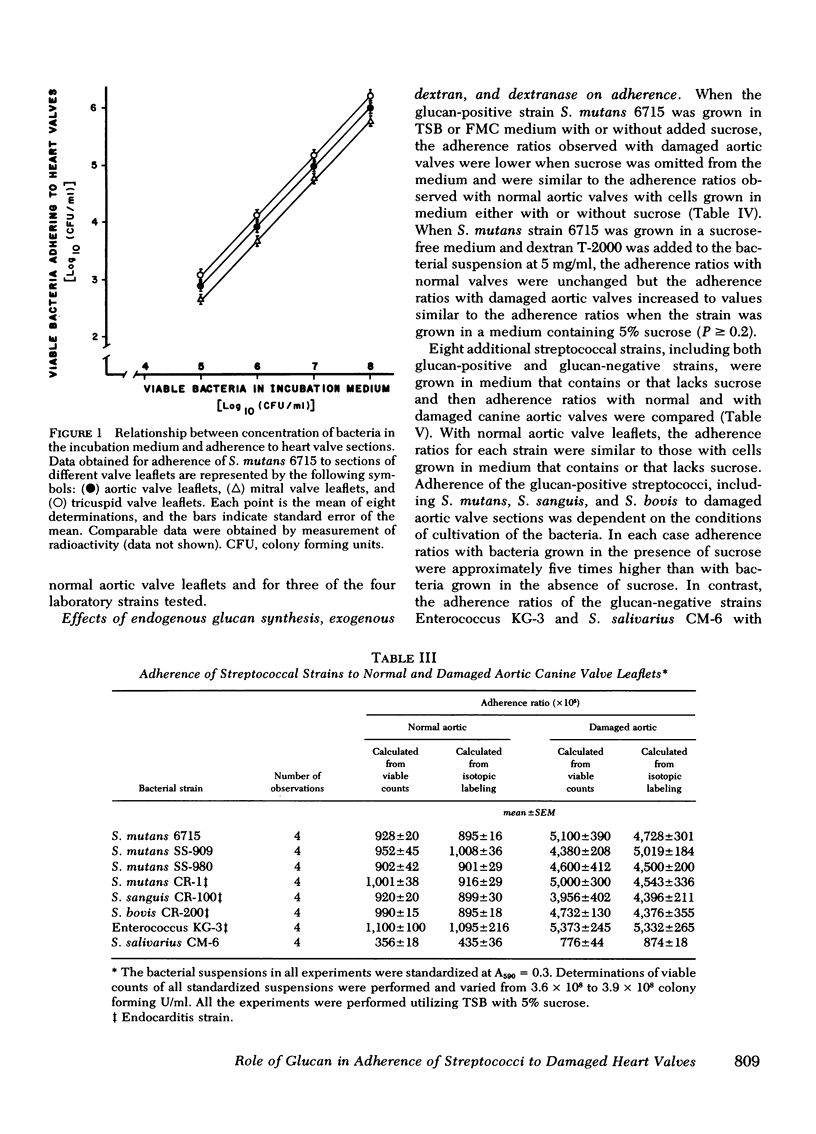
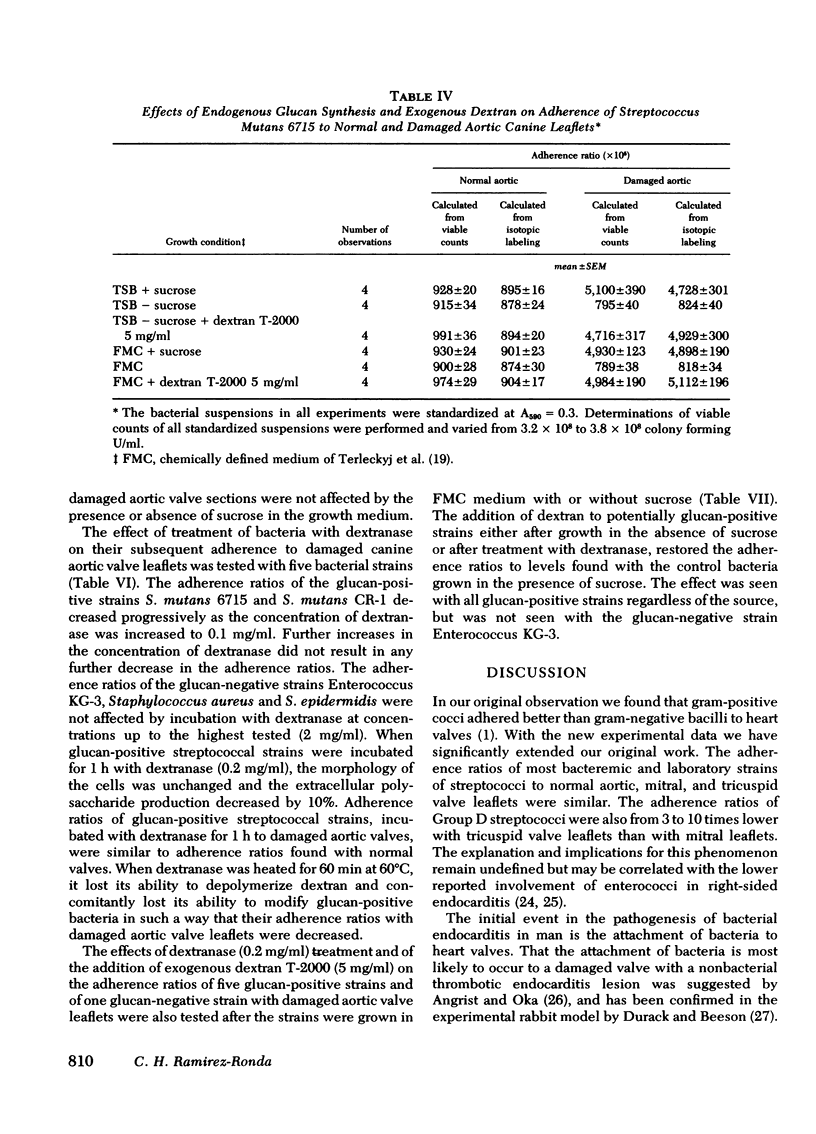
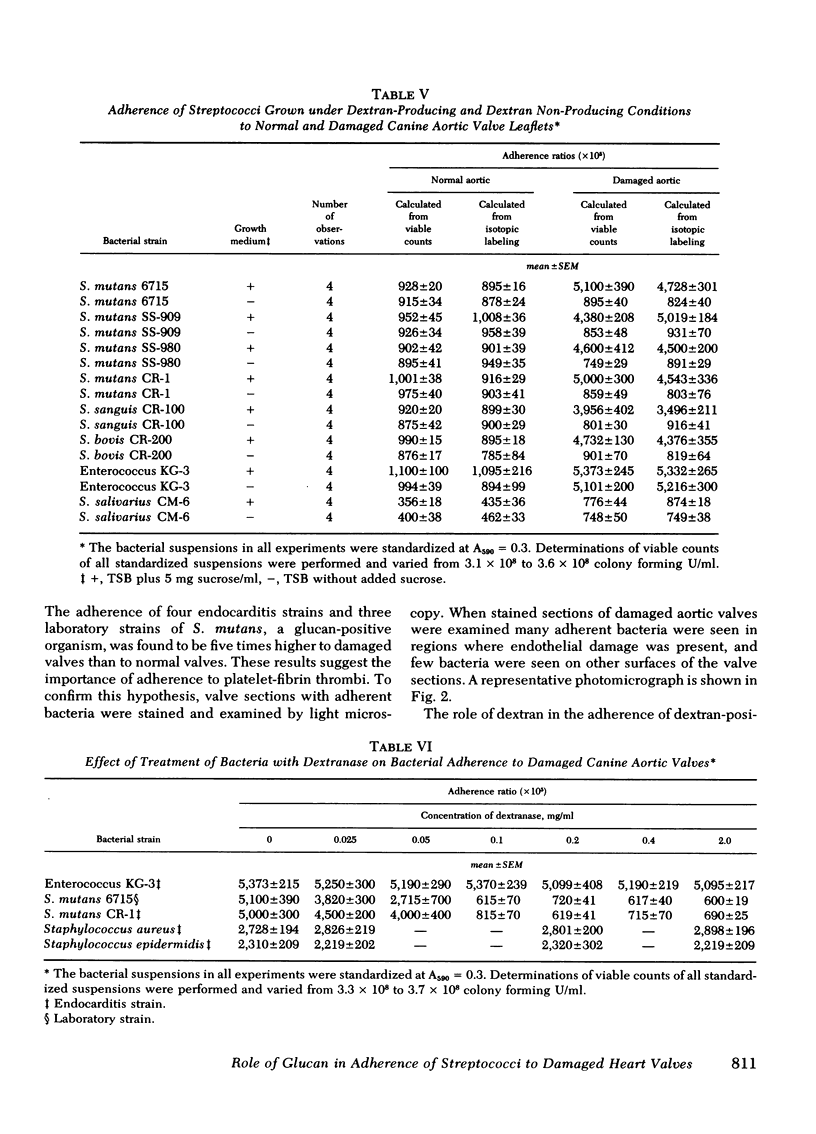
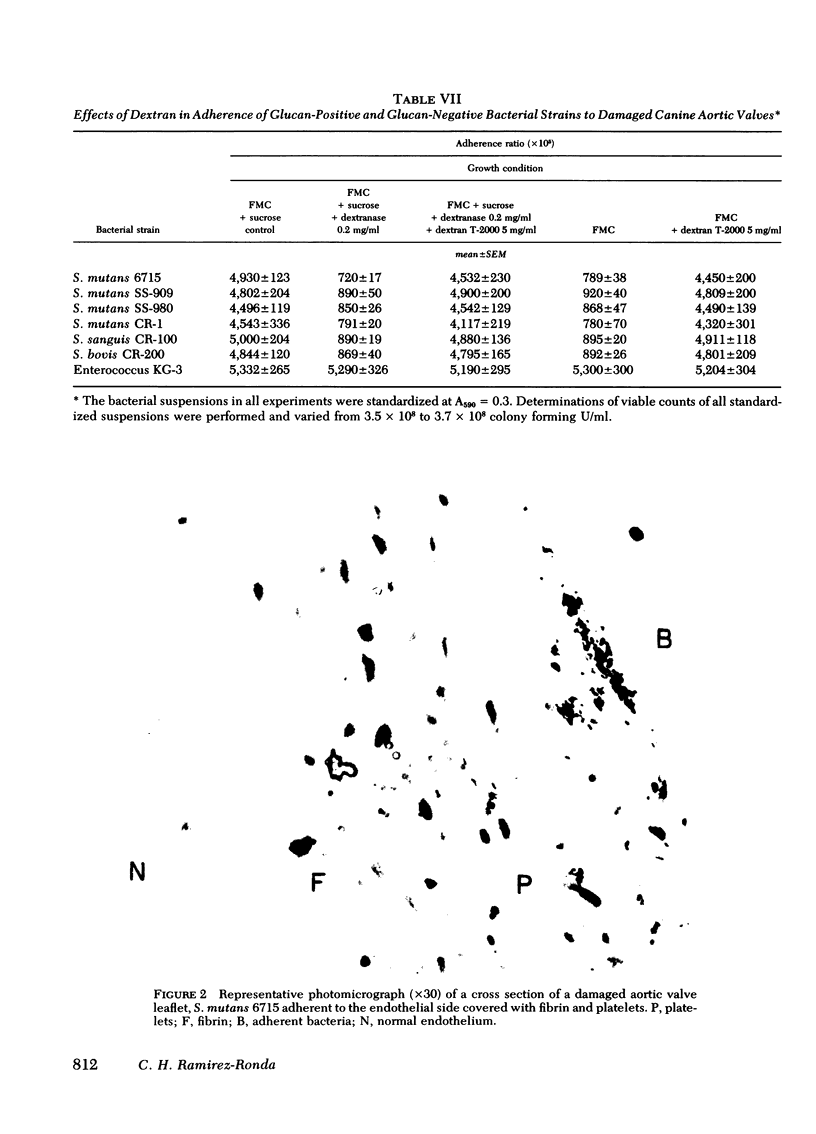
Adherence ratios for glucan-positive and glucan-negative strains of streptococci with normal and with damaged aortic valve leaflets were also compared. The adherence ratios of the glucan-positive streptococci (S. mutans, S. sanguis, and S. bovis) and one glucan-negative enterococcal strain (KG-3) were approximately five times higher with damaged aortic valves (0.039-0.051) than with normal aortic valves (0.009-0.010). For glucan-positive strains, adherence ratios with normal aortic leaflets were similar when bacteria were grown in media which contains or lacks sucrose. In striking contrast, growth of the glucan-positive strains in medium which lacks sucrose, with resultant deficiency of glucan production, decreased the adherence ratios with damaged aortic valve leaflets to those found with normal aortic leaflets. Treatment of glucan-positive strains with dextranase resulted in a decrease in their adherence ratios to levels seen with bacteria grown in medium lacking sucrose, but the higher adherence ratios could be restored in the presence of exogenous dextran.
It is concluded that glucan production is one quantitatively important factor that contributes to the greater adherence of glucan-positive streptococci to damaged rather than to normal aortic heart valve leaflets. However, glucan production is not the only factor that determines preferential adherence of streptococci to damaged heart valves, because glucan-negative strains may also show some degree of increased adherence to damaged valves. Thus, bacterial glucan production is one of the factors that could contribute to the pathogenesis of bacterial endocarditis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGRIST A. A., OKA M. Pathogenesis of bacterial endocarditis. JAMA. 1963 Jan 26;183:249–252. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.63700040009010b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeau G., McBride B. C. Dextran-mediated interbacterial aggregation between dextran-synthesizing streptococci and Actinomyces viscosus. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1228–1234. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1228-1234.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubin C. E., Neu H. C. Infective endocarditis at the Presbyterian Hospital in New York City from 1938-1967. Am J Med. 1971 Jul;51(1):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Beeson P. B. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. I. Colonization of a sterile vegetation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Feb;53(1):44–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. Parameters affecting the adherence and tissue tropisms of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):85–91. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.85-91.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., Jones G. W. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: nature of the interaction with intact mucosal surfaces. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):246–256. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.246-256.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Banghart S. B. Synthesis of extracellular dextran by cariogenic bacteria and its presence in human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Jan;12(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Fitzgerald R. J. Dextran-induced agglutination of Streptococcus mutans, and its potential role in the formation of microbial dental plaques. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):341–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.341-346.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Spinell D. M., Skobe Z. Selective adherence as a determinant of the host tropisms of certain indigenous and pathogenic bacteria. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):238–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.238-246.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Selective bacterial adherence to oral epithelial surfaces and its role as an ecological determinant. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):567–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.567-573.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K., Ramirez-Ronda C. H., Holmes R. K., Sanford J. P. Adherence of bacteria to heart valves in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1364–1370. doi: 10.1172/JCI108216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B., Schroeder H. E. Biochemical and morphological aspects of extracellular polysaccharides produced by cariogenic streptococci. Helv Odontol Acta. 1967 Oct;11(2):131–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Mizuno J., Murayama Y., Ooshima Y., Masuda N. Effect of dextranase on the extracellular polysaccharide synthesis of Streptococcus mutans; chemical and scanning electron microscopy studies. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1415-1425.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Funder-Nielsen T. D. Adhesion of dextran to Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Apr;81(2):485–489. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-2-485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of adherence of Streptococcus mutans to smooth surfaces. I. Roles of insoluble dextran-levan synthetase enzymes and cell wall polysaccharide antigen in plaque formation. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):555–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.555-562.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of adherence of Streptococcus mutans to smooth surfaces. II. Nature of the binding site and the adsorption of dextran-levan synthetase enzymes on the cell-wall surface of the streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):419–429. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.419-429.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama Y., Wada H., Hayashi H., Uchida T., Yokomizo E. Effects of dextranase from Spicaria violaceae (IFO 6120) on the polysaccharides produced by oral streptococci and on human dental plaque. J Dent Res. 1973 Jul-Aug;52(4):658–667. doi: 10.1177/00220345730520040401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh P. A., Westtöm L. Adherence of bacterial to vaginal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):661–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.661-666.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefe L. I., Chretien J. H., Delaha E. C., Garagusi V. F. Streptococcus mutans endocarditis. Confusion with enterococcal endocarditis by routine laboratory testing. JAMA. 1974 Dec 2;230(9):1298–1299. doi: 10.1001/jama.230.9.1298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTERFIELD J. S. Classification of the streptococci of subacute bacterial endocarditis. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 Jan;4(1):92–101. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-1-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. T., Ball L. C. Streptococci and aerococci associated with systemic infection in man. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Aug;9(3):275–302. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-3-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. A., Hu P. C., Wilson M., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Attachment of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to respiratory epithelium. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):959–966. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.959-966.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. C., Buchbinder N. A. Right-sided valvular infective endocarditis. A clinicopathologic study of twelve necropsy patients. Am J Med. 1972 Jul;53(1):7–19. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Valone J. A., Sande M. A. Bacterial adherence in the pathogenesis of endocarditis. Interaction of bacterial dextran, platelets, and fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1394–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI109057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houte J., Gibbons R. J., Pulkkinen A. J. Adherence as an ecological determinant for streptococci in the human mouth. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Oct;16(10):1131–1141. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houte J., Jordan H. V., Bellack S. Proportions of Streptococcus sanguis, an organism associated with subacute bacterial endocarditis, in human feces and dental plaque. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):658–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.658-659.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L., Rubin R. H. Infective endocarditis--1973. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1973 Nov-Dec;16(3):239–274. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(73)80001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]