Abstract
We previously showed that collagen, α-chains, and collagen-derived peptide fragments induce chemotactic migration of human fibroblasts in vitro. We now describe biochemical and immunological evidence showing there are binding sites for collagen peptides on fibroblast membranes.
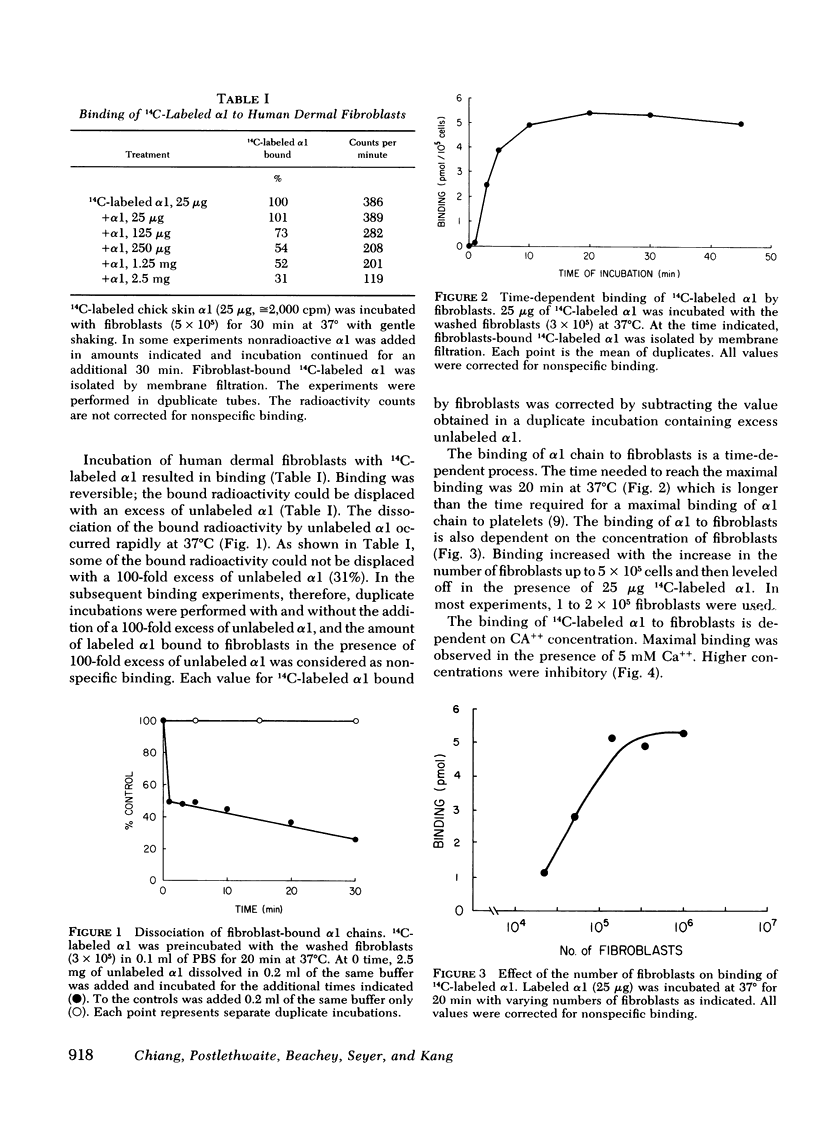
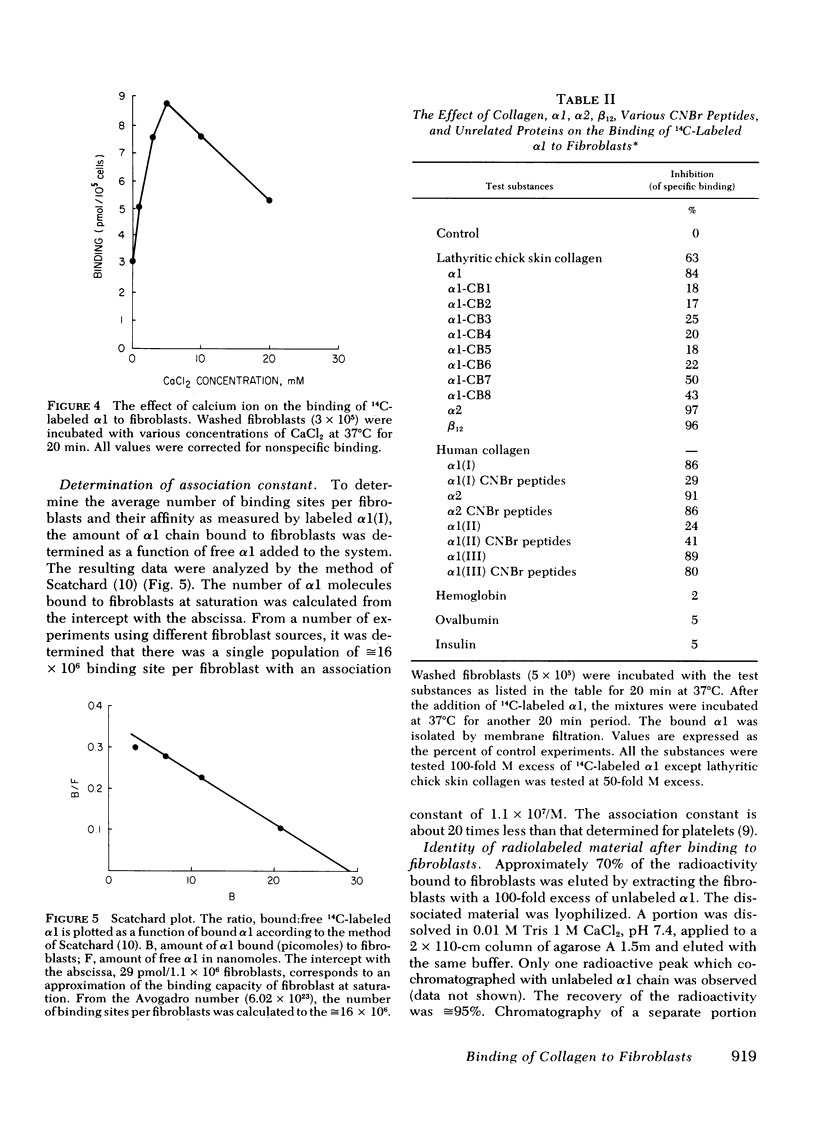
By the use of 14C-labeled α1(I) chain, binding to intact fibroblasts was demonstrated. The process was reversible, and time- and fibroblast concentration-dependent. Scatchard plot analyses of the data obtained for the binding of α1(I) suggested that there are ≅ 16 × 106 binding sites per fibroblast with an association constant of 1.1 × 107/M for α1(I). Dissociation of the bound radioactivity and subsequent chromatographic analysis on agarose A-1.5 m revealed that the α1 was unaltered. The binding of 14C-labeled α1 was inhibited by each of the CNBr peptides derived from α1 chain of chick skin collagen and CNBr peptide mixtures of various genetic types of collagen chains.
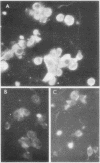
Immunofluorescence studies with anti-α1 antibody showed that α1-treated fibroblasts exhibited strong immunofluorescence. The intensity of fluorescence was markedly diminished by prior absorption of the antibody with α1. The α1-treated cells stained with preimmune sera did not show significant fluorescence.
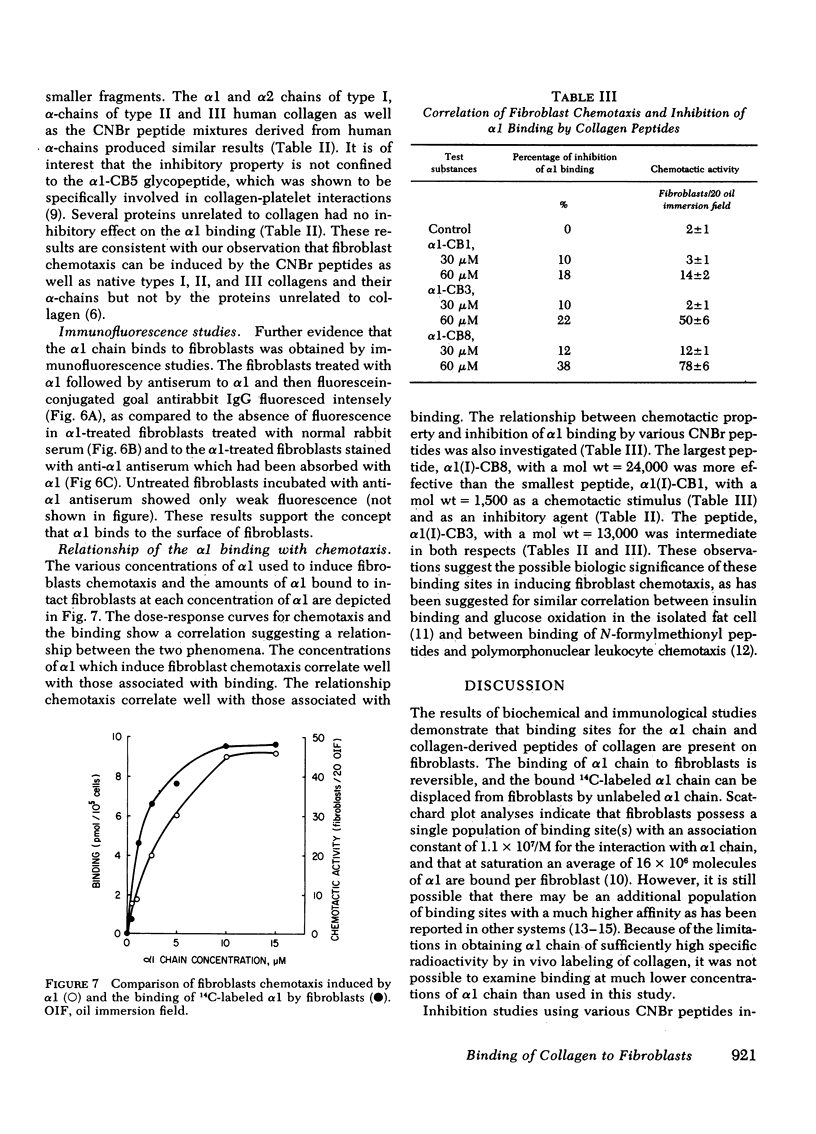
Dose-response curves of fibroblast chemotaxis induced by α1 and the binding of α1 by fibroblasts correlate closely. Furthermore, the potency of α1-CNBr peptides as chemotactic agents correlates with their ability to inhibit the binding of labeled α1(I). These data suggest the hypothesis that collagenderived peptides cause fibroblast chemotactic migration by acting on fibroblast membranes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abercrombie M., Heaysman J. E., Pegrum S. M. The locomotion of fibroblasts in culture. IV. Electron microscopy of the leading lamella. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Aug;67(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90420-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J. L. Source of the fibroblast in central corneal wound healing. Arch Ophthalmol. 1971 Apr;85(4):473–477. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1971.00990050475014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang T. M., Beachey E. H., Kang A. H. Binding of collagen alpha1 chains to human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):405–411. doi: 10.1172/JCI108653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D. The role of three cytoplasmic fibers in BHK-21 cell motility. I. Microtubules and the effects of colchicine. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):752–762. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Krane S. M. Collagenases (first of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 12;291(11):557–563. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409122911105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Smith R. M., Crespin S. R. Epinephrine binding to rat adipocytes and their subcellular fractions. Endocrinology. 1974 Mar;94(3):719–729. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-3-719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang A. H., Piez K. A., Gross J. Characterization of the alpha-chains of chick skin collagen and the nature of the NH2-terminal cross-link region. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3648–3655. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang A. H., Piez K. A., Gross J. Characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha 1 chain of chick skin collagen. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1506–1514. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus G. S., Daniels J. R., Brown R. S., Bladen H. A., Fullmer H. M. Degradation of collagen by a human granulocyte collagenolytic system. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2622–2629. doi: 10.1172/JCI105945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. The effects of spontaneous obesity on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation of isolated rat adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):842–851. doi: 10.1172/JCI108360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Chemotactic attraction of human fibroblasts to type I, II, and III collagens and collagen-derived peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):871–875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Snyderman R., Kang A. H. The chemotactic attraction of human fibroblasts to a lymphocyte-derived factor. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1188–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Gross J. Some properties of the products of reaction of tadpole collagenase with collagen. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):518–528. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen D. M., Feagler J. R., Majerus P. W. The binding of thrombin to the surface of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2646–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Zurier R. B., Spieler P. J., Goldstein I. M. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from leukocytes exposed to immune complexes and other particles. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):149s–165s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]