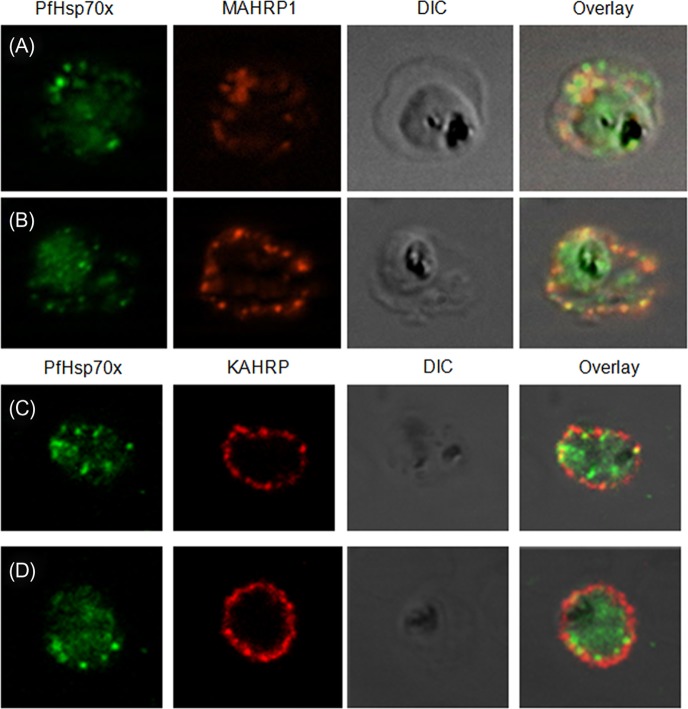
Figure 6.
PfHsp70-x partially associates with Maurer’s clefts but not with knobs: (A–B) Panel I: the signal for PfHsp70-x (green) was obtained in the parasite compartment along with few punctate spots in the erythrocyte compartment. Panel II: MAHRP1 (red) stained discrete foci representative of Maurer’s clefts in the erythrocyte periphery. Panel III: the DIC image of the infected erythrocyte. Panel IV: merged image overlaid with DIC image reveals that MAHRP1 and PfHsp70-x partially co-localize in the erythrocyte compartment, suggesting that PfHsp70-x possibly associates with Maurer’s clefts. (C-D) Panel I: the signal for PfHsp70-x (green) was obtained in the parasite compartment along with few punctate spots in the erythrocyte compartment. Panel II: KAHRP (red), being a constituent of knobs, stained the entire erythrocyte membrane. Panel III shows the DIC image of the infected erythrocyte. Panel IV: no co-localization is observed between KAHRP and PfHsp70-x, suggesting that PfHsp70-x does not associate with knobs on the infected erythrocyte membrane.