Abstract
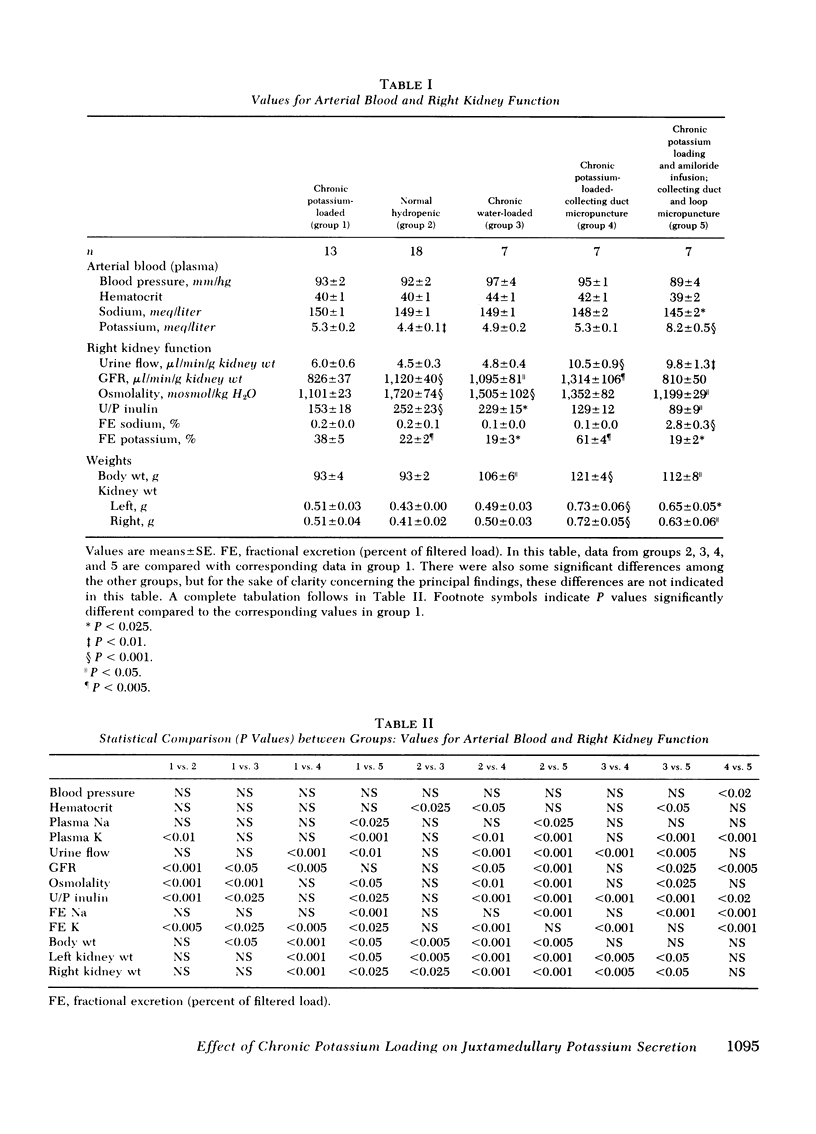
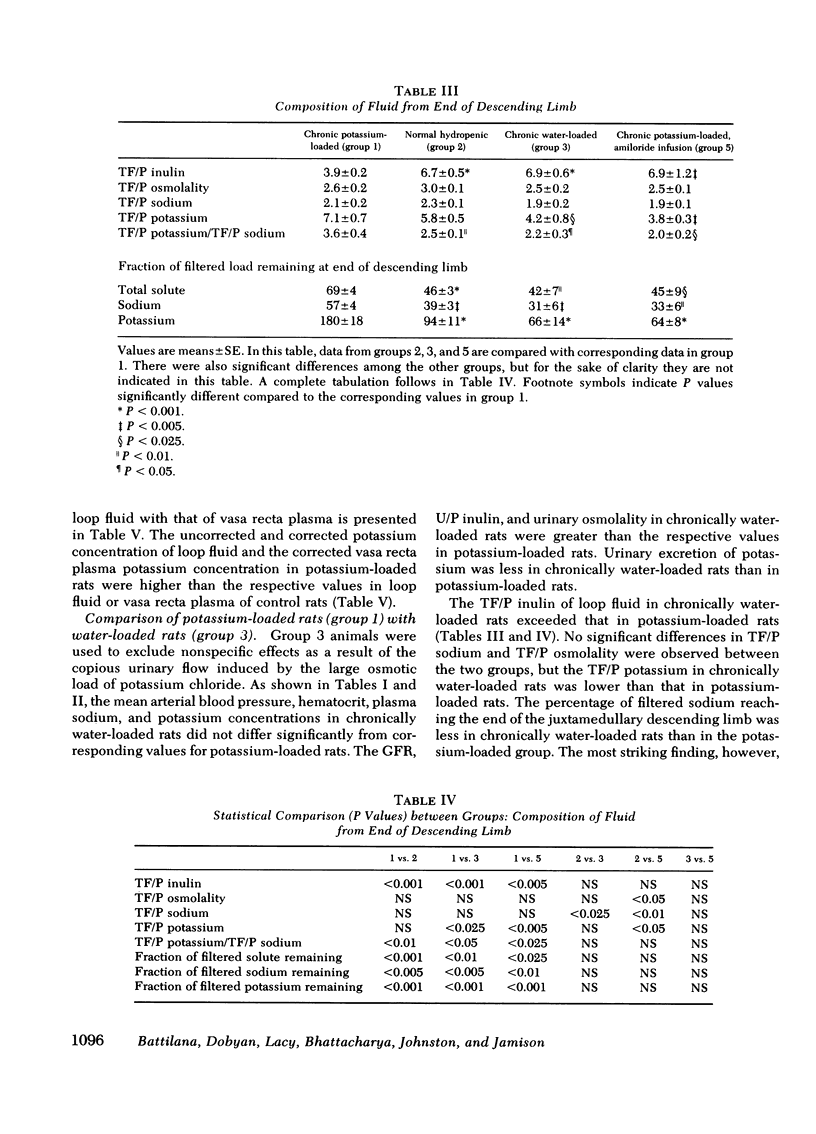
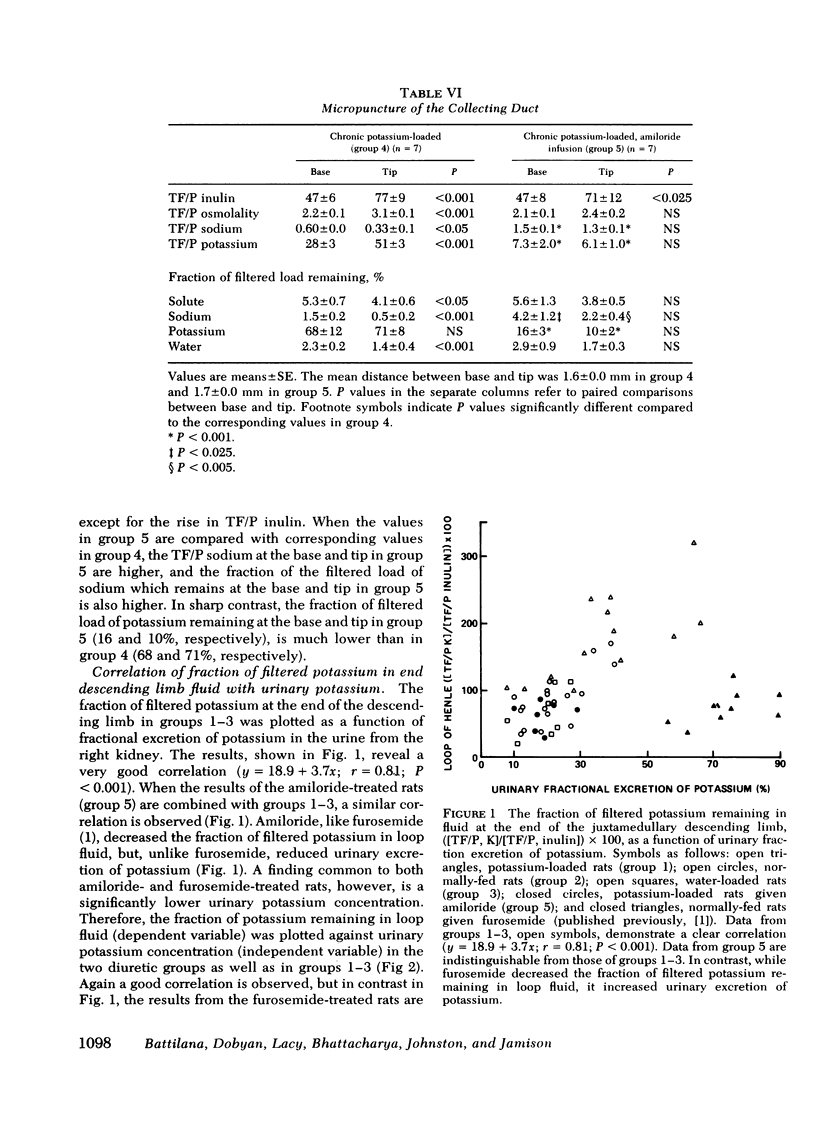
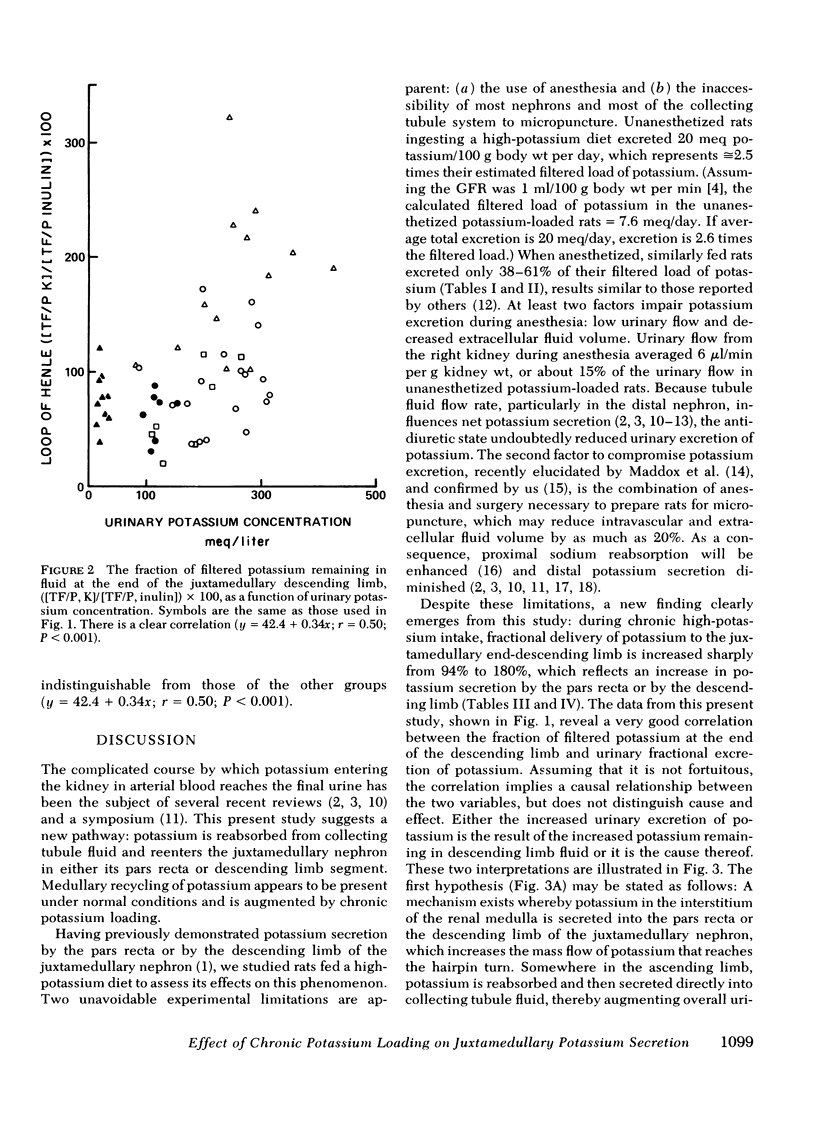
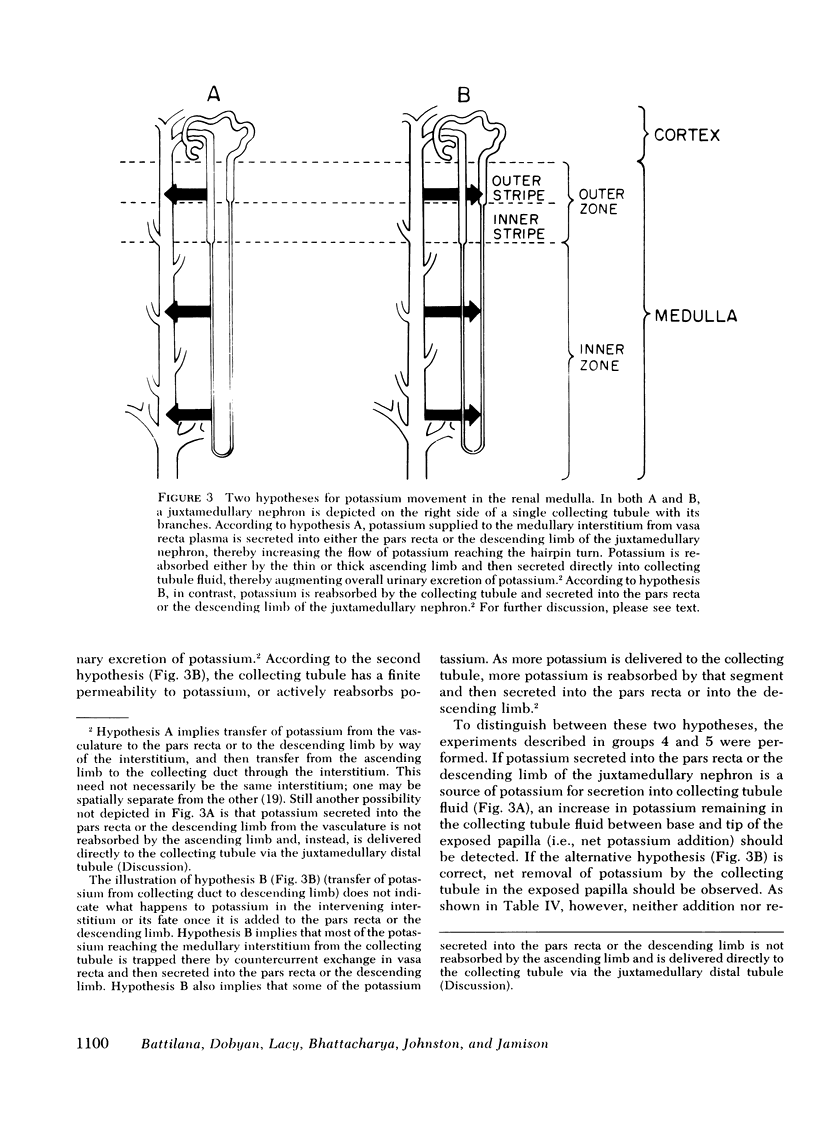
Recently we demonstrated potassium secretion by the pars recta or by the descending limb of the juxtamedullary nephron. The purpose of this present investigation is to study the effect of a chronic high-potassium intake on this phenomenon. Fractional reabsorption of water and sodium by the juxtamedullary proximal nephron was decreased when compared to that in normal hydropenic rats. There was a striking increase in the fraction of filtered potassium at the end of the juxtamedullary descending limb from 94+/11% to 180+/18%, which was principally a result of enhanced potassium secretion. When the concentration of potassium in the collecting tubule fluid of potassium-loaded rats was reduced after the administration of amiloride, a sharp fall was observed in the amount of potassium which reached the end of the descending limb (64+/8%). A direct correlation was observed between the fraction of filtered potassium at the descending limb and the potassium concentration in the final urine (P less than 0.001). The findings suggest that potassium, like urea, normally undergoes medullary recycling, which is enhanced by chronic potassium loading.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diezi J., Michoud P., Aceves J., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of electrolyte transport across papillary collecting duct of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1973 Mar;224(3):623–634. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duarte C. G., Chomety F., Giebisch G. Effect of amiloride, ouabain, and furosemide on distal tubular function in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Aug;221(2):632–640. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.2.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebisch G. Some reflections on the mechanism of renal tubular potassium transport. Yale J Biol Med. 1975 Sep;48(4):315–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Kurg M. B., Obloff J. The nature of transtubular Na and K transport in isolated rabbit renal collecting tubules. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1815–1826. doi: 10.1172/JCI106399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIERHOLZER K. Secretion of potassium and acidification in collecting ducts of mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol. 1961 Aug;201:318–324. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.2.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Kokko J. P. Sodium chloride, urea, and water transport in the thin ascending limb of Henle. Generation of osmotic gradients by passive diffusion of solutes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):393–402. doi: 10.1172/JCI107572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. L., Lacy F. B., Pennell J. P., Sanjana V. M. Potassium secretion by the decending limb or pars recta of the juxtamedullary nephron in vivo. Kidney Int. 1976 Apr;9(4):323–332. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. L. Micropuncture study of segments of thin loop of Henle in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):236–242. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. L. Micropuncture study of superficial and juxtamedullary nephrons in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jan;218(1):46–55. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Battilana C. A., Lacy F. B., Jamison R. L. Evidence for a concentration gradient favoring outward movement of sodium from the thin loop of Henle. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):234–240. doi: 10.1172/JCI108633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khuri R. N., Strieder W. N., Giebisch G. Effects of flow rate and potassium intake on distal tubular potassium transfer. Am J Physiol. 1975 Apr;228(4):1249–1261. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.4.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriz W. Der architektonische und funktionelle Aufbau der Rattenniere. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;82(4):495–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunau R. T., Jr, Webb H. L., Borman S. C. Characteristics of the relationship between the flow rate of tubular fluid and potassium transport in the distal tubule of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1488–1495. doi: 10.1172/JCI107897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALNIC G., KLOSE R. M., GIEBISCH G. MICROPUNCTURE STUDY OF RENAL POTASSIUM EXCRETION IN THE RAT. Am J Physiol. 1964 Apr;206:674–686. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.4.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox D. A., Price D. C., Rector F. C., Jr Effects of surgery on plasma volume and salt and water excretion in rats. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):F600–F606. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.6.F600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., De Mello Aires M., Giebisch G. Potassium transport across renal distal tubules during acid-base disturbances. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1192–1208. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. J., Martin C. M. Origin of electrical PD's in hamster thin ascending limbs of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1977 Apr;232(4):F348–F357. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.4.F348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng K. Comparison of the local effects of amiloride hydrochloride on the isotonic fluid absorption in the distal and proximal convoluted tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1975;357(1-2):91–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00584547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineck H. J., Osgood R. W., Ferris T. F., Stein J. H. Potassium transport in the distal tubule and collecting duct of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1975 Nov;229(5):1403–1409. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.5.1403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanjana V. M., Johnston P. A., Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M., Jamison R. L. Hydraulic and oncotic pressure measurements in inner medulla of mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1921–1926. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva P., Brown R. S., Epstein F. H. Adaptation to potassium. Kidney Int. 1977 Jun;11(6):466–475. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva P., Ross B. D., Charney A. N., Besarab A., Epstein F. H. Potassium transport by the isolated perfused kidney. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):862–869. doi: 10.1172/JCI108165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. H., Osgood R. W., Kunau R. T., Jr Direct measurement of papillary collecting duct sodium transport in the rat. Evidence for heterogeneity of nephron function during Ringer loading. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):767–773. doi: 10.1172/JCI108527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner L. C., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Ion transport in cortical collecting tubule; effect of amiloride. Am J Physiol. 1974 Aug;227(2):453–459. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. W., Weinman E. J., Kashgarian M., Hayslett J. P. Accelerated reabsorption in the proximal tubule produced by volume depletion. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1379–1385. doi: 10.1172/JCI106620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright F. S., Strieder N., Fowler N. B., Giebisch G. Potassium secretion by distal tubule after potassium adaptation. Am J Physiol. 1971 Aug;221(2):437–448. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.2.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



