Abstract
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of adenine arabinoside (ara-A) in rabbit kidney microtiter tissue cultures (RK-13) to a prototype strain of herpes simplex virus, type 1 (E115) based upon inhibition of cytopathic effects is 1.5 μg/ml. In this system, the MIC of arabinosylhypoxanthine (ara-Hx), the major in vivo metabolic derivative of ara-A, is 75 μg/ml. Inhibition of cytopathic effects of herpes simplex virus, type 1 (HSV-1) in microtiter wells of RK-13 cells varies directly with the concentrations of ara-A or ara-Hx, and inversely with residual HSV-1. The MIC of ara-A for HSV-1 in RK-13 cells is 5-20 times lower than similar measures with vero renal, mouse embryo, or human foreskin cultures. With RK-13 tissue cultures in microtiter plates, an assay for “ara-A equivalents” in human body fluids was developed which compares in sensitivity with high pressure liquid chromatography and has the advantage of simultaneously measuring combined antiherpesvirus effects of ara-A and its major metabolic derivative, ara-Hx.
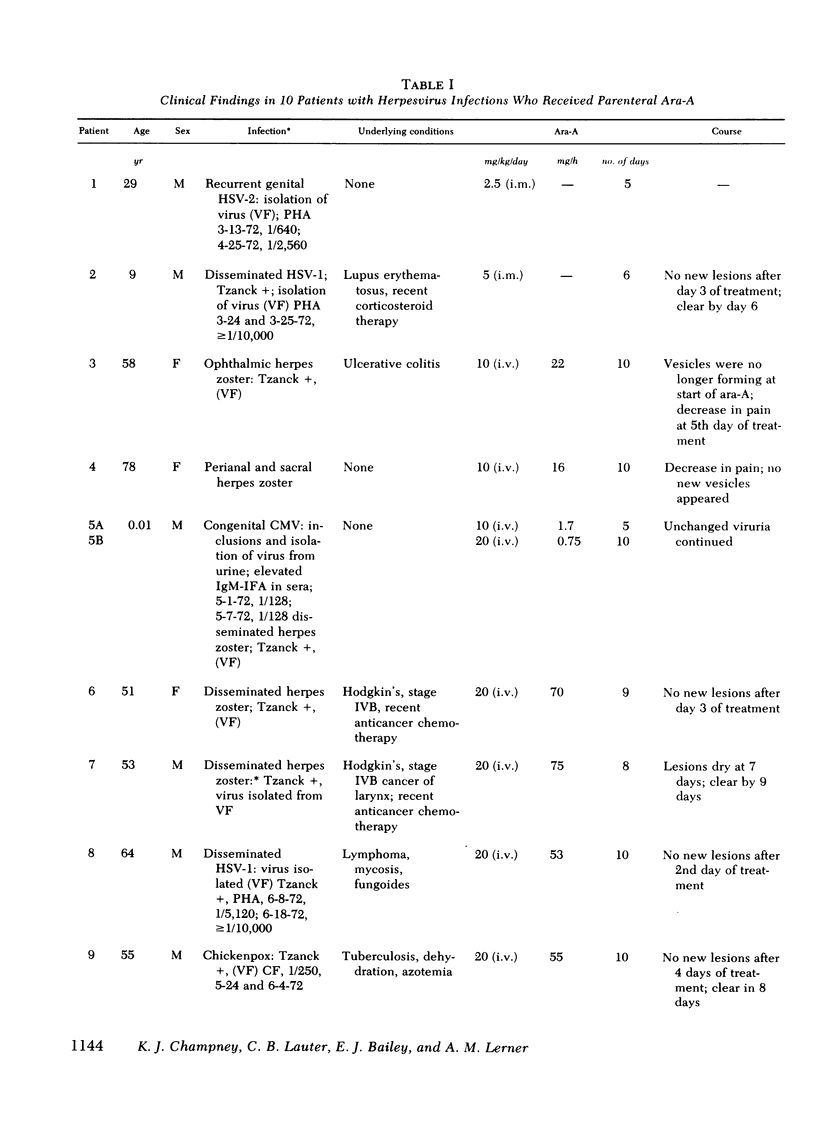
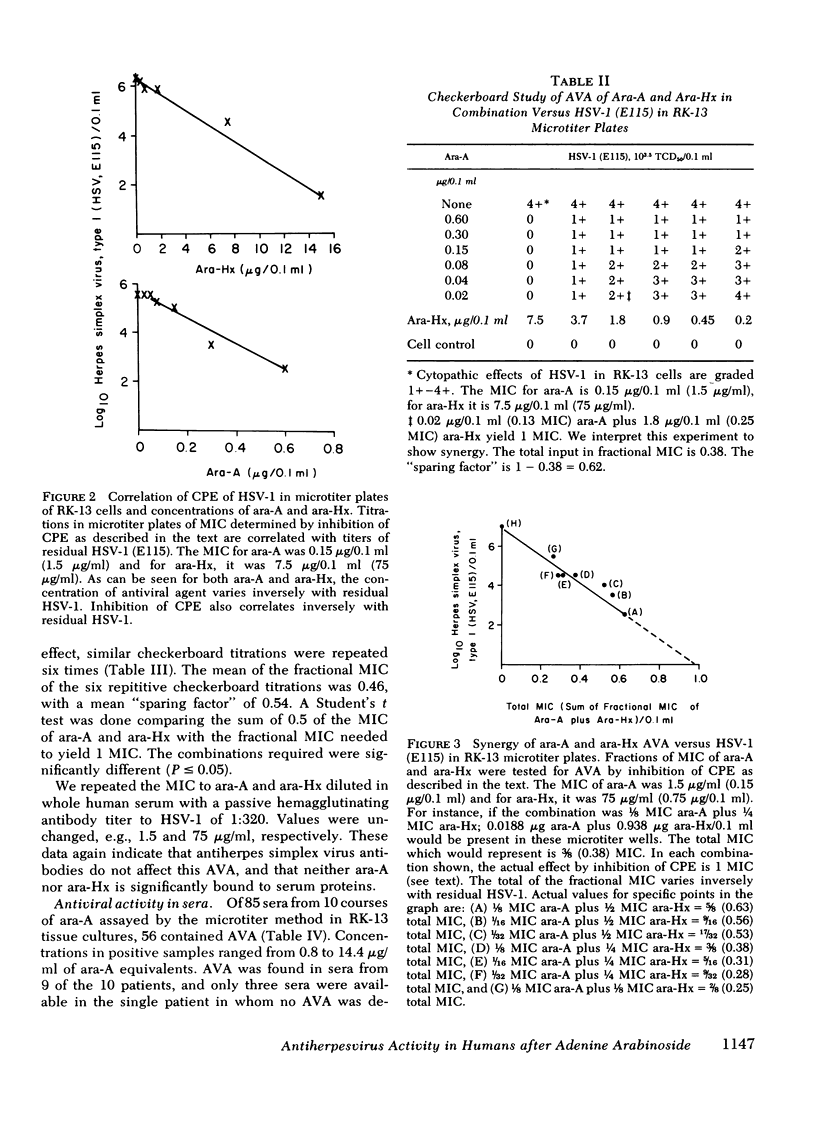
In vitro checkerboard studies in RK-13 cells confirmed that ara-A and ara-Hx in combination had antiviral effects which are synergistic. The total of the fractional MIC of ara-A plus ara-Hx in combination also varies inversely with residual HSV-1 in microtiter wells. Because virus adsorption is complete at 2 h before specimens to be tested are added in this assay, and because human interferon is not measured in rabbit cells, the antiviral assay is not affected by the presence of type-specific antiherpesvirus antibody or human interferon.
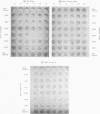
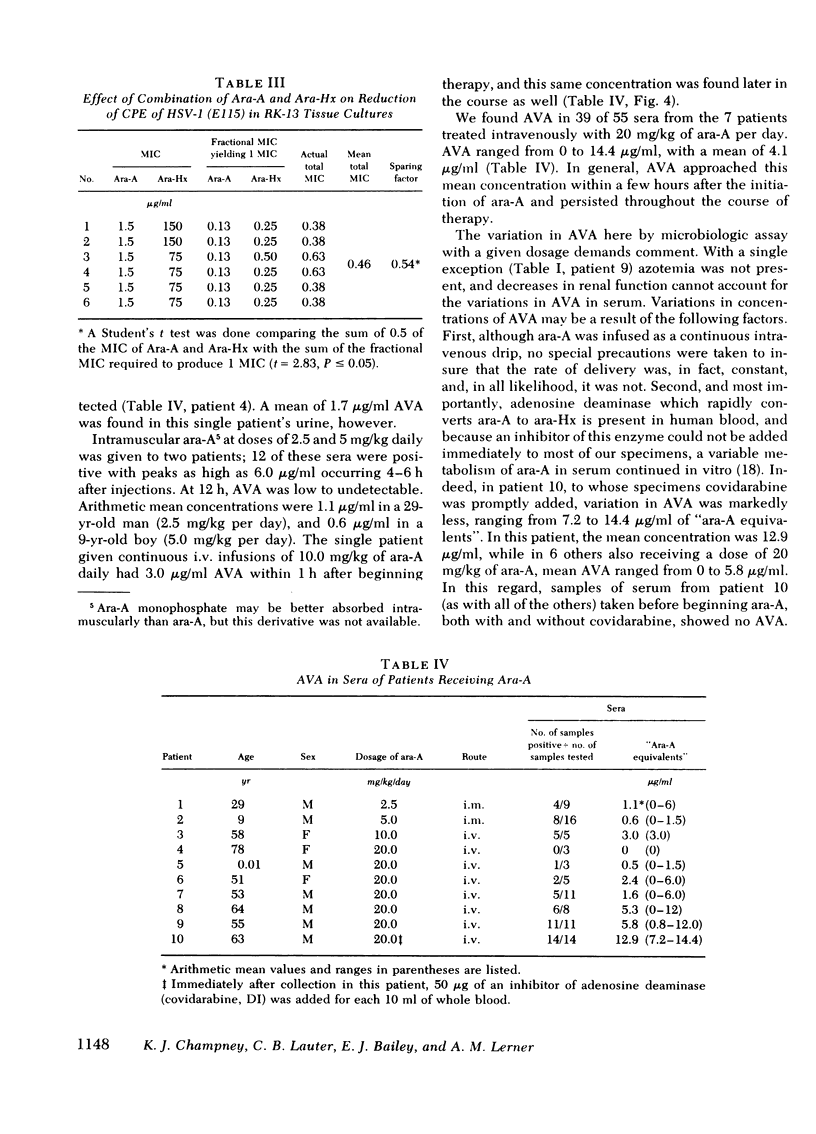
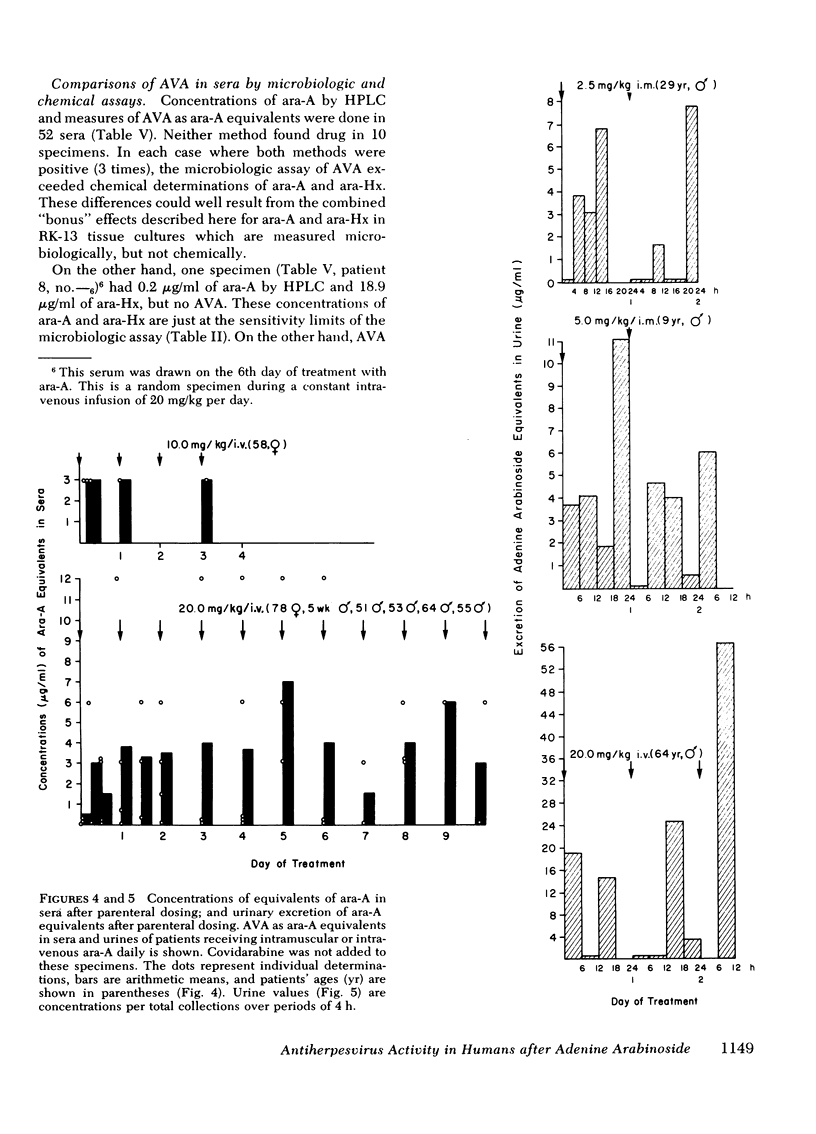
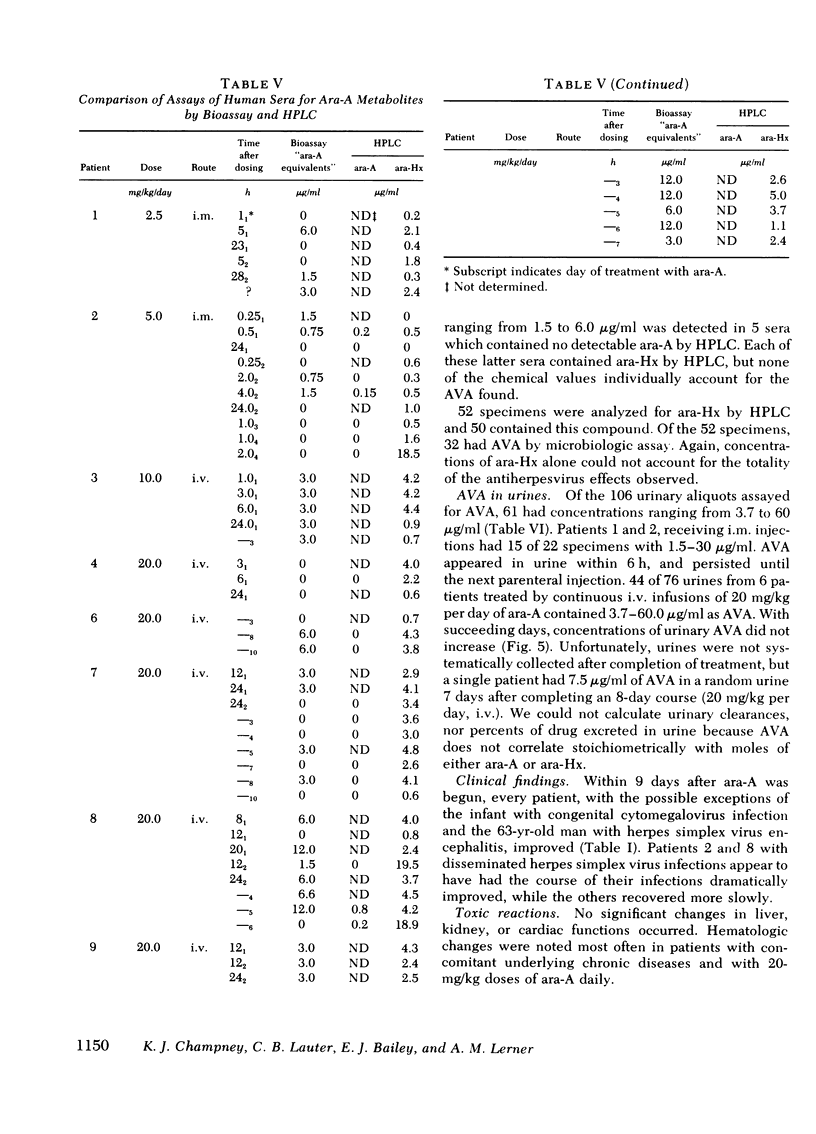
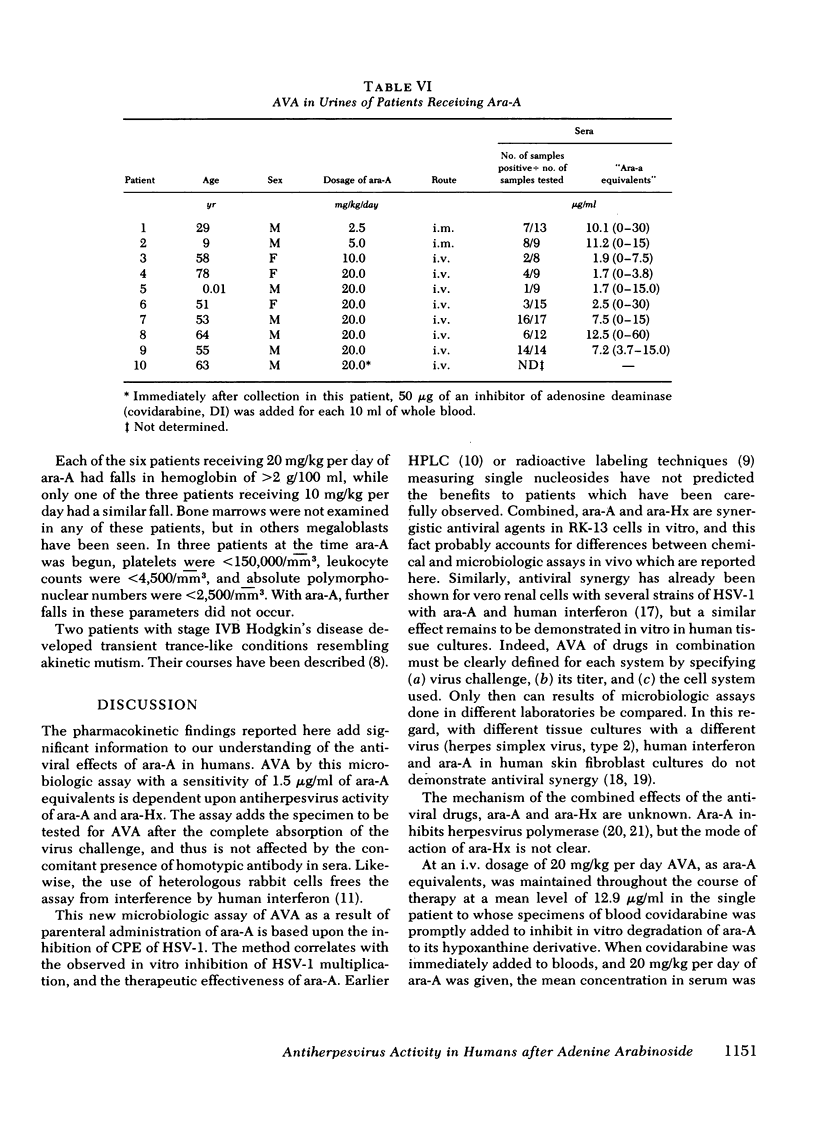
Antiviral activity (AVA) was assayed as ara-A equivalents in sera and urines from 10 patients with serious herpesvirus infections who received 2.5-20 mg/kg daily of ara-A by intramuscular or intravenous routes. When a dosage schedule of 10 mg/kg per day or more was used, sustained concentrations of AVA that ranged from 0.8 to 14.4 μg/ml were found. When an inhibitor of adenosine deaminase (covidarabine) was not added to the specimens, mean serum concentrations were ≅3.0 μg/ml (10 mg/kg per day, i.v.), and 4.1 μg/ml (20 mg/kg per day). However, in a single patient given 20 mg/kg of ara-A daily with covidarabine immediately added to the sera, the mean concentration of AVA was 12.9 μg/ml. Urines contained even higher AVA. Assays of 19 sera were performed both by microbiologic assay for AVA and by high pressure liquid chromatography for ara-A and ara-Hx. AVA was greater by microbiologic assay, and was greater than that which could be accounted for by stoichiometric chromatographic measures of ara-A and ara-Hx. These results with sera of treated patients are consistent both with the in vitro synergy of ara-A and ara-Hx found by checkerboard titrations, and with the beneficial responses to ara-A of patients with herpesvirus infections reported here and elsewhere.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abel R., Jr, Kaufman H. E., Sugar J. Intravenous adenine arabinoside against herpes simplex keratouveitis in humans. Am J Ophthalmol. 1975 Apr;79(4):659–664. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(75)90807-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson Y. J., Kronenberg L. H. Combined antiviral effects of interferon, adenine, arabinoside, hypoxanthine arabinoside, and adenine arabinoside-5'-monophosphate in human fibroblast cultures. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):299–306. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson Y., Connor J. D., Sweetman L., Carey S., Stuckey M. A., Buchanan R. Determination of plaque inhibitory activity of adenine arabinoside (9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine) for herpesviruses using an adenosine deaminase inhibitor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jul;6(1):98–101. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ien L. T., Cannon N. J., Charamella L. J., Dismukes W. E., Whitley R. J., Buchanan R. A., Alford C. A., Jr Effect of adenine arabinoside on severe Herpesvirus hominis infections in man. J Infect Dis. 1973 Nov;128(5):658–663. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.5.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ien L. T., Whitley R. J., Nahmias A. J., Lewin E. B., Linnemann C. C., Jr, Frenkel L. D., Bellanti J. A., Buchanan R. A., Alford D. A., Jr Antiviral chemotherapy and neonatal herpes simplex virus infecition: a pilot study--experience with adenine arabinoside (ARA-A). Pediatrics. 1975 May;55(5):678–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koplan J. P., Monsur K. A., Foster S. O., Huq F., Rahaman M. M., Huq S., Buchanan R. A., Ward N. A. Treatment of variola major with adenine arabinoside. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jan;131(1):34–39. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauter C. B., Bailey E. J., Lerner A. M. Assessment of cytosine arabinoside as an antiviral agent in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):598–602. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauter C. B., Bailey E. J., Lerner A. M. Microbiologic assays and neurological toxicity during use of adenine arabinoside in humans. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):75–79. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A. M., Bailey E. J. Concentrations of idoxuridine in serum, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with suspected diagnoses of Herpesvirus hominis encephalitis. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):45–49. doi: 10.1172/JCI106795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A. M., Bailey E. J. Differential sensitivity of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 to human interferon: antiviral effects of interferon plus 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. J Infect Dis. 1976 Oct;134(4):400–404. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.4.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A. M., Bailey E. J. Synergy of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine and human interferon against Herpes simplex virus, type 1. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):549–552. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A. M., Lauter C. B., Nolan D. C., Shippey M. J. Passive hemagglutinating antibodies in cerebrospinal fluids in herpesvirus hominis encephalitis. 1. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Sep;140(4):1460–1466. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A. M., Shippey M. J., Crane L. R. Serologic responses to herpes simplex virus in rabbits: complement-requiring neutralizing, conventional neutralizing, and passive hemagglutinating antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):623–636. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. P., Lauter C. B., Lerner A. M. Simultaneous serum and CSF antibodies in herpes simplex virus encephalitis. JAMA. 1978 Jul 28;240(4):356–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipman C., Jr, Smith S. H., Carlson R. H., Drach J. C. Antiviral activity of arabinosyladenine and arabinosylhypoxanthine in herpes simplex virus-infected KB cells: selective inhibition of viral deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in synchronized suspension cultures. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):120–127. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J., Ch'ien L. T., Dolin R., Galasso G. J., Alford C. A., Jr Adenine arabinoside therapy of herpes zoster in the immunosuppressed. NIAID collaborative antiviral study. N Engl J Med. 1976 May 27;294(22):1193–1199. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197605272942201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J., Soong S. J., Dolin R., Galasso G. J., Ch'ien L. T., Alford C. A. Adenine arabinoside therapy of biopsy-proved herpes simplex encephalitis. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases collaborative antiviral study. N Engl J Med. 1977 Aug 11;297(6):289–294. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197708112970601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. B., Bailey E. J., Lerner A. M. Inhibitory and lethal concentrations of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine and its hypoxanthine-derivative versus herpes simplex virus, type 1. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Apr;89(4):687–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. B., Lerner A. M. Antiviral activity of an adenosine deaminase inhibitor: decreased replication of herpes simplex virus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):673–677. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]