Abstract
AIM: To present a new technique of end-to-side, duct-to-mucosa pancreaticojejunostomy with seromuscular jejunal flap formation, and insertion of a silicone stent.
METHODS: We present an end-to-side, duct-to-mucosa pancreaticojejunostomy with seromuscular jejunal flap formation, and the insertion of a silicone stent. This technique was performed in thirty-two consecutive patients who underwent a pancreaticoduodenectomy procedure by the same surgical team, from January 2005 to March 2011. The surgical procedure performed in all cases was classic pancreaticoduodenectomy, without preservation of the pylorus. The diagnosis of pancreatic leakage was defined as a drain output of any measurable volume of fluid on or after postoperative day 3 with an amylase concentration greater than three times the serum amylase activity.
RESULTS: There were 32 patients who underwent end-to-side, duct-to-mucosa pancreaticojejunostomy with seromuscular jejunal flap formation. Thirteen of them were women and 19 were men. These data correspond to 40.6% and 59.4%, respectively. The mean age was 64.2 years, ranging from 55 to 82 years. The mean operative time was 310.2 ± 40.0 min, and was defined as the time period from the intubation up to the extubation of the patient. Also, the mean time needed to perform the pancreaticojejunostomy was 22.7 min, ranging from 18 to 25 min. Postoperatively, one patient developed a low output pancreatic fistula, three patients developed surgical site infection, and one patient developed pneumonia. The rate of overall morbidity was 15.6%. There was no 30-d postoperative mortality.
CONCLUSION: This modification appears to be a significantly safe approach to the pancreaticojejunostomy without adversely affecting operative time.
Keywords: Whipple, Pancreaticojejunostomy, Technique, Seromuscular jejunal flap, Pancreatic fistula
Core tip: Pancreaticojejunostomy represents one of the most challenging technical aspects of the Whipple procedure, mainly due to its failure, and to the resulting morbidity and mortality rates. Several technical variations have been proposed, in an effort to minimize postoperative pancreatic fistula rates. The technique we describe is an end-to-side, duct-to-mucosa two-layer pancreaticojejunostomy intended to promote enhanced healing process, through the creation of a seromuscular jejunal flap. This technique appears to be safe and reliable; however, these are preliminary results.
INTRODUCTION
The first pancreaticoduodenectomy was performed by a German surgeon, Kausch, in 1909[1-3]. It has been considered the surgical procedure of choice for ampullary cancer, after Whipple et al[4] had described three cases in 1935. Nowadays, it has become the standard procedure in the management of pancreatic head and periampullary carcinoma[2]. In recent years, the mortality rate of pancreatico-duodenectomy has been decreased to below 5%[5-7]. However, the postoperative morbidity rate remains high, ranging from 30% to 50%[7-10]. Pancreatic fistula[11,12] is the most common complication and its reported incidence varies from 2% to 40%[8,11,13]. Several different anastomotic surgical techniques have been used, in order to minimize pancreatic fistula occurrence after pancreaticoduodenectomy, although it is still debated which of them has any clear advantage[2,9,10,14,15]. We present a modification for duct to mucosa end-to-side pancreaticojejunostomy, with a seromuscular jejunal flap, in order to increase the safety of the anastomosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
During the period January 2005 to March 2011, 32 consecutive patients underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy by the same surgical team. There were 13 women and 19 men, with a mean age of 64.2 years (range 55-82 years). The underlying diseases of these patients are shown in Table 1. The surgical procedure performed in all cases was classic pancreaticoduodenectomy, without preservation of the pylorus. The diagnosis of pancreatic leakage was defined as a drain output of any measurable volume of fluid on or after postoperative day 3 with an amylase concentration greater than three times the serum amylase activity[11].
Table 1.
Underlying diseases of the patients who underwent end-to-side, duct to mucosa pancreaticojejunostomy with seromuscular jejunal flap formation after pancreaticoduodenectomy
| Disease | Patients (n) |
| Pancreatic head carcinoma | 15 |
| Ampullary carcinoma | 12 |
| Distal common bile duct carcinoma | 5 |
| Total | 32 |
Technique
A scalpel is used to sharply transect the pancreas at the level of the portal vein. Hemostasis of the bleeding points of the pancreatic stump is achieved either with 4-0 non-absorbable suture and/or with electrocautery. After the pancreaticoduodenectomy specimen has been removed, the pancreatic remnant is dissected free of the underlying structures for a distance of approximately 2 cm. The transected jejunum is brought through the bed of the resected duodenum (i.e., posterior to the mesenteric vessels).
The jejunal seromuscular layer is incised starting about 2 cm distal to the jejunal stump, along the antimesenteric border. The length of this incision is just smaller than the cephalo-caudal diameter of the pancreatic stump. Using a scalpel the seromuscular layer of the jejunum is dissected free from the underlying submucosa, towards both sides of the aforementioned incision, in order to create two seromuscular flaps (i.e., one dorsal and one ventral flap), and to expose the underlying submucosa, which must remain intact (Figure 1). The extent of the dissection is determined by the antero-posterior diameter of the pancreatic stump, in order to fit the surface of the pancreatic cut edge on the surface area of the exposed mucosa.
Figure 1.
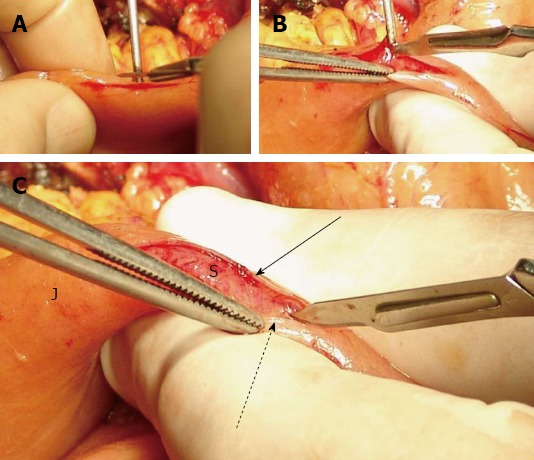
Preparation of the jejunal stump. A: Incision on the jejunum; B: Seromuscular flap formation; C: The seromuscular layers are dissected free from the submucosa. J: Jejunum; S: Submucosa; Arrow: Posterior seromuscular flap; Dotted arrow: Anterior seromuscular flap.
Following this, a segment of nelaton catheter is inserted into the main pancreatic duct, and is fixed with a 4-0 absorbable monofilament suture (polydioxanone, PDS II, Ethicon, Inc.). The tube girth is selected to exactly fit the diameter of the main pancreatic duct. On the intraductal part of the stent, several holes are created on different positions, at a distance of 1 cm from each other, in order to ensure uninhibited outflow of the pancreatic fluid. The extraductal part of the stent left is about 5 cm in length.
The next step is to create the first of all four suturing layers. The dorsal part of the jejunal seromuscular layer and the dorsal part of the capsular parenchyma of the pancreatic stump are sutured with 3-0 silk interrupted stitches of 0.5-1 cm distance from each other. This is the dorsal external suturing layer (Figure 2A).
Figure 2.
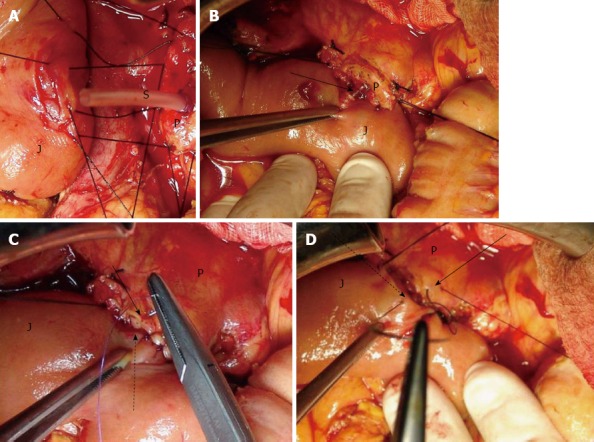
The posterior, anterior external layer of sutures and stent in place. A: The posterior (dorsal) external layer of sutures; B: Stent in place. Arrow: The stent enters the jejunal small opening, which has been created in the middle of the dissected submucosal surface; C: The anterior (ventral) internal layer of sutures. Arrow: Anterior pancreatic cut edge border; Dotted arrow: Anterior seromuscular flap; D: The anterior (ventral) external layer of sutures. Arrow: Anterior pancreatic part of the capsular parenchyma; Dotted arrow: Anterior part of the jejunal seromuscular layer. J: Jejunum; S: Stent; P: Pancreatic stump cut surface.
Then, the dorsal cut edge border of the pancreatic stump is sutured to the edge of the dorsal jejunal seromuscular flap with 4-0 polydioxanone sutures (PDS) II interrupted stitches 0.5 to 1 cm apart. This is the dorsal internal layer.
A small hole in the jejunal mucosa is made, in accordance with the diameter of the main pancreatic duct. The free end of the stent tube is advanced through this hole into the jejunal lumen (Figure 2B). The mucosa at the site of the hole and the edge of the main pancreatic duct are sutured with two interrupted stitches of 4-0 PDS II.
The third layer is created by the approximation of the ventral cut edge border of the pancreatic stump and the edge of the ventral jejunal seromuscular flap with 4-0 PDS II interrupted stitches, 0.5-1 cm apart (Figure 2C). This is the ventral internal layer.
The final layer of sutures, the ventral external layer, is created by suturing the ventral part of the jejunal seromuscular layer and the ventral part of the capsular parenchyma of pancreatic stump, with 3-0 silk interrupted stitches (Figure 2D). Figure 3 shows a drawing of the jejunal and pancreatic sites of anastomosis.
Figure 3.
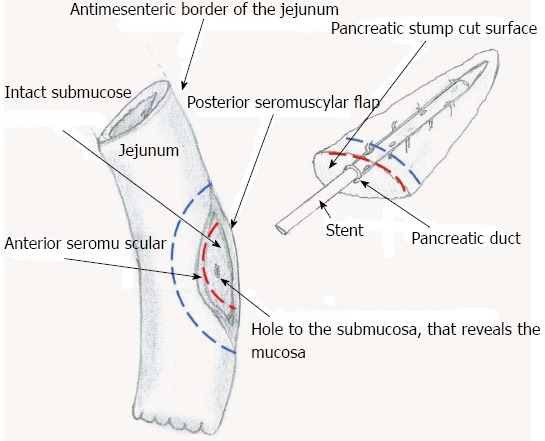
This is a schema that shows the dissected surface of the jejunum and the cut surface of the pancreas that are approximated. The red dotted line represents the ventral internal suturing layer (i.e., the 3rd one). The blue dotted line represents the ventral external suturing layer (i.e., the 4th one).
Statistical analysis
There were only descriptive measures used, since there was no control group in this study and its main purpose was to describe a surgical technique.
RESULTS
There were 32 consecutive patients that underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy with the above described pancreaticojejunostomy technique. There were 13 women and 19 men, with a mean age of 64.2 years (range 55-82 years). The underlying diseases of these patients are shown in Table 1. The mean operative time was 310.2 ± 40.0 min, and the mean time needed to perform the pancreaticojejunostomy was 22.7 min (range 18-25 min). One patient developed low output pancreatic fistula. Three patients developed surgical site infection and one patient developed pneumonia, postoperatively. The overall morbidity rate was 15.6%. There was no postoperative mortality.
DISCUSSION
Pancreaticojejunostomy represents one of the most challenging technical aspects of the Whipple procedure, because of its failure rates, as well as the resulting morbidity and mortality. Several technical variations have been proposed, in an effort to minimize postoperative pancreatic fistula rates[1,2,9,10,14-20]. The most important risk factors identified are technique, soft pancreatic texture and main pancreatic duct diameter of 3 mm or less[13,21-26]. The technique we describe is an end-to-side, duct-to-mucosa two-layer pancreaticojejunostomy. Each step of the procedure already described adheres to a rationale focused on the elimination of pancreatic leakage. First, the exposure of intact jejunal mucosa was thought to promote vascularization and enhance the healing process between the mucosa and the cut surface of the pancreatic stump[27]. Such an approach has been employed in the past with favorable results, but still carried a significant fistula occurrence.
With this in mind, we incorporated the dissection of the seromuscular flaps and their fixation to the border of the pancreatic stump aiming to offer a more reliable sealing of the anastomosis. In the same context, we proposed the internal layer of sutures, which was not previously employed, in order to keep the two traumatic surfaces firmly in contact to further favor the healing process between them. Finally, stenting the main pancreatic duct ensures duct patency, while eliminating undesired distention. In one of our cases, the stent was present in situ even on the six-year follow-up.
In conclusion, this technique appears to be safe and reliable. Because this is a preliminary report of a small series, it is of essential importance that it is evaluated via a prospective study in a larger series, before firm conclusions can be drawn.
Furthermore, while of sound reasoning, the assumption that healing is significantly augmented by exposing the intestinal submucosa is yet to be experimentally proved.
COMMENTS
Background
Pancreatic fistula following pancreaticoduodenectomy is a serious complication associated with high morbidity rates. Various factors have been implicated as contributors to pancreatic anastomotic leak, the incidence of which has been as high as 28% in some series.
Research frontiers
Pancreatic texture, main pancreatic duct diameter and anastomotic technique are considered the most significant factors contributing to higher risk for pancreatic fistula. Among them, anastomotic technique is the only factor that can be evolved.
Innovations and breakthroughs
The authors present a modification for duct to mucosa end-to-side pancreatico- jejunostomy, with a seromuscular jejunal flap, in order to increase the safety of the anastomosis.
Applications
This modification appears to be a significantly safe approach to the pancreaticojejunostomy without adversely affecting operative time.
Peer review
In this manuscript, authors have presented the new procedure of pancreaticojejunostomy in pancreaticoduodenectomy to prevent pancreatic fistula. They concluded the new procedure could decrease the occurrence rate of pancreatic fistula. The results are basically interesting for readers.
Footnotes
P- Reviewer Ochiai T S- Editor Gou SX L- Editor O’Neill M E- Editor Li JY
References
- 1.Cameron JL, Riall TS, Coleman J, Belcher KA. One thousand consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies. Ann Surg. 2006;244:10–15. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000217673.04165.ea. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Abu Hilal M, Malik HZ, Hamilton-Burke W, Verbeke C, Menon KV. Modified Cattell’s pancreaticojejunostomy, buttressing for soft pancreases and an isolated biliopancreatic loop are safety measurements that improve outcome after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a pilot study. HPB (Oxford) 2009;11:154–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2009.00028.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kausch W. Das Carcinoma der Papilla Duodeni und seine Vadikale Entfernung. Bietrage zur Klinischen Chirugen. 1912;78:439–486. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Whipple AO, Parsons WB, Mullins CR. Treatment of carcinoma of the ampulla of vater. Ann Surg. 1935;102:763–779. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193510000-00023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Poon RT, Lo SH, Fong D, Fan ST, Wong J. Prevention of pancreatic anastomotic leakage after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Am J Surg. 2002;183:42–52. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(01)00829-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shapiro TM. Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: a statistical analysis of biliary bypass vs Whipple resection in good risk patients. Ann Surg. 1975;182:715–721. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197512000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bassi C, Falconi M, Molinari E, Mantovani W, Butturini G, Gumbs AA, Salvia R, Pederzoli P. Duct-to-mucosa versus end-to-side pancreaticojejunostomy reconstruction after pancreaticoduodenectomy: results of a prospective randomized trial. Surgery. 2003;134:766–771. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6060(03)00345-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Haddad LB, Scatton O, Randone B, Andraus W, Massault PP, Dousset B, Soubrane O. Pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy: the conservative treatment of choice. HPB (Oxford) 2009;11:203–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2009.00007.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Takano S, Ito Y, Watanabe Y, Yokoyama T, Kubota N, Iwai S. Pancreaticojejunostomy versus pancreaticogastrostomy in reconstruction following pancreaticoduodenectomy. Br J Surg. 2000;87:423–427. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.2000.01395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Birkmeyer JD, Siewers AE, Finlayson EV, Stukel TA, Lucas FL, Batista I, Welch HG, Wennberg DE. Hospital volume and surgical mortality in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1128–1137. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa012337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bassi C, Dervenis C, Butturini G, Fingerhut A, Yeo C, Izbicki J, Neoptolemos J, Sarr M, Traverso W, Buchler M. Postoperative pancreatic fistula: an international study group (ISGPF) definition. Surgery. 2005;138:8–13. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2005.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bassi C, Butturini G, Molinari E, Mascetta G, Salvia R, Falconi M, Gumbs A, Pederzoli P. Pancreatic fistula rate after pancreatic resection. The importance of definitions. Dig Surg. 2004;21:54–59. doi: 10.1159/000075943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Butturini G, Daskalaki D, Molinari E, Scopelliti F, Casarotto A, Bassi C. Pancreatic fistula: definition and current problems. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2008;15:247–251. doi: 10.1007/s00534-007-1301-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rault A, SaCunha A, Klopfenstein D, Larroudé D, Epoy FN, Collet D, Masson B. Pancreaticojejunal anastomosis is preferable to pancreaticogastrostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy for longterm outcomes of pancreatic exocrine function. J Am Coll Surg. 2005;201:239–244. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.03.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cattell RB, Pyrtek LJ. An Appraisal of Pancreatoduodenal Resection: A Follow-up Study of 61 Cases. Ann Surg. 1949;129:840–848. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cameron JL, Pitt HA, Yeo CJ, Lillemoe KD, Kaufman HS, Coleman J. One hundred and forty-five consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies without mortality. Ann Surg. 1993;217:430–435; discussion 435-438. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199305010-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Suzuki Y, Fujino Y, Tanioka Y, Hiraoka K, Takada M, Ajiki T, Takeyama Y, Ku Y, Kuroda Y. Selection of pancreaticojejunostomy techniques according to pancreatic texture and duct size. Arch Surg. 2002;137:1044–1047; discussion 1048. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.137.9.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Strasberg SM, Drebin JA, Mokadam NA, Green DW, Jones KL, Ehlers JP, Linehan D. Prospective trial of a blood supply-based technique of pancreaticojejunostomy: effect on anastomotic failure in the Whipple procedure. J Am Coll Surg. 2002;194:746–758; discussion 759-760. doi: 10.1016/s1072-7515(02)01202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Peng SY, Wang JW, Lau WY, Cai XJ, Mou YP, Liu YB, Li JT. Conventional versus binding pancreaticojejunostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a prospective randomized trial. Ann Surg. 2007;245:692–698. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000255588.50964.5d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dai XW, Ma K, Wang FX, Yang FQ, Wang BS, Zhao HY, Sun W, Liu BL, Qiu F, Pu XM, et al. Prevention of pancreaticojejunal anastomotic leakage after pancreaticoduodenectomy with separate internal drainage of bile and pancreatic fluid. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2003;2:131–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yeh TS, Jan YY, Jeng LB, Hwang TL, Wang CS, Chen SC, Chao TC, Chen MF. Pancreaticojejunal anastomotic leak after pancreaticoduodenectomy--multivariate analysis of perioperative risk factors. J Surg Res. 1997;67:119–125. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1996.4974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Sohn TA, Coleman J, Sauter PK, Hruban RH, Pitt HA, Lillemoe KD. Pancreaticoduodenectomy with or without extended retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy for periampullary adenocarcinoma: comparison of morbidity and mortality and short-term outcome. Ann Surg. 1999;229:613–622; discussion 622-624. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199905000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Maher MM, Sauter PK, Zahurak ML, Talamini MA, Lillemoe KD, Pitt HA. A prospective randomized trial of pancreaticogastrostomy versus pancreaticojejunostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ann Surg. 1995;222:580–588; discussion 588-592. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199510000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Lillemoe KD, Sauter PK, Coleman J, Sohn TA, Campbell KA, Choti MA. Does prophylactic octreotide decrease the rates of pancreatic fistula and other complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy Results of a prospective randomized placebo-controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2000;232:419–429. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200009000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sampaio JA, Pereira-Lima JC, Rhoden EL, Waechter FL, Smith M, Cardoso F, Pinto RD, Pereira-Lima L. Pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a comparison between patients with periampullary tumors and chronic pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology. 1998;45:1855–1858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.van Berge Henegouwen MI, De Wit LT, Van Gulik TM, Obertop H, Gouma DJ. Incidence, risk factors, and treatment of pancreatic leakage after pancreaticoduodenectomy: drainage versus resection of the pancreatic remnant. J Am Coll Surg. 1997;185:18–24. doi: 10.1016/s1072-7515(97)00007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fueki K. Experimental and clinical studies on operative methods of pancreaticojejunostomy in reference to the process of wound healing and postoperative pancreatic function. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1985;86:725–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


