Abstract
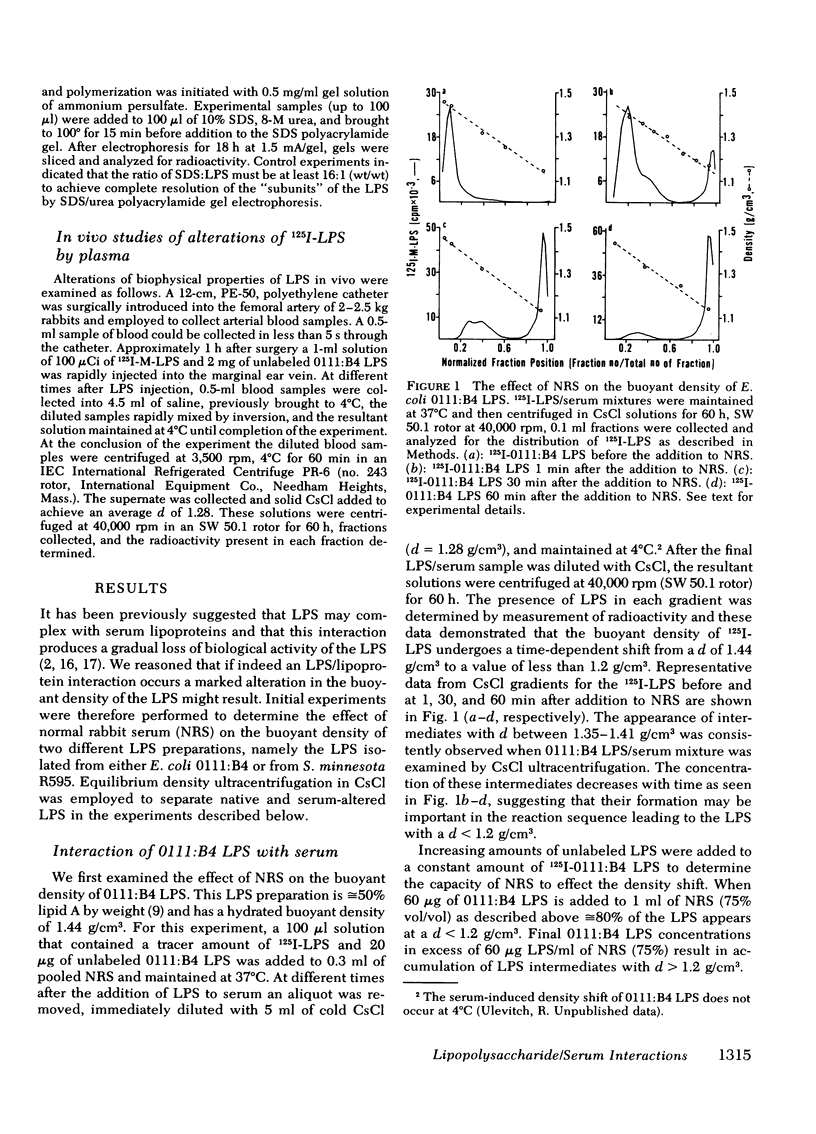
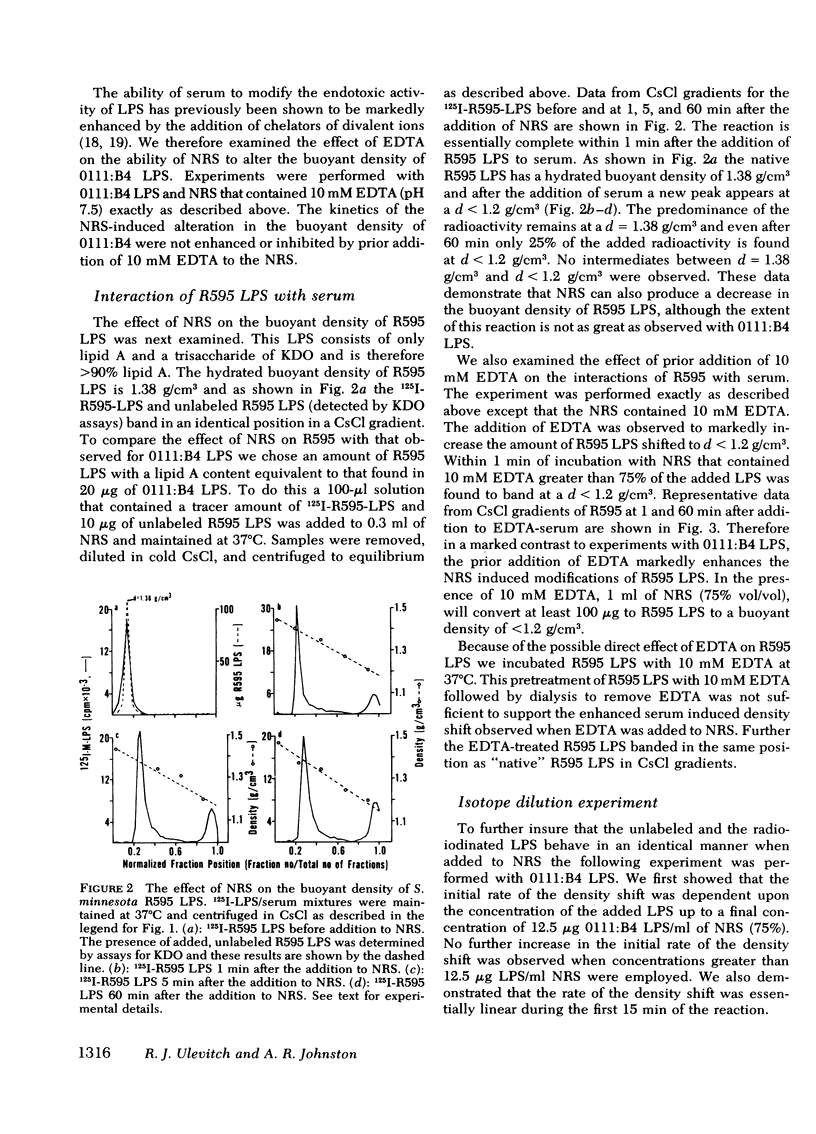
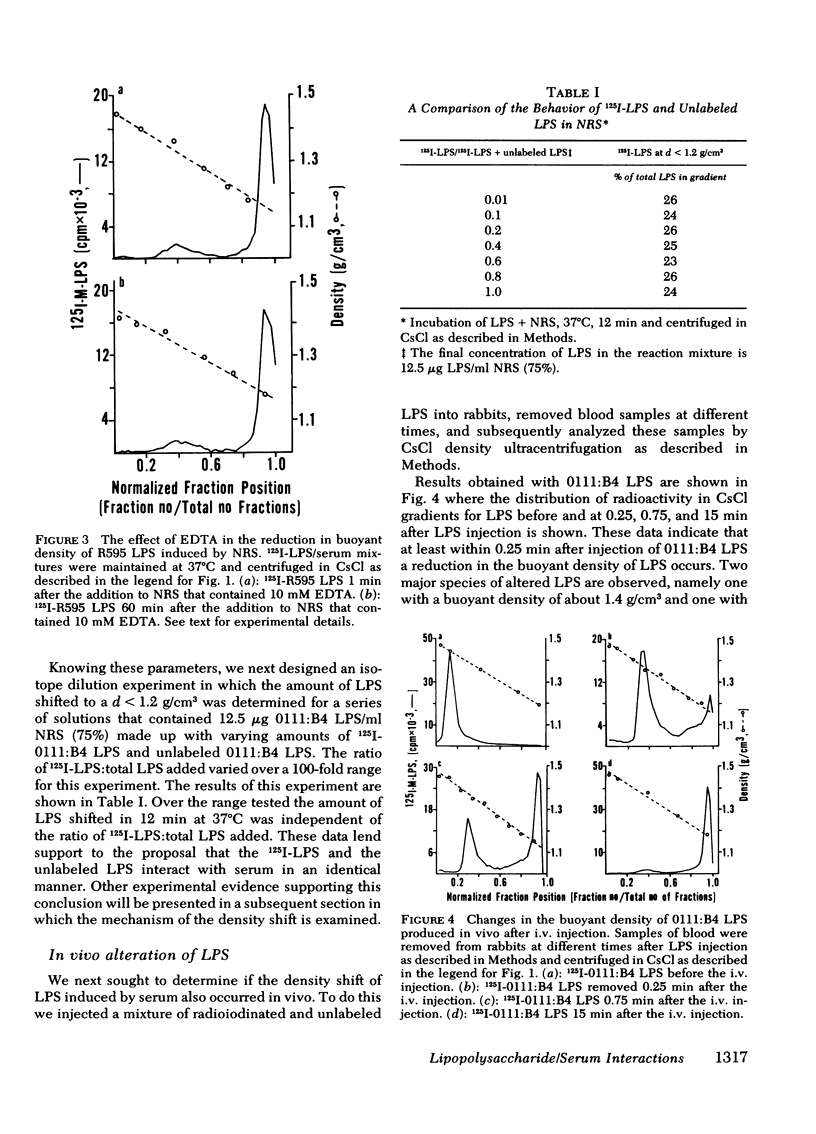
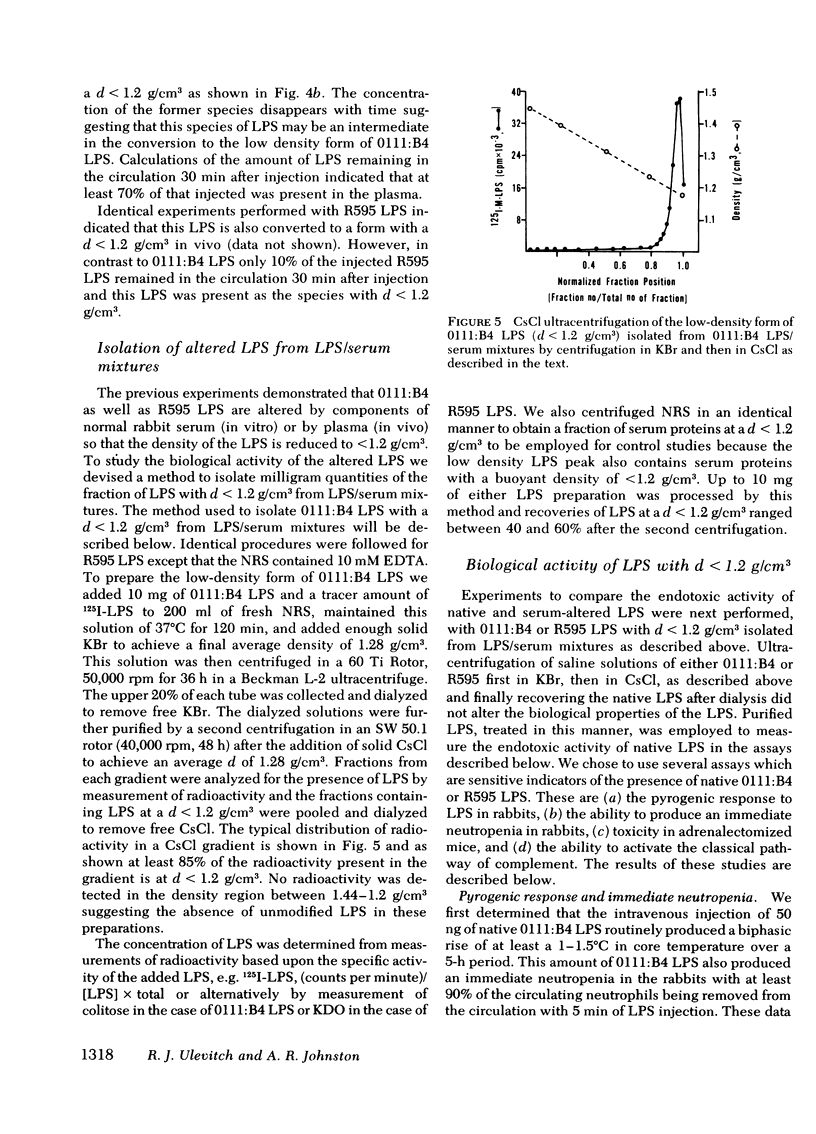
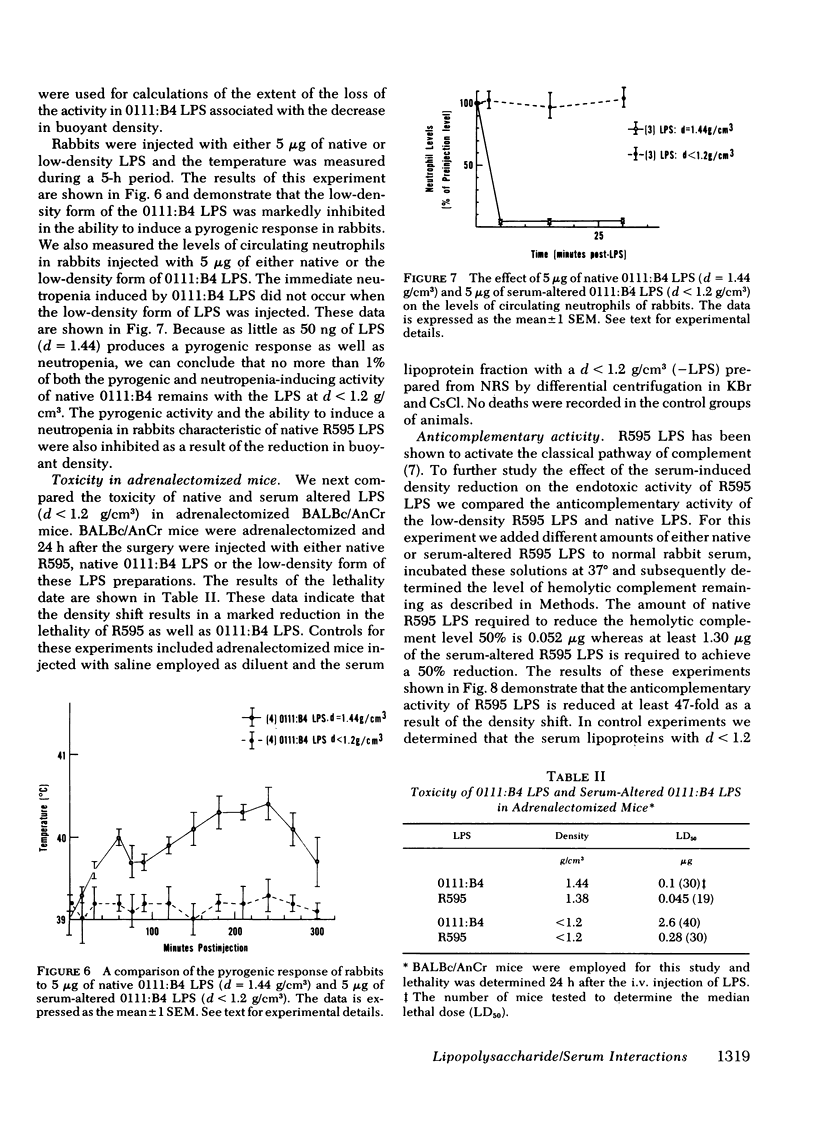
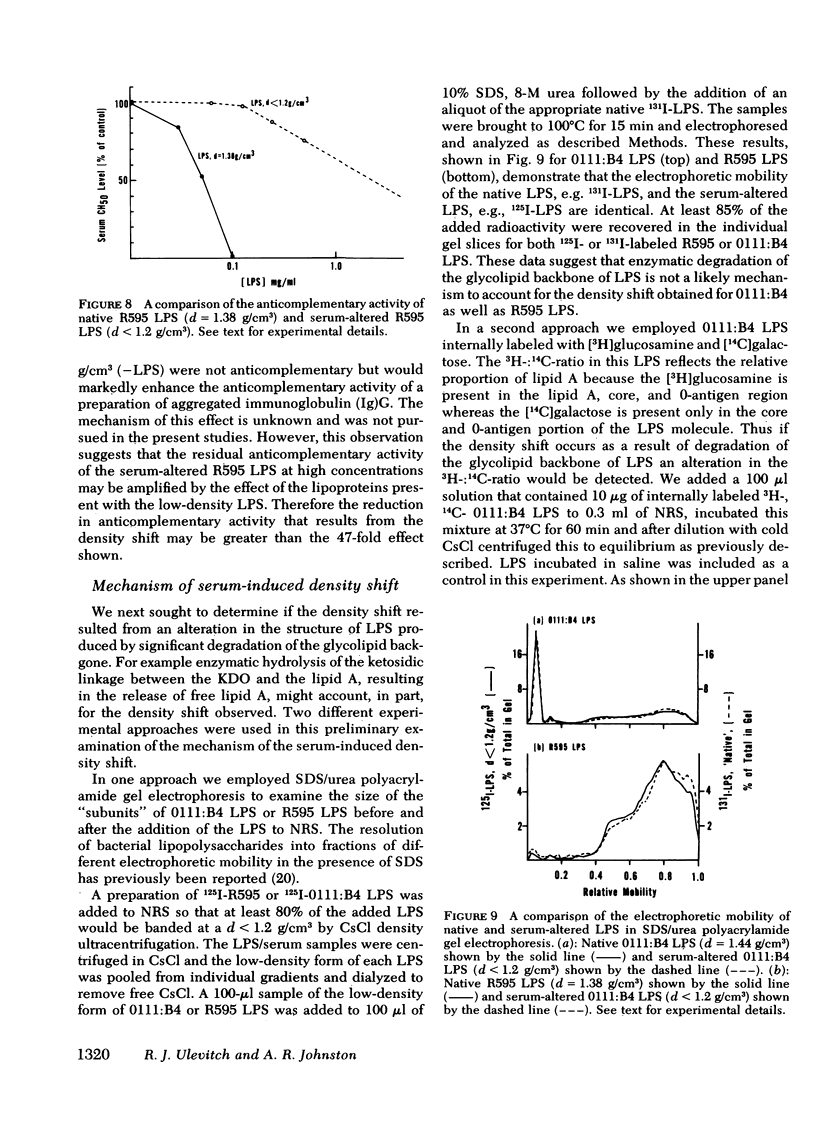
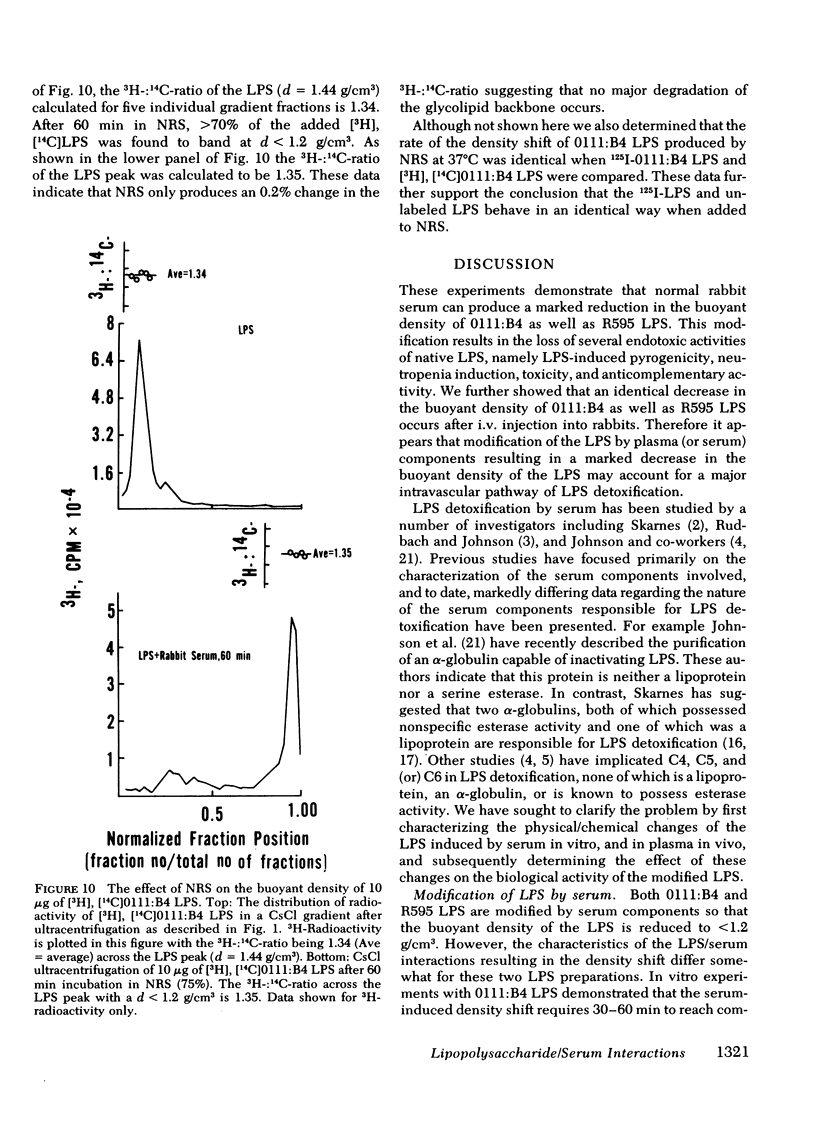
Normal rabbit serum reduces the buoyant density of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Escherichia coli 0111:B4 (d = 1.44 g/cm3) and Salmonella minnesota R595 (d = 1.38 g/cm3) to a value less than g/cm3. This density shift is associated with the inhibition of a number of endotoxic activities of the LPS; namely, the pyrogenic activity, the ability to produce an immediate neutropenia in rabbits, lethality in adrenalectomized mice, and anticomplementary activity. A qualitatively similar change in buoyant density was observed to occur after intravenous injection of the LPS into rabbits. Preliminary evidence suggests that the density shift does not occur as a result of the degradation of the glycolipid backbone of the LPS. These data suggest that the interactions of LPS with plasma (or serum) components leading to reduction in buoyant density may account for a major pathway of LPS detoxification.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CYNKIN M. A., ASHWELL G. Estimation of 3-deoxy sugars by means of the malonaldehyde-thiobarbituric acid reaction. Nature. 1960 Apr 9;186:155–156. doi: 10.1038/186155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dea I. C., McKinnon A. A., Rees D. A. Tertiary and quaternary structure in aqueous polysaccharide systems which model cell wall cohesion: reversible changes in conformation and association of agarose, carrageenan and galactomannans. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 14;68(1):153–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downer N. W., Robinson N. C. Characterization of a seventh different subunit of beef heart cytochrome c oxidase. Similarities between the beef heart enzyme and that from other species. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2930–2936. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Reske K., Jann K. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides. Analysis of polysaccharide chain lengths by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A., Goralnick S., Osborn M. J. Isolation from human serum of an inactivator of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Am J Pathol. 1977 Sep;88(3):559–574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. The requirement for serum complement in the detoxification of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNIKER W. T., COCHRANE C. G. PATHOGENIC FACTORS IN VASULAR LESIONS OF EXPERIMENTAL SERUM SICKNESS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:83–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May J. E., Kane M. A., Frank M. M. Host defense against bacterial endotoxemia-contribution of the early and late components of complement to detoxification. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):893–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Kline L. F. Activation of the classical and properdin pathways of complement by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):362–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Leive L. Fractions of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli O111:B4 prepared by two extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2911–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL D. P., GASKINS J. R., KELLY M. G. Reduction of febrile response to bacterial polysaccharide following incubation with serum. Am J Physiol. 1957 Mar;188(3):559–562. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.188.3.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN F. S., SKARNES R. C., LANDY M., SHEAR M. J. Inactivation of endotoxin by a humoral component. III. Role of divalent cation and a dialyzable component. J Exp Med. 1958 Nov 1;108(5):701–711. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.5.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDBACH J. A., JOHNSON A. G. RESTORATION OF ENDOTOXIN ACTIVITY FOLLOWING ALTERATION BY PLASMA. Nature. 1964 May 23;202:811–812. doi: 10.1038/202811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKARNES R. C., ROSEN F. S., SHEAR M. J., LANDY M. Inactivation of endotoxin by a humoral component. II. Interaction of endotoxin with serum and plasma. J Exp Med. 1958 Nov 1;108(5):685–699. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.5.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C. Host defense against bacterial endotoxemia: mechanism in normal animals. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):300–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C. In vivo interaction of endotoxin with a plasma lipoprotein having esterase activity. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2031–2034. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2031-2034.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Cochrane C. G., Henson P. M., Morrison D. C., Doe W. F. Mediation systems in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced hypotension and disseminated intravascular coagulation. I. The role of complement. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1570–1590. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J. The preparation and characterization of a radioiodinated bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Immunochemistry. 1978 Mar;15(3):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIOKA M., JOHNSON A. G. Characteristics of endotoxin altering fractions derived from normal human serum. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:326–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



