Abstract
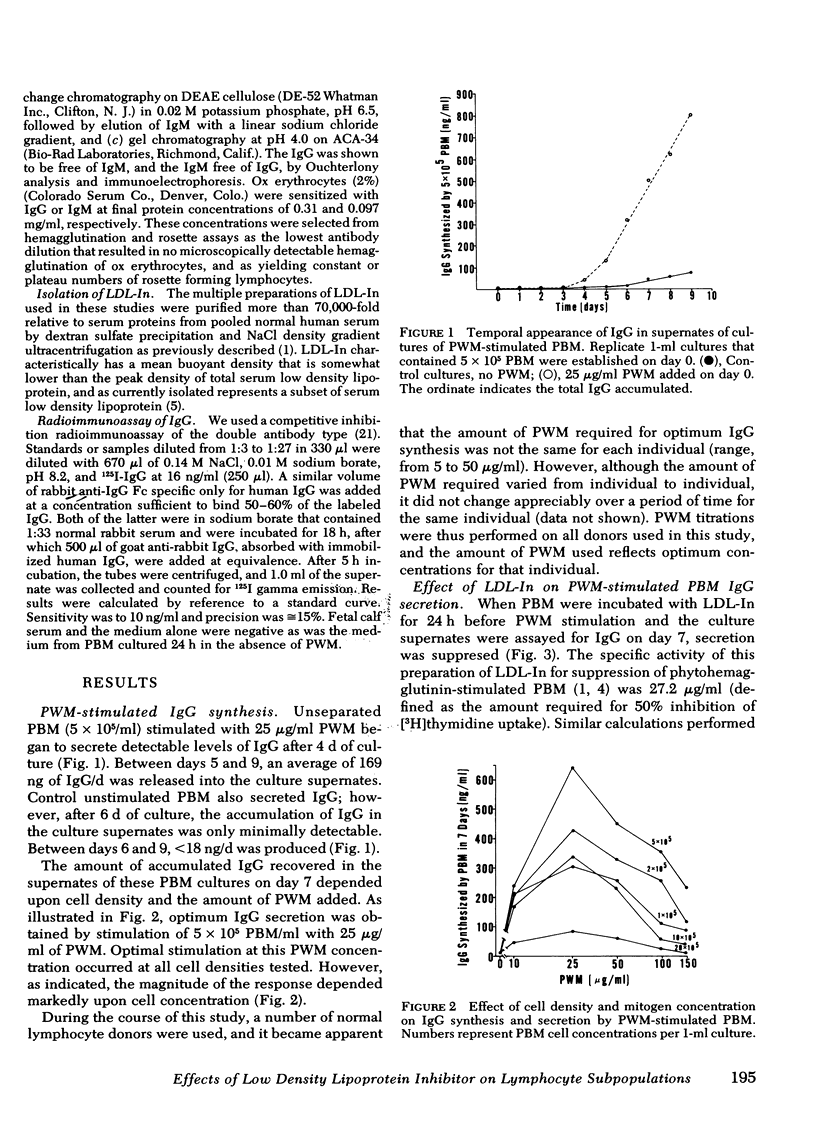
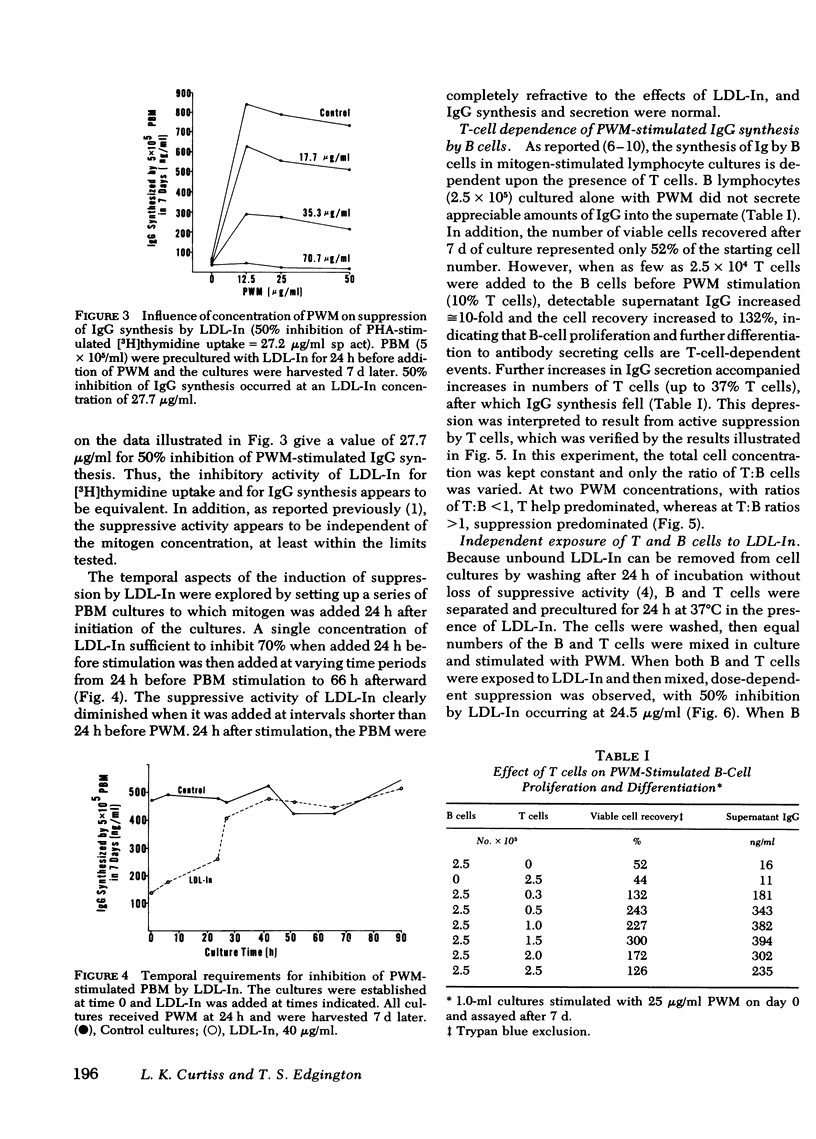
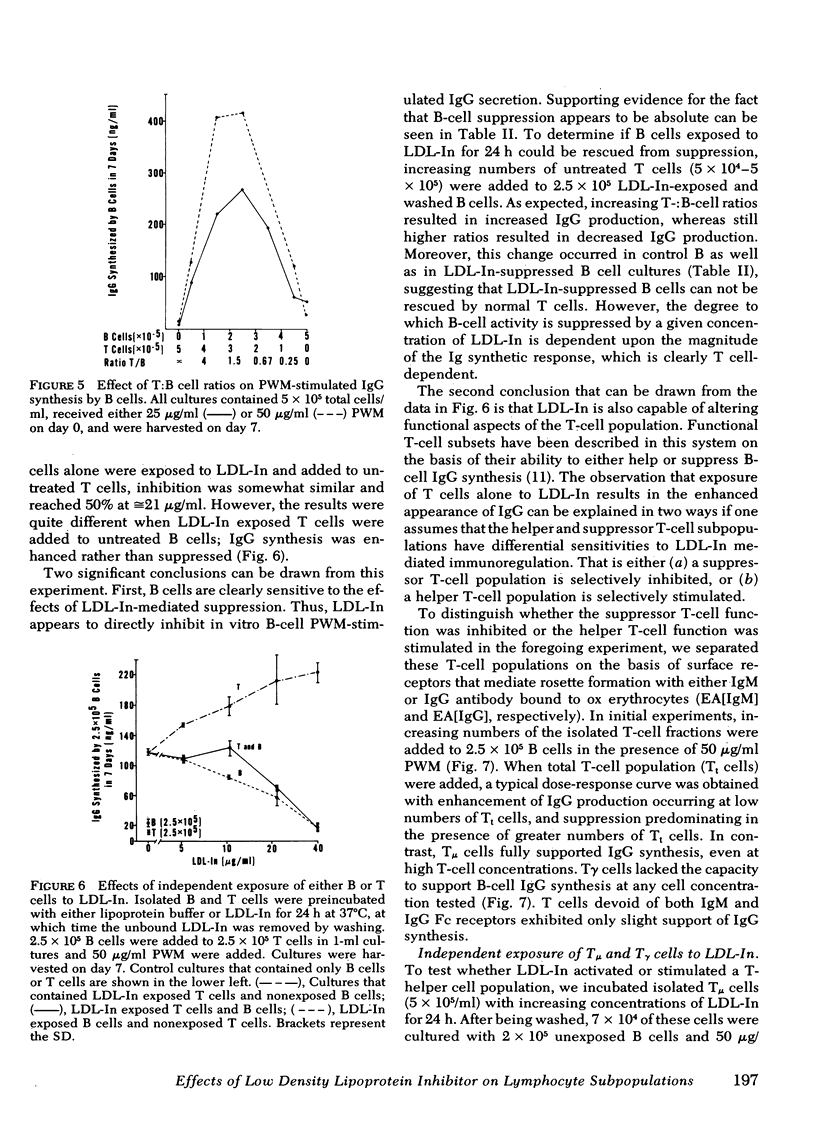
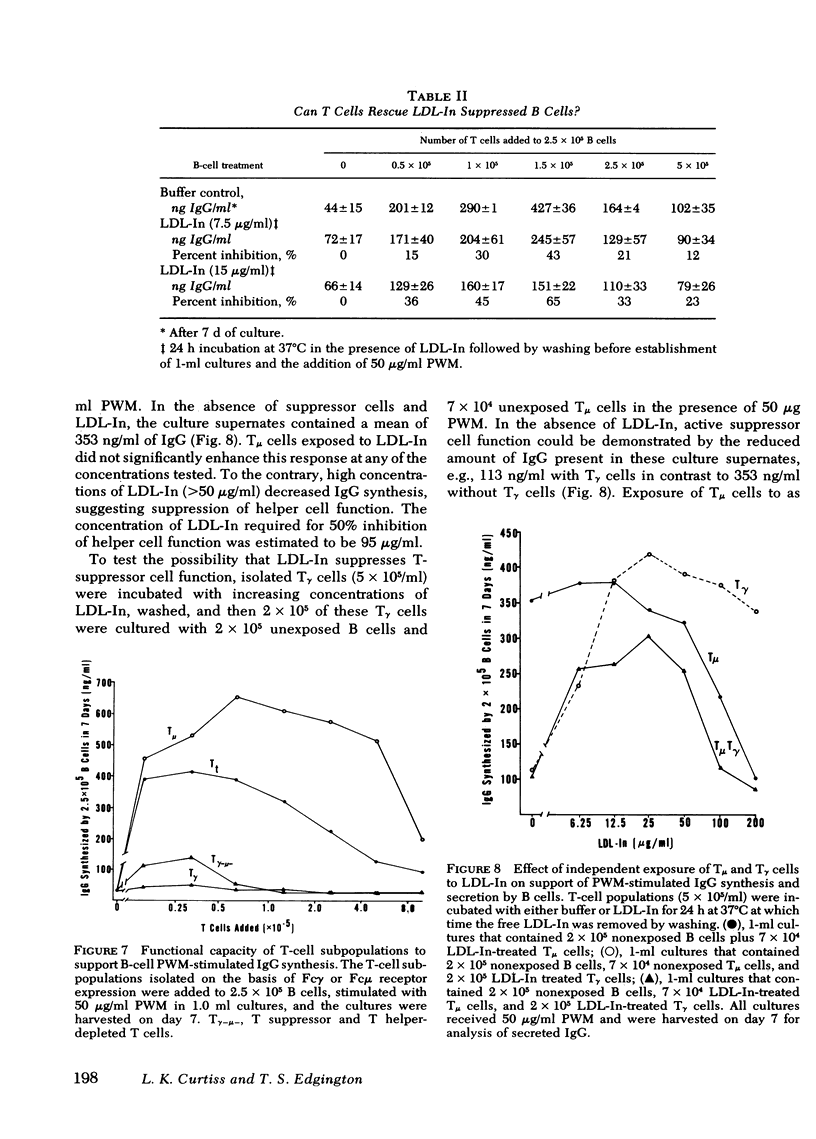
Reports by a number of investigators have described the thymus-derived (T)-cell dependence of immunoglobulin synthesis by pokeweed mitogen (PWM) stimulated human peripheral blood bone marrow-derived (B) cells. Because of the cooperative nature of this in vitro system, it was chosen for examination of the differential effects of low density lipoprotein inhibitor (LDL-In) on B- and T-cell functions. Supernates from 7-d cultures that contained either peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBM) or combinations of isolated lymphocyte populations were assayed for immunoglobulin (Ig)G by competitive inhibition radio-immunoassay. LDL-In suppression of whole PBM IgG synthesis occurred at 5-20 μg protein/ml and was independent of PWM concentration. Maximal suppression required preincubation of cells with LDL-In before stimulation. Suppression was also observed when B cells alone were exposed for 24 h to LDL-In before PWM stimulation; these suppressed B cells were not rescued by normal T cells. Exposure of T cells alone to low doses of LDL-In for 24 h augmented, but high doses suppressed, IgG synthesis, suggesting a differential effect on T-helper vs T-suppressor cell populations. Independent LDL-In exposure of T-helper or T-suppressor cell enriched populations, separated by rosetting with IgG- or IgM-coated ox erythrocytes, identified the T-suppressor cell populations as the most sensitive of the lymphocyte populations tested. The sensitivities of lymphocyte subpopulations to LDL-In, relative to PBM, were 2.8, 1.2, and 0.3 for the T-suppressor cells, B cells and T-helper cells, respectively. Thus, both B and T lymphocytes are sensitive to and can be regulated by LDL-In. In addition, the biologic activity observed when unseparated PBM are exposed to LDL-In appears to represent a composite of the sensitivity of each of the lymphocyte subpopulations.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chisari F. V., Routenberg J. A., Edgington T. S. Mechanisms responsible for defective human T-lymphocyte sheep erythrocyte rosette function associated with hepatitis B virus infections. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1227–1238. doi: 10.1172/JCI108391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., DeHeer D. H., Edgington T. S. In vivo suppression of the primary immune response by a species of low density serum lipoprotein. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):648–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Effect of LDL-In, a normal immunoregulatory human serum low density lipoprotein, on the interaction of macrophages with lymphocytes proliferating in response to mitogen and allogeneic stimulation. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):1966–1970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Identification of a lymphocyte surface receptor for low density lipoprotein inhibitor, an immunoregulatory species of normal human serum low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1298–1308. doi: 10.1172/JCI109047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Regulatory serum lipoproteins: regulation of lymphocyte stimulation by a species of low density lipoprotein. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1452–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Pratt K. R., Whalen G. Activation of human B lymphocytes. II. Cellular interactions in the PFC response of human tonsillar and peripheral blood B lymphocytes to polyclonal activation by pokeweed mitogen. J Immunol. 1976 Dec;117(6):2100–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Pratt K. R., Whalen G. Activation of human B lymphocytes. IV. Regulatory effects of corticosteroids on the triggering signal in the plaque-forming cell response of human peripheral blood B lymphocytes to polyclonal activation. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):598–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarini M., Moretta L., Abrile R., Durante M. L. Receptors for IgG molecules on human lymphocytes forming spontaneous rosettes with sheep red cells. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Jan;5(1):70–72. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Schlesinger M. The formation of stable E rosettes after neuraminidase treatment of either human peripheral blood lymphocytes or of sheep red blood cells. J Immunol. 1974 May;112(5):1628–1634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg W. W., Finkelman F. D., Lipsky P. E. Circulating and mitogen-induced immunoglobulin-secreting cells in human peripheral blood: evaluation by a modified reverse hemolytic plaque assay. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):33–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger M., Mayer M. M. NORMAL HUMAN STROMATA AS ANTIGENS FOR COMPLEMENT FIXATION IN THE SERA OF PATIENTS WITH RELAPSING VIVAX MALARIA. Science. 1944 Oct 20;100(2599):359–360. doi: 10.1126/science.100.2599.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Kuritani T., Kishimoto T., Yamamura Y. In vitro immune response of human peripheral lymphocytes. I. The mechanism(s) involved in T cell helper functions in the pokeweed mitogen-induced differentiation and proliferation of B cells. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1235–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Gomez de la Concha E., Luquetti A., Snajdr M. J., Waxdal M. J., Platts-Mills T. A. T-cell regulation of immunoglobulin synthesis and proliferation in pokeweed (Pa-1)-stimulated human lymphocyte cultures. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(1-2):109–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keightley R. G., Cooper M. D., Lawton A. R. The T cell dependence of B cell differentiation induced by pokeweed mitogen. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1538–1544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., Ginsburg W. W., Finkelman F. D., Ziff M. Control of human B lymphocyte responsiveness: enhanced suppressor T cell activity after in vitro incubation. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):902–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell I., Hurd C. M. Lymphocyte receptors. II. Receptors for rabbit IgM on human T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1976 Jun;30(6):835–839. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Ferrarini M., Durante M. L., Mingari M. C. Expression of a receptor for IgM by human T cells in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Aug;5(8):565–569. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Ferrarini M., Mingari M. C., Moretta A., Webb S. R. Subpopulations of human T cells identified by receptors for immunoglobulins and mitogen responsiveness. J Immunol. 1976 Dec;117(6):2171–2174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Webb S. R., Grossi C. E., Lydyard P. M., Cooper M. D. Functional analysis of two human T-cell subpopulations: help and suppression of B-cell responses by T cells bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):184–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Hougie C., Edgington T. S. Neoantigenic expressions engendered by plasmin cleavage of fibrinogen. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1496–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Siegal M. Enhancement by irradiated T cells of human plasma cell production: dissection of helper and suppressor functions in vitro. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):642–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strelkauskas A. J., Wilson B. S., Callery R. T., Chess L., Schlossman S. F. T-cell regulation of human peripheral blood B-cells responsiveness. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1765–1772. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


