Abstract
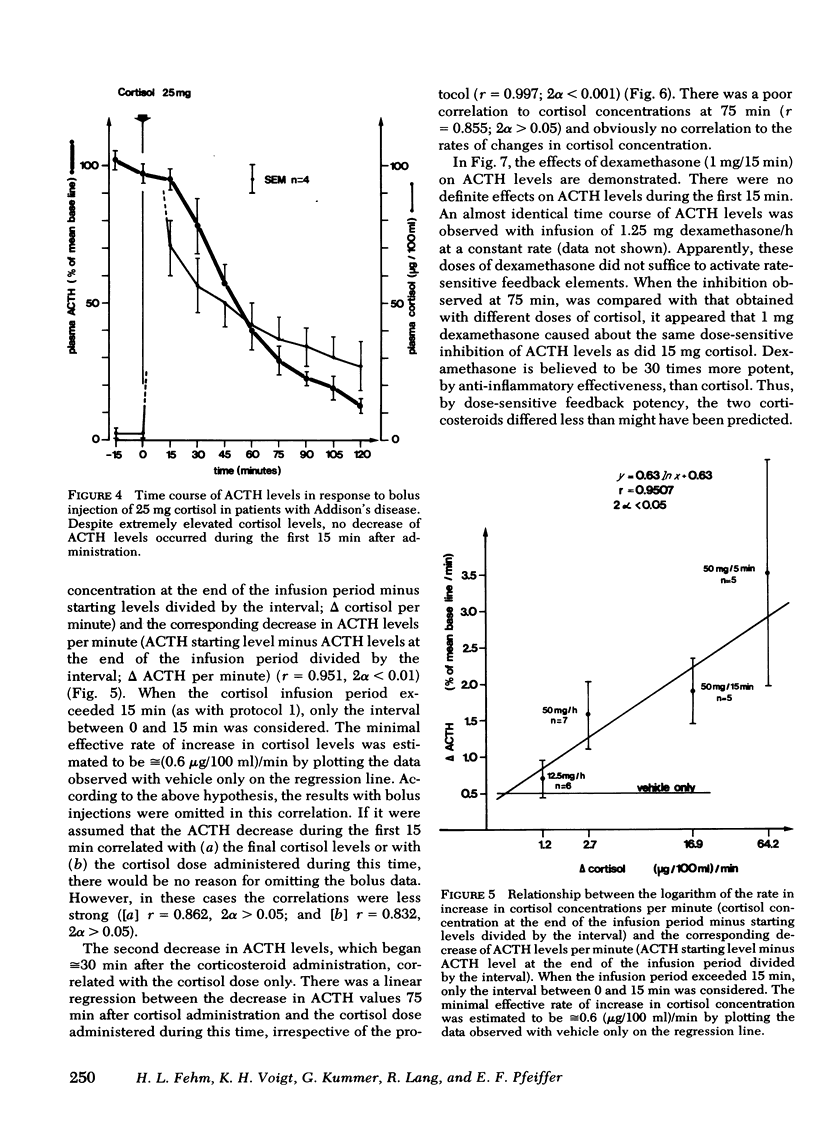
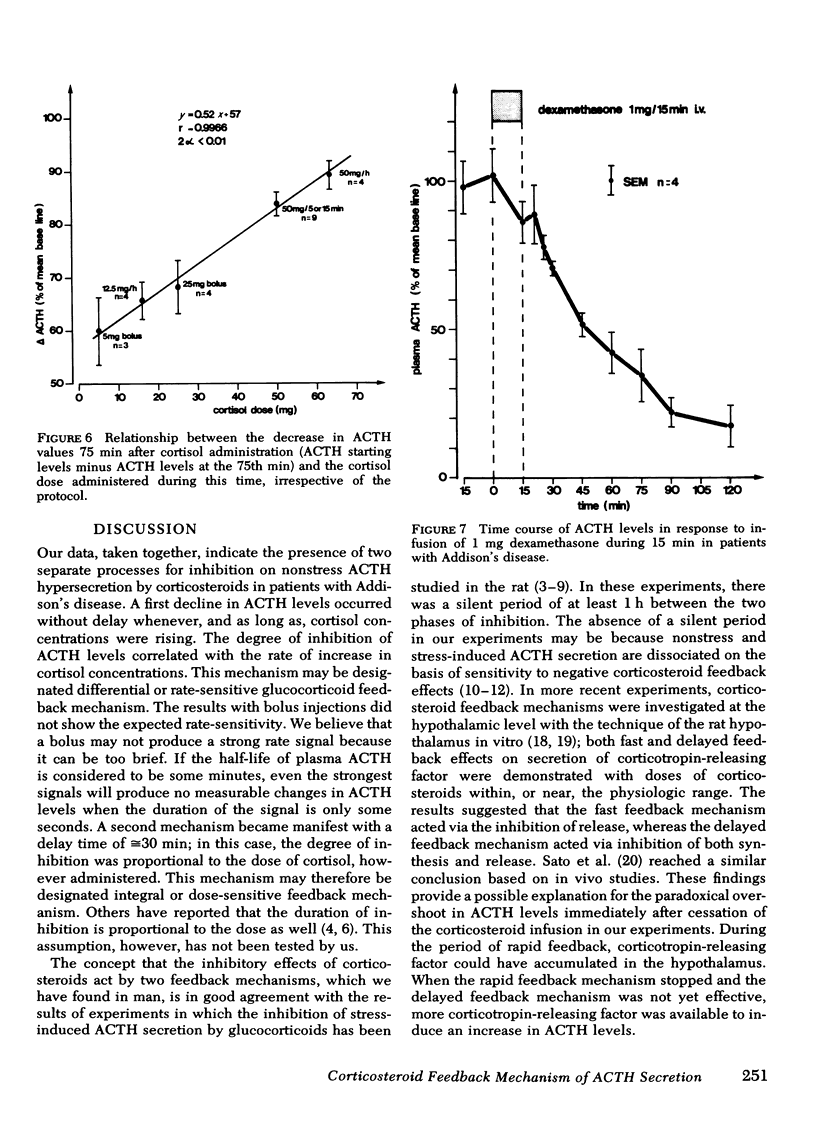
Recent work suggests the existence of a dual corticosteroid feedback mechanism of stress-induced ACTH secretion in the rat. This possibility led us to study the kinetics of suppression of ACTH levels by corticosteroid administration in patients with nonstress ACTH hypersecretion secondary to hypoadrenocorticism. Cortisol was administered according to different protocols, which were chosen to provide extreme variations of the input signal. By this means, two phases of suppression of ACTH levels could be differentiated. A first decrease occurred without latency whenever, and as long as, plasma cortisol levels were rising. There was a linear regression between the logarithm of the increments in cortisol concentrations and the decrease in ACTH levels per minute (r = 0.951) (differential or rate-sensitive feedback mechanism). Neither the absolute doses of cortisol, nor plasma cortisol concentrations were closely correlated with the degree of suppression of ACTH by this rapid mechanism. A second decrease in ACTH levels began ≅30 min after corticosteroid administration. In this case there was a significant linear regression between the degree of inhibition of ACTH levels and the cortisol doses (r = 0.997) (integral or dose-sensitive feedback mechanism).
The dose-sensitive feedback effects of dexamethasone were less than might have been predicted from its relative anti-inflammatory potency. No rate-sensitive effects were seen with dexamethasone doses of 1.0 or 1.25 mg.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acs Z., Stark E. Effect of cortexolone on the feedback action of dexamethasone. Experientia. 1975 Nov 15;31(11):1365–1366. doi: 10.1007/BF01945830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher B., Koch B., Mialhe C. Sur l'existence d'un mécanisme de "feedback rapide" ACTH-corticostérone. J Physiol (Paris) 1973;66(2):199–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYNES M. Unidirectional rate sensitivity: a biocybernetic law of reflex and humoral systems as physiologic channels of control and communication. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Jul 28;92:946–969. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb40968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens A. H., Chang P. H., Myers R. W. The development of Biostator, a Glucose Controlled Insulin Infusion System (GCIIS). Horm Metab Res. 1977;Suppl 7:23–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. F., Yates F. E. Dynamic asymmetries in the corticosteroid feedback path and distribution-metabolism-binding elements of the adrenocortical system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Apr 21;156(2):696–721. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb14008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engeland W. C., Shinsako J., Winget C. M., Vernikos-Danellis J., Dallman M. F. Circadian patterns of stress-induced ACTH secretion are modified by corticosterone responses. Endocrinology. 1977 Jan;100(1):138–147. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-1-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehm H. L., Voight K. H., Lang R. E., Beinert K. E., Kummer G. W., Pfeiffer E. F. Paradoxical ACTH response to glucocorticoids in Cushing's disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Oct 27;297(17):904–907. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197710272971703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehm H. L., Voigt K. H., Pfeiffer E. F. Problems and artefacts in ACTH assay. Horm Metab Res. 1972 Nov;4(6):477–481. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1094009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillhouse E. W., Jones M. T. Effect of bilateral adrenalectomy and corticosteroid therapy on the secretion of corticotrophin-releasing factor activity from the hypothalamus of the rat in vitro. J Endocrinol. 1976 Oct;71(1):21–30. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0710021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. T., Brush F. R., Neame R. L. Characteristics of fast feedback control of corticotrophin release by corticosteroids. J Endocrinol. 1972 Dec;55(3):489–497. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0550489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. T., Hillhouse E. W. Structure-activity relationship and the mode of action of corticosteroid feedback on the secretion of corticotrophin-releasing factor (corticoliberin). J Steroid Biochem. 1976 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):1189–1202. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(76)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. T., Tiptaft E. M., Brush F. R., Fergusson D. A., Neame R. L. Evidence for dual corticosteroid-receptor mechanisms in the feedback control of adrenocorticotrophin secretion. J Endocrinol. 1974 Feb;60(2):223–233. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0600223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerner W., Thum C., Tamás G., Beischer W., Clemens A. H., Pfeiffer E. F. Attempts at perfect normalization of glucose tolerance test of severe diabetics by artificial beta cell. Horm Metab Res. 1976 Jul;8(4):256–261. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. E. Some studies of the protein-binding of steroids and their application to the routine micro and ultramicro measurement of various steroids in body fluids by competitive protein-binding radioassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jul;27(7):973–990. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-7-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakura M., Saito Y., Takebe K., Ishii K. Studies on fast feedback mechanisms by endogenous glucocorticoids. Endocrinology. 1976 Apr;98(4):954–957. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-4-954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Sato M., Shinsako J., Dallman M. F. Corticosterone-induced changes in hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) content after stress. Endocrinology. 1975 Aug;97(2):265–274. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe K., Kunita H., Sakakura M., Horiuchi Y., Mashimo K. Suppressive effect of dexamethasone on the rise of CRF activity in the median eminence induced by stress. Endocrinology. 1971 Oct;89(4):1014–1019. doi: 10.1210/endo-89-4-1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt K. H., Fehm H. L., Reck R., Pfeiffer E. F. Spontaneous and stimulated secretion of QUSO-extractable immunoassayable ACTH in man. Klin Wochenschr. 1974 Jun 1;52(11):516–521. doi: 10.1007/BF01468721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YATES F. E., LEEMAN S. E., GLENISTER D. W., DALLMAN M. F. Interaction between plasma corticosterone concentration and adrenocorticotropin-releasing stimuli in the rat: evidence for the reset of an endocrine feedback control. Endocrinology. 1961 Jul;69:67–80. doi: 10.1210/endo-69-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann E., Critchlow V. Negative feedback and pituitary-adrenal function in female rats. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jan;216(1):148–155. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.1.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann E., Critchlow V. Suppression of pituitary-adrenal function with physiological plasma levels of corticosterone. Neuroendocrinology. 1969;5(3):183–192. doi: 10.1159/000121859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


