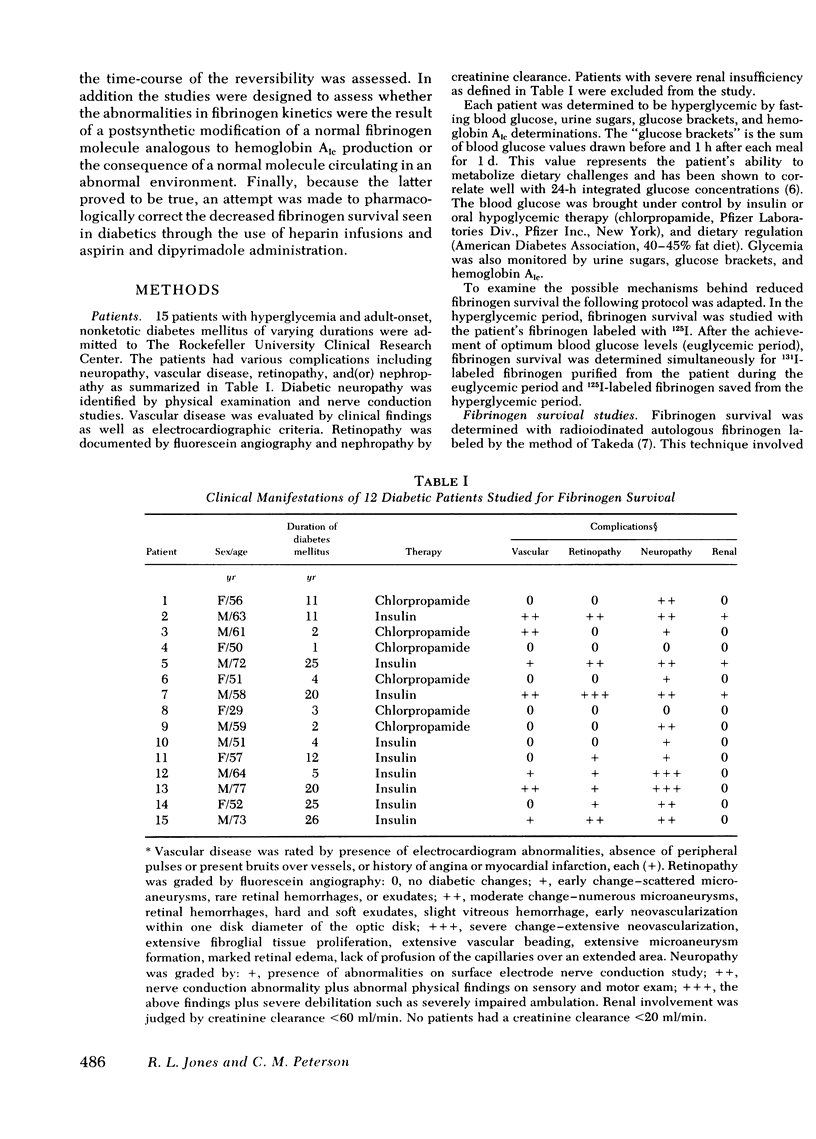
Abstract
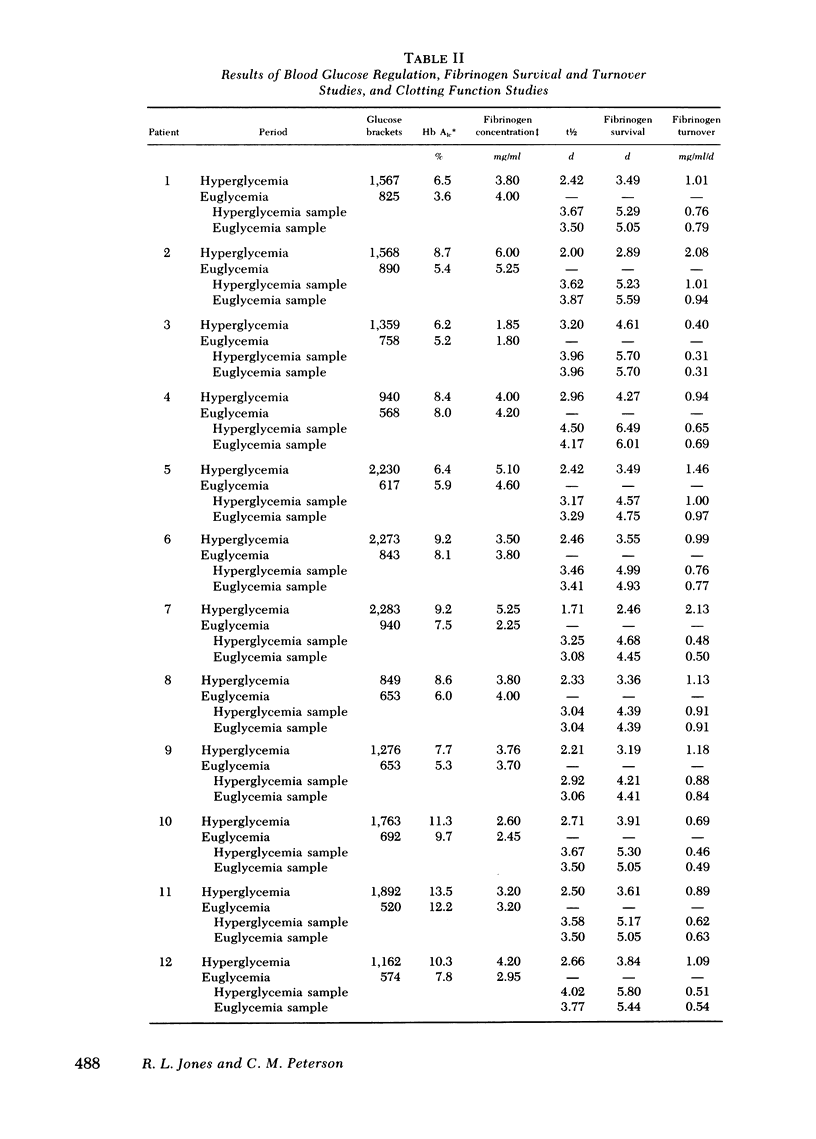
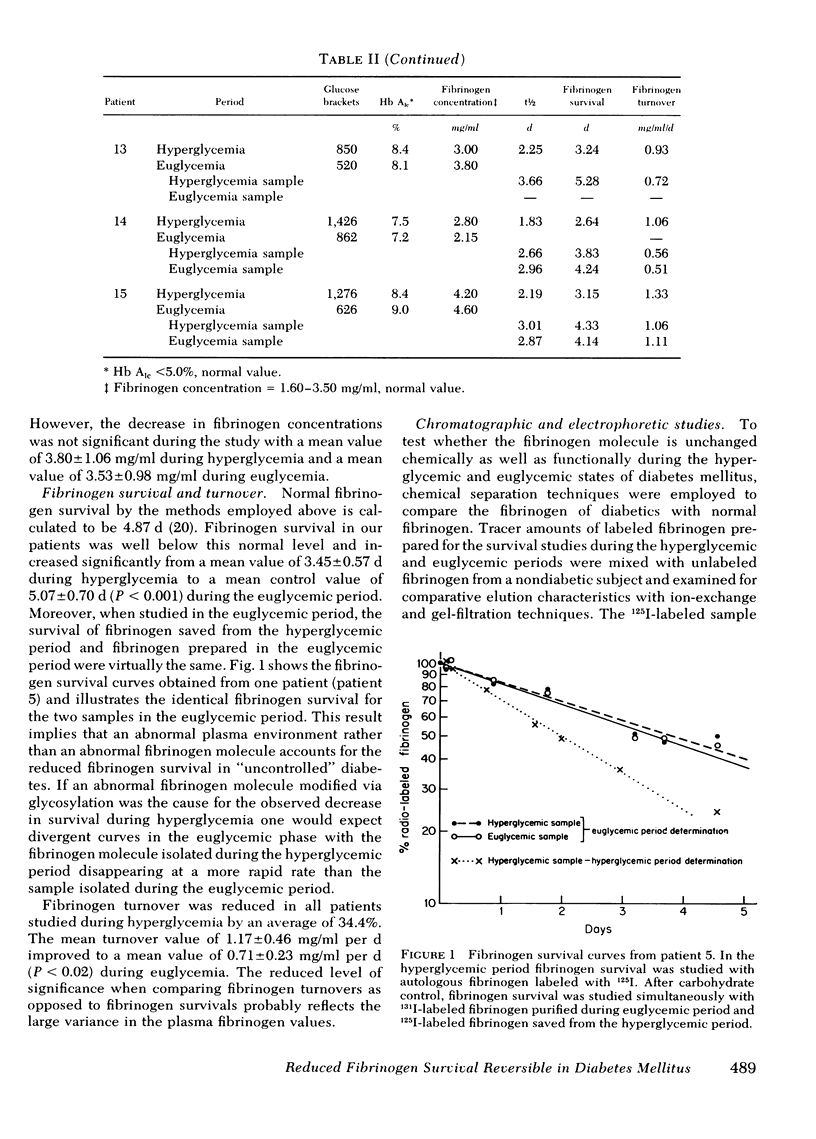
Fibrinogen survival and turnover were examined in 15 adult-onset diabetic patients. 125I-labeled fibrinogen was prepared from each patient during the period of poor carbohydrate control, or hyperglycemic period, and fibrinogen survival determined. Improved control was established in each patient and during this euglycemic period, fibrinogen survival was determined simultaneously with 125I-fibrinogen saved from the hyperglycemic period and 131I-labeled fibrinogen prepared from the patient during the euglycemic period. The results confirm reduced fibrinogen survival in hyperglycemic diabetic patients and demonstrate reversal of the fibrinogen abnormality when euglycemia is achieved. The results of the double-label experiments in the euglycemic period suggest that the fibrinogen molecule is not altered functionally and that an abnormal plasma or vascular environment is a more likely basis for reduced fibrinogen survival during hyperglycemia. Electrophoretic and chromatographic experiments demonstrated no gross chemical differences between the fibrinogens prepared from the hyperglycemic and euglycemic periods and normal fibrinogen. Fibrinogen survival gave a better correlation with serial glucose measurements than with correction of hemoglobin AIc levels indicating that the reduced fibrinogen survival noted in diabetics is a rapidly reversible phenomenon.
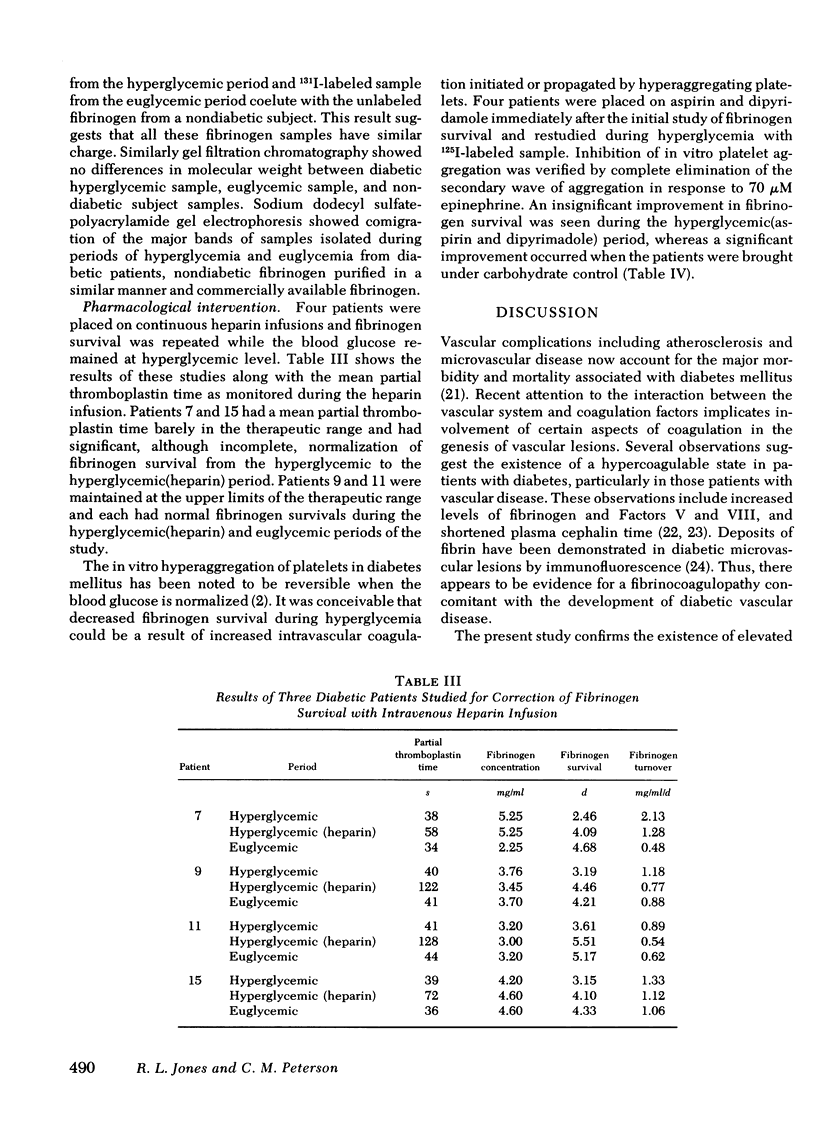
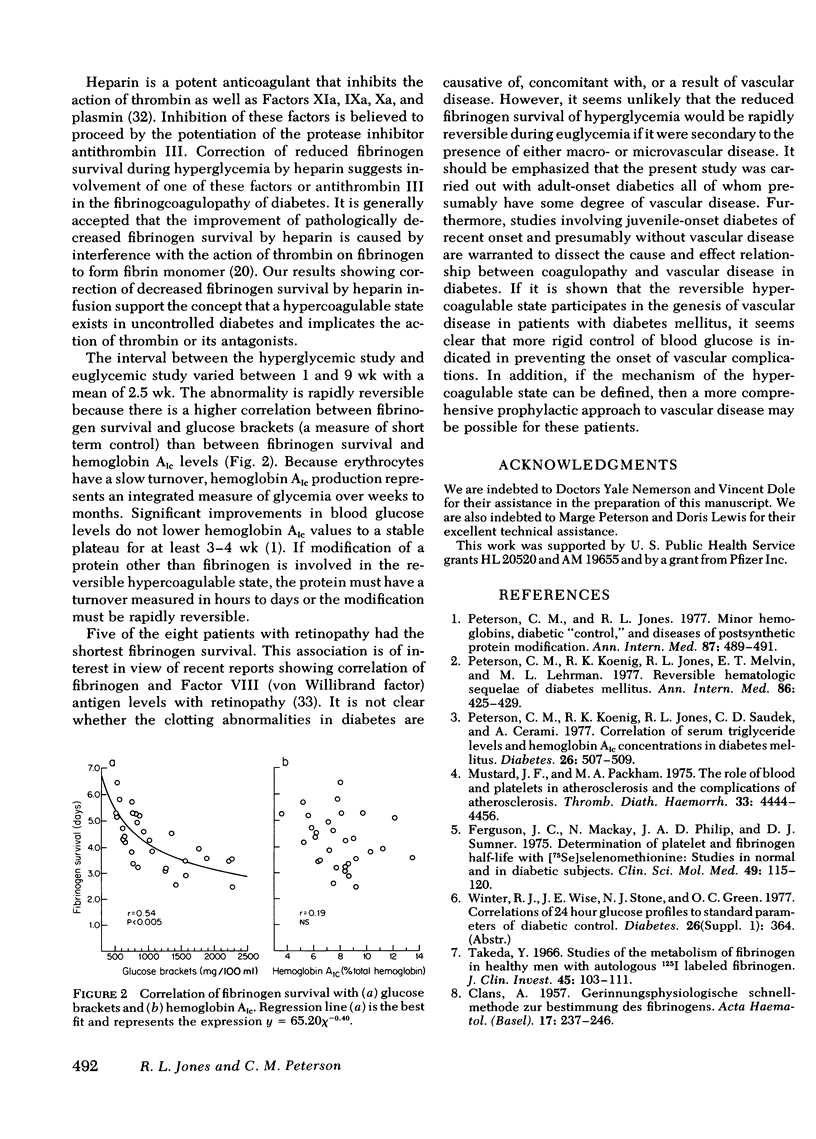
During the hyperglycemic period, pharmacological intervention with aspirin and dipyrimadole was attempted to examine the role of platelets in reduced fibrinogen survival. No significant change in fibrinogen survival was observed. Heparin infusion during hyperglycemia normalized the fibrinogen kinetics of hyperglycemic diabetic patients, suggesting that reduced fibrinogen survival during hyperglycemia is secondary to an effect on thrombin or one of its antagonists.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERG W., KORSAN-BENGTSEN K. Separation of human fibrinogen and plasminogen by means of gel filtration. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1963 Apr 15;9:151–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee R. N., Sahni A. L., Kumar V. Fibrinocoagulopathy in maturity onset diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1973 Sep 15;30(1):123–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedi H. K., Vyas B. R., Bomb B. S., Agarwal M. L., Bedi T. Fibrinogen content and fibrinolytic activity of blood in diabetics, before and after antidiabetic drugs. J Assoc Physicians India. 1977 Mar;25(3):181–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F., Haney D. N., Kamin S., Gabbay K. H., Gallop P. M. The biosynthesis of human hemoglobin A1c. Slow glycosylation of hemoglobin in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1652–1659. doi: 10.1172/JCI108436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Frank R. N., Milton R. C., Gralnick H. R. Plasma cofactors of platelet function: correlation with diabetic retinopathy and hemoglobins Ala-c. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Mar;88(3):311–316. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-3-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson J. C., Mackay N., Philip J. A., Sumner D. J. Determination of platelet and fibrinogen half-life with [75Se]selenomethionine: studies in normal and in diabetic subjects. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 Aug;49(2):115–120. doi: 10.1042/cs0490115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath H., Brigden W. D., Canever J. V., Pollock J., Hunter P. R., Kelsey J., Bloom A. Platelet adhesiveness and aggregation in relation to diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia. 1971 Oct;7(5):308–315. doi: 10.1007/BF01219463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javid J., Pettis P. K., Koenig R. J., Cerami A. Immunologic characterization and quantification of haemoglobin A1c. Br J Haematol. 1978 Mar;38(3):329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb01051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAZAL L. A., AMSEL S., MILLER O. P., TOCANTINS L. M. THE PREPARATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF FIBRINOGEN PRECIPITATED FROM HUMAN PLASMA BY GLYCINE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Aug-Sep;113:989–994. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwaan H. C., Colwell J. A., Cruz S., Suwanwela N., Dobbie J. G. Increased platelet aggregation in diabetes mellitus. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Aug;80(2):236–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne E. E., Bridges J. M., Weaver J. A. Platelet adhesiveness, plasma fibrinogen and factor 8 levels in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1970 Aug;6(4):436–440. doi: 10.1007/BF01212078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. M., Jones R. L., Koenig R. J., Melvin E. T., Lehrman M. L. Reversible hematologic sequelae of diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Apr;86(4):425–429. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-4-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. M., Jones R. L. Minor hemoglobins, diabetic "control", and diseases of postsynthetic protein modification. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Oct;87(4):489–491. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-4-489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. J., Rouzer C. A., Monnier V. M., Cerami A. Diabetic cataract formation: potential role of glycosylation of lens crystallins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. J., Vlassara H., Abati A., Cerami A. Nonenzymatic glycosylation of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2998–3002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y. Studies of the metabolism and distribution of fibrinogen in healthy men with autologous 125-I-labeled fibrinogen. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):103–111. doi: 10.1172/JCI105314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trivelli L. A., Ranney H. M., Lai H. T. Hemoglobin components in patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1971 Feb 18;284(7):353–357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197102182840703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


