Abstract
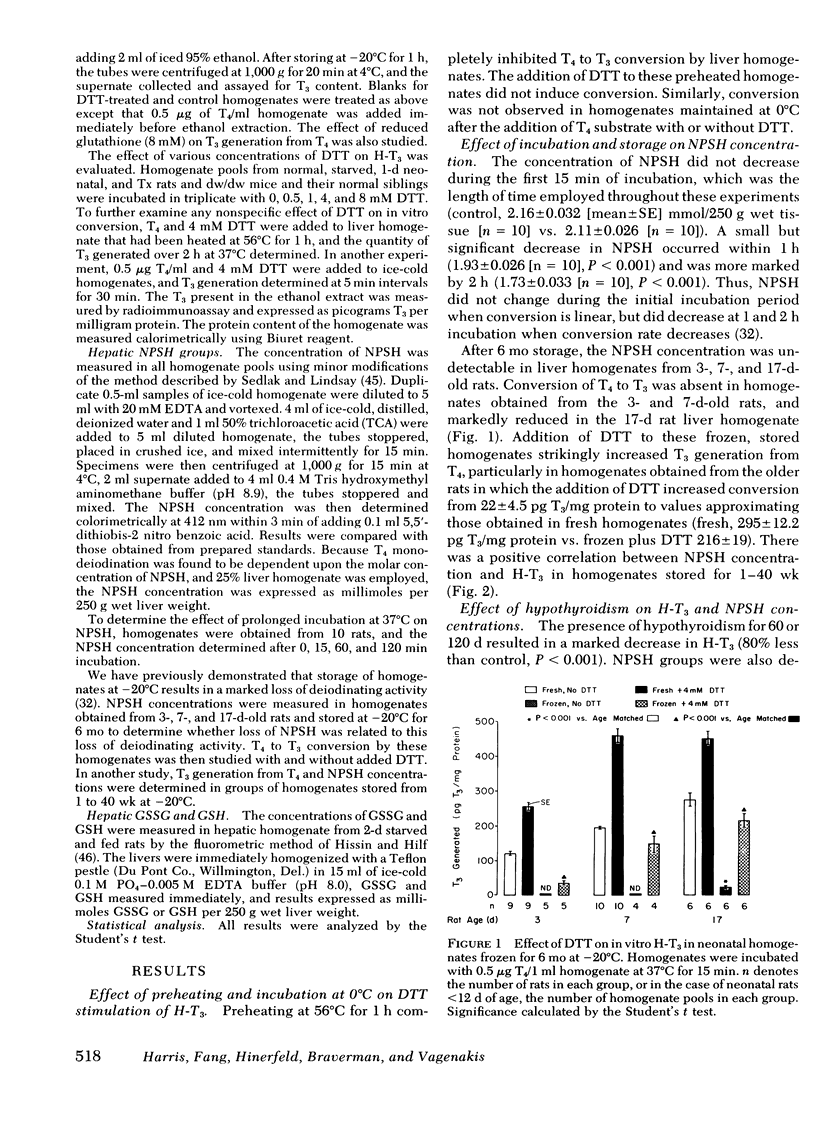
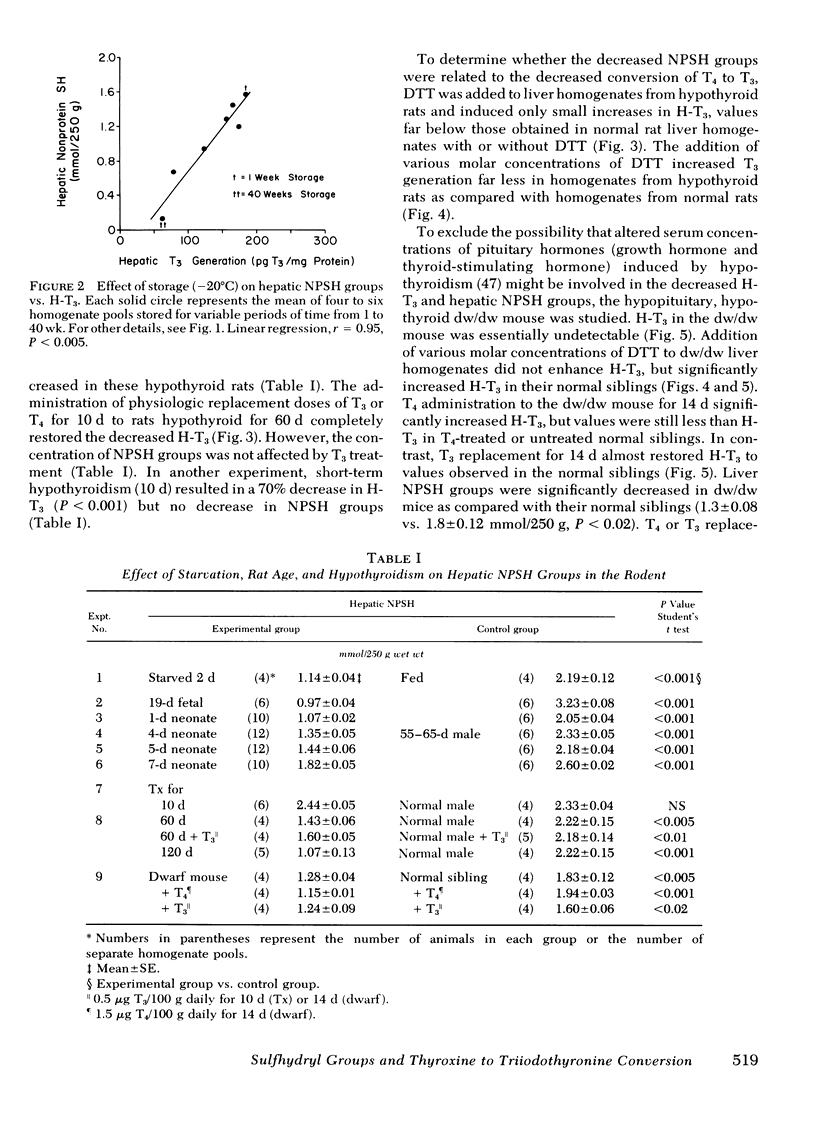
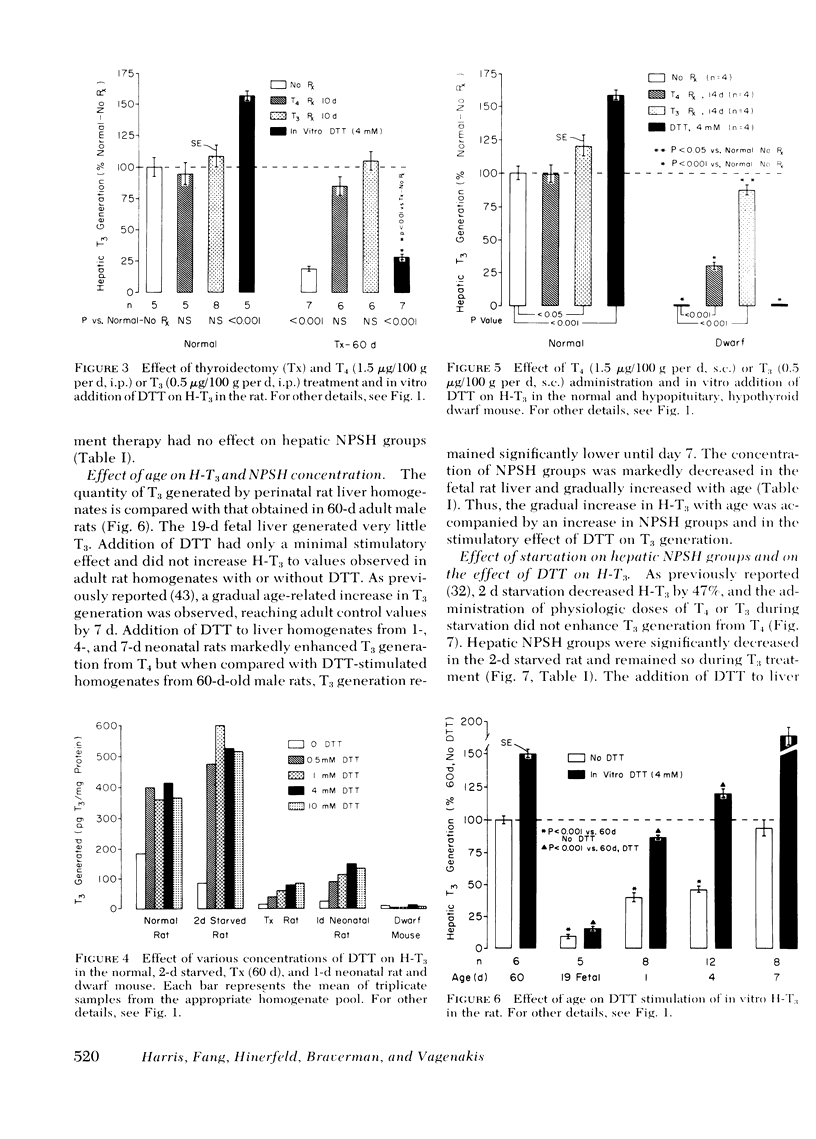
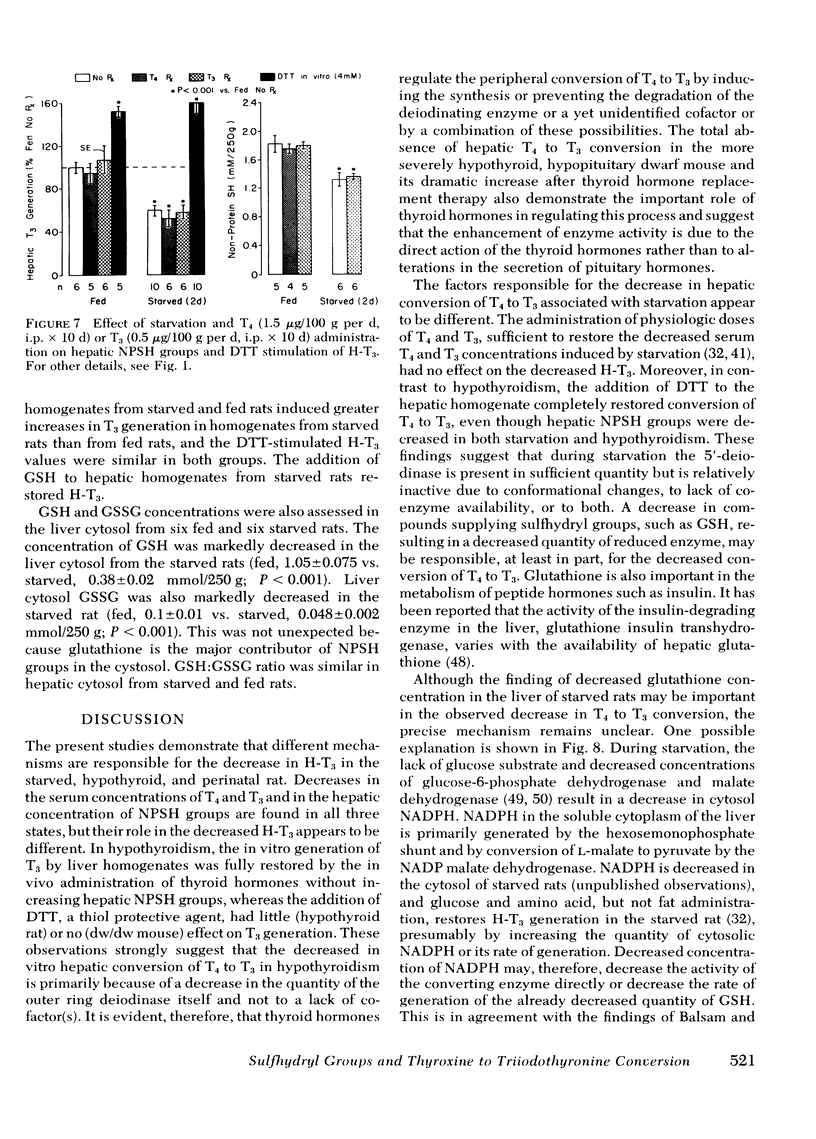
The role of nonprotein sulfhydryl groups (NPSH) in the decreased in vitro hepatic 3′,3,5-triiodothyronine (T3) generation from thyroxine (T4) in the starved, hypothyroid, fetal and 1- to 4-d-old neonatal rat and dwarf mouse was assessed. NPSH were measured in fresh 25% liver homogenates prepared in 0.1 M PO4/10 mM EDTA buffer. As compared with values in adult male rats, NPSH concentration was decreased in the 2-d-starved (1.1±0.04 (mean±SE) vs. 2.2±0.15 mmol/250 g wet liver weight, P < 0.001), fetal (1.0±0.04 vs. 3.2±0.08, P < 0.001), 1-d-old neonatal (1.1±0.03 vs. 2.1±0.04, P < 0.001), and hypothyroid (thyroidectomized 60 d) (1.4±0.06 vs. 2.2±0.15 P < 0.001) rat. NPSH were also decreased in the hypothyroid, hypopituitary dwarf mouse as compared with values in their normal litter mates (1.3±0.03 vs. 2.0±0.2, P < 0.01). Chronic administration of T3 (0.5 μg/100 g body wt per d) markedly increased hepatic T3 generation from T4 in the thyroidectomized rat and in the dwarf mouse to values similar to those observed in the normal rodent without affecting NPSH concentration. In contrast, T3 administration to the starved rat did not alter either hepatic T3 generation from T4 or NPSH. Reduced glutathione concentration was also markedly decreased in the starved rat (fed; 1.05±0.075 mmol/250 g wet tissue vs. starved 0.38±0.02, P < 0.001). Dithiothreitol (DTT), a thiol reducing agent, increased hepatic T3 generation from T4 in the normal adult male rat by 45±5% in six experiments. When compared to DTT-stimulated control homogenates, the addition of DTT completely restored hepatic T3 generation in starved rats, partially restored T3 generation in 1- and 4-d-old neonates, but had little or no effect in the fetal and hypothyroid rat and dwarf mouse. Liver homogenates stored for 6 mo at −20°C lost their capacity to generate T3 from T4. NPSH concentrations in the frozen homogenates decreased progressively with increasing storage and were absent by 6 mo. 5′-Deiodinase activity correlated with NPSH concentration in the stored homogenates (r = 0.95, P < 0.005). Addition of DTT partially restored hepatic T3 generation in the frozen homogenate. It is concluded that NPSH are important for the action of the liver 5′-deiodinase. The decreased hepatic T3 generation in the starved rat is associated with decreased NPSH but not with a decrease in the absolute quantity of 5′-deiodinase because provision of sulfhydryl groups restored hepatic T3 generation to normal. In contrast, the decreased hepatic T3 generation in the adult hypothyroid rodent and in the fetal rat is probably due to a decrease in the enzyme concentration per se. In the 1- and 4-d neonatal rat, the decrease in hepatic T3 generation is secondary to a decrease in NPSH and the deiodinating enzyme.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBRIGHT E. C., LARSON F. C. Metabolism of L-thyroxine by human tissue slices. J Clin Invest. 1959 Nov;38:1899–1903. doi: 10.1172/JCI103967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrams G. M., Larsen P. R. Triiodothyronine and thyroxine in the serum and thyroid glands of iodine-deficient rats. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2522–2531. doi: 10.1172/JCI107443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsam A., Ingbar S. H. The influence of fasting, diabetes, and several pharmacological agents on the pathways of thyroxine metabolism in rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):415–424. doi: 10.1172/JCI109143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez F., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. High incidence of decreased serum triiodothyronine concentration in patients with nonthyroidal disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Jul;41(1):27–40. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. E., Ingbar S. H., Sterling K. Conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) in athyreotic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):855–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI106304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman K. D. Recent developments in thyroid hormone metabolism: interpretation and significance of measurements of reverse T3, 3,3'T2, and thyroglobulin. Metabolism. 1978 May;27(5):615–630. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürgi H., Wimpfheimer C., Burger A., Zaunbauer W., Rösler H., Lemarchand-Béraud T. Changes of circulating thyroxine, triiodothyronine and reverse triiodothyronine after radiographic contrast agents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Dec;43(6):1203–1210. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-6-1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiraseveenuprapund P., Buergi U., Goswami A., Rosenberg I. N. Conversion of L-thyroxine to triiodothyronine in rat kidney homogenate. Endocrinology. 1978 Feb;102(2):612–622. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-2-612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. A study of extrathyroidal conversion of thyroxine (T4) to 3,3',5-triiodothyronine (T3) in vitro. Endocrinology. 1977 Aug;101(2):453–463. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-2-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. An assessment of daily production and significance of thyroidal secretion of 3, 3', 5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3) in man. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):32–40. doi: 10.1172/JCI108456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Chopra U., Smith S. R., Reza M., Solomon D. H. Reciprocal changes in serum concentrations of 3,3',5-triiodothyronine (T3) in systemic illnesses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Dec;41(06):1043–1049. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-6-1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. Sulfhydryl groups and the monodeiodination of thyroxine to triiodothyronine. Science. 1978 Feb 24;199(4331):904–906. doi: 10.1126/science.622575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conversion of thyroxine into tri-iodothyronine by rat liver homogenate. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):489–493. doi: 10.1042/bj1500489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein Z., Hagg S., Vagenakis A. G., Fang S. L., Ransil B., Burger A., Balsam A., Braverman L. E., Ingbar S. H. Effect of starvation on the production and peripheral metabolism of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine in euthyroid obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Oct;47(4):889–893. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-4-889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A., Chopra I. J., Dussault J. H. Extrathyroidal conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in sheep. Endocrinology. 1972 Oct;91(4):1141–1144. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-4-1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. R., Fang S. L., Prosky J., Braverman L. E., Vagenakis A. G. Decreased outer ring monodeiodination of thyroxine and reverse triiodothyronine in the fetal and neonatal rat. Endocrinology. 1978 Dec;103(6):2216–2222. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-6-2216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. R., Fang S. L., Vagenakis A. G., Braverman L. E. Effect of starvation, nutriment replacement, and hypothyroidism on in vitro hepatic T4 to T3 conversion in the rat. Metabolism. 1978 Nov;27(11):1680–1690. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90290-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hervas F., Morreale de Escobar G., Escobar Del Rey F. Rapid effects of single small doses of L-thyroxine and triiodo-L-thyronine on growth hormone, as studied in the rat by radioimmunoassy. Endocrinology. 1975 Jul;97(1):91–101. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesch R. D., Brunner G., Söling H. D. Conversion of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) and the subcellular localisation of the converting enzyme. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Mar 10;59(2):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hissin P. J., Hilf R. A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jul;74(1):214–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90326-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffken B., Ködding R., Von Zur Mühlen A., Hehrmann T., Jüppner H., Hesch R. D. Regulation of thyroid hormone metabolism in rat liver fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 13;539(1):114–124. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M., Utiger R. D. Iodothyronine metabolism in liver and kidney homogenates from hyperthyroid and hypothyroid rats. Endocrinology. 1978 Jul;103(1):156–161. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-1-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M., Utiger R. D. Iodothyronine metabolism in rat liver homogenates. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):459–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI108957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Green W. L. Degradation of thyroid hormones by phagocytosing human leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):60–72. doi: 10.1172/JCI107174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSON F. C., ALBRIGHT E. C. Inhibition of L-thyroxine monodeiodination by thyroxine analogs. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jul;40:1132–1138. doi: 10.1172/JCI104342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSON F. C., TOMITA K., ALBRIGHT E. C. The deiodination of thyroxine to triiodothyronine by kidney slices of rats with varying thyroid function. Endocrinology. 1955 Sep;57(3):338–344. doi: 10.1210/endo-57-3-338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nace C. S., Szepesi B. Dietary fatty acids on the control of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and malic enzyme in the starved-refed rat. J Nutr. 1976 Feb;106(2):285–291. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Pittman C. S., Chambers J. B., Jr, Buck M. W., Shimizu T. Reduced peripheral conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):643–652. doi: 10.1172/JCI108134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Propylthiouracil inhibits the conversion of L-thyroxine to L-triiodothyronine. An explanation of the antithyroxine effect of propylthiouracil and evidence supporting the concept that triiodothyronine is the active thyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2493–2497. doi: 10.1172/JCI107063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman C. S., Chambers J. B., Jr, Read V. H. The extrathyroidal conversion rate of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1187–1196. doi: 10.1172/JCI106596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnay G. I., O'Brian J. T., Bush J., Vagenakis A. G., Azizi F., Arky R. A., Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E. The effect of starvation on the concentration and binding of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in serum and on the response to TRH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Jul;39(1):191–194. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz J. L., Hercker E. S. Thyroxine: convesion to triiodothyronine by isolated perfused rat heart. Science. 1971 Sep 24;173(4003):1242–1243. doi: 10.1126/science.173.4003.1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Matalon R., Bigazzi M. Metabolism of L-thyroxine (T4) and L-triiodothyronine (T3) by human fibroblasts in tissue culture: evidence for cellular binding proteins and conversion of T4 to T3. Endocrinology. 1972 Oct;91(4):934–947. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-4-934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin S., Bollinger J., Nejad I., Sullivan P. Tissue thyroid hormone concentration of rat and man determined by radiommunoassay: biologic significance. Mt Sinai J Med. 1973 May-Jun;40(3):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saberi M., Sterling F. H., Utiger R. D. Reduction in extrathyroidal triiodothyronine production by propylthiouracil in man. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):218–223. doi: 10.1172/JCI107924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel M., Utiger R. D. Thyroidal and peripheral production of thyroid hormones. Review of recent findings and their clinical implications. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Dec;87(6):760–768. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-6-760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Quantitation of extrathyroidal conversion of L-thyroxine to 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI106584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedlak J., Lindsay R. H. Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman's reagent. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):192–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A., Saldanha V. F. Conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine by cultured human cells. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1000–1001. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szepesi B., Berdanier C. D., Diachenko S. K., Moser P. B. Effect of repeated starvation on serum insulin level and the enzyme overshoot in liver. Can J Biochem. 1971 Mar;49(3):393–395. doi: 10.1139/o71-057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vagenakis A. G., Burger A., Portnary G. I., Rudolph M., O'Brian J. R., Azizi F., Arky R. A., Nicod P., Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E. Diversion of peripheral thyroxine metabolism from activating to inactivating pathways during complete fasting. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Jul;41(1):191–194. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vagenakis A. G., Portnay G. I., O'Brian J. T., Rudolph M., Arky R. A., Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E. Effect of starvation on the production and metabolism of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in euthyroid obese patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Dec;45(6):1305–1309. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-6-1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser T. J., Does-Tobé I., Docter R., Hennemann G. Subcellular localization of a rat liver enzyme converting thyroxine into tri-iodothyronine and possible involvement of essential thiol groups. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):479–482. doi: 10.1042/bj1570479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woeber K. A., Ingbar S. H. Metabolism of L-thyroxine by phagocytosing human leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):1796–1803. doi: 10.1172/JCI107361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



