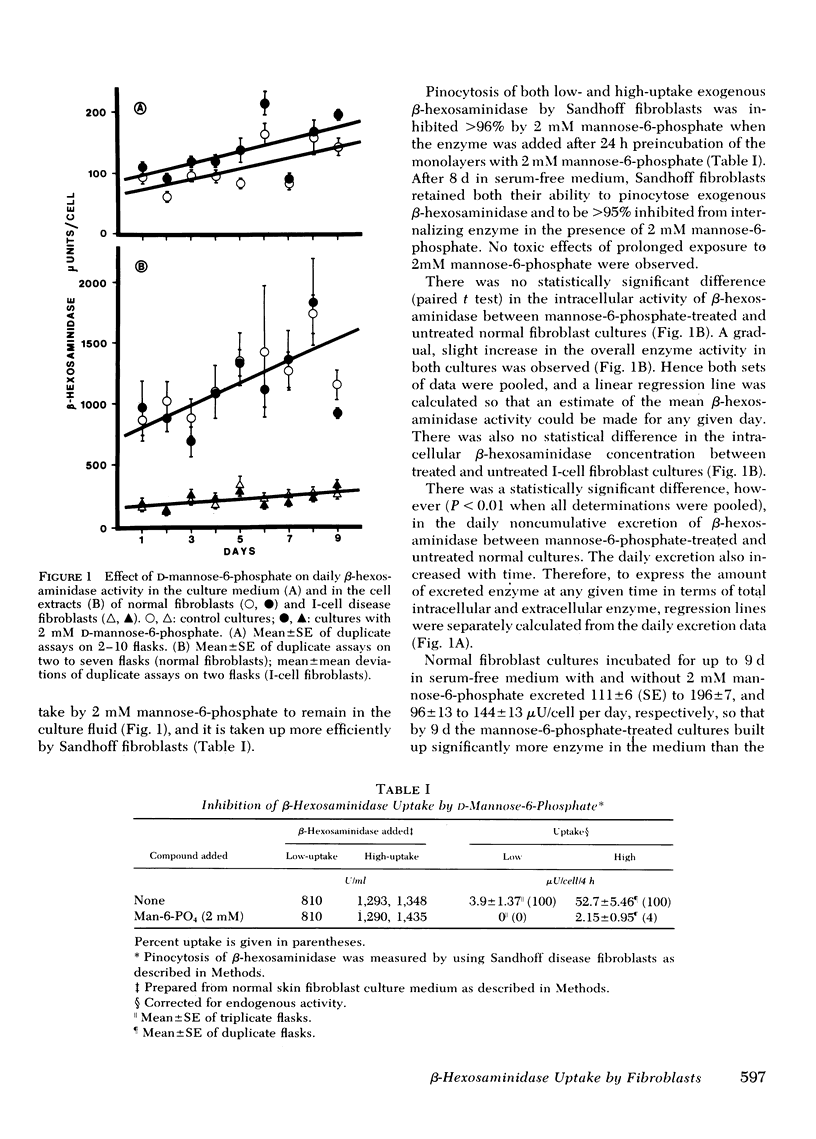
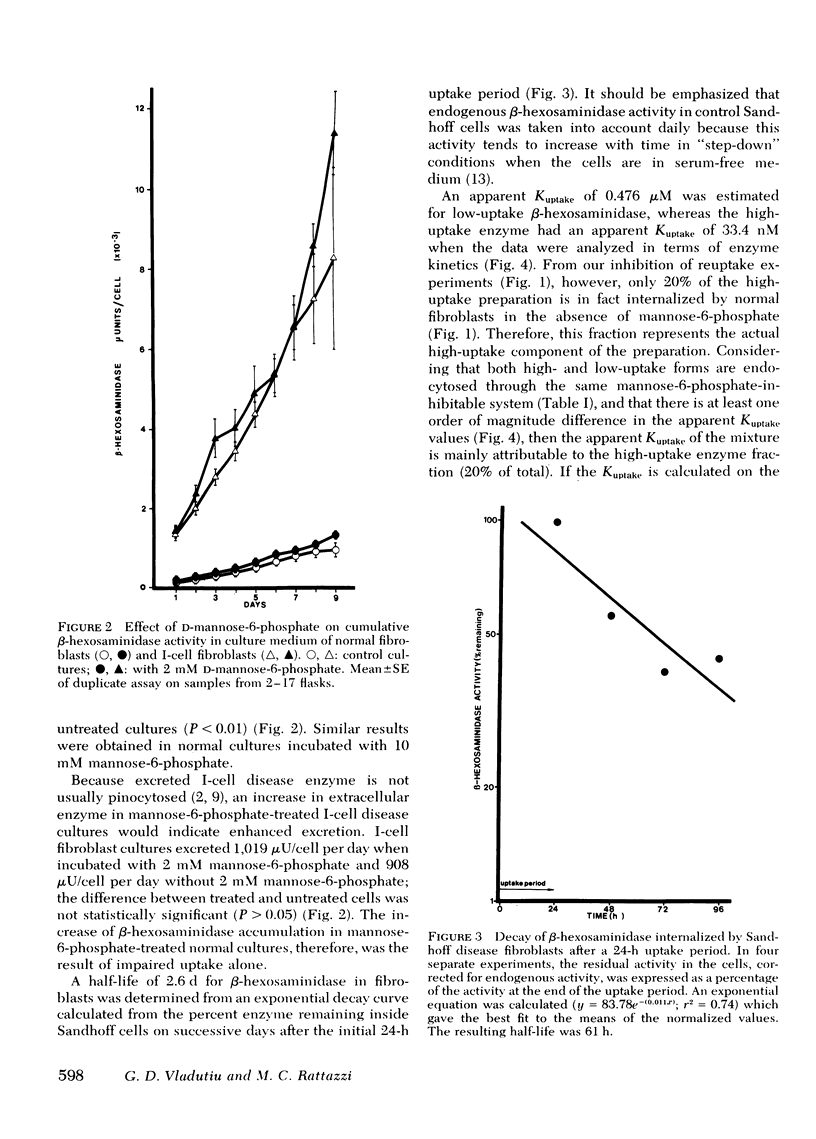
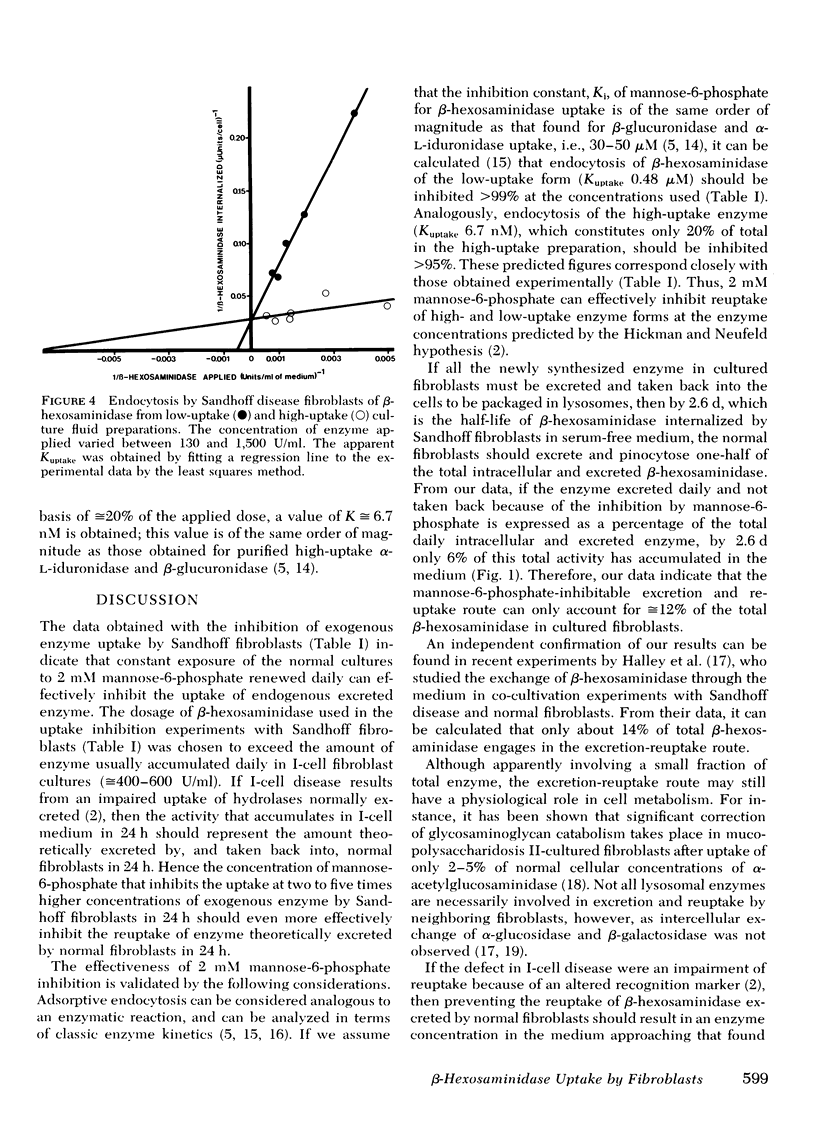
Abstract
It has been proposed that in cultured fibroblasts the final packaging of enzymes in lysosomes requires excretion followed by pinocytosis by neighboring cells via a carbohydrate-specific receptor mechanism. It has also been proposed that the abnormally high activity of lysosomal enzymes in the medium of cultured fibroblasts from patients with I-cell disease (mucolipidosis II) results from an altered carbohydrate recognition residue on the enzymes which prevents reuptake into the cells. With β-hexosaminidase as a marker, and competitive inhibition of uptake by 2 mM mannose-6-phosphate, we have determined that only 12% of the total (intra- and extracellular) β-hexosaminidase in normal fibroblasts is channeled through the excretion-reuptake route. After 9 d of exposure to mannose-6-phosphate, normal fibroblast cultures accumulated in the medium only a fraction of the enzyme excreted by I-cell disease fibroblasts in the same period. Furthermore, this minimal loss of enzyme to the medium did not result in a decrease of intracellular enzyme activity. Finally, if the defect in I-cell disease were only because of an impairment of a reuptake mechanism that involves only 12% of the total enzyme, then 88% of the newly synthesized enzyme should be retained by I-cell fibroblasts, resulting in intracellular activity three to nine times higher than that which is observed. These data are consistent with our previous proposal that excessive lysosomal enzyme activity in the medium of I-cell disease fibroblasts results from preferential exocytosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cantz M., Kresse H. Sandhoff disease: defective glycosaminoglycan catabolism in cultured fibroblasts and its correction by beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 16;47(3):581–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Arnon R. Chemical characterization and subunit structure of human N-acetylhexosaminidases A and B. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 10;15(16):3484–3493. doi: 10.1021/bi00661a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser J. H., Roozen K. J., Brot F. E., Sly W. S. Multiple isoelectric and recognition forms of human beta-glucuronidase activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Feb;166(2):536–542. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halley D. J., de Wit-Verbeek H. A., Reuser A. J., Galjaard H. The distribution of hydrolytic enzyme activities in human fibroblast cultures and their intercellular transfer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jun 29;82(4):1176–1182. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90310-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Neufeld E. F. A hypothesis for I-cell disease: defective hydrolases that do not enter lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Shapiro L. J., Neufeld E. F. A recognition marker required for uptake of a lysosomal enzyme by cultured fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80356-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A., Achord D. T., Sly W. S. Phosphohexosyl components of a lysosomal enzyme are recognized by pinocytosis receptors on human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2026–2030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A., Fischer D., Achord D., Sly W. Phosphohexosyl recognition is a general characteristic of pinocytosis of lysosomal glycosidases by human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1088–1093. doi: 10.1172/JCI108860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A., Fischer D., Sly W. S. Correlation of structural features of phosphomannans with their ability to inhibit pinocytosis of human beta-glucuronidase by human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):647–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. Modulation of lysosomal enzyme levels in cultured cells: effects of alterations in cell density, balanced growth, and endocytosis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Apr 30;187(2):376–386. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. B. Cellular transport of lysosomal enzymes: an alternative hypothesis. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):281–282. doi: 10.1042/bj1640281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann S. J. Kinetics of phagocytosis. II. Analysis of in vivo clearance with demonstration of competitive inhibition between similar and dissimilar foreign particles. Lab Invest. 1974 Aug;31(2):161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Miller A. L., Loverde A. W., Veath M. L. Sanfilippo disease type B: enzyme replacement and metabolic correction in cultured fibroblasts. Science. 1973 Aug 24;181(4101):753–755. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4101.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuser A., Halley D., de Wit E., Hoogeveen A., van der Kamp M., Mulder M., Galjaard H. Intercellular exchange of lysosomal enzymes: enzyme assays in single human fibroblasts after co-cultivation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 22;69(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90523-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando G. N., Neufeld E. F. Recognition and receptor-mediated uptake of a lysosomal enzyme, alpha-l-iduronidase, by cultured human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):619–627. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K., Mersmann G., Weber E., Von Figura K. Evidence for lysosomal enzyme recognition by human fibroblasts via a phosphorylated carbohydrate moiety. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):643–650. doi: 10.1042/bj1700643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vladutiu G. D., Carmody P. J., Rattazzi M. C. Immunoaffinity chromatography of human beta-hexosaminidase A. Prep Biochem. 1975;5(2):147–159. doi: 10.1080/00327487508061567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vladutiu G. D., Rattazzi M. C. Abnormal lysosomal hydrolases excreted by cultured fibroblasts in I-cell disease (mucolipidosis II). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):956–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90768-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vladutiu G. D., Rattazzi M. C. Cell disease: desialylation of beta-hexosaminidase and its effect on uptake by fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 13;539(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesmann U. N., Lightbody J., Vassella F., Herschkowitz N. N. Multiple lysosomal deficiency due to enzyme leakage? N Engl J Med. 1971 Jan 14;284(2):109–110. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197101142840221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


