Abstract
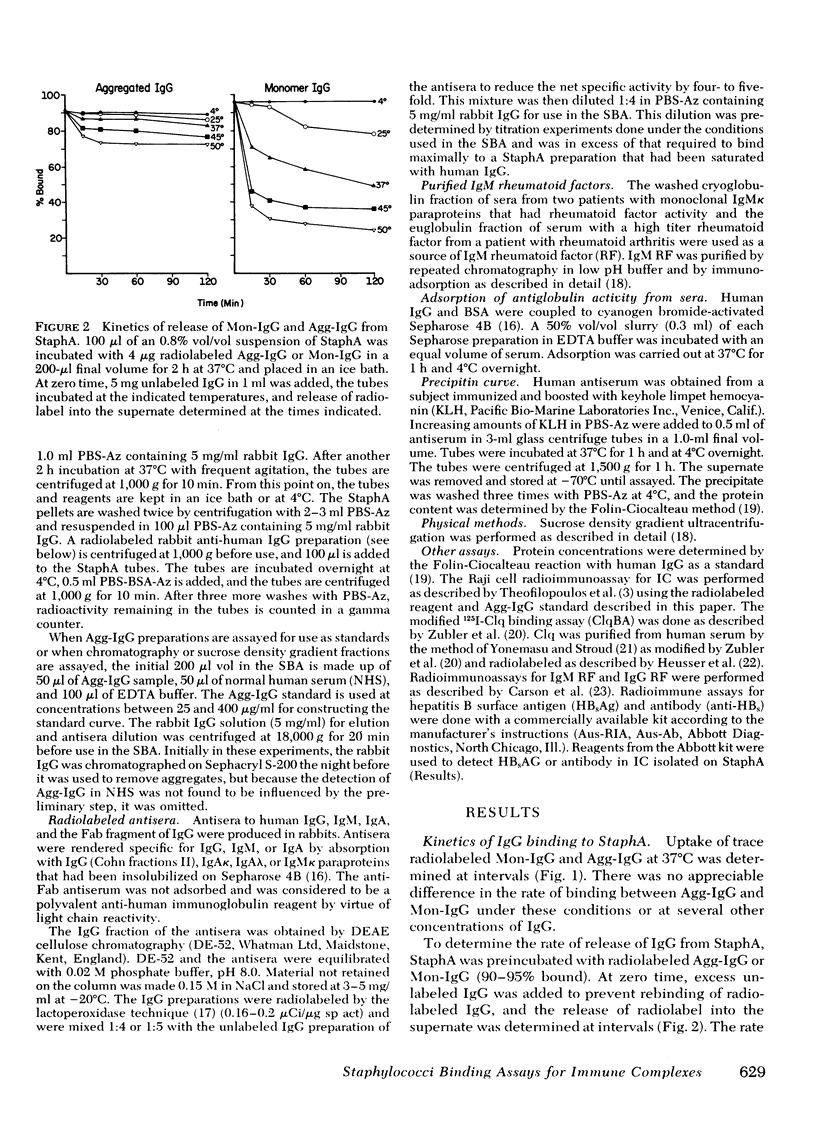
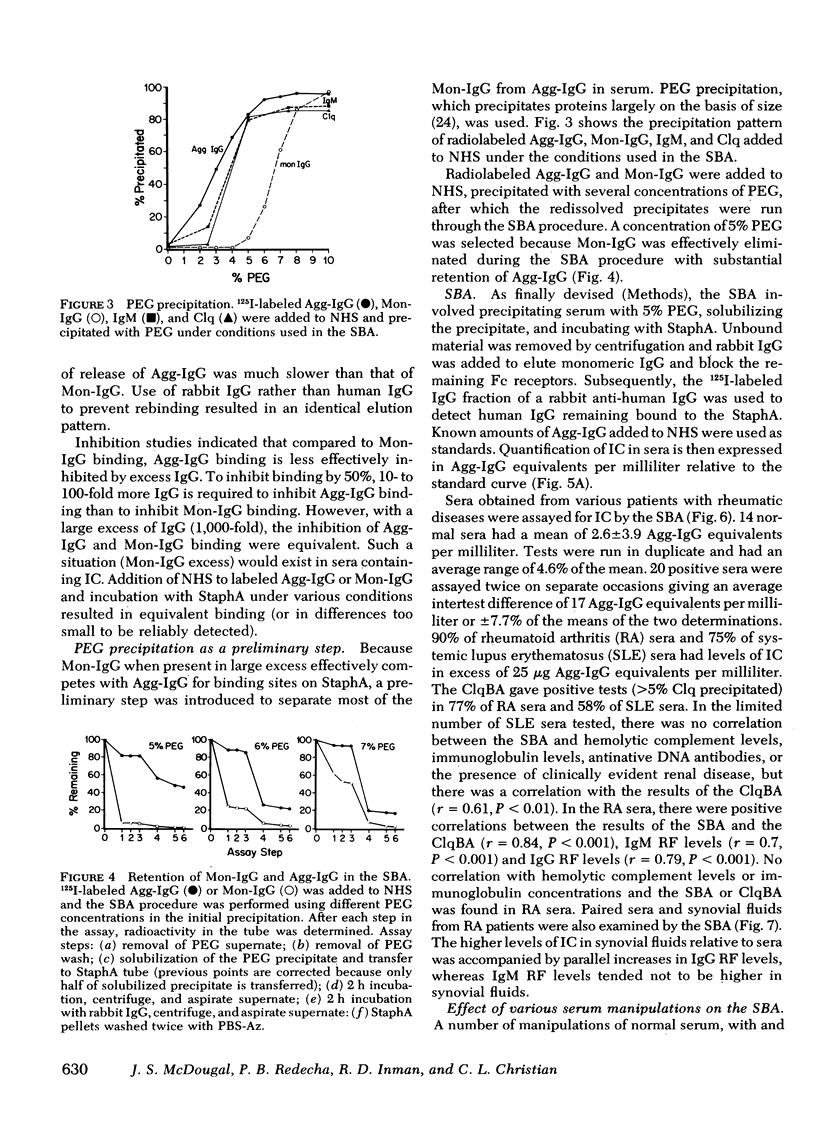
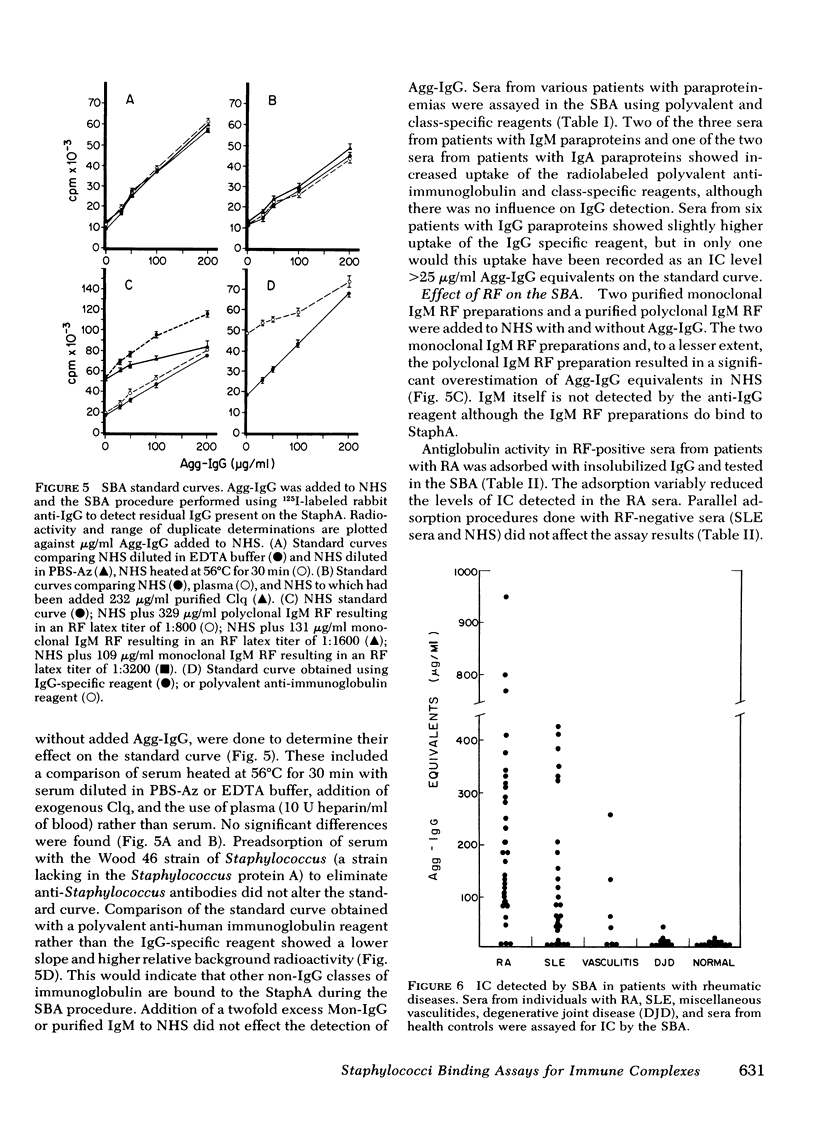
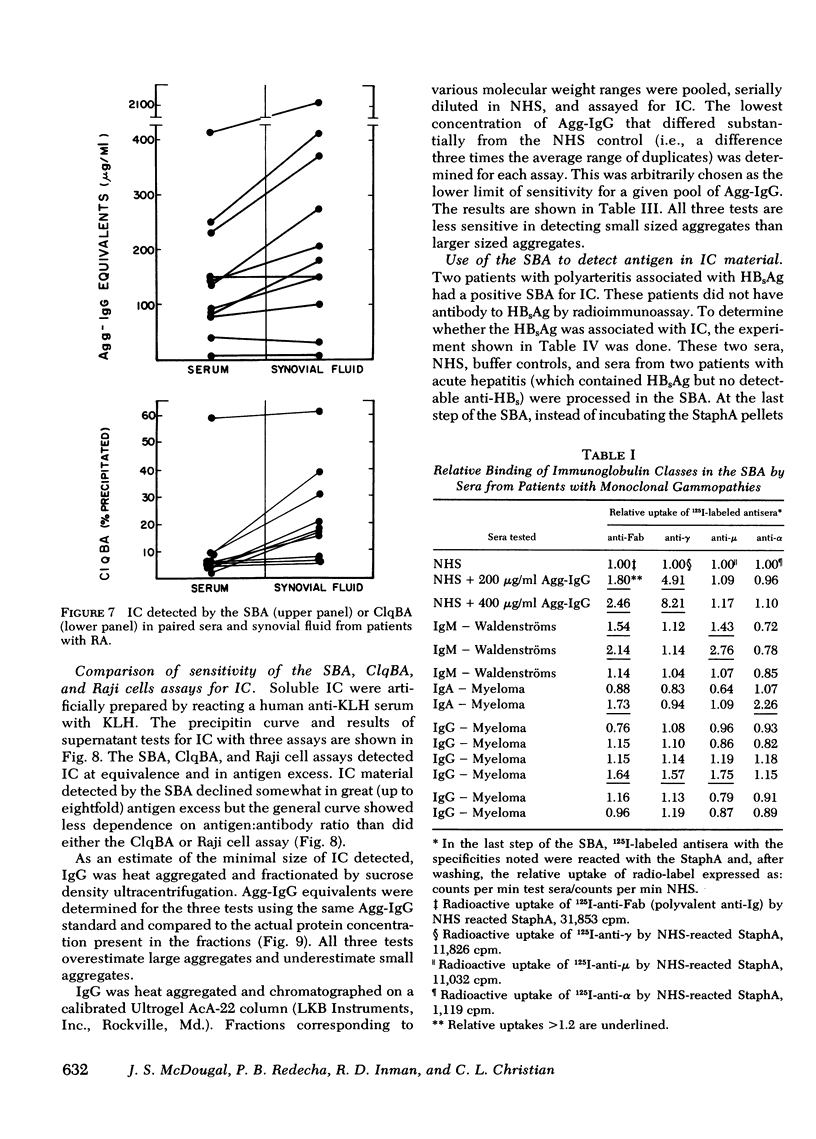
Using the Cowan I strain of Staphylococcus aureus, we compared the binding properties of human monomeric immunoglobulin (Ig)G and oligomeric or complexed IgG. Heat-aggregated IgG served as a model for complexed IgG and heat-killed, formalin-fixed S. aureus (StaphA) as a cellular receptor for IgG, in determining the parameters for oligomeric and monomeric binding. Because of its capacity for multipoint attachment, complexed IgG binding was favored over monomeric IgG binding, and this preferential binding was demonstrated kinetically in equivalent forward rates of binding but in a much slower rate of release from StaphA receptors. From binding studies, we determined which conditions maximize complexes IgG binding and minimized monomeric IgG binding and applied them to the development of an assay for aggregated IgG and immune complexes in human sera. The StaphA binding assay that was devised is quantitative, sensitive, and not complement dependent. It is relatively unaffected by factors such as heparin, complement fixation, native antibodies, and immunoglobulin concentrations, but is affected by the presence of rheumatoid factors. It compares favorably with two other complement-dependent assays of immune complexes, the 125I-Clq binding assay and the Raji cell assay, in terms of sensitivity and the size of immune complexes detected. Studies on the potential of the assay for detecting, isolating, and characterizing immune complexes in biological fluids are presented.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Mannik M. The macrophage receptor for IgG: number and affinity of binding sites. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1455–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Lawrance S., Catalano M. A., Vaughan J. H., Abraham G. Radioimmunoassay of IgG and IgM rheumatoid factors reacting with human IgG. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):295–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell C., Sogaard H., Svehag S. E. Detection of IgG aggregates or immune complexes using solid-phase C1q and protein A-rich Staphylococcus aureus as an indicator system. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(7):673–680. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02675.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grov A., Oeding P., Myklestad B., Aasen J. Reactions of staphylococcal antigens with normal sera, gamma G-globulins, and gamma G-globulin fragments of various species origin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1970;78(1):106–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1970.tb04275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg T. In vitro cytotoxicity of human lymphocytes for sensitized chicken erythrocytes is inhibited by sera from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(4):329–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb03298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Fölling I. Recognition of two distinct groups of human IgM and IgA based on different binding to staphylococci. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(4):471–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harisdangkul V., McDougal J. S., Knapp M., Christian C. L. Naturally occurring low molecular weight IgM in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and macroglobulinemia. I. Purification and immunologic studies. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):216–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusser C., Boesman M., Nordin J. H., Isliker H. Effect of chemical and enzymatic radioiodination on in vitro human Clq activities. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):820–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällgren R., Wide L. Detection of circulating IgG aggregates and immune complexes using 125I protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Aug;35(4):306–313. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.4.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Differences in anti-protein A activity among IgG subgroups. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):828–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind I., Harboe M., Folling I. Protein A reactivity of two distinct groups of human monoclonal IgM. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(8):843–848. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb03726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myllylä G. Aggregation of human blood platelets by immune complexes in the sedimentation pattern test. Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1973;19:1–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onyewotu I. I., Holborow E. J., Johnson G. D. Detection and radioassay of soluble circulating immune complexes using guinea pig peritoneal exudate cells. Nature. 1974 Mar 8;248(5444):156–159. doi: 10.1038/248156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Hurwitz E. Binding of affinity cross-linked oligomers of IgG to cells bearing Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1338–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. The Raji cell radioimmune assay for detecting immune complexes in human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):169–182. doi: 10.1172/JCI108257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemasu K., Stroud R. M. Clq: rapid purification method for preparation of monospecific antisera and for biochemical studies. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):304–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



