Abstract
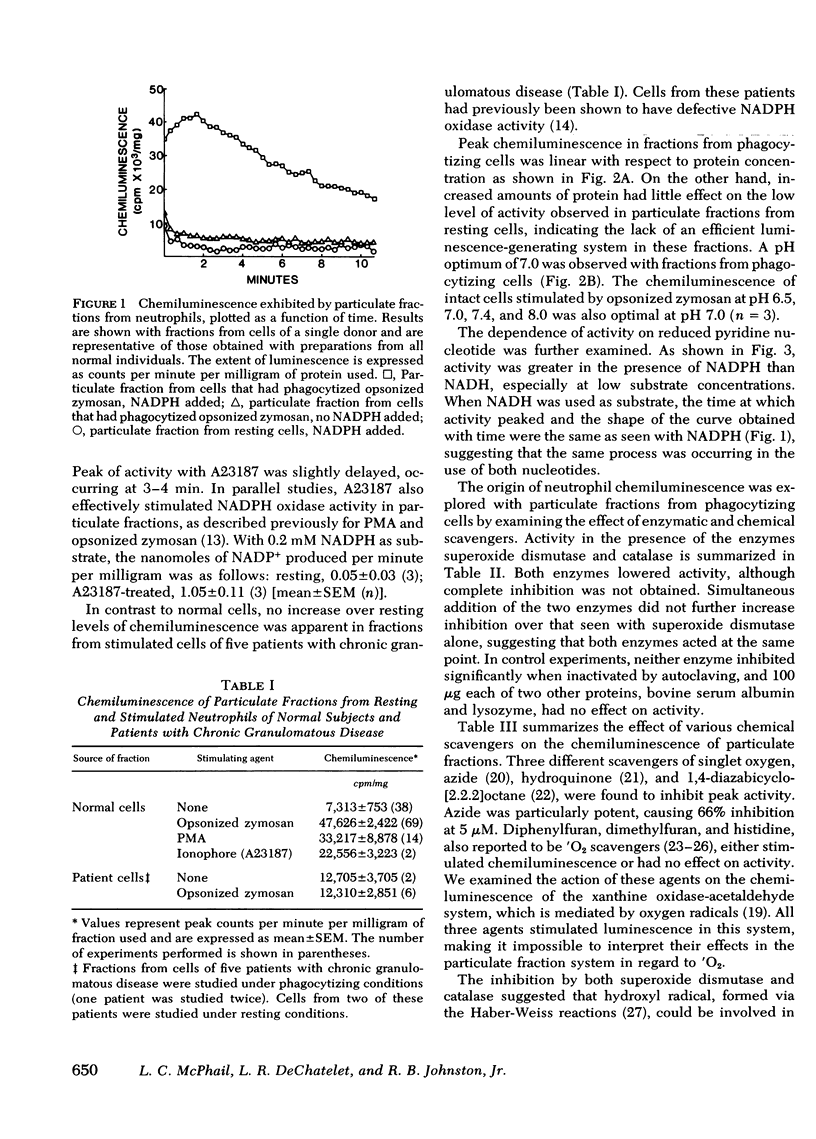
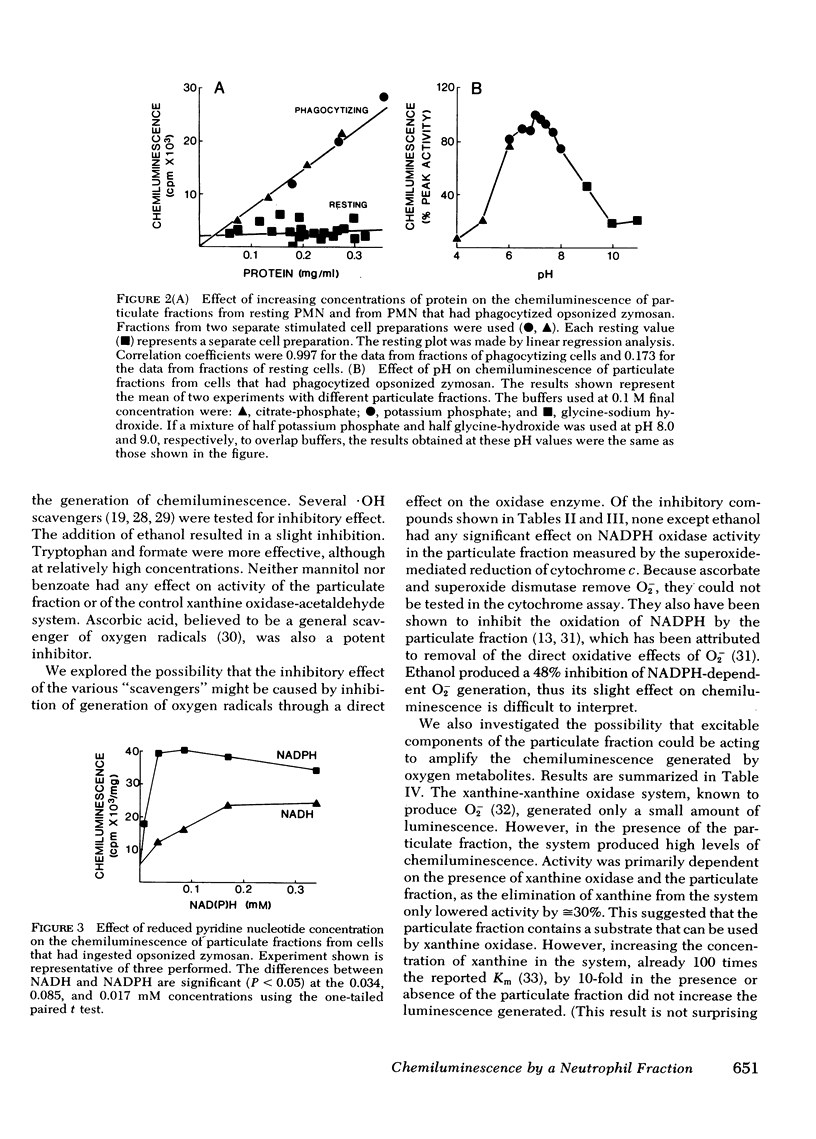
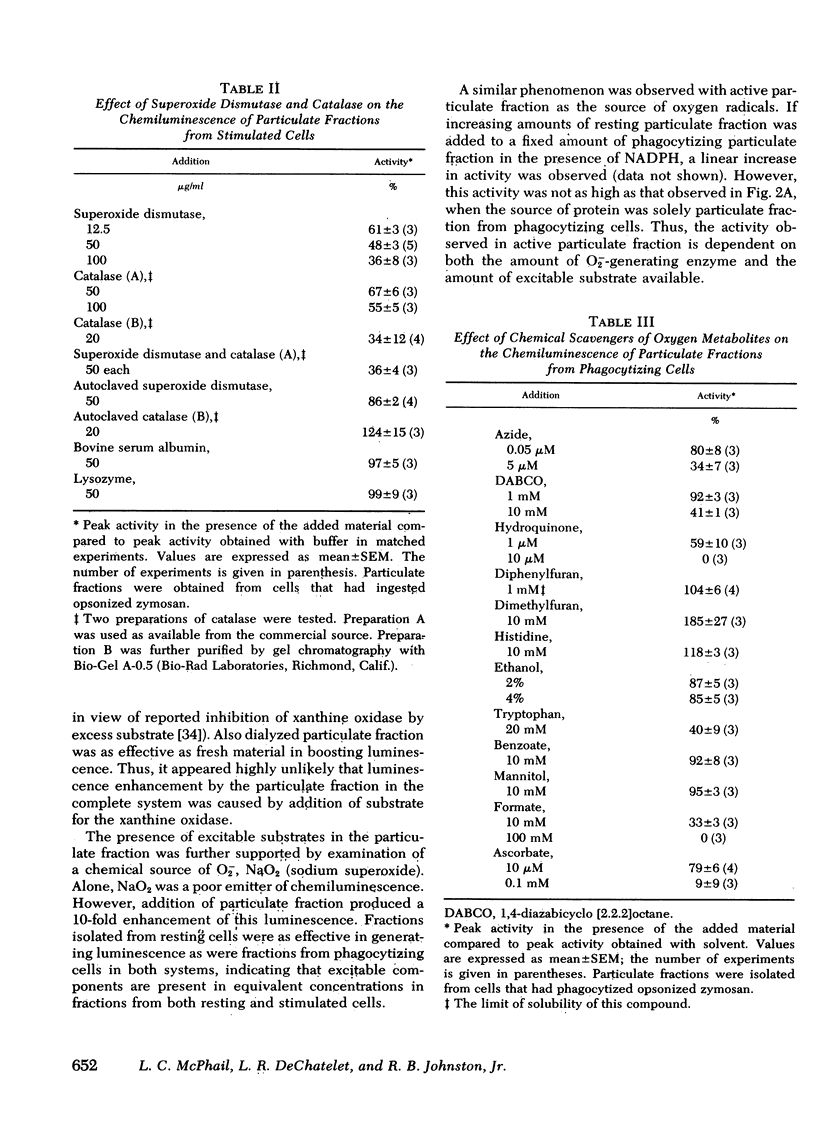
A particulate fraction isolated from human neutrophils by homogenization, then centrifugation at 27,000 g, was demonstrated to generate chemiluminescence. This luminescence required the addition of reduced pyridine nucleotide and was very low in fractions from resting normal cells. Stimulation of neutrophils with opsonized zymosan, phorbol myristate acetate, or ionophore A23187 resulted in marked enhancement of the chemiluminescence measured in subsequently isolated particulate fractions. Stimulation did not boost the luminescence produced by fractions from cells of patients with chronic granulomatous disease. The chemiluminescence of particulate fractions from stimulated neutrophils was linear with increasing protein concentration, had a pH optimum of 7.0, and was higher with NADPH as substrate than with NADH. These results confirm previous studies suggesting that the enzyme system responsible for the respiratory burst in neutrophils is present in this fraction. The particulate fraction was used to examine the nature and origin of neutrophil luminescence by investigating the effect on this phenomenon of certain chemical and enzymatic scavengers of oxygen metabolites. Results suggest that the energy responsible for the luminescence of particulate fractions and, presumably, the intact cell, is derived from more than one oxygen species and that luminescence is a product of the interaction of these species and excitable substrates within the cell.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Stjernholm R. L., Steele R. H. Evidence for the generation of an electronic excitation state(s) in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and its participation in bactericidal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):679–684. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen B. R., Brendzel A. M., Lint T. F. Chemiluminescence spectra of human myeloperoxidase and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):62–66. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.62-66.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arneson R. M. Substrate-induced chemiluminescence of xanthine oxidase and aldehyde oxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Feb;136(2):352–360. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Curnutte J. T., McMurrich B. J. The particulate superoxide-forming system from human neutrophils. Properties of the system and further evidence supporting its participation in the respiratory burst. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):989–996. doi: 10.1172/JCI108553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Nathan D. G., Karnovsky M. L. Correction of metabolic deficiencies in the leukocytes of patients with chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):865–870. doi: 10.1172/JCI106305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheson B. D., Christensen R. L., Sperling R., Kohler B. E., Babior B. M. The origin of the chemiluminescence of phagocytosing granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):789–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI108530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., McPhail L. C., Mullikin D., McCall C. E. An isotopic assay for NADPH oxidase activity and some characteristics of the enzyme from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI107981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIDOVICH I., HANDLER P. Xanthine oxidase. III. Sulfite oxidation as an ultra sensitive assay. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1578–1580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENLEE L., FRIDOVICH I., HANDLER P. Chemiluminescence induced by operation of iron-flavoproteins. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:779–783. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFSTEE B. H. On the mechanism of inhibition of xanthine oxidase by the substrate xanthine. J Biol Chem. 1955 Sep;216(1):235–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held A. M., Hurst J. K. Ambiguity associated with use of singlet oxygen trapping agents in myeloperoxidase-catalyzed oxidations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 14;81(3):878–885. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson E. K., Fridovich I. The mechanism of the activity-dependent luminescence of xanthine oxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):202–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn D. C., Lehrer R. I. NADPH oxidase deficiency in X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):707–713. doi: 10.1172/JCI107980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Keele B. B., Jr, Misra H. P., Lehmeyer J. E., Webb L. S., Baehner R. L., RaJagopalan K. V. The role of superoxide anion generation in phagocytic bactericidal activity. Studies with normal and chronic granulomatous disease leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1357–1372. doi: 10.1172/JCI108055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg E. W., 3rd, Fridovich I. Superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and singlet oxygen in lipid peroxidation by a xanthine oxidase system. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8812–8817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. M., Lai E. K., McCay P. B. Singlet oxygen production associated with enzyme-catalyzed lipid peroxidation in liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6496–6502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Antimicrobial mechanisms in neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Semin Hematol. 1975 Apr;12(2):117–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinsky N. I. Singlet excited oxygen as a mediator of the antibacterial action of leukocytes. Science. 1974 Oct 25;186(4161):363–365. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4161.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson I. B., Etheridge R. D., Kratowich N. R., Lee J. The quenching of singlet oxygen by amino acids and proteins. Photochem Photobiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):165–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1975.tb06647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Day E. D., Jr Superoxide-dependent production of hydroxyl radical catalyzed by iron-EDTA complex. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., DeChatelet L. R., Shirley P. S. A comparison between the NADPH oxidase activity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and the oxidase activity of several purified peroxidases. Biochem Med. 1977 Oct;18(2):210–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(77)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., DeChatelet L. R., Shirley P. S. Further characterization of NADPH oxidase activity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):774–780. doi: 10.1172/JCI108528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., DeChatelet L. R., Shirley P. S., Wilfert C., Johnston R. B., Jr, McCall C. E. Deficiency of NADPH oxidase activity in chronic granulomatous disease. J Pediatr. 1977 Feb;90(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80632-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson R., Merkel P. B., Kearns D. R. Unambiguous evidence for the participation of singlet oxygen ( 1 ) in photodynamic oxidation of amino acids. Photochem Photobiol. 1972 Aug;16(2):117–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1972.tb07343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikimi M. Oxidation of ascorbic acid with superoxide anion generated by the xanthine-xanthine oxidase system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Mar 17;63(2):463–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90710-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patriarca P., Dri P., Kakinuma K., Tedesco F., Rossi F. Studies on the mechanism of metabolic stimulation in polymorphonuclear leucocytes during phagocytosis. I. Evidence for superoxide anion involvement in the oxidation of NADPH2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 7;385(2):380–386. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Formation of singlet oxygen by the myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4803–4810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjernholm R. L., Allen R. C., Steele R. H., Waring W. W., Harris J. A. Impaired chemiluminescence during phagocytosis of opsonized bacteria. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):313–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.313-314.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I., Babior B. M. Evidence for hydroxyl radical production by human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):374–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI108786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb L. S., Keele B. B., Jr, Johnston R. B., Jr Inhibition of phagocytosis-associated chemiluminescence by superoxide dismutase. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1051–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1051-1056.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Rustagi P. K., LoBuglio A. F. Human granulocyte generation of hydroxyl radical. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):316–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



