Abstract
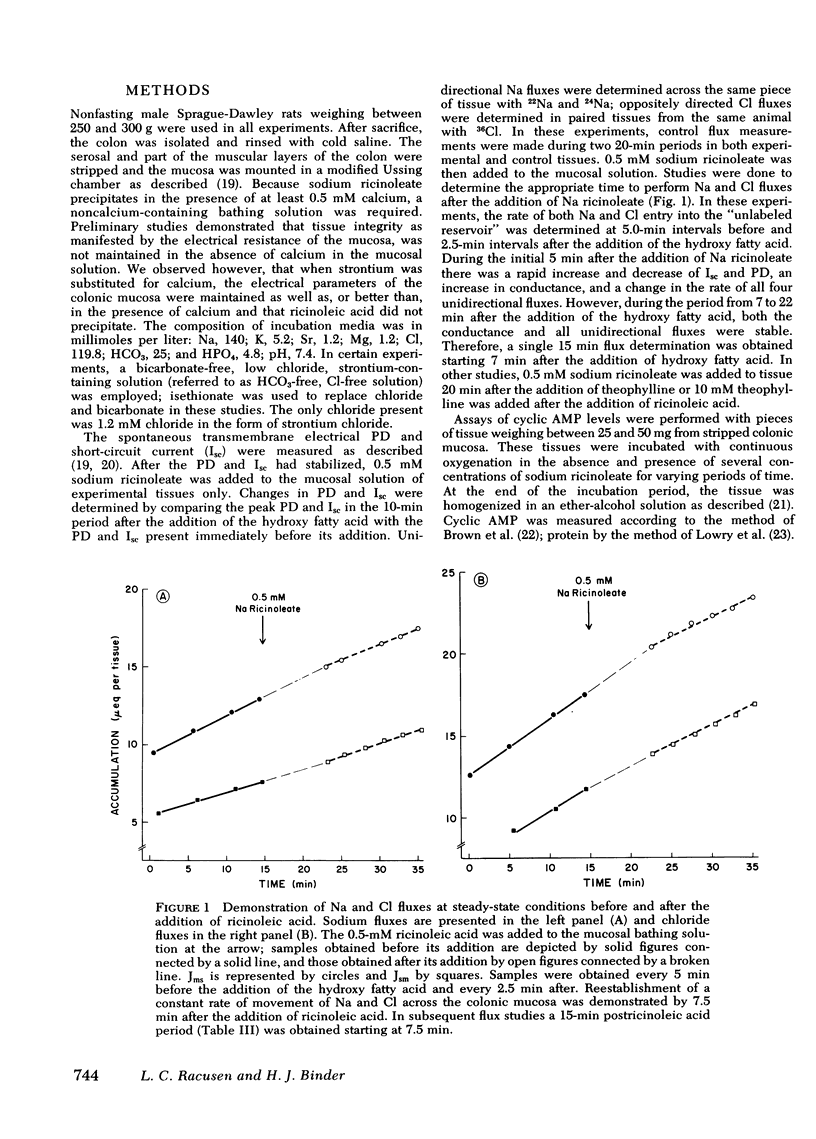
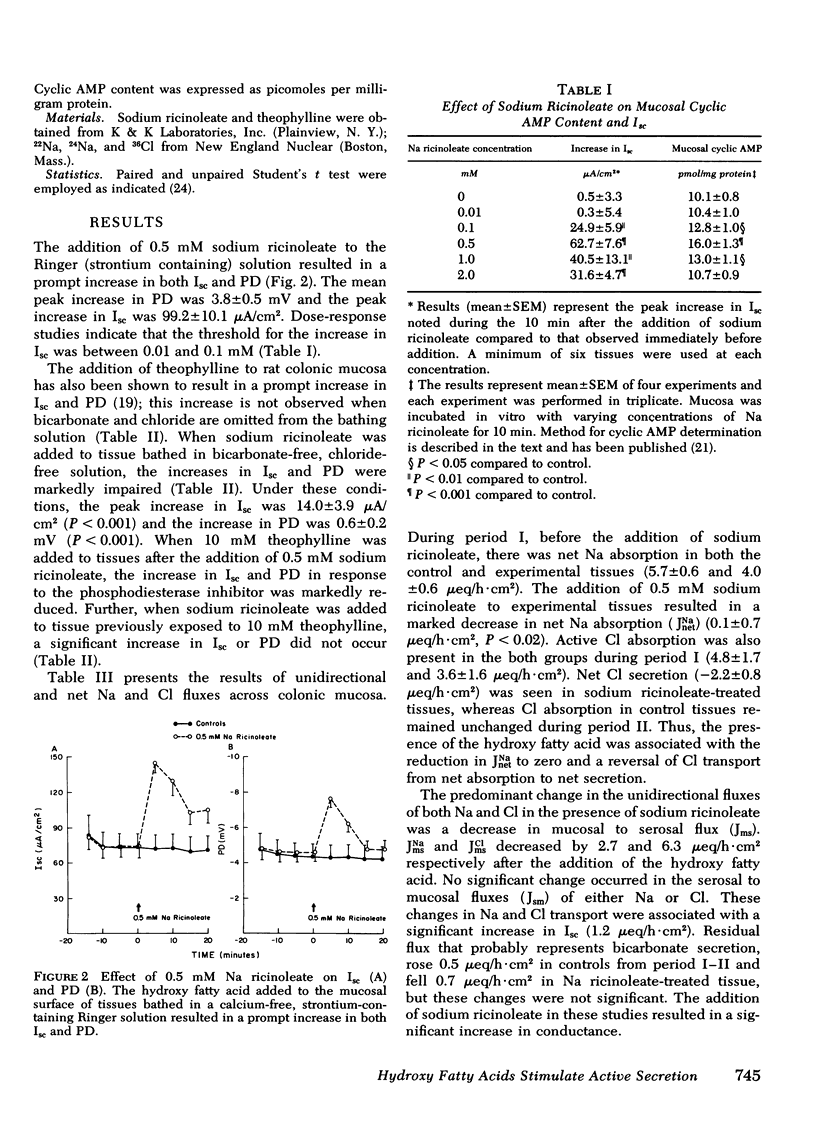
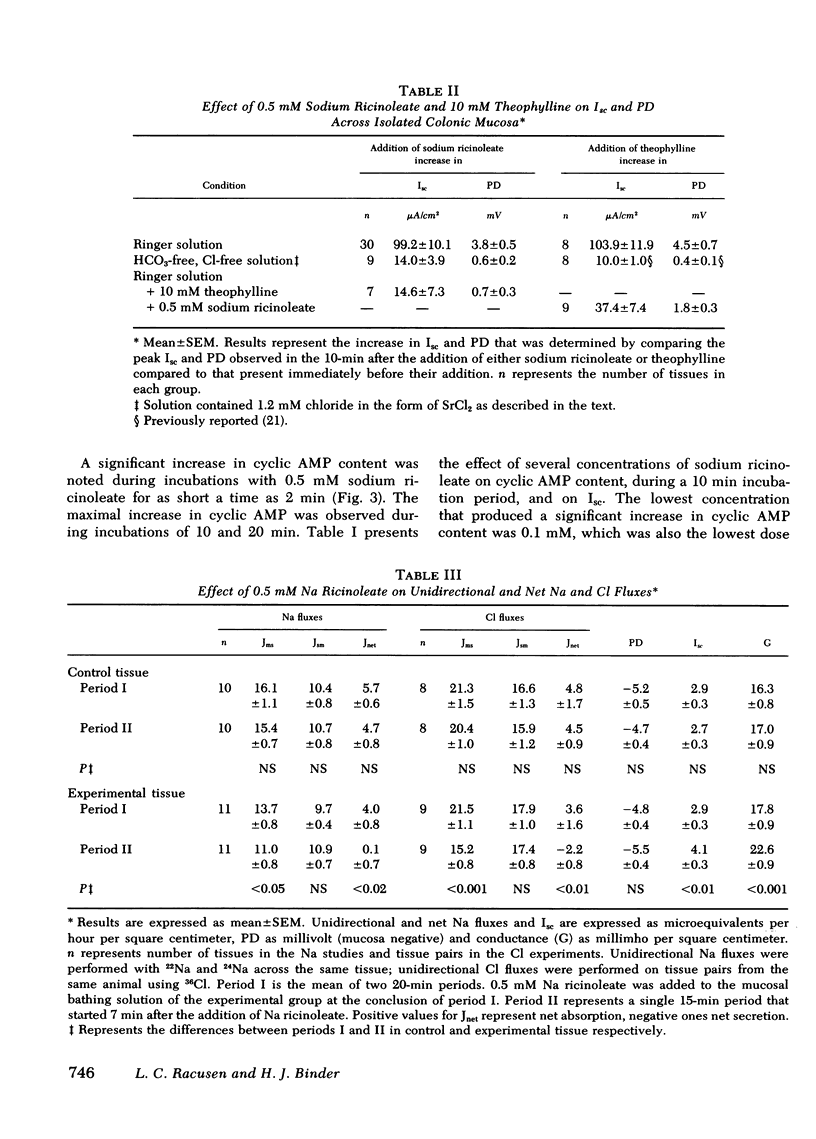
Perfusion of the colon with ricinoleic acid produces fluid and electrolyte accumulation. The mechanism of these changes in water and electrolyte movement is uknown. These studies were designed to determine whether ricinoleic acid effects active ion transport across isolated rat colonic mucosa. 0.5 mM Na ricinoleate produced significant increases in potential difference (3.8 +/- 0.5 mV) and short-circuit current (Isc) (99.2 +/- 10.1 muA/cm2). The increases in Isc produced by Na ricinoleate were inhibited by both removal of bicarbonate and chloride and by the presence of theophylline. The hydroxy fatty acid also resulted in a significant decrease in net Na absorption from 4.7 +/- 0.8 to 0.1 +/- 0.7 mueq/h cm2 and reversed net Cl transport from absorption (+ 4.5 +/- 0.9) to secretion (-2.2 +/- mueq/h cm2). In parallel studies 0.5 mM Na ricinoleate increased mucosal cyclic AMP content by 58%. The concentrations of Na ricinoleate required to produce detectable and maximal increases in both Isc and cyclic AMP were the same. These results provide evidence in support of the concept that hydroxy fatty acid-induced fluid and electrolyte accumulation is driven by an active ion secretory process.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammon H. V., Phillips S. F. Inhibition of colonic water and electrolyte absorption by fatty acids in man. Gastroenterology. 1973 Nov;65(5):744–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. V., Thomas P. J., Phillips S. F. Effects of oleic and ricinoleic acids on net jejunal water and electrolyte movement. Perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):374–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI107569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Filburn C., Volpe B. T. Bile salt alteration of colonic electrolyte transport: role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Gastroenterology. 1975 Mar;68(3):503–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Rawlins C. L. Effect of conjugated dihydroxy bile salts on electrolyte transport in rat colon. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1460–1466. doi: 10.1172/JCI107320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Rawlins C. L. Electrolyte transport across isolated large intestinal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1973 Nov;225(5):1232–1239. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.5.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bright-Asare P., Binder H. J. Stimulation of colonic secretion of water and electrolytes by hydroxy fatty acids. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jan;64(1):81–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. L., Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Sgherzi A. M. A simple and sensitive saturation assay method for the measurement of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):561–562. doi: 10.1042/bj1210561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Freeman B. W. Circular muscle electromyogram in the cat colon: local effect of sodium ricinoleate. Gastroenterology. 1972 Dec;63(6):1011–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline W. S., Lorenzsonn V., Benz L., Bass P., Olsen W. A. The effects of sodium ricinoleate on small intestinal function and structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):380–390. doi: 10.1172/JCI108482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyne M. J., Bonorris G. G., Chung A., Conley D., Schoenfield L. J. Propranolol inhibits bile acid and fatty acid stimulation of cyclic AMP in human colon. Gastroenterology. 1977 Nov;73(5):971–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbins J. W., Binder H. J. Effect of bile salts and fatty acids on the colonic absorption of oxalate. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jun;70(6):1096–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz M., Binder H. J. Effect of enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae, Escherichia coli, and Shigella dysenteriae type 1 on fluid and electrolyte transport in the colon. J Infect Dis. 1976 Aug;134(2):135–143. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., al-Awqati Q., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effect of cholera enterotoxin on ion transport across isolated ileal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):796–804. doi: 10.1172/JCI106874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. II. Effects of cyclic 3', 5'-AMP. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):992–997. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Dugas M. C., Schultz S. G. Sodium chloride transport by rabbit gallbladder. Direct evidence for a coupled NaCl influx process. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jun;65(6):769–795. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.6.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Chadwick V. S., Debongnie J. C., Lewis J. C., Phillips S. F. Perfusion of rabbit colon with ricinoleic acid: dose-related mucosal injury, fluid secretion, and increased permeability. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jul;73(1):95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Lewis J. C., Phillips S. F. Ricinoleic acid effects on rabbit intestine: an ultrastructural study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1976 Sep;51(9):569–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Phillips S. F., Dozois R. R., Go V. L. Stimulation of adenylate cyclase in homogenates of isolated intestinal epithelial cells from hamsters. Effects of gastrointestinal hormones, prostaglandins, and deoxycholic and ricinoleic acids. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jan;74(1):11–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., Frey W., 2nd, Carr D. W., Goldberg N. D. Stimulation of human platelet guanylate cyclase by fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1279–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullikson G. W., Cline W. S., Lorenzsonn V., Benz L., Olsen W. A., Bass P. Effects of anionic surfactants on hamster small intestinal membrane structure and function: relationship to surface activity. Gastroenterology. 1977 Sep;73(3):501–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias J. R., Martin J. L., Burns T. W., Carlson G. M., Shields R. P. Ricinoleic acid effect on the electrical activity of the small intestine in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):640–644. doi: 10.1172/JCI108975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellans H. N., Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Coupled sodium-chloride influx across the brush border of rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol. 1973 Aug;225(2):467–475. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.2.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellans H. N., Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Effect of acetazolamide on sodium and chloride transport by in vitro rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1808–1814. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orly J., Schramm M. Fatty acids as modulators of membrane functions: catecholamine-activated adenylate cyclase of the turkey erythrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3433–3437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Binder H. J., Curran P. F. Active electrolyte secretion stimulated by choleragen in rabbit ileum in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1973 Oct;225(4):781–787. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.4.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racusen L. C., Binder H. J. Alteration of large intestinal electrolyte transport by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1977 Oct;73(4 Pt 1):790–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. J., Kimberg D. V., Sheerin H. E., Field M., Said S. I. Vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulation of adenylate cyclase and active electrolyte secretion in intestinal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):536–544. doi: 10.1172/JCI107790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. J., Gaginella T. S., Bass P. Actions of ricinoleic acid and structurally related fatty acids of the gastrointestinal tract. I. Effects on smooth muscle contractility in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Nov;195(2):347–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. J., Gaginella T. S., Olsen W. A., Bass P. Inhibitory actions of laxatives on motility and water and electrolyte transport in the gastrointestinal tract. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Feb;192(2):458–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Pastan I. Stimulation of guanylate cyclase of fibroblasts by free fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5802–5809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau W. M., Makhlouf G. M. Different effects of hormonal peptides and cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate on colonic transport in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1974 Oct;67(4):662–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



