Abstract
Background
The vast majority of medical interventions introduced into clinical development prove unsafe or ineffective. One prominent explanation for the dismal success rate is flawed preclinical research. We conducted a systematic review of preclinical research guidelines and organized recommendations according to the type of validity threat (internal, construct, or external) or programmatic research activity they primarily address.
Methods and Findings
We searched MEDLINE, Google Scholar, Google, and the EQUATOR Network website for all preclinical guideline documents published up to April 9, 2013 that addressed the design and conduct of in vivo animal experiments aimed at supporting clinical translation. To be eligible, documents had to provide guidance on the design or execution of preclinical animal experiments and represent the aggregated consensus of four or more investigators. Data from included guidelines were independently extracted by two individuals for discrete recommendations on the design and implementation of preclinical efficacy studies. These recommendations were then organized according to the type of validity threat they addressed. A total of 2,029 citations were identified through our search strategy. From these, we identified 26 guidelines that met our eligibility criteria—most of which were directed at neurological or cerebrovascular drug development. Together, these guidelines offered 55 different recommendations. Some of the most common recommendations included performance of a power calculation to determine sample size, randomized treatment allocation, and characterization of disease phenotype in the animal model prior to experimentation.
Conclusions
By identifying the most recurrent recommendations among preclinical guidelines, we provide a starting point for developing preclinical guidelines in other disease domains. We also provide a basis for the study and evaluation of preclinical research practice.
Please see later in the article for the Editors' Summary
Editors' Summary
Background
The development process for new drugs is lengthy and complex. It begins in the laboratory, where scientists investigate the causes of diseases and identify potential new treatments. Next, promising interventions undergo preclinical research in cells and in animals (in vivo animal experiments) to test whether the intervention has the expected effect and to support the generalization (extension) of this treatment–effect relationship to patients. Drugs that pass these tests then enter clinical trials, where their safety and efficacy is tested in selected groups of patients under strictly controlled conditions. Finally, the government bodies responsible for drug approval review the results of the clinical trials, and successful drugs receive a marketing license, usually a decade or more after the initial laboratory work. Notably, only 11% of agents that enter clinical testing (investigational drugs) are ultimately licensed.
Why Was This Study Done?
The frequent failure of investigational drugs during clinical translation is potentially harmful to trial participants. Moreover, the costs of these failures are passed onto healthcare systems in the form of higher drug prices. It would be good, therefore, to reduce the attrition rate of investigational drugs. One possible explanation for the dismal success rate of clinical translation is that preclinical research, the key resource for justifying clinical development, is flawed. To address this possibility, several groups of preclinical researchers have issued guidelines intended to improve the design and execution of in vivo animal studies. In this systematic review (a study that uses predefined criteria to identify all the research on a given topic), the authors identify the experimental practices that are commonly recommended in these guidelines and organize these recommendations according to the type of threat to validity (internal, construct, or external) that they address. Internal threats to validity are factors that confound reliable inferences about treatment–effect relationships in preclinical research. For example, experimenter expectation may bias outcome assessment. Construct threats to validity arise when researchers mischaracterize the relationship between an experimental system and the clinical disease it is intended to represent. For example, researchers may use an animal model for a complex multifaceted clinical disease that only includes one characteristic of the disease. External threats to validity are unseen factors that frustrate the transfer of treatment–effect relationships from animal models to patients.
What Did the Researchers Do and Find?
The researchers identified 26 preclinical guidelines that met their predefined eligibility criteria. Twelve guidelines addressed preclinical research for neurological and cerebrovascular drug development; other disorders covered by guidelines included cardiac and circulatory disorders, sepsis, pain, and arthritis. Together, the guidelines offered 55 different recommendations for the design and execution of preclinical in vivo animal studies. Nineteen recommendations addressed threats to internal validity. The most commonly included recommendations of this type called for the use of power calculations to ensure that sample sizes are large enough to yield statistically meaningful results, random allocation of animals to treatment groups, and “blinding” of researchers who assess outcomes to treatment allocation. Among the 25 recommendations that addressed threats to construct validity, the most commonly included recommendations called for characterization of the properties of the animal model before experimentation and matching of the animal model to the human manifestation of the disease. Finally, six recommendations addressed threats to external validity. The most commonly included of these recommendations suggested that preclinical research should be replicated in different models of the same disease and in different species, and should also be replicated independently.
What Do These Findings Mean?
This systematic review identifies a range of investigational recommendations that preclinical researchers believe address threats to the validity of preclinical efficacy studies. Many of these recommendations are not widely implemented in preclinical research at present. Whether the failure to implement them explains the frequent discordance between the results on drug safety and efficacy obtained in preclinical research and in clinical trials is currently unclear. These findings provide a starting point, however, for the improvement of existing preclinical research guidelines for specific diseases, and for the development of similar guidelines for other diseases. They also provide an evidence-based platform for the analysis of preclinical evidence and for the study and evaluation of preclinical research practice. These findings should, therefore, be considered by investigators, institutional review bodies, journals, and funding agents when designing, evaluating, and sponsoring translational research.
Additional Information
Please access these websites via the online version of this summary at http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001489.
The US Food and Drug Administration provides information about drug approval in the US for consumers and for health professionals; its Patient Network provides a step-by-step description of the drug development process that includes information on preclinical research
The UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) provides information about all aspects of the scientific evaluation and approval of new medicines in the UK; its My Medicine: From Laboratory to Pharmacy Shelf web pages describe the drug development process from scientific discovery, through preclinical and clinical research, to licensing and ongoing monitoring
The STREAM website provides ongoing information about policy, ethics, and practices used in clinical translation of new drugs
The CAMARADES collaboration offers a “supporting framework for groups involved in the systematic review of animal studies” in stroke and other neurological diseases
Introduction
The process of clinical translation is notoriously arduous and error-prone. By recent estimates, 11% of agents entering clinical testing are ultimately licensed [1], and only 5% of “high impact” basic science discoveries claiming clinical relevance are successfully translated into approved agents within a decade [2]. Such large-scale attrition of investigational drugs is potentially harmful to individuals in trials, and consumes scarce human and material resources [3]. Costs of failed translation are also propagated to healthcare systems in the form of higher drug costs.
Preclinical studies provide a key resource for justifying clinical development. They also enable a more meaningful interpretation of unsuccessful efforts during clinical development [4]. Various commentators have reported problems such as difficulty in replicating preclinical studies [5],[6], publication bias [7], and the prevalence of methodological practices that result in threats to validity [8].
To address these concerns, several groups have issued guidelines on the design and execution of in vivo animal experiments supporting clinical development (“preclinical efficacy studies”). Preclinical studies employ a vast repertoire of experimental, cognitive, and analytic practices to accomplish two generalized objectives [9]. First, they aim to demonstrate causal relationships between an investigational agent (treatment) and a disease-related phenotype or phenotype proxy (effect) in an animal model. Various factors can confound reliable inferences about such cause-and-effect relationships. For example, biased outcome assessment due to experimenter expectation can lead to spurious inferences about treatment response. Such biases present “threats to internal validity,” and are addressed by practices such as masking outcome assessors to treatment allocation.
The second aim of preclinical efficacy studies is to support generalization of treatment–effect relationships to human patients. This generalization can fail in two ways. Researchers might mischaracterize the relationship between experimental systems and the phenomena they are intended to represent. For instance, a researcher might err in using only rotational behavior in animals to represent human parkinsonism—a condition with a complex clinical presentation including tremor and cognitive symptoms. Such errors in theoretical relationships are “threats to construct validity.” Ways to address such threats include selecting well-justified model systems or outcome measures when designing preclinical studies, or confirming that the drug triggers molecular responses predicted by the theory of drug action.
Clinical generalization can also be threatened if causal mediators that are present in model systems are not present in patients. Responses in an inbred mouse, for example, may be particular to the strain, thus limiting generalizability to other mouse models or patients. Unforeseen factors that frustrate the transfer of cause-and-effect relationships from one system to another related system are “threats to external validity.” Researchers often address threats to external validity by replicating treatment effects in multiple model systems, or using multiple treatment formulations.
Many accounts of preclinical study design describe the concepts of internal and external validity. However, they often subsume the concept of “construct validity” under the label of “external validity.” We think that the separation of construct and external validity categories highlights the distinctiveness between the kinds of experimental operations that enhance clinical generalizability (see Box 1). Whereas addressing external validity threats involves conducting replication studies that vary experimental conditions, construct validity threats are reduced by articulating, addressing, and confirming theoretical presuppositions underlying clinical generalization.
Box 1. Construct Validity and Preclinical Research
Construct Validity concerns the degree to which inferences are warranted from the sampling particulars of an experiment (e.g., the units, settings, treatments, and outcomes) to the entities these samples are intended to represent. In preclinical research, “construct validity” has often been used to describe the relationship between behavioral outcomes in animal experiments and human behaviors they are intended to model (e.g., whether diminished performance of a rat in a “forced swim test” provides an adequate representation of the phenomenology of human depression).
Our analysis extends this more familiar notion to the animals themselves, as well as treatments and causal pathways. When researchers perform preclinical experiments, they are implicitly positing theoretical relationships between their experimental operations and the clinical scenario they are attempting to emulate. Clinical generalization is threatened whenever these theoretical relationships are in error.
There are several ways construct validity can be threatened in preclinical studies. First, preclinical researchers might use treatments, animal models, or outcome assessments that are poorly matched to the clinical setting, as when preclinical studies use an acute disease model to represent a chronic disease in human beings. Another way construct validity can be threatened is if preclinical researchers err in executing experimental operations. For example, researchers intending to represent intravenous drug administration can introduce a threat to construct validity if, when performing tail vein administration in rats, they inadvertently administer a drug subcutaneously. A third canonical threat to construct validity in preclinical research is when the physiological derangements driving human disease are not present in the animal models used to represent them. Note that, in all three instances, a preclinical study can—in principle—be externally valid if theories are adjusted. Studies in acute disease, while not “construct valid” for chronic disease, may retain generalizability for acute human disease.
To identify experimental practices that are commonly recommended by preclinical researchers for enhancing the validity of treatment effects and their clinical generalizations, we performed a systematic review of guidelines addressing the design and execution of preclinical efficacy studies. We then extracted specific recommendations from guidelines and organized them according to the principal type of validity threat they aim to address, and which component of the experiment they concerned. Based on the premise that recommendations recurring with the highest frequency represent priority validity threats across diverse drug development programs, we identified the most common recommendations associated with each of the three validity threat types. Additional aims of our systematic review are to provide a common framework for planning, evaluating, and coordinating preclinical studies and to identify possible gaps in formalized guidance.
Methods
Search Strategy
We developed a multifaceted search methodology to construct our sample of guidelines (See Table 1) from searches in MEDLINE, Google Scholar, Google, and the EQUATOR Network website. MEDLINE was searched using three strategies with unlimited date ranges up to April 2, 2013. Our first search (MEDLINE 1) used the terms “animals/and guidelines as topic.mp” and combined results with the exploded MeSH terms “research,” “drug evaluation, preclinical,” and “disease models, animal”. Our second search (MEDLINE 2) combined the results from four terms: “animal experimentation,” “models, animal,” “drug evaluation, preclinical,” and “translational research.” Results were limited to entries with the publication types “Consensus Development Conference,” “Consensus Development Conference, NIH,” “Government Publications,” or “Practice Guideline.” The third search (MEDLINE 3) combined the results of the exploded terms “animal experimentation,” “models, animal,” “drug evaluation, preclinical,” and “translational research” with the publication types “Consensus Development Conference,” “Consensus Development Conference, NIH,” and “Government Publications.”
Table 1. Summary of preclinical guidelines for in vivo experiments identified through various database searches.
| Database Search or Sourcea | Date of Search/Acquisition | Unique Guidelines Identifiedb |
| MEDLINE 1 | April 2, 2013 | STAIR [10],[12] c |
| Ludolph et al. [37] | ||
| Rice et al. [38] | ||
| Schwartz et al. [44] | ||
| Verhagen et al. [45] | ||
| García-Bonilla et al. [46] | ||
| Kelloff et al. [47] | ||
| Kamath et al. [48] | ||
| MEDLINE 2 | April 2, 2013 | Bellomo et al. [49] |
| MEDLINE 3 | April 2, 2013 | Moreno et al. [50] |
| Google Scholar | January 19, 2012 | Scott et al. [25] |
| Curtis et al. [51],[52] c | ||
| Piper et al. [53] | ||
| Liu et al. [54] | ||
| Google Scholar | April 9, 2013 | Margulies and Hicks [36] |
| Landis et al. [55] | ||
| January 24, 2012 | Bolon et al. [56] | |
| Macleod et al. [57] | ||
| NINDS-NIH [58] | ||
| Pullen et al. [59] | ||
| Shineman et al. [60] | ||
| Willmann et al. [40] | ||
| Bolli et al. [61] | ||
| Correspondence | April 5–31, 2013 | Grounds et al. [39] |
| Savitz et al. [62],[63] c | ||
| Katz et al. [64] |
No unique guidelines that had not been previously identified through previous search strategies were found by searching the EQUATOR Network or through hand searching of references in identified guidelines.
The guidelines are listed under the search strategy by which they were first identified.
Guidelines that were grouped together during analysis (e.g., identical guidelines that were published in more than one journal).
NINDS-NIH, US National Institutes of Health National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
We conducted two Google Scholar searches. The first used the search terms “animal studies,” “valid,” “model,” and “guidelines” with no date restrictions. We limited our eligibility screening to the first 300 records, as returns became minimal after this point in screening. The second Google Scholar search was designed to identify preclinical efficacy guidelines that were published in the wake of the Stroke Therapy Academic Industry Roundtable (STAIR) guidelines—the best-known example of preclinical guidance. We searched for articles or statements citing the most recent STAIR guideline [10]. Results were screened for new guidelines. We also conducted a Google search seeking guidelines that might not be published in the peer-reviewed literature (e.g., granting agency statements). The terms “guidelines” and “preclinical” and “bias” were searched with no restrictions. We limited our eligibility screening to the first 400 records.
We searched the EQUATOR Network [11] website for guidelines, and reviewed the citations of included guidelines for additional guidelines. Authors of eligible guidelines were contacted for additional preclinical design/conduct guidelines.
Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible, guidelines had to pertain to in vivo animal experiments. During title and abstract screening, we excluded guidelines that exclusively addressed (a) use of animals in teaching, (b) toxicology experiments, (c) testing of veterinary or agricultural interventions, (d) clinical experiments like assays on human tissue specimens, or (e) ethics or welfare, and guidelines that (f) did not offer targeted practice recommendations or (g) were strictly about reporting, rather than study design and conduct. We applied two further exclusion criteria during full-text screening. First, we excluded guidelines that did not address whole experiments, but merely focused on single elements of experiments (e.g., model selection): included guidelines must have recommended at least one practice aimed at addressing threats to internal validity (e.g., allocation concealment, selection of controls, or randomization). Second, we excluded guidelines listing four authors or fewer, except where articles reported using a formalized process to aggregate expert opinion (e.g., interviews). This was done to distinguish guidelines reflecting aggregated consensus from those reflecting the opinion of small teams of investigators. Where guidelines were later amended (e.g., [10],[12]) or where one guideline was published nearly verbatim in parallel venues (e.g., [13]–[15]), we consolidated the recommendations, and the group of related guidelines was treated as one unit during extraction and analysis. In the absence of well-characterized quality parameters for preclinical guideline documents (such as the AGREE II instrument for clinical guideline evaluation [16]), we did not include or exclude guidelines based on a quality score.
The application of our eligibility criteria was piloted in 100 citations to standardize implementation. Title and abstract screening of citations was conducted by one author (J. K. or V. C. H.). Guidelines meeting initial eligibility were screened by both J. K. and V. C. H. at the full-text level to ensure full eligibility for extraction.
Extraction
We extracted discrete recommendations on the design and implementation of preclinical efficacy studies. These recommendations were categorized according to (a) which experimental component they concerned, using unit (animal), treatment, and outcome elements [17], and (b) the type of validity threat that they addressed, using the typology of validity described by Shadish et al. [9]. We also recorded the methodology used to develop the guidelines, and whether the guidelines cited evidence to support any recommendations.
Extraction was piloted by J. K., and each eligible guideline was extracted independently by two individuals (J. K. and V. C. H.). Extraction and categorization disagreements were resolved by discussion until consensus was reached.
In performing extractions, we made several simplifying assumptions. First, since nearly every recommendation has implications for all three validity types, we made inferences (when possible, based on explanations within the guidelines) about the type of validity threat authors seemed most concerned about when issuing a recommendation. Second, when guidelines offered nondescript recommendations to “blind experiments,” we assumed these recommendations pertained to blinded outcome assessment, not blinded treatment allocation. Third, some guidelines contained both reporting and design/conduct recommendations. We inferred that recommendations concerning reporting reflected tacit endorsements of certain design/conduct practices (i.e., the recommendation “report method of treatment allocation” was interpreted as suggesting that method of treatment allocation is relevant for inferential reliability, and, accordingly, randomized treatment allocation is to be preferred). Fourth, some recommendations could be categorized differently depending on whether an experiment was randomized or not. For example, the recommendation “characterize animals before study” (in relation to a variable disease status at baseline) addresses an internal validity threat for nonrandom studies, but a construct validity threat for studies using randomization, since variation would be randomly distributed across both arms. We assumed that such recommendations pertained to construct validity, since most preclinical efficacy studies are actively controlled, and many preclinical researchers intend phenotypes to be identical at baseline in treatment and control groups. Fifth, some guidelines explicitly endorsed another guideline in our sample. When this occurred, we assumed all recommendations in the endorsed previous guideline were recommended, regardless of whether the present guideline made explicit reference to the practices (see Table 2). Of our 26 included guidelines (see Table 1), 23 had contactable (i.e., not deceased, authorship reported) corresponding authors. We contacted authors to verify that we had comprehensively captured and accurately interpreted all recommendations contained in their guidelines; overall response rate of guideline authors was 58% (15/26).
Table 2. Results of recommendation extraction from guidelines addressing validity threats in preclinical experiments.
| Recommendation Number | Validity Type | Application | Topic Addressed by the Recommendation | Number of Guidelines | General | Neurological and Cerebrovascular | Cardiac and Circulatory | Neuromuscular | Chemoprevention | Pain | Endometriosis | Arthritis | Sepsis | Renal Failure | Infectious Diseases | |||||||||||||||
| Landis et al. | Ludolph et al. | NINDS-NIH | Scott et al. | Shineman et al. | Moreno et al. | Katz et al. | STAIR | Macleod et al. | Liu et al.a | García-Bonilla et al. | Savitz et al. | Margulies and Hicksa | Curtis et al. | Schwartz et al. | Bolli et al. | Willmann et al. | Grounds et al. | Verhagen et al. | Kelloff et al. | Rice et al. | Pullen et al. | Bolon et al. | Piper et al. | Bellomo et al.b | Kamath et al. | |||||
| 1 | IV | U | Matching or balancing treatment allocation of animals | 7 | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | IV | U | Standardized handling of animals | 8 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | IV | U | Randomized allocation of animals to treatment | 20 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | X | Δ | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | ||||||
| 4 | IV | U | Monitoring emergence of confounding characteristics in animals | 12 | X | Δ | X | Ŧ | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | ||||||||||||||
| 5 | IV | U | Specification of unit of analysis | 1 | X | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | IV | T | Addressing confounds associated with anesthesia or analgesia | 5 | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | IV | T | Selection of appropriate control groups | 15 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | X | |||||||||||
| 8 | IV | T | Concealed allocation of treatment | 14 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | X | Ŧ | X | X | Ŧ | ||||||||||||
| 9 | IV | T | Study of dose–response relationships | 15 | X | X | X | X | X | X | Ŧ | X | Δ | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| 10 | IV | O | Use of multiple time points for measuring outcomes | 5 | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | IV | O | Consistency of outcome measurement | 8 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | IV | O | Blinding of outcome assessment | 20 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | X | Δ | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | ||||||
| 13 | IV | Total | Establishment of primary and secondary end points | 4 | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | IV | Total | Precision of effect size | 6 | X | X | X | X | X | Ŧ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | IV | Total | Management of interest conflicts | 8 | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | Ŧ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | IV | Total | Choice of statistical methods for inferential analysis | 14 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||
| 17 | IV | Total | Flow of animals through an experiment | 16 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | X | Ŧ | X | X | X | X | X | Ŧ | ||||||||||
| 18 | IV | Total | A priori statements of hypothesis | 3 | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | IV | Total | Choice of sample size | 23 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | X | Ŧ | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | |||
| 20 | CV | U | Matching model to human manifestation of the disease | 19 | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | X | X | Ŧ | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | X | |||||||
| 21 | CV | U | Matching model to sex of patients in clinical setting | 9 | X | X | X | Ŧ | X | X | Δ | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| 22 | CV | U | Matching model to co-interventions in clinical setting | 7 | X | Ŧ | X | Δ | X | X | Ŧ | |||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | CV | U | Matching model to co-morbidities in clinical setting | 10 | X | Ŧ | X | X | Ŧ | X | X | X | X | Δ | ||||||||||||||||
| 24 | CV | U | Matching model to age of patients in clinical setting | 11 | X | X | X | Ŧ | X | X | Ŧ | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||
| 25 | CV | U | Characterization of animal properties at baseline | 20 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | X | Ŧ | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Ŧ | ||||||
| 26 | CV | U | Comparability of control group characteristics to those of previous studies | 1 | X | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | CV | T | Optimization of complex treatment parameters | 5 | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | CV | T | Matching timing of treatment delivery to clinical setting | 10 | X | X | X | X | Ŧ | X | Δ | X | X | Ŧ | ||||||||||||||||
| 29 | CV | T | Matching route/method of treatment delivery to clinical setting | 8 | X | X | X | Ŧ | X | Ŧ | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| 30 | CV | T | Pharmacokinetics to support treatment decisions | 9 | X | X | X | X | Ŧ | X | Δ | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| 31 | CV | T | Matching the duration/exposure of treatment to clinical setting | 10 | X | X | X | X | X | Ŧ | X | Δ | X | X | ||||||||||||||||
| 32 | CV | T | Definition of treatment | 2 | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33 | CV | T | Faithful delivery of intended treatment | 6 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 34 | CV | T | Addressing confounds associated with treatment | 9 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Ŧ | |||||||||||||||||
| 35 | CV | O | Matching outcome measure to clinical setting | 14 | X | X | X | Ŧ | X | Ŧ | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | Δ | ||||||||||||
| 36 | CV | O | Degree of characterization and validity of outcome measure chosen | 9 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| 37 | CV | O | Treatment response along mechanistic pathway | 15 | X | X | X | X | X | Ŧ | X | Δ | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| 38 | CV | O | Assessment of multiple manifestations of disease phenotype | 10 | X | X | X | X | Δ | X | Δ | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||
| 39 | CV | O | Assessment of outcome at late/clinically relevant time points | 7 | X | X | Ŧ | X | Δ | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| 40 | CV | O | Addressing treatment interactions with clinically relevant co-morbidities | 1 | X | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 41 | CV | O | Use of validated assay for molecular pathways assessment | 1 | X | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 42 | CV | O | Definition of outcome measurement criteria | 7 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| 43 | CV | O | Addressing confounds associated with experimental setting | 3 | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 44 | CV | Total | Addressing confounds associated with setting | 8 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| 45 | EV | U | Replication in different models of the same disease | 13 | X | X | X | X | Δ | X | Δ | X | X | X | X | X | Ŧ | |||||||||||||
| 46 | EV | U | Replication in different species | 8 | X | X | Ŧ | X | Δ | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| 47 | EV | U | Replication at different ages | 1 | X | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 48 | EV | U | Replication at different levels of disease severity | 1 | X | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 49 | EV | T | Replication using variations in treatment | 2 | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50 | EV | Total | Independent replication | 12 | X | X | X | X | X | Ŧ | X | X | Δ | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||
| 51 | PROG | O | Inter-study standardization of end point choice | 3 | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 52 | PROG | Total | Define programmatic purpose of research | 4 | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 53 | PROG | Total | Inter-study standardization of experimental design | 14 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||
| 54 | PROG | Total | Research within multicenter consortia | 3 | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 55 | PROG | Total | Critical appraisal of literature or systematic review during design phase | 2 | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Explicit endorsement Piper et al. [53].
CV, threat to construct validity; EV, threat to external validity; IV, threat to internal validity; O, outcome; PROG, research program recommendations; T, treatment; Ŧ, recommendation imported from an endorsed guideline but not otherwise stated in the endorsing guideline; U, units (animals); Δ, recommendation imported from an endorsed guideline and also explicitly stated in the endorsing guideline; Total, all parts of the experiment; X, recommendation explicitly stated in the guideline.
NINDS-NIH, US National Institutes of Health National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Data Synthesis
Discrete recommendations from each guideline were slotted into general recommendation categories. We confirmed that all extracted recommendations within a general category were consistent with one another. Recommendations were then reviewed by all study authors to determine whether some recommendations should be combined, and whether recommendations were categorized into appropriate validity types. All authors voted on each categorization; disagreements were resolved by discussion and consensus.
Data were synthesized by providing a matrix of the recommendations captured by each of the guidelines and were presented as simple presence or absence of the recommendation. The proportion of guidelines that addressed each recommendation was expressed as a simple proportion.
A PRISMA 2009 checklist for our review can be found in Checklist S1.
Results
Guideline Characteristics
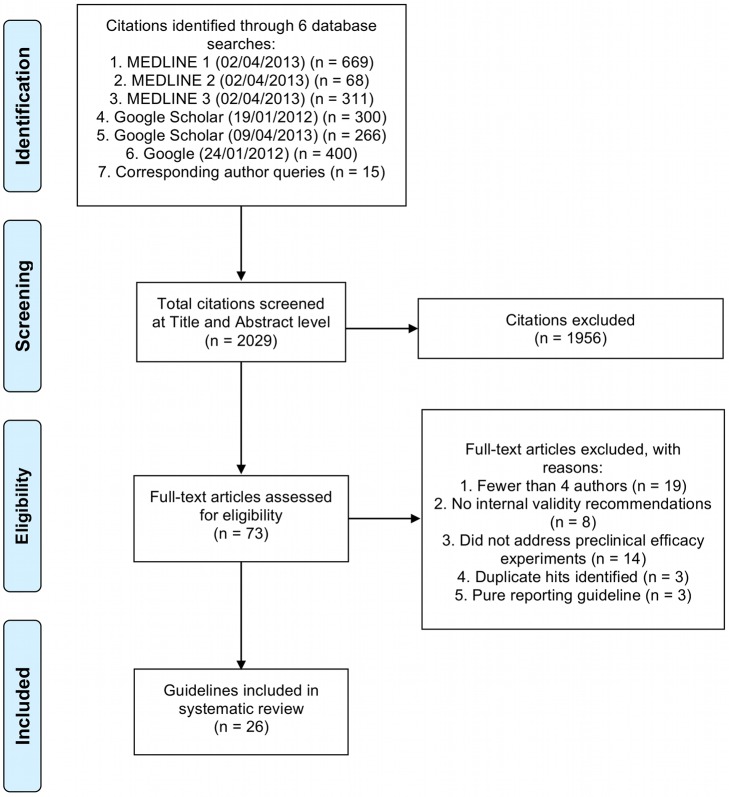
A total of 2,029 citations were identified by our literature search strategies. Of those, 73 met our initial screening criteria, and 26 guidelines on design of preclinical studies met our full eligibility criteria (see Figure 1). Almost all guidelines were published in the peer-reviewed literature (n = 25, 96%). In addition, we identified two guidelines [18],[19] addressing the synthesis of preclinical animal data (i.e., systematic review and meta-analysis). Given so few data, extraction and synthesis of these guidelines was not conducted.
Figure 1. Flow of database searches and eligibility screening for guideline documents addressing preclinical efficacy experiments.
Sample sizes at the identification stage reflect the raw output of the search and do not reflect the removal of duplicate entries between search strategies.
Twelve guidelines on preclinical study design addressed various neurological and cerebrovascular drug development areas, and three addressed cardiac and circulatory disorders; other disorders covered in guidelines included sepsis, pain, and arthritis. Most guidelines (n = 24, 92%) had been published within the last decade. Most were derived from workshop discussions, and only three described a clear methodology for their development. Though all but five guidelines (n = 21, 81%) cited evidence in support of one or more recommendations, reference to published evidence supporting individual recommendations was sporadic.
Collectively, guidelines offered 55 different recommendations for preclinical design. On average, each guideline offered 18 recommendations (see Table 3). Fourteen recommendations were present in over 50% of relevant guidelines. The most common recommendations within each validity category are shown in Table 4. Recommendations contained in guidelines addressed all three components of preclinical efficacy studies—animals (units), treatments, and outcomes—though we counted more recommendations pertaining to the animals (148 in all) than to treatments (110) or outcomes (103). Many recommendations reflected in the 55 categories embodied a variety of particular experimental operations. In Table 4 we describe some of the many operations captured under a few representative recommendation categories.
Table 3. To what extent individual guidelines address each type of validity threat and make recommendations regarding the overall research program.
| Category | Study | Number (Percent) of Recommendations Addressing Each Validity Type | Total (n = 55) | |||
| IV (n = 19) | CV (n = 25) | EV (n = 6) | PROG (n = 5) | |||
| General | Landis et al. | 10 (53) | 2 (8) | 1 (17) | 0 (0) | 13 (24) |
| Neurological and cerebrovascular | Ludolph et al. | 5 (26) | 12 (48) | 3 (50) | 3 (60) | 23 (42) |
| NINDS-NIH | 9 (47) | 4 (16) | 1 (17) | 0 (0) | 14 (25) | |
| Scott et al. | 8 (42) | 2 (8) | 0 (0) | 1 (20) | 11 (20) | |
| Shineman et al. | 15 (79) | 12 (48) | 1 (17) | 1 (20) | 29 (53) | |
| Moreno et al. | 10 (53) | 10 (40) | 0 (0) | 1 (20) | 21 (38) | |
| Katz et al. | 10 (53) | 11 (44) | 2 (33) | 2 (40) | 25 (45) | |
| STAIR | 8 (42) | 14 (56) | 3 (50) | 0 (0) | 25 (45) | |
| Macleod et al. | 8 (42) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 9 (16) | |
| Liu et al. | 12 (63) | 10 (40) | 3 (50) | 1 (20) | 26 (47) | |
| García-Bonilla et al. | 11 (58) | 8 (32) | 1 (17) | 1 (20) | 21 (38) | |
| Savitz et al. | 3 (16) | 16 (64) | 3 (50) | 1 (20) | 23 (42) | |
| Margulies and Hicks | 8 (42) | 10 (40) | 5 (83) | 2 (40) | 25 (45) | |
| Cardiac and circulatory | Curtis et al. | 11 (58) | 11 (44) | 3 (50) | 2 (40) | 27 (49) |
| Schwartz et al. | 9 (47) | 10 (40) | 1 (17) | 0 (0) | 20 (36) | |
| Bolli et al. | 6 (32) | 6 (24) | 3 (50) | 2 (40) | 17 (31) | |
| Neuromuscular | Willmann et al. | 6 (32) | 6 (24) | 0 (0) | 3 (60) | 15 (27) |
| Grounds et al. | 6 (32) | 7 (28) | 0 (0) | 1 (20) | 14 (25) | |
| Chemoprevention | Verhagen et al. | 8 (42) | 10 (40) | 1 (17) | 0 (0) | 19 (35) |
| Kelloff et al. | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 1 (17) | 0 (0) | 2 (4) | |
| Pain | Rice et al. | 9 (47) | 10 (40) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 19 (35) |
| Endometriosis | Pullen et al. | 5 (26) | 4 (16) | 1 (17) | 1 (20) | 11 (20) |
| Arthritis | Bolon et al. | 6 (32) | 7 (28) | 0 (0) | 1 (20) | 14 (25) |
| Sepsis | Piper et al. | 9 (47) | 7 (28) | 1 (17) | 2 (40) | 19 (35) |
| Renal failure | Bellomo et al. | 10 (53) | 4 (16) | 2 (33) | 0 (0) | 16 (29) |
| Infectious diseases | Kamath et al. | 1 (5) | 1 (4) | 1 (17) | 1 (20) | 4 (7) |
CV, threat to construct validity; EV, threat to external validity; IV, threat to internal validity; NINDS-NIH, US National Institutes of Health National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; PROG, research program recommendations.
Table 4. Most frequent recommendations appearing in preclinical research guidelines for in vivo animal experiments.
| Validity Type | Recommendation Category | Examples | n (Percent) of Guidelines Citing |
| Internal | Choice of sample size | Power calculation, larger sample sizes | 23 (89) |
| Randomized allocation of animals to treatment | Various methods of randomization | 20 (77) | |
| Blinding of outcome assessment | Blinded measurement or analysis | 20 (77) | |
| Flow of animals through an experiment | Recording animals excluded from treatment through to analysis | 16 (62) | |
| Selection of appropriate control groups | Using negative, positive, concurrent, or vehicle control groups | 15 (58) | |
| Study of dose–response relationships | Testing above and below optimal therapeutic dose | 15 (58) | |
| Construct | Characterization of animal properties at baseline | Characterizing inclusion/exclusion criteria, disease severity, age, or sex | 20 (77) |
| Matching model to human manifestation of the disease | Matching mechanism, chronicity, or symptoms | 19 (73) | |
| Treatment response along mechanistic pathway | Characterizing pathway in terms of molecular biology, histology, physiology, or behaviour | 15 (58) | |
| Matching outcome measure to clinical setting | Using functional or non-surrogate outcome measures | 14 (54) | |
| Matching model to age of patients in clinical setting | Using aged or juvenile animals | 11 (42) | |
| External | Replication in different models of the same disease | Different transgenics, strains, or lesion techniques | 13 (50) |
| Independent replication | Different investigators or research groups | 12 (46) | |
| Replication in different species | Rodents and nonhuman primates | 8 (31) | |
| Research Program a | Inter-study standardization of experimental design | Coordination between independent research groups | 14 (54) |
| Defining programmatic purpose of research | Study purpose is preclinical, proof of concept, or exploratory | 4 (15) |
Recommendations concerning the coordination of experimental design practices across a program of research.
Threats to Internal Validity, Construct Validity, and External Validity
We identified 19 different recommendations addressing threats to internal validity, accounting for 35% of all 55 recommendations. The six most common are presented in Table 4. Practices endorsed in 50% or more guidelines but not reflected in Table 4 included the appropriate use of statistical methods and concealed allocation of treatment.
All guidelines, save one, contained recommendations to address construct validity threats. Twenty-five discrete construct validity recommendations were identified (Table 2), with the five most common presented in Table 4. Nine concerned matching the procedures used in preclinical studies—such as timing of drug delivery—to those planned for clinical studies. Three concerned directly addressing and ruling out factors that might impair clinical generalization, and another four involved confirming that experimental operations were implemented properly (e.g., if tail vein delivery of a drug is intended, confirming that the technically demanding procedure did not accidentally introduce the drug subcutaneously).
Recommendations concerning external validity threats were provided in 19 guidelines, and consisted of six recommendations. The most common was the recommendation that researchers reproduce their treatment effects in more than one animal model type, followed closely by independent replication of experiments (Table 4).
Research Program Recommendations
Many guidelines contained recommendations that pertained to experimental programs rather than individual experiments. These programmatic or coordinating recommendations invariably implicated all three types of validity. In total, 17 guidelines (65%) contained at least one recommendation promoting coordinated research activities. For instance, 14 guidelines recommended the use of standardized experimental designs (54%), and two recommended critical appraisal (e.g., through systematic review) of prior evidence (8%). Such practices facilitate synthesis of evidence prior to clinical development, thereby enabling more accurate and precise estimates of treatment effect (internal validity), clarification of theory and clinical generalizability (construct validity), and exploration of causal robustness in humans (external validity).
Discussion
We identified 26 guidelines that offered recommendations on the design and conduct of preclinical efficacy studies. Together, guidelines offered 55 prescriptions concerning threats to valid causal inference in preclinical efficacy studies. In recent years, numerous initiatives have sought to improve the reliability, interpretability, generalizability, and connectivity of laboratory investigations of new drugs. These include the establishment of preclinical data repositories [20], minimum reporting checklists for biomedical investigations [21], biomedical data ontologies [22], and reporting standards for animal studies [15]. Our review drew upon another set of initiatives—guidelines for the design and conduct of preclinical studies—to identify key experimental operations believed to address threats to clinical generalizability.
Numerous studies have documented that many of the recommendations identified in our study are not widely implemented in preclinical research. With respect to internal validity threats, a recent systematic analysis found that 13% and 14% of animals studies reported use of randomization or blinding respectively [23]. Several studies have revealed unaddressed construct validity threats in preclinical studies as well. For instance, one study found that the time between cardiac arrest and delivery of advanced cardiac life support is substantially shorter in preclinical studies than in clinical trials [24]. This represents a construct validity threat because the interval used in preclinical studies is not a faithful representation of that used in typical clinical studies. Similarly, most preclinical efficacy studies using the SOD1G93A murine model for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis do not measure disease response directly, but instead measure random biologic variability, in part because of a lack of disease phenotype characterization (via quantitative genotyping of copy number) prior to the experiment [25].
The implementation of operations to address external validity has not been studied extensively. For instance, we are unaware of any attempts to measure the frequency with which preclinical studies used to support clinical translation are tested for their ability to withstand replication over variations in experimental conditions. Nevertheless, a recent commentary by a former Amgen scientist revealed striking problems with replication in preclinical experiments [5], and a systematic review of stroke preclinical studies found high variability in the number of experimental paradigms used to test drug candidates [26].
Whether failure to implement the procedures described above explains the frequent discordance between preclinical effect sizes and those in clinical trials is unclear. Certainly there is evidence that many practices captured in Table 2 are relevant in clinical trials [27],[28], and recommendations like those concerning justification of sample size or selection of models have an irrefutable logic. Several studies provide suggestive—if inconclusive—evidence that practices like unconcealed treatment allocation [29] and unmasked outcome assessment [30] may bias toward larger effect sizes in preclinical efficacy studies. Some studies have also investigated whether certain practices related to construct validity improve clinical predictivity. One study aggregated individual animal data from 15 studies of the stroke drug NXY-059 and found that when animals were hypertensive—a condition that is extremely common in acute stroke patients—effect sizes were greatly attenuated [31]. Another study suggested that nonpublication of negative studies resulted in an overestimation of effect sizes by one-third [7]. Though evidence that implementation of recommendations leads to better translational outcomes is very limited [32], we think there is a plausible case insofar as such practices have been shown to be relevant in the clinical realm [33].
We regard it as encouraging that distinct guidelines are available for different disease areas. Validity threats can be specific to disease domains, models, or intervention platforms. For instance, confounding of anesthetics with disease response presents a greater validity threat in cardiovascular preclinical studies than in cancer, since anesthetics can interact with cardiovascular function but rarely interfere with tumor growth. We therefore support customizing recommendations on preclinical research to disease domains or intervention platforms (e.g., cell therapy). By classing specific guideline recommendations into “higher order” experimental recommendations and identifying recommendations that are shared across many guidelines (see Table 4 and Checklist S2), our analysis provides researchers in other domains a starting point for developing their own guidelines. We further suggest that these consensus recommendations provide a template for developing consolidated minimal design/practice principles that would apply across all disease domains. Of course, developing such a guideline would require a formalized process that engages various preclinical research communities [21].
The practices identified above also provide a starting point for evaluating planned clinical investigations. In considering proposals to conduct early phase trials, ethics committees and investigators might use items identified in this report to evaluate the strength of preclinical evidence supporting clinical testing, or to prioritize agents for clinical development. We have created a checklist for the design and evaluation of preclinical studies intended to support clinical translation by identifying all design and research practices that are endorsed by guidelines in at least four different disease domains (Checklist S2). Funding agencies and ethics committees might use this checklist when evaluating applications proposing clinical translation. In addition, various commentators have called for a “science of drug development” [34]. Future investigations should determine whether the recommendations in our checklist and/or Table 4 result in treatment effect measurements that are more predictive of clinical response.
Our findings identify several gaps in preclinical guidance. We initially set out to capture guidelines addressing two levels of preclinical observation: individual experiments and aggregation of multiple experiments (i.e., systematic review of preclinical efficacy studies). However, because we were unable to identify a critical mass of guidelines addressing aggregation [18],[19], we could not advance these guidelines to extraction. The scarcity of this guidance type reveals a gap in the literature and could reflect the slow adoption of systematic review and meta-analytic procedures in preclinical research [35]. Second, guidelines are clustered in disease domains. For instance, just under half of the guidelines cover neurological or cerebrovascular diseases; none address cancer therapies—which have the highest rate of drug development attrition [1]. We think these gaps identify opportunities for improving the scientific justification of drug development: cancer researchers should consider developing guidelines for their disease domain, and researchers in all domains should consider developing guidelines for the synthesis of animal evidence. A third intriguing finding is the comparative abundance of recommendations addressing internal and construct validity as compared with recommendations addressing external validity. Where some guidelines urge numerous practices for addressing threats to external validity (e.g., guidelines for studies of traumatic brain injury [36], amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [37], and stroke [10],[12]), others offer none (e.g., guidelines for studies of pain [38] and Duchenne muscular dystrophy [39],[40]). As addressing external validity threats involves quasi-replication, guidelines could be more prescriptive regarding how researchers might better coordinate replication within research domains. Fourth, our findings suggest a need for formalizing the process of guideline development. In clinical medicine, there are elaborate protocols and processes for development of evidence-based guidelines [41],[42]. Very few of the guidelines in our sample used an explicit methodology, and use of evidence to support recommendations was sporadic.
Our analysis is subject to several important limitations. First, our search strategy may not have been optimal because of a lack of standardized terms for preclinical guidelines for in vivo animal experiments. We note that many eligible statements were not indexed as guidelines in databases, greatly complicating their retrieval. Both guideline authors and database curators should consider steps for improving the indexing of research guidelines. Second, experiments are systems of interlocking operations, and procedures directed at addressing one validity threat can amplify or dampen other validity threats. Dose–response curves, though aimed at supporting cause-and-effect relationships (internal validity), also clarify the mechanism of the treatment effect (construct validity) and define the dose envelope where treatment effects are reproducible (external validity). Our approach to classifying recommendations was based on what we viewed as the validity threat that guideline developers were most concerned about when issuing each recommendation, and our classification process was transparent and required the consensus of all authors. Further to this, slotting recommendations from guidelines into discrete categories of validity threat required a considerable amount of interpretation, and it is possible others would organize recommendations differently. Third, though many of the recommendations listed in Table 2 have counterparts in clinical research, it is important to recognize how their operationalization in preclinical research may be different. For instance, allocation concealment may necessitate steps in preclinical research that are not normally required in trials, such as masking various personnel involved in caring for the animals, delivering lesions or establishing eligibility, delivering treatment, and following animals after treatment. Last, our review excluded guidelines strictly concerned with reporting studies, and should therefore not be viewed as capturing all initiatives aimed at addressing the valid interpretation and application of preclinical research.
Conclusions
We identified and organized consensus recommendations for preclinical efficacy studies using a typology of validity. Apart from findings mentioned above, the relationship between implementation of consensus practices and outcomes of clinical translation are not well understood. Nevertheless, by systematizing widely shared recommendations, we believe our analysis provides a more comprehensive, transparent, evidence-based, and theoretically informed rationale for analysis of preclinical studies. Investigators, institutional review boards, journals, and funding agencies should give these recommendations due consideration when designing, evaluating, and sponsoring translational investigations.
Supporting Information
The PRISMA checklist.
(DOC)
STREAM (Studies of Translation, Ethics and Medicine) checklist for design and evaluation of preclinical efficacy studies supporting clinical translation.
(PDF)
Acknowledgments
We thank Will Shadish, Alex John London, Charles Weijer, and Spencer Hey for helpful discussions. We also thank Spencer Hey for assistance with the checklist. Finally, we are grateful to guideline corresponding authors who responded to our queries.
Abbreviations
- STAIR
Stroke Therapy Academic Industry Roundtable
Note Added in Proof
It has come to our attention that the Nature Publishing Group has recently implemented reporting guidelines for new article submissions [43] that include a checklist to be completed by authors (http://www.nature.com/authors/policies/checklist.pdf).
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (EOG 111391). The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Kola I, Landis J (2004) Can the pharmaceutical industry reduce attrition rates? Nat Rev Drug Discov 3: 711–715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Contopoulos-Ioannidis DG, Ntzani E, Ioannidis JP (2003) Translation of highly promising basic science research into clinical applications. Am J Med 114: 477–484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. London AJ, Kimmelman J, Emborg ME (2010) Research ethics. Beyond access vs. protection in trials of innovative therapies. Science 328: 829–830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Kimmelman J, Anderson JA (2012) Should preclinical studies be registered? Nat Biotechnol 30: 488–489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Begley CG, Ellis LM (2012) Drug development: raise standards for preclinical cancer research. Nature 483: 531–533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Prinz F, Schlange T, Asadullah K (2011) Believe it or not: how much can we rely on published data on potential drug targets? Nat Rev Drug Discov 10: 712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Sena ES, van der Worp HB, Bath PM, Howells DW, Macleod MR (2010) Publication bias in reports of animal stroke studies leads to major overstatement of efficacy. PLoS Biol 8: e1000344 doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000344 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. van der Worp HB, Howells DW, Sena ES, Porritt MJ, Rewell S, et al. (2010) Can animal models of disease reliably inform human studies? PLoS Med 7: e1000245 doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shadish WR, Cook TD, Campbell DT (2002) Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
- 10. Fisher M, Feuerstein G, Howells DW, Hurn PD, Kent TA, et al. (2009) Update of the stroke therapy academic industry roundtable preclinical recommendations. Stroke 40: 2244–2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Altman DG, Simera I, Hoey J, Moher D, Schulz K (2008) EQUATOR: reporting guidelines for health research. Lancet 371: 1149–1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Recommendations for standards regarding preclinical neuroprotective and restorative drug development. Stroke 30: 2752–2758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Kilkenny C, Browne W, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2010) Animal research: reporting in vivo experiments: the ARRIVE guidelines. Br J Pharmacol 160: 1577–1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Kilkenny C, Browne W, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2011) Animal research: reporting in vivo experiments—the ARRIVE guidelines. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31: 991–993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2010) Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol 8: e1000412 doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000412 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Brouwers MC, Kho ME, Browman GP, Burgers JS, Cluzeau F, et al. (2010) AGREE II: advancing guideline development, reporting, and evaluation in health care. Prev Med 51: 421–424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cronbach LJ, Shapiro K (1982) Designing evaluations of educational and social programs. Hoboken (New Jersey): Jossey-Bass. 374 p.
- 18. Lamontagne F, Briel M, Duffett M, Fox-Robichaud A, Cook DJ, et al. (2010) Systematic review of reviews including animal studies addressing therapeutic interventions for sepsis. Crit Care Med 38: 2401–2408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Rushton L, Abrams KR (2006) A systematic review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of animal experiments with guidelines for reporting. J Environ Sci Health B 41: 1245–1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Briggs K, Cases M, Heard DJ, Pastor M, Pognan F, et al. (2012) Inroads to predict in vivo toxicology—an introduction to the eTOX Project. Int J Mol Sci 13: 3820–3846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Taylor CF, Field D, Sansone SA, Aerts J, Apweiler R, et al. (2008) Promoting coherent minimum reporting guidelines for biological and biomedical investigations: the MIBBI project. Nat Biotechnol 26: 889–896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Smith B, Ashburner M, Rosse C, Bard J, Bug W, et al. (2007) The OBO Foundry: coordinated evolution of ontologies to support biomedical data integration. Nat Biotechnol 25: 1251–1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kilkenny C, Parsons P, Kadyszewski E, Festing MF, Cuthill IC, et al. (2010) Survey of the quality of experimental design, statistical analysis and reporting of research using animals. PLoS One 4: e7824 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007824 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Reynolds JC, Rittenberger JC, Menegazzi JJ (2007) Drug administration in animal studies of cardiac arrest does not reflect human clinical experience. Resuscitation 74: 13–26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Scott S, Kranz JE, Cole J, Lincecum JM, Thompson K, et al. (2008) Design, power, and interpretation of studies in the standard murine model of ALS. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 9: 4–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. O'Collins VE, Macleod MR, Donnan GA, Horky LL, van der Worp BH, et al. (2006) 1,026 experimental treatments in acute stroke. Ann Neurol 59: 467–477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Noseworthy JH, Ebers GC, Vandervoort MK, Farquhar RE, Yetisir E, et al. (1994) The impact of blinding on the results of a randomized, placebo-controlled multiple sclerosis clinical trial. Neurology 44: 16–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Wood L, Egger M, Gluud LL, Schulz KF, Juni P, et al. (2008) Empirical evidence of bias in treatment effect estimates in controlled trials with different interventions and outcomes: meta-epidemiological study. BMJ 336: 601–605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Crossley NA, Sena E, Goehler J, Horn J, van der Worp B, et al. (2008) Empirical evidence of bias in the design of experimental stroke studies: a metaepidemiologic approach. Stroke 39: 929–934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Rooke ED, Vesterinen HM, Sena ES, Egan KJ, Macleod MR (2011) Dopamine agonists in animal models of Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 17: 313–320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Bath PM, Gray LJ, Bath AJ, Buchan A, Miyata T, et al. (2009) Effects of NXY-059 in experimental stroke: an individual animal meta-analysis. Br J Pharmacol 157: 1157–1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Hackam DG, Redelmeier DA (2006) Translation of research evidence from animals to humans. JAMA 296: 1731–1732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Odgaard-Jensen J, Vist GE, Timmer A, Kunz R, Akl EA, et al. (2011) Randomisation to protect against selection bias in healthcare trials. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011: MR000012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Woodcock J, Woosley R (2008) The FDA critical path initiative and its influence on new drug development. Annu Rev Med 59: 1–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gauthier C, Koëter H, Griffin G, Hendriksen C, Kavlock R, et al.. (2011) Montréal declaration on the synthesis of evidence to advance the 3Rs principles in science. Eighth World Congress on Alternatives and Animal Use in the Life Sciences; 21–25 August 2011; Montréal, Canada.
- 36. Margulies S, Hicks R (2009) Combination therapies for traumatic brain injury: prospective considerations. J Neurotrauma 26: 925–939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Ludolph AC, Bendotti C, Blaugrund E, Chio A, Greensmith L, et al. (2010) Guidelines for preclinical animal research in ALS/MND: a consensus meeting. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 11: 38–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Rice AS, Cimino-Brown D, Eisenach JC, Kontinen VK, Lacroix-Fralish ML, et al. (2008) Animal models and the prediction of efficacy in clinical trials of analgesic drugs: a critical appraisal and call for uniform reporting standards. Pain 139: 243–247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Grounds MD, Radley HG, Lynch GS, Nagaraju K, De Luca A (2008) Towards developing standard operating procedures for pre-clinical testing in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurobiol Dis 31: 1–19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Willmann R, Luca AD, Benatar M, Grounds M, Dubach J, et al. (2012) Enhancing translation: guidelines for standard pre-clinical experiments in mdx mice. Neuromuscul Disord 22: 43–49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Eccles M, Clapp Z, Grimshaw J, Adams PC, Higgins B, et al. (1996) North of England evidence based guidelines development project: methods of guideline development. BMJ 312: 760–762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Graham R, Mancher M, Wolman DM, Greenfield S, Steinberg E, editors (2011) Clinical practice guidelines we can trust. Washington (District of Columbia): The National Academies Press. [PubMed]
- 43. Announcement: Reducing our irreproducibility. Nature 496: 398. [Google Scholar]
- 44. Schwartz RS, Edelman E, Virmani R, Carter A, Granada JF, et al. (2008) Drug-eluting stents in preclinical studies: updated consensus recommendations for preclinical evaluation. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 1: 143–153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Verhagen H, Aruoma OI, van Delft JH, Dragsted LO, Ferguson LR, et al. (2003) The 10 basic requirements for a scientific paper reporting antioxidant, antimutagenic or anticarcinogenic potential of test substances in in vitro experiments and animal studies in vivo. Food Chem Toxicol 41: 603–610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. García-Bonilla L, Rosell A, Torregrosa G, Salom JB, Alborch E, et al. (2011) Recommendations guide for experimental animal models in stroke research. Neurologia 26: 105–110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kelloff GJ, Johnson JR, Crowell JA, Boone CW, DeGeorge JJ, et al.. (1994) Guidance for development of chemopreventive agents. J Cell Biochem (Suppl 20): 25–31. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 48. Kamath AT, Fruth U, Brennan MJ, Dobbelaer R, Hubrechts P, et al. (2005) New live mycobacterial vaccines: the Geneva consensus on essential steps towards clinical development. Vaccine 23: 3753–3761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P (2004) Acute renal failure—definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care 8: R204–R212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Moreno B, Espejo C, Mestre L, Suardiaz M, Clemente D, et al. (2012) [Guidelines on the appropriate use of animal models for developing therapies in multiple sclerosis.]. Rev Neurol 54: 114–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Walker MJ, Curtis MJ, Hearse DJ, Campbell RW, Janse MJ, et al. (1988) The Lambeth Conventions: guidelines for the study of arrhythmias in ischaemia infarction, and reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res 22: 447–455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Curtis M, Hancox J, Farkas A, Wainwright C, Stables C, et al. (2013) The Lambeth Conventions (II): guidelines for the study of animal and human ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias. . Pharmacol Ther E-pub ahead of print. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.04.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Piper RD, Cook DJ, Bone RC, Sibbald WJ (1996) Introducing critical appraisal to studies of animal models investigating novel therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med 24: 2059–2070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Liu S, Zhen G, Meloni BP, Campbell K, Winn HR (2009) Rodent stroke model guidelines for preclinical stroke trials (1st edition). J Exp Stroke Transl Med 2: 2–27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Landis SC, Amara SG, Asadullah K, Austin CP, Blumenstein R, et al. (2012) A call for transparent reporting to optimize the predictive value of preclinical research. Nature 490: 187–191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Bolon B, Stolina M, King C, Middleton S, Gasser J, et al. (2011) Rodent preclinical models for developing novel antiarthritic molecules: comparative biology and preferred methods for evaluating efficacy. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011: 569068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Macleod MR, Fisher M, O'Collins V, Sena ES, Dirnagl U, et al. (2009) Good laboratory practice: preventing introduction of bias at the bench. Stroke 40: e50–e52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.US National Institutes of Health National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (2011) Improving the quality of NINDS-supported preclinical and clinical research through rigorous study design and transparent reporting. Bethesda (Maryland): US National Institutes of Health National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
- 59. Pullen N, Birch CL, Douglas GJ, Hussain Q, Pruimboom-Brees I, et al. (2011) The translational challenge in the development of new and effective therapies for endometriosis: a review of confidence from published preclinical efficacy studies. Hum Reprod Update 17: 791–802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Shineman DW, Basi GS, Bizon JL, Colton CA, Greenberg BD, et al. (2011) Accelerating drug discovery for Alzheimer's disease: best practices for preclinical animal studies. Alzheimers Res Ther 3: 28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Bolli R, Becker L, Gross G, Mentzer R Jr, Balshaw D, et al. (2004) Myocardial protection at a crossroads: the need for translation into clinical therapy. Circ Res 95: 125–134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Stem Cell Therapies as an Emerging Paradigm in Stroke Participants (2009) Stem Cell Therapies as an Emerging Paradigm in Stroke (STEPS): bridging basic and clinical science for cellular and neurogenic factor therapy in treating stroke. Stroke 40: 510–515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Savitz SI, Chopp M, Deans R, Carmichael ST, Phinney D, et al. (2011) Stem Cell Therapy as an Emerging Paradigm for Stroke (STEPS) II. Stroke 42: 825–829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Katz DM, Berger-Sweeney JE, Eubanks JH, Justice MJ, Neul JL, et al. (2012) Preclinical research in Rett syndrome: setting the foundation for translational success. Dis Model Mech 5: 733–745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The PRISMA checklist.
(DOC)
STREAM (Studies of Translation, Ethics and Medicine) checklist for design and evaluation of preclinical efficacy studies supporting clinical translation.
(PDF)