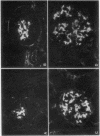
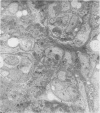
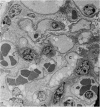
Abstract
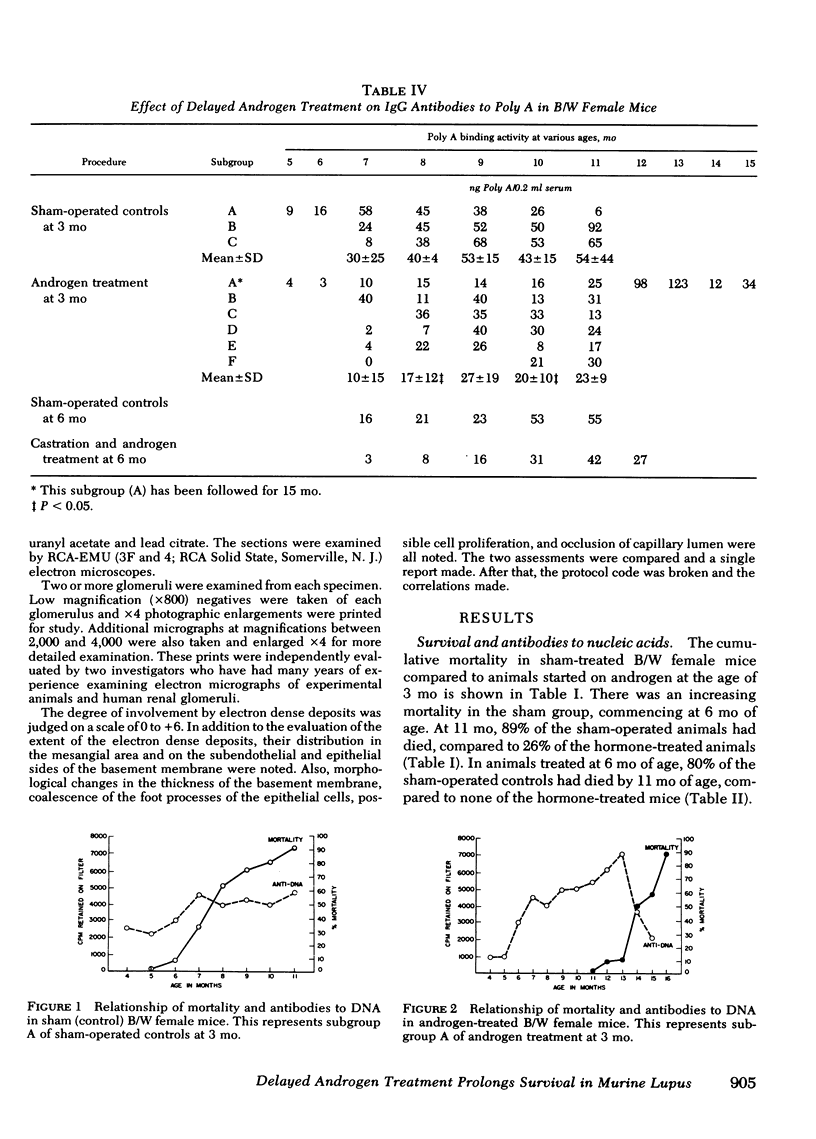
Female NZB/NZW F1 mice were treated as adults with 5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone powder packed into subcutaneous implants. Two treatment protocols were followed: (a) 3-mo-old mice received 6 mg of androgen, and (b) 6-mo-old mice were castrated and given 12 mg of androgen. Sham females received empty implants. Mice were followed monthly for surival, for antibodies to DNA and polyadenylic acid, and for renal histopathology. The percent survival at 11 mo was 74% for mice treated at 3 mo, compared to 11% for the sham controls, and 100% for mice treated at 6 mo, compared to 20% for their sham controls. Androgen-treated mice had less immune complex glomerulonephritis as determined by immunofluorescent and electron microscopy. Surprisingly, treated mice had no significant sustained reduction in antibodies to DNA although they had reduced antibodies to polyadenylic acid. These results suggest that androgens can still prolong survival and reduce immune complex deposition even when treatment is delayed to an age when disease is relatively established. After delayed androgen treatment, mice survive despite the presence of high levels of IgG antibodies to DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attias M. R., Sylvester R. A., Talal N. Filter radioimmunoassay for antibodies to reovirus RNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Nov-Dec;16(6):719–725. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., EVANS R. R. A BIOCHEMICAL ABNORMALITY IN HEREDIATRY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: ABSENCE OF SERUM INHIBITOR OF C' 1-ESTERASE. Am J Med. 1963 Jul;35:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Takahashi M., Nussenzweig V. Purificaiton and characterization of mouse serum protein with specific binding affinity for C4 (Ss protein). J Exp Med. 1977 Oct 1;146(4):1001–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.4.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Sherins R. J., Alling D. W., Frank M. M. Treatment of hereditary angioedema with danazol. Reversal of clinical and biochemical abnormalities. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 23;295(26):1444–1448. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612232952602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie J. B., Helyer B. J. The immunology and pathology of NZB mice. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:215–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raveche E. S., Klassen L. W., Steinberg A. D. Sex differences in formation of anti-T-cell antibodies. Nature. 1976 Sep 30;263(5576):415–416. doi: 10.1038/263415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubinian J. R., Papoian R., Talal N. Androgenic hormones modulate autoantibody responses and improve survival in murine lupus. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1066–1070. doi: 10.1172/JCI108729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubinian J. R., Talal N., Greenspan J. S., Goodman J. R., Siiteri P. K. Effect of castration and sex hormone treatment on survival, anti-nucleic acid antibodies, and glomerulonephritis in NZB/NZW F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1568–1583. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D. C. The S region of the mouse major histocompatibility complex (H-2): genetic variation and functional role in complement system. Transplant Rev. 1976;32:140–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N. Immunologic and viral factors in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):887–894. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]