Abstract
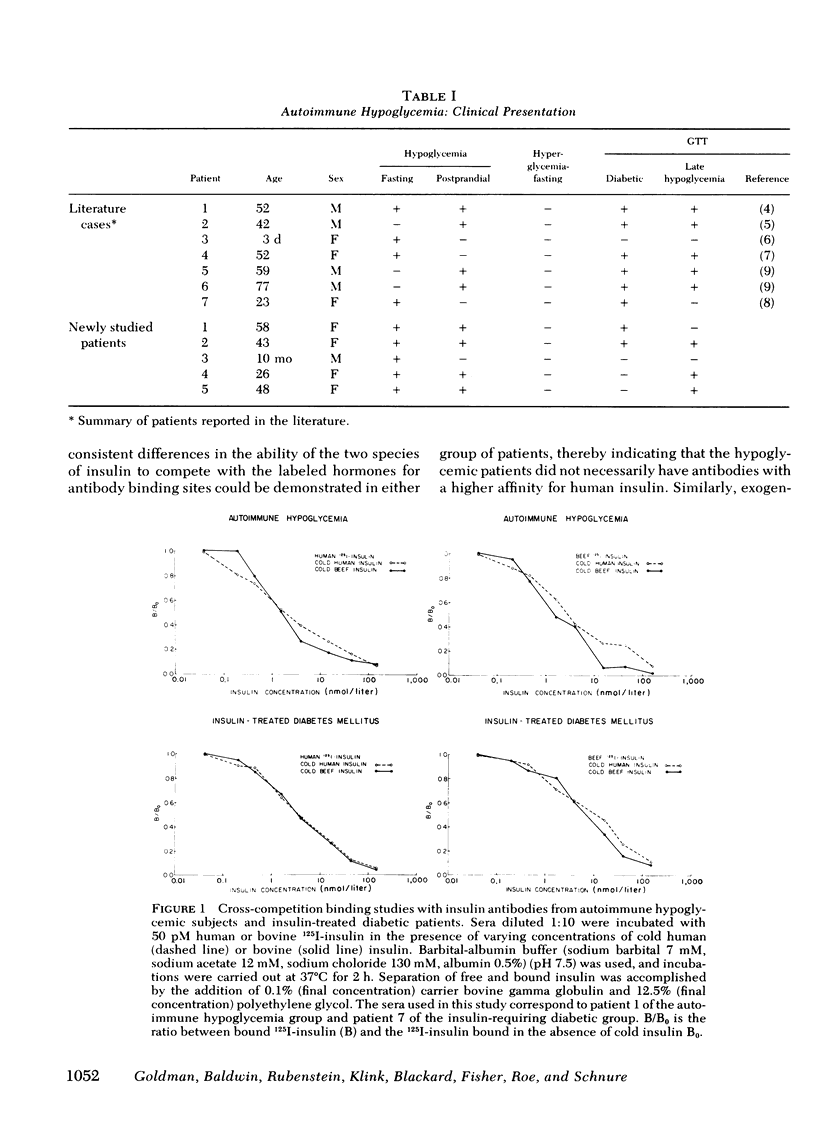
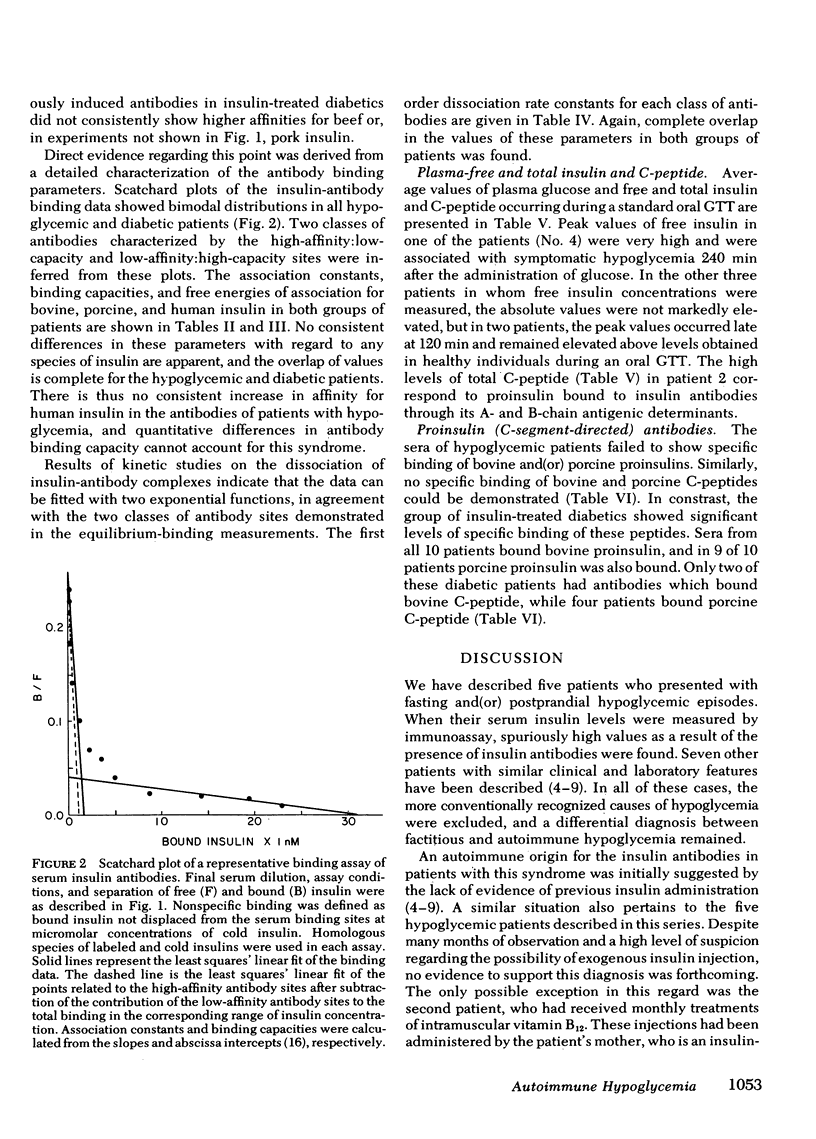
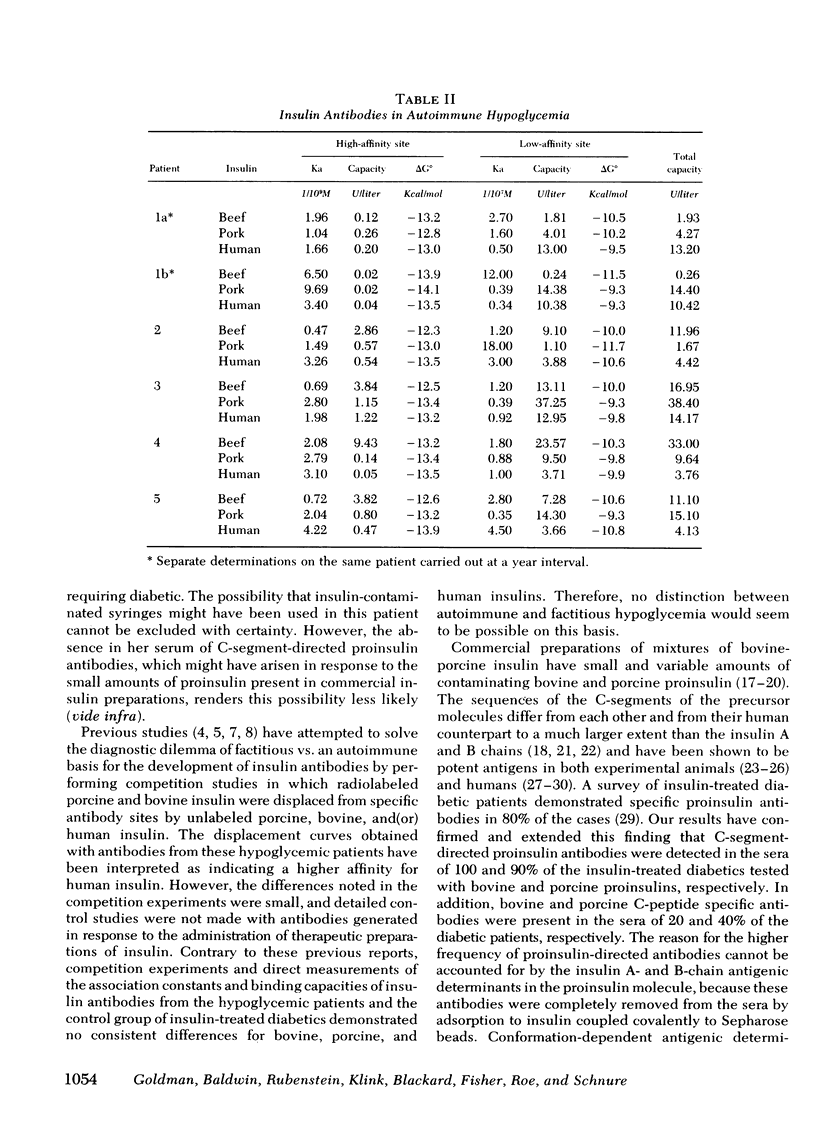
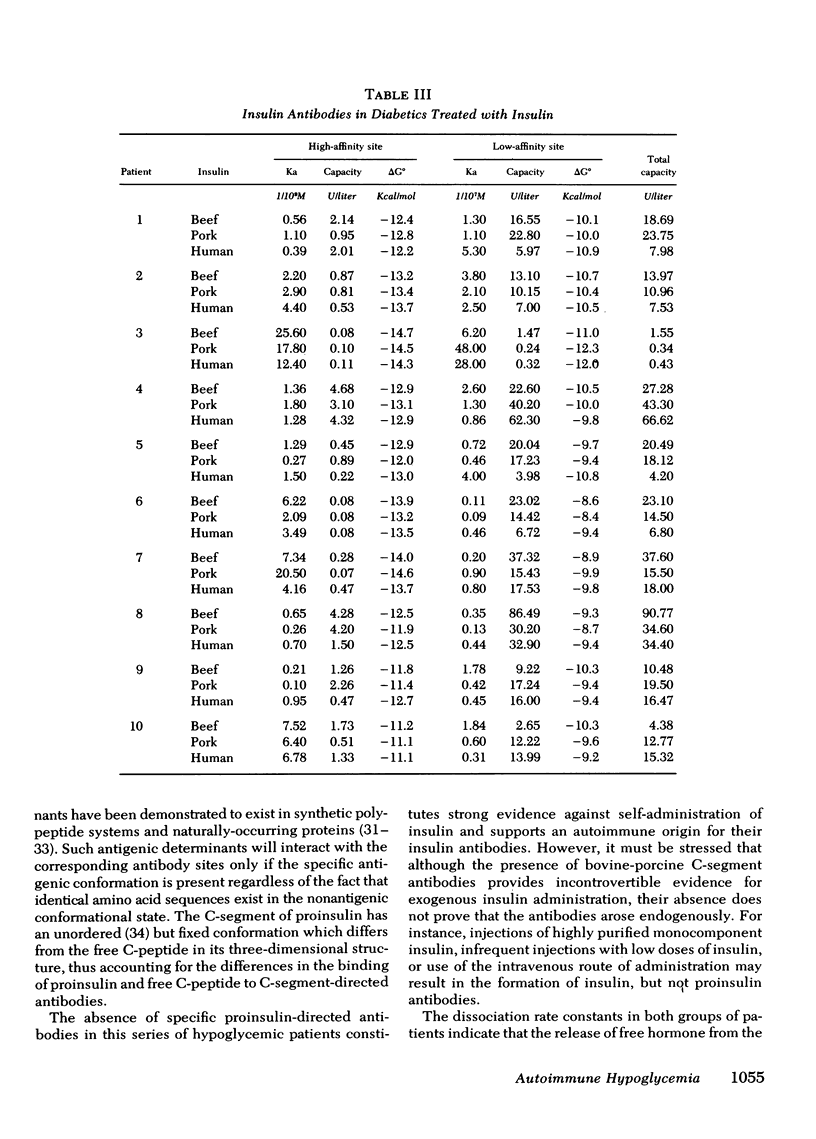
Five patients with fasting and(or) postprandial hypoglycemia were found to have insulin antibodies in the absence of previously documented immunization. Studies on the equilibrium-binding of insulin to the autoantibodies revealed two classes of binding sites with association constants and binding capacities analogous to those of insulin antibodies from insulin-treated diabetic patients. Similarly, no consistent differences in these parameters were found in both groups of patients with insulins of bovine, porcine, and human origin. Proinsulin (C-segment directed) antibodies capable of binding bovine or porcine proinsulin were present in 10 of 10 and 9 of 10 insulin-treated diabetics serving as controls, respectively, and, when present, provide incontrovertible evidence of exogenous insulin administration. No such antibodies could be detected in the hypoglycemic patients with autoimmune insulin antibodies. The kinetics of dissociation of the insulin-antibody complexes were consistent with the existence of two classes of antibody sites. The corresponding dissociation rate constants were large enough to predict that significant amounts of free hormone may be generated by this mechanism and provide a plausible pathogenesis for the hypoglycemia in these patients.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. H., Jr, Blackard W. G., Goldman J., Rubenstein A. H. Diabetes and hypoglycemia due to insulin antibodies. Am J Med. 1978 May;64(5):868–873. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S., BAUMAN A., ROTHSCHILD M. A., NEWERLY K. Insulin-I131 metabolism in human subjects: demonstration of insulin binding globulin in the circulation of insulin treated subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):170–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI103262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba S., Morita S., Mizuno N., Okada K. Letter: Autoimmunity to glucagon in a diabetic not on insulin. Lancet. 1976 Sep 11;2(7985):585–585. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91846-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance R. E., Ellis R. M., Bromer W. W. Porcine proinsulin: characterization and amino acid sequence. Science. 1968 Jul 12;161(3837):165–167. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3837.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folling I., Norman N. Hyperglycemia, hypoglycemic attacks, and production of anti-insulin antibodies without previous known immunization. Immunological and functional studies in a patient. Diabetes. 1972 Jul;21(7):814–826. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.7.814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. H., Sela M. Recovery of specific activity upon reoxidation of completely reduced polyalanyl rabbit antibody. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 25;241(22):5225–5232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland B. C., Baxter E., Evans R. S. Red-cell antibodies in acquired hemolytic anemia with negative antiglobulin serum tests. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 29;285(5):252–256. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107292850503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding P. L., Smith M., Williams R. Multisystem involvement in chronic liver disease. Studies on the incidence and pathogenesis. Am J Med. 1973 Dec;55(6):772–782. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J., Baldwin D., Pugh W., Rubenstein A. H. Equilibrium binding assay and kinetic characterization of insulin antibodies. Diabetes. 1978 Jun;27(6):653–660. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.6.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARWOOD R. Insulin-binding antibodies and "spontaneous" hypoglycemia. N Engl J Med. 1960 May 12;262:978–979. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196005122621908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H. J., Menzel R., Gottschling H. D., Jahr D. Enhancement of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from isolated rat pancreatic islets by human insulin antibodies. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1976 Sep;83(1):123–132. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0830123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Ishizu H. Elevated insulin-binding capacity of serum proteins in a case with spontaneous hypoglycemia and mild diabetes not treated with insulin. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1972 Jul;107(3):277–286. doi: 10.1620/tjem.107.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Tominaga M., Ito J. I., Noguchi A. Spontaneous hypoglycemia with insulin autoimmunity in Graves' disease. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Aug;81(2):214–218. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-2-214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara K., Shima K., Saito Y., Nonaka K., Tarui S. Mechanism of hypoglycemia observed in a patient with insulin autoimmune syndrome. Diabetes. 1977 May;26(5):500–506. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.5.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Flier J. S., Bar R. S., Archer J. A., Gorden P., Martin M. M., Roth J. The syndromes of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. Insulin-receptor disorders in man. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):739–745. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpatkin S., Strick N., Karpatkin M. B., Siskind G. W. Cumulative experience in the detection of antiplatelet antibody in 234 patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, systemic lupus erythematosus and other clinical disorders. Am J Med. 1972 Jun;52(6):776–785. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawazu S., Kanazawa Y., Kajinuma H., Miki E., Kuzuya T., Kosaka K. Demonstration of anti-"a-component" antibody--a possible means to differentiate patients with auto-antibodies to endogenous insulin from insulin-treated patients. Diabetologia. 1975 Jun;11(3):169–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00422317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerp L., Steinhilber S., Kasemir H. Besitzt die Proinsulinverunreinigung kommerzieller Insulinpräparate Bedeutung für die Stimulierung von Insulinantikörpern. Klin Wochenschr. 1970 Jul 15;48(14):884–885. doi: 10.1007/BF01583916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar D., Miller L. V. Proinsulin-specific antibodies in human sera. Diabetes. 1973 May;22(5):361–366. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.5.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar D., Miller L. V. The prevalence of proinsulin-specific antibodies in diabetic patients. Horm Metab Res. 1973 Jan;5(1):1–3. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzuya H., Blix P. M., Horwitz D. L., Steiner D. F., Rubenstein A. H. Determination of free and total insulin and C-peptide in insulin-treated diabetics. Diabetes. 1977 Jan;26(1):22–29. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis L. A., deWolfe V. D., Butkus A., Page I. H. Autoimmune hyperlipidemia in a patient. Atherosclerotic course and chaning immunoglobulin pattern during 21 years of study. Am J Med. 1975 Aug;59(2):208–218. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90355-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLS J. A., HABER E. THE EFFECT ON ANTIGENIC SPECIFICITY OF CHANGES IN THE MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF RIBONUCLEASE. J Immunol. 1963 Oct;91:536–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa S., Suda N., Kudo M., Kawasaki M. A new type of hypoglycaemia in a newborn infant. Diabetologia. 1973 Oct;9(5):367–375. doi: 10.1007/BF01239429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan C., Margoliash E., Peterson J. D., Steiner D. F. The structure of bovine proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2780–2795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oneda A., Matsuda K., Sato M., Yamagata S., Sato T. Hypoglycemia due to apparent autoantibodies to insulin. Characterization of insulin-binding protein. Diabetes. 1974 Jan;23(1):41–50. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyer P. E., Cho S., Peterson J. D., Steiner D. F. Studies on human proinsulin. Isolation and amino acid sequence of the human pancreatic C-peptide. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1375–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root M. A., Chance R. E., Galloway J. A. Immunogenicity of insulin. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):657–660. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F., Cho S., Lawrence A. M., Kirsteins L. Immunological properties of bovine proinsulin and related fractions. Diabetes. 1969 Sep;18(9):598–605. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.9.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Welbourne W. P., Mako M., Melani F., Steiner D. F. Comparative immunology of bovine, porcine and human proinsulins and C-peptides. Diabetes. 1970 Aug;19(8):546–553. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.8.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichtkrull J., Brange J., Christiansen A. H., Hallund O., Heding L. G., Jorgensen K. H. Clinical aspects of insulin--antigenicity. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):649–656. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Taylor J. M., McKnight G. S., Palacios R., Gonzalez C., Kiely M. L., Schimke R. T. Isolation of hen oviduct ovalbumin and rat live albumin polysomes by indirect immunoprecipitation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3665–3671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Hallund O., Rubenstein A., Cho S., Bayliss C. Isolation and properties of proinsulin, intermediate forms, and other minor components from crystalline bovine insulin. Diabetes. 1968 Dec;17(12):725–736. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.12.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Logothetopoulos J. A specific anti-proinsulin serum and the presence of proinsulin in calf serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):415–419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



