Abstract
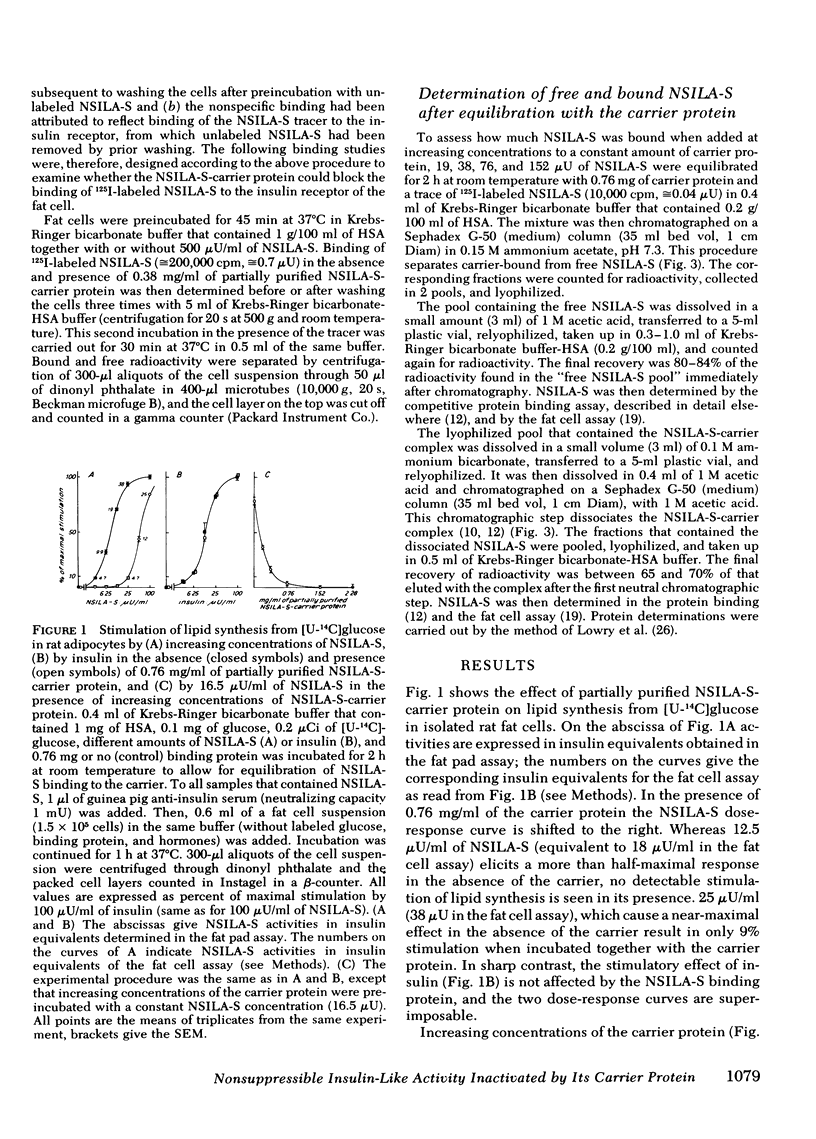
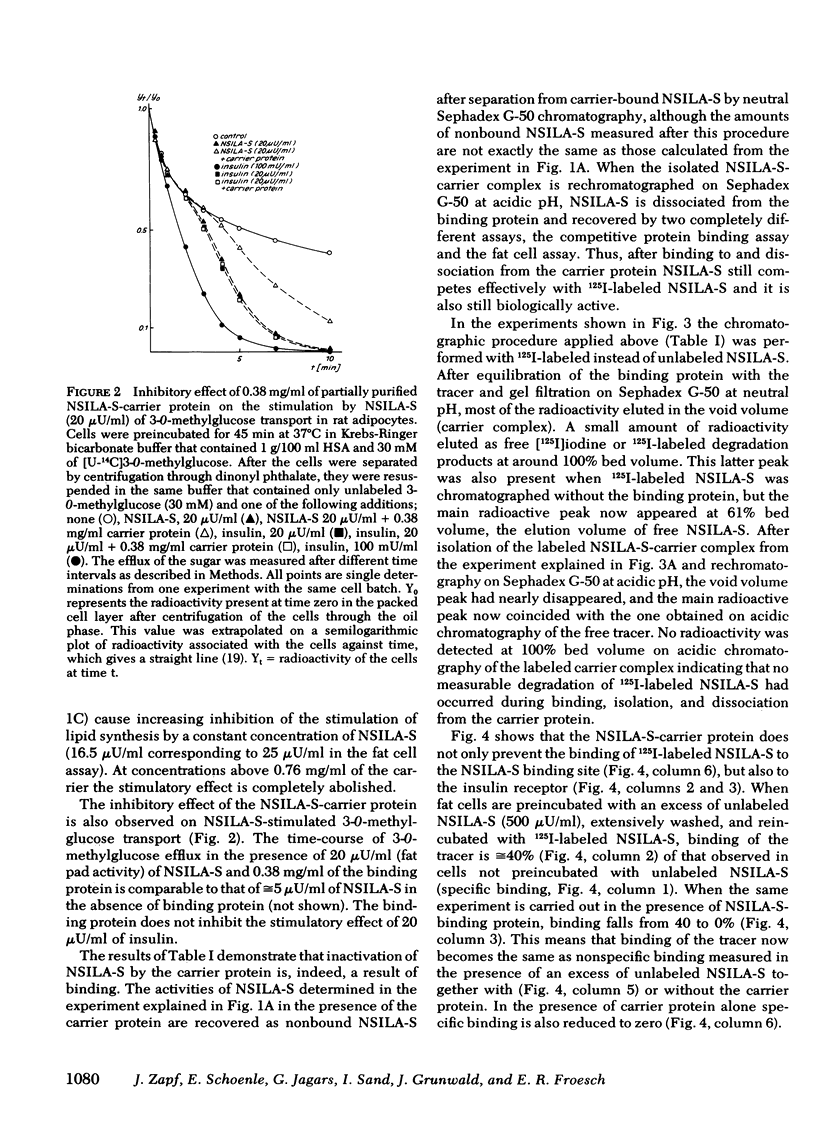
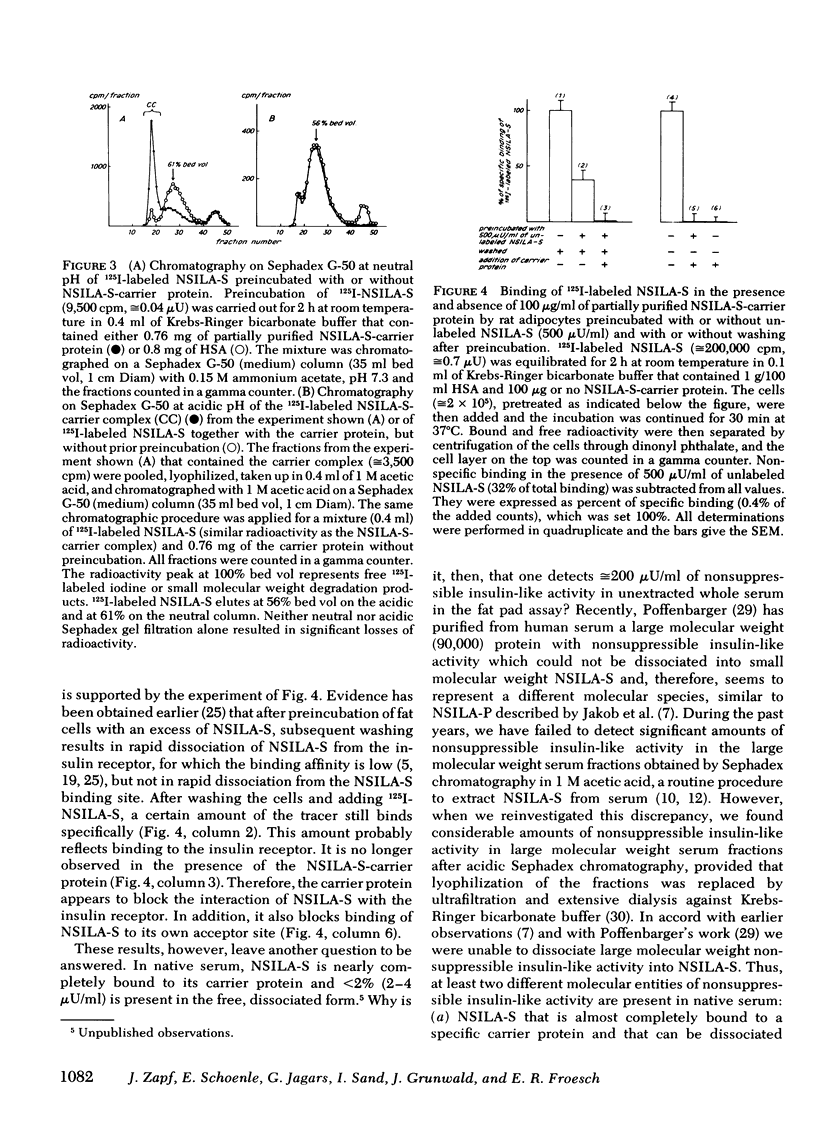
Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity extracted and purified from human serum (NSILA-S) mimics all insulin-like effects in vitro and, after injection, in vivo in the presence of excess insulin antibodies. However, there is no evidence that it exerts acute insulin-like effects in its native form in the circulation, where it is almost completely bound to a specific large molecular weight carrier protein. In this paper we show that partially purified NSILA-S-carrier protein, devoid of endogenous insulin-like activity, inhibits the stimulatory effect of NSILA-S, but not of insulin, on 3-0-methylglucose transport and on lipogenesis from [U-14C]glucose in isolated rat fat cells. Concomitantly, it prevents binding of 125I-labeled NSILA-S to the insulin receptor and to the NSILA-S-binding site.
The following explanation is, therefore, offered for the absence of acute insulin-like effects of native NSILA-S in vivo: In native serum NSILA-S occurs almost exclusively as NSILA-S-carrier complex. According to recent findings the passage of this complex through blood capillaries is restricted. The present results indicate that, in addition, it is metabolically inactive, or, at least, possesses reduced metabolic activity. The well-known phenomenon that whole serum, nevertheless, exerts pronounced nonsuppressible insulin-like effects on adipose tissue in vitro seems, therefore, to be mainly caused by the presence of a large molecular weight insulin-like protein not identical to the NSILA-S-carrier complex.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bürgi H., Müller W. A., Humbel R. E., Labhart A., Froesch E. R. Non-suppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. I. Physicochemical properties, extraction and partial purification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 29;121(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chochinov R. H., Daughaday W. H. Current concepts of somatomedin and other biologically related growth factors. Diabetes. 1976 Oct;25(10):994–1004. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.10.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAUGHADAY W. H., SALMON W. D., Jr, ALEXANDER F. Sulfation factor activity of sera from patients with pituitary disorders. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1959 Jul;19(7):743–758. doi: 10.1210/jcem-19-7-743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROESCH E. R., BUERGI H., RAMSEIER E. B., BALLY P., LABHART A. ANTIBODY-SUPPRESSIBLE AND NONSUPPRESSIBLE INSULIN-LIKE ACTIVITIES IN HUMAN SERUM AND THEIR PHYSIOLOGIC SIGNIFICANCE. AN INSULIN ASSAY WITH ADIPOSE TISSUE OF INCREASED PRECISION AND SPECIFICITY. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1816–1834. doi: 10.1172/JCI104866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Müller W. A., Bürgi H., Waldvogel M., Labhart A. Non-suppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. II. Biological properties of plasma extracts with non-suppressible insulin-like activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 29;121(2):360–374. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Zapf J., Audhya T. K., Ben-Porath E., Segen B. J., Gibson K. D. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity and thyroid hormones: major pituitary-dependent sulfation factors for chick embryo cartilage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2904–2908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Osterlind K., Vinten J., Gammeltoft S. A procedure for measurement of distribution spaces in isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 24;286(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakob A., Hauri C., Froesch E. R. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity in human serum. 3. Differentiation of two distinct molecules with nonsuppressible ILA. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2678–2688. doi: 10.1172/JCI105951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann U., Zapf J., Torretti B., Froesch E. R. Demonstration of a specific serum carrier protein of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Jan;44(1):160–166. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-1-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megyesi K., Kahn C. R., Roth J., Gorden P. Circulating NSILA-s in man: Preliminary studies of stimuli in vivo and of binding to plasma components. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Sep;41(3):475–484. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-3-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuli C., Froesch E. R. Binding of insulin and nonsuppressible insulin-like activity to isolated perfused rat heart muscle. Evidence for two separate binding sites. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Nov;177(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuli C., Froesch E. R. Insulin and nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S) stimulate the same glucose transport system via two separate receptors in rat heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 11;75(3):689–695. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuli C., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. NSILA-carrier protein abolishes the action of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S) on perfused rat heart. Diabetologia. 1978 Apr;14(4):255–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01219425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell B., Froesch E. R. Fibroblasts as an experimental tool in metabolic and hormone studies. II. Effects of insulin and nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S) on fibroblasts in culture. Eur J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;3(2):119–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1973.tb00338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelz O., Jakob A., Froesch E. R. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) of human serum. V. Hypoglycaemia and preferential metabolic stimulation of muscle by NSILA-S. Eur J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;1(1):48–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1970.tb00596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poffenbarger P. L. The purification and partial characterization of an insulin-like protein from human serum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1455–1463. doi: 10.1172/JCI108226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasio E. A., Mack E., Egdahl R. H., Herrera M. G. Passage of insulin and inulin across vascular membranes in the dog. Diabetes. 1968 Nov;17(11):668–672. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.11.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Goldfine I. D., Wells C. A. DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts: stimulation by insulin and by nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Sep;39(3):512–521. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-3-512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Amino-terminal sequences of two polypeptides from human serum with nonsuppressible insulin-like and cell-growth-promoting activities: evidence for structural homology with insulin B chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4379–4381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Polypeptides with nonsuppressible insulin-like and cell-growth promoting activities in human serum: isolation, chemical characterization, and some biological properties of forms I and II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2365–2369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlumpf U., Heimann R., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Non-suppressible insulin-like activity and sulphaton activity in serum extracts of normal subjects, acromegalics and pituitary dwarfs. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1976 Jan;81(1):28–42. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0810028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Binding of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) to isolated fat cells: evidence for two separate membrane acceptor sites. FEBS Lett. 1976 Aug 15;67(2):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Effects of insulin and NSILA on adipocytes of normal and diabetic rats: receptor binding, glucose transport and glucose metabolism. Diabetologia. 1977 May;13(3):243–249. doi: 10.1007/BF01219707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Receptor binding and effects of insulin and NSILA-S on glucose transport and metabolism in adipocytes from hypophysectomized rats. Diabetologia. 1979 Jan;16(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00423149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinten J., Gliemann J., Osterlind K. Exchange of 3-O-methylglucose in isolated fat cells. Concentration dependence and effect of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):794–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Jagars G., Sand I., Froesch E. R. Evidence for the existence in human serum of large molecular weight nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) different from the small molecular weight forms. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 1;90(1):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Kaufmann U., Eigenmann E. J., Froesch E. R. Determination of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity in human serum by a sensitive protein-binding assay. Clin Chem. 1977;23(4):677–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Mäder M., Waldvogel M., Schalch D. S., Froesch E. R. Specific binding of nonsupressible insulinlike activity to chicken embryo fibroblasts and to a solubilized fibroblast receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):630–637. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90295-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) from human serum: recent accomplishments and their physiologic implications. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12):1803–1828. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors I and II: some biological actions and receptor binding characteristics of two purified constituents of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):285–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Binding of nonsuppressible insulinlike activity to human serum. Evidence for a carrier protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):638–645. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zingg A. E., Froesch E. R. Effects of partially purified preparations with nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S) on sulfate incorporation into rat and chicken cartilage. Diabetologia. 1973 Dec;9(6):472–476. doi: 10.1007/BF00461691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


