Abstract
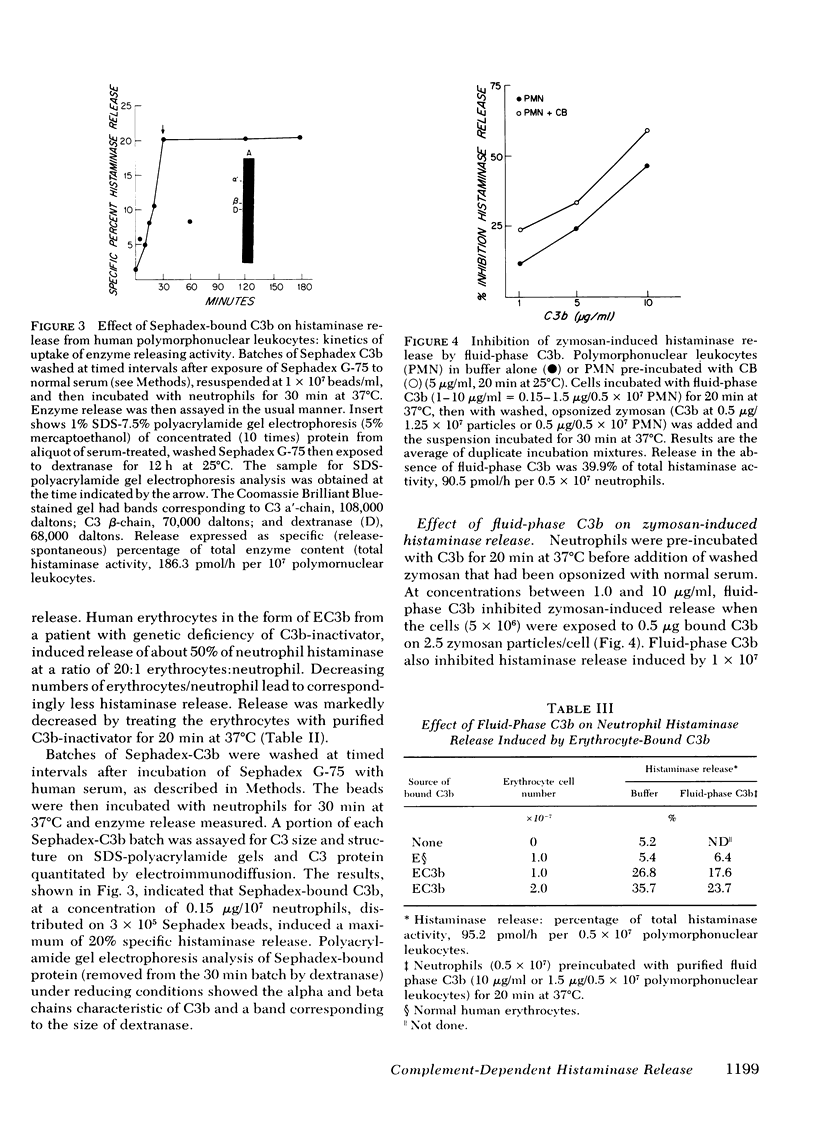
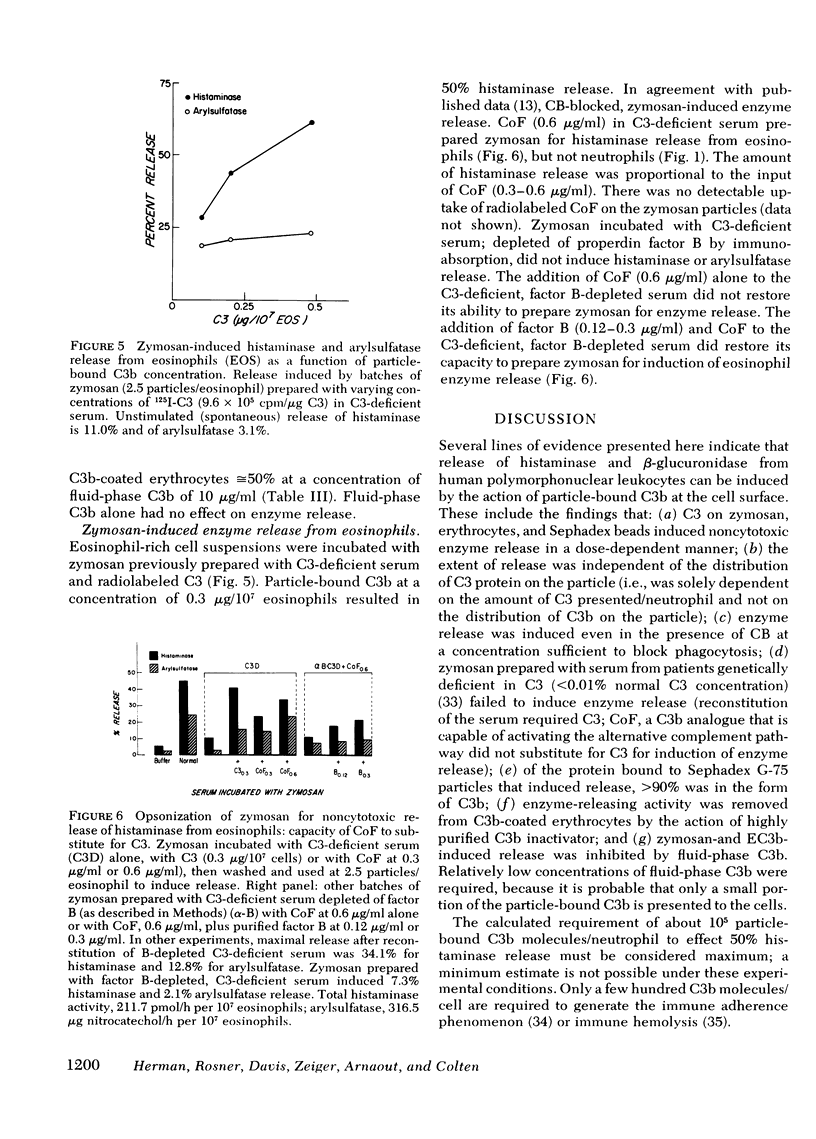
The role of particle-bound complement proteins in the induction of noncytotoxic enzyme release from human granulocytes was investigated with the use of sera genetically deficient in complement and highly purified complement components. Release of histaminase, one of two important histamine catabolizing enzymes, and beta-glucuronidase from polymorphonuclear leukocytes was solely dependent on particle-bound C3b (the larger cleavage product of the third component of complement) when fluid-phase complement was excluded. The extent of enzyme release was a function of particle-bound C3b input, was reduced by exposing the particles to C3b inactivator, and was blocked by fluid-phase C3b. Phagocytosis of the C3b-coated particles was not required for enzyme release from neutrophils. In contrast, phagocytosis of "opsonized" particles was required for noncytotoxic release of histaminase and arylsulfatase from eosinophils; other proteins, as well as C3b, were able to opsonize particles for induction of enzyme release from eosinophils. These studies suggest a dual role for complement (particularly C3) in modulating vascular permeability phenomena, i.e., release of vasoactive mediators by the action of C3a and C5a, and release of the corresponding enzymes that inactivate the mediators by C3b.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson N., Alper C. A., Lachmann P. J., Rosen F. S., Jandl J. H. Deficiency of C3 inactivator in man. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Colten H. R., Rosen F. S., Rabson A. R., Macnab G. M., Gear J. S. Homozygous deficiency of C3 in a patient with repeated infections. Lancet. 1972 Dec 2;2(7788):1179–1181. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92598-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Genetics of the complement system. Adv Hum Genet. 1976;7:141–188. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0659-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballow M., Cochrane C. G. Two anticomplementary factors in cobra venom: hemolysis of guinea pig erythrocytes by one of them. J Immunol. 1969 Nov;103(5):944–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boenisch T., Alper C. A. Isolation and properties of a glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein of human serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 22;221(3):529–535. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Cochrane C. G. Isolation of a fragment (C3a) of the third component of human complement containing anaphylatoxin and chemotactic activity and description of an anaphylatoxin inactivator of human serum. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1109–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of leucocytes from human blood. A two-phase system for removal of red cells with methylcellulose as erythrocyte-aggregating agent. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:9–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R., Alper C. A. Hemolytic efficiencies of genetic variants of human C3. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1184–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels C. A., Borsos T., Rapp H. J., Snyderman R., Notkins A. L. Neutralization of sensitized virus by purified components of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):528–535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I., Hoffstein S., Gallin J., Weissmann G. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes: microtubule assembly and membrane fusion induced by a component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2916–2920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R., Hugli T. E., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Release of histamine from rat mast cells by the complement peptides C3a and C5a. Immunology. 1975 Jun;28(6):1067–1080. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN L. M., OSLER A. G. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISMS OF HYPERSENSITIVITY PHENOMENA. IX. HISTAMINE RELEASE FROM HUMAN LEUKOCYTES BY RAGWEED POLLEN ANTIGEN. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:507–530. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe D. D., Gadek J. E., Raphael G. D., Frank M. M., Kaplan A. P., Kaliner M. Human eosinophil adherence to serum-treated sepharose: granule-associated enzyme release and requirement for activation of the alternative complement pathway. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1744–1750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON U. R., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. ISOLATION OF BETA IF-GLOBULIN FROM HUMAN SERUM AND ITS CHARACTERIZATION AS THE FIFTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:277–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson U. R., Mandle R. J., Jr, McConnell-Mapes J. A. Human C3 and C5: subunit structure and modifications by trypsin and C42-C423. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):815–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E., Fauci A. S. Human eosinophils. Purification and cytotoxic capability of eosinophils from patients with the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood. 1978 Mar;51(3):457–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P., Kulczycki A., Jr, Mendoza G., Metzger H. Ionophore A-23187 induced histamine release from rat mast cells and rat basophil leukemia (RBL-1) cells. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1599–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULMER D. D., VALLEE B. L., WACKER W. E. Metalloenzymes and myocardial infarction. II. Malic and lactic dehydrogenase activities and zinc concentrations in serum. N Engl J Med. 1956 Sep 6;255(10):450–456. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195609062551001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD P. A., COCHRANE C. G., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. THE ROLE OF SERUM COMPLEMENT IN CHEMOTAXIS OF LEUKOCYTES IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:327–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I., Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Inactivation of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis by human eosinophil arylsulfatase. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):645–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger R. S., Colten H. R. Histaminase release from human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):540–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger R. S., Twarog F. J., Colten H. R. Histaminase release from human granulocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1049–1061. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger R. S., Yurdin D. L., Colten H. R. Histamine metabolism. II. Cellular and subcellular localization of the catabolic enzymes, histaminase and histamine methyl transferase, in human leukocytes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1976 Jul;58(1 Pt 2):172–179. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(76)90152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger R. S., Yurdin D. L., Twarog F. J. Histamine metabolism. I. Thin-layer radiochromatographic assays for histaminase and histidine decarboxylase enzyme activities. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jun;87(6):1065–1074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler J. B., Alper C. A., Rosen R. S., Lachmann P. J., Sherington L. Restoration by purified C3b inactivator of complement-mediated function in vivo in a patient with C3b inactivator deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):668–672. doi: 10.1172/JCI107975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


