Abstract
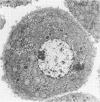
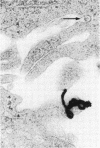
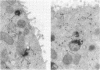
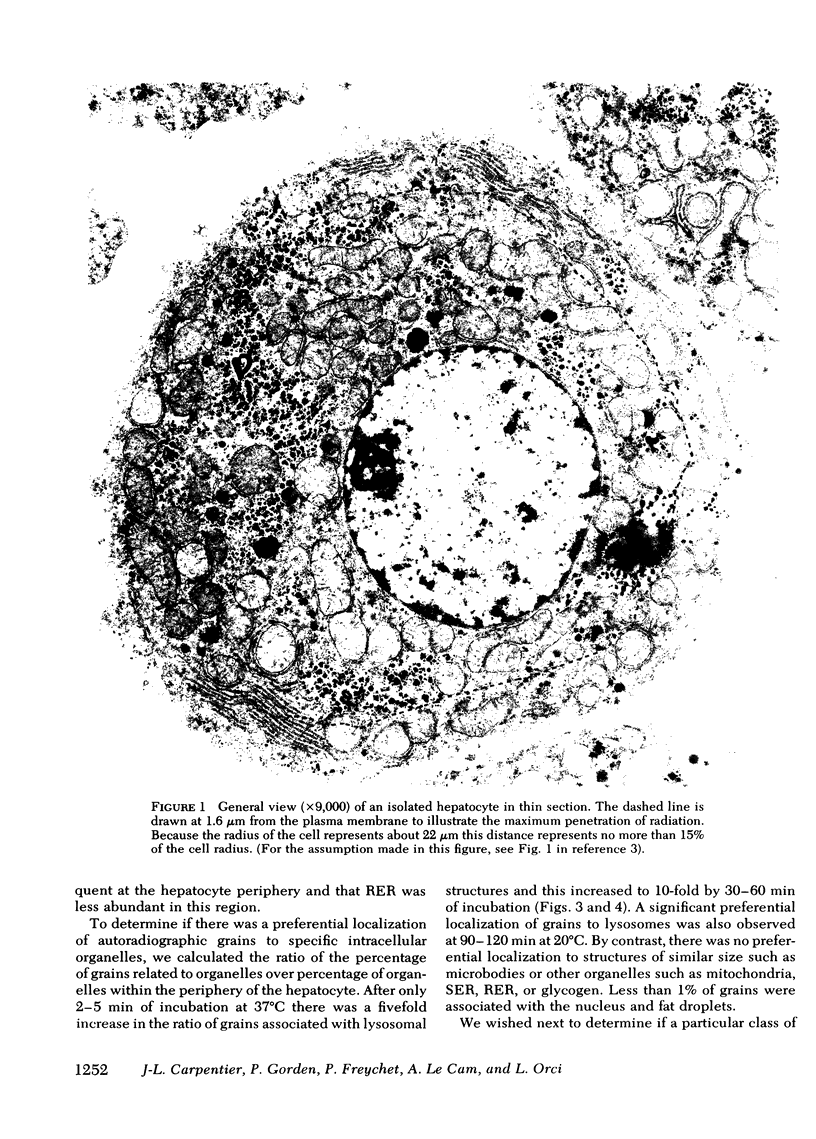
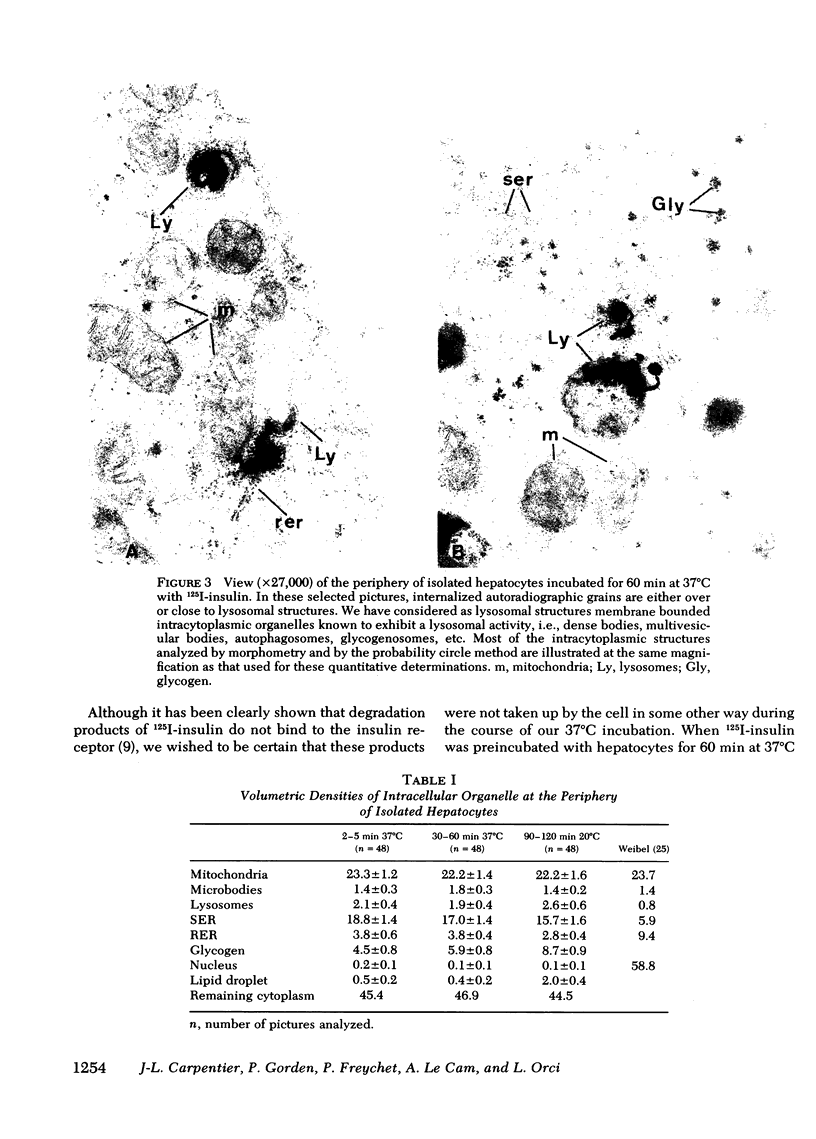
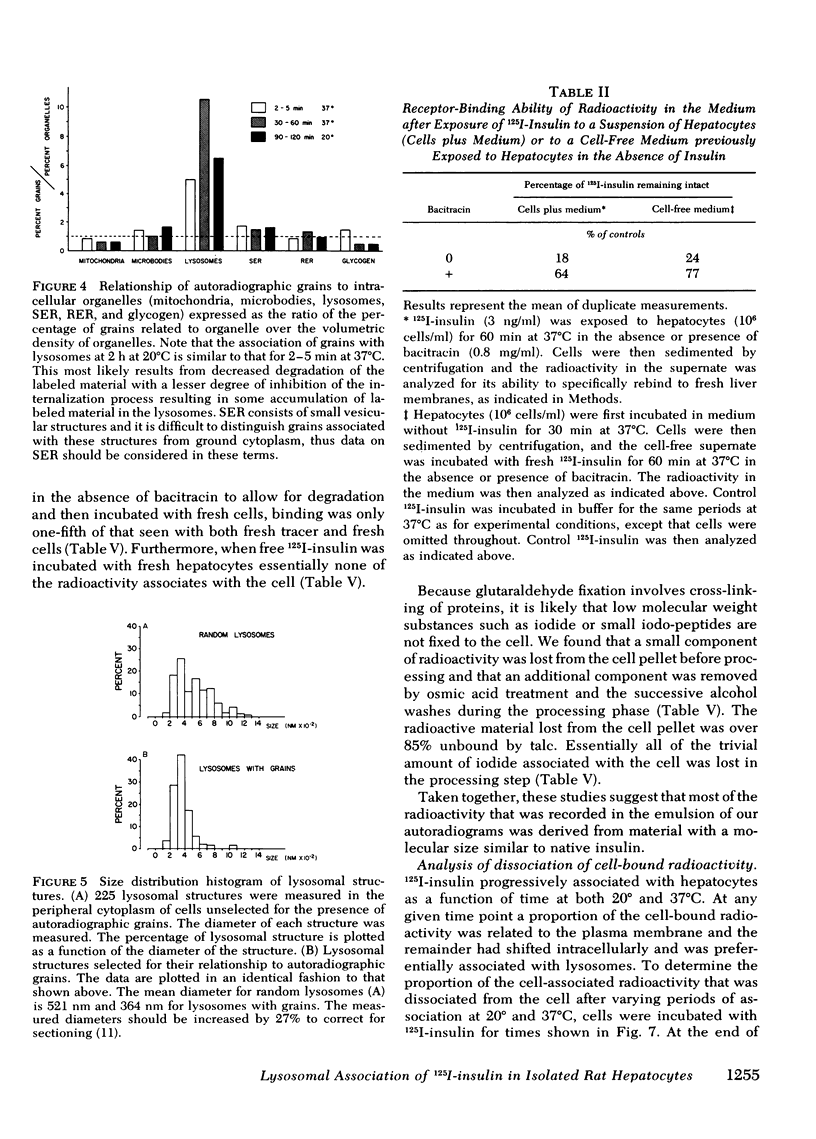
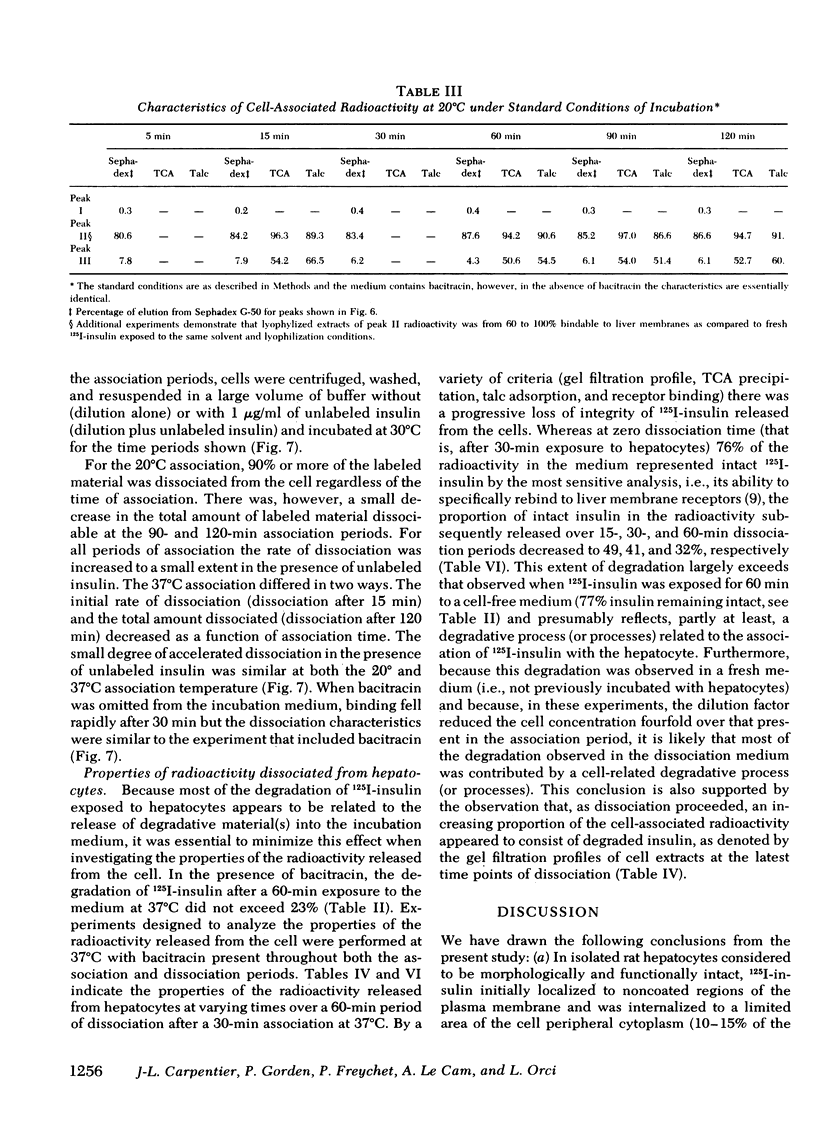
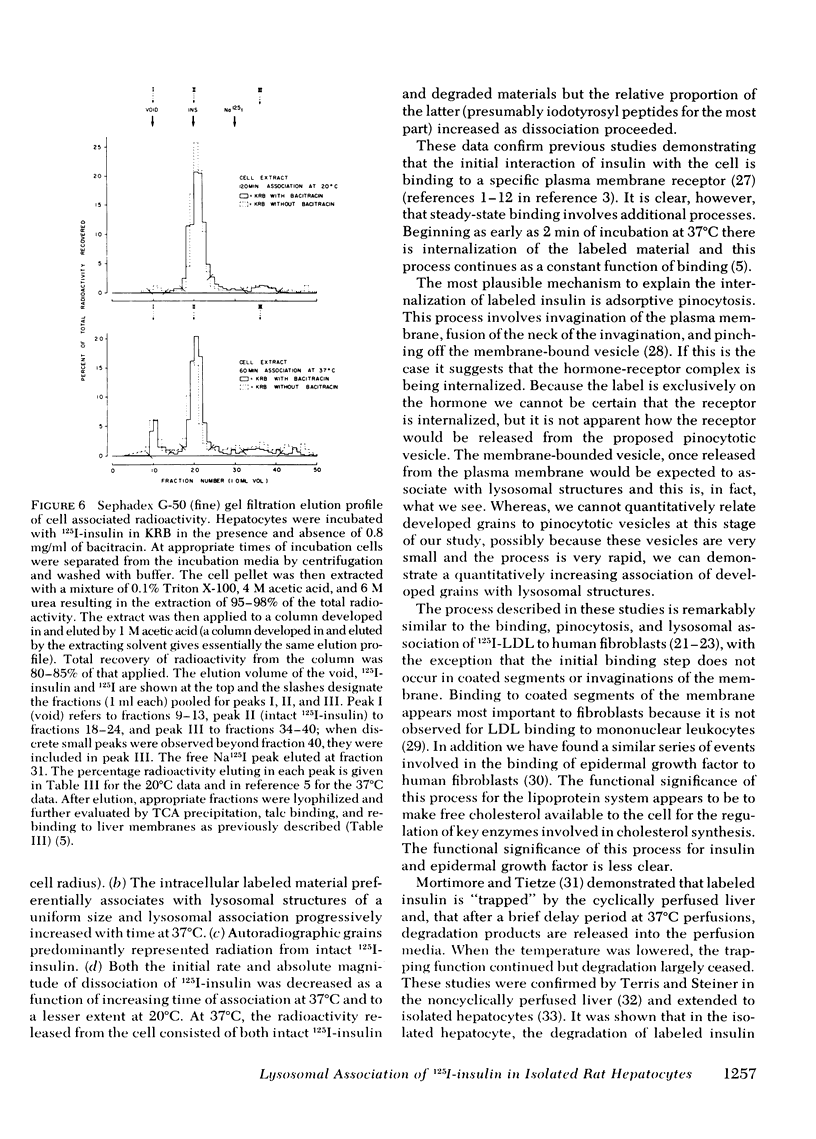
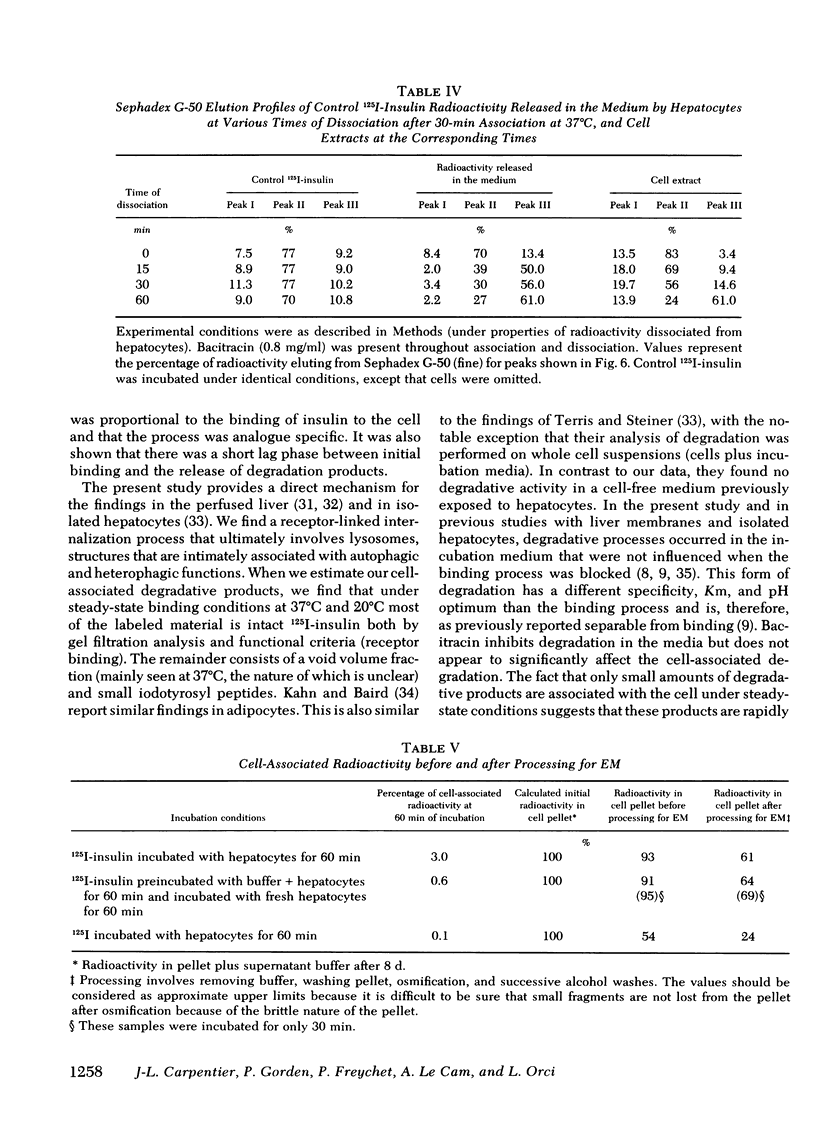
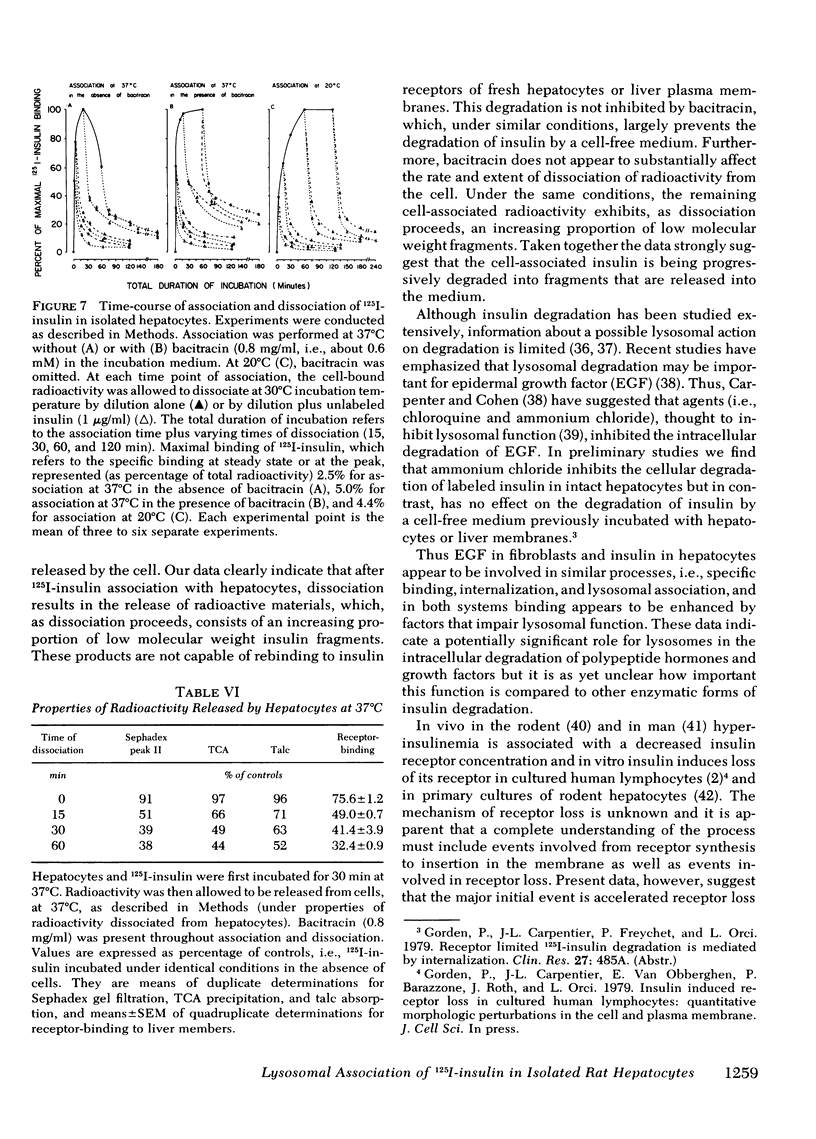
Quantitative electron microscopic autoradiographic studies in cultured human lymphocytes and isolated rat hepatocytes have demonstrated that labeled insulin initially localizes to the plasma membrane and is subsequently internalized to a limited region of the peripheral cytoplasm. When 0.5 nm 125I-insulin is incubated with isolated rat hepatocytes, binding to the plasma membrane occurs at both 20 degrees C and 37 degrees C. Under steady-state binding conditions approximately equal to 30--40% of the labeled hormone is internalized to a distance of approximately equal to 15% of the radius of the cell. When the localization of the internalized labeled material is analyzed, by 2--5 min of incubation at 37 degrees C there is a fivefold preferential association of autoradiographic grains with lysosomal structures, and by 30--60 min of incubation at 37 degrees C there is a 10-fold preferential association. When the cell-associated radioactivity is extracted and filtered on Sephadex G-50 at each time point of incubation, radioactivity elutes predominantly in the position of 125I-insulin and is predominantly in the position of 125I-insulin and is predominantly trichloracetic acid precipitable, bindable to talc, and rebindable to liver membranes. With increasing time of association at 37 degrees C the initial rate and absolute amount of labeled material dissociable from the cell is reduced. With increasing time of dissociation both the cell-associated radioactivity and the radioactivity released into the incubation medium is progressively degraded. These data demonstrate that in isolated rat hepatocytes labeled insulin initially localizes to the plasma membrane, is progressively internalized, and associates preferentially with lysosomal structures. These events may provide a mechanism that links cell surface binding to the degradation of insulin and to insulin-induced loss of its specific receptor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Role of the coated endocytic vesicle in the uptake of receptor-bound low density lipoprotein in human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Localization of low density lipoprotein receptors on plasma membrane of normal human fibroblasts and their absence in cells from a familial hypercholesterolemia homozygote. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2434–2438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorge S., Bohley P., Kirschke H., Langner J., Hanson H. Metabolism of insulin and glucagon. Breakdown of radioiodinated insulin and glucagon in rat liver cell fractions. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 11;19(2):283–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Gorden P., Roth J., Kahn C. R., De Meyts P. Fluctuations in the affinity and concentration of insulin receptors on circulating monocytes of obese patients: effects of starvation, refeeding, and dieting. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1123–1135. doi: 10.1172/JCI108565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron J. J., Levine G., Sikstrom R., O'Shaughnessy D., Kopriwa B., Nadler N. J., Posner B. I. Polypeptide hormone binding sites in vivo: initial localization of 125I-labeled insulin to hepatocyte plasmalemma as visualized by electron microscope radioautography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5051–5055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron J. J., Posner B. I., Josefsberg Z., Sikstrom R. Intracellular polypeptide hormone receptors. The demonstration of specific binding sites for insulin and human growth hormone in Golgi fractions isolated from the liver of female rats. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):4058–4066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L. Genetics of the low density lipoprotein receptor. Diminished receptor activity in lymphocytes from heterozygotes with familial hypercholesterolemia. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):678–696. doi: 10.1172/JCI108980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Guzelian P. S., Small M. E. Down regulation of insulin receptors in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes in monolayer. Endocrinology. 1978 Aug;103(2):548–553. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-2-548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO L. G., VAN TUBERGEN R. P., KOLB J. A. High-resolution autoradiography. I. Methods. J Cell Biol. 1962 Nov;15:173–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Amherdt M., Van Obberghen E., Kahn C. R., Orci L. 125I-insulin binding to cultured human lymphocytes. Initial localization and fate of hormone determined by quantitative electron microscopic autoradiography. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1057–1070. doi: 10.1172/JCI109005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Duve C., Wattiaux R. Functions of lysosomes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1966;28:435–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.28.030166.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeyts P., Bainco A. R., Roth J. Site-site interactions among insulin receptors. Characterization of the negative cooperativity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1877–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drochmans P., Wanson J. C., Mosselmans R. Isolation and subfractionation on ficoll gradients of adult rat hepatocytes. Size, morphology, and biochemical characteristics of cell fractions. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jul;66(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Kahn C. R., Jarrett D. B., Roth J. Autoantibodies to the insulin receptor. Effect on the insulin-receptor interaction in IM-9 lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;60(4):784–794. doi: 10.1172/JCI108832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Jones A. L., Hradek G. T., Wong K. Y., Mooney J. S. Entry of insulin into human cultured lymphocytes: electron microscope autoradiographic analysis. Science. 1978 Nov 17;202(4369):760–763. doi: 10.1126/science.715440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Smith G. J. Binding of insulin to isolated nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1427–1431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Smith G. J., Wong K. Y., Jones A. L. Cellular uptake and nuclear binding of insulin in human cultured lymphocytes: evidence for potential intracellular sites of insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1368–1372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Carpentier J. L., Cohen S., Orci L. Epidermal growth factor: morphological demonstration of binding, internalization, and lysosomal association in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5025–5029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Carpentier J. L., Freychet P., LeCam A., Orci L. Intracellular translocation of iodine-125-labeled insulin: direct demonstration in isolated hepatocytes. Science. 1978 May 19;200(4343):782–785. doi: 10.1126/science.644321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisolia S., Wallace R. Insulin degradation by lysosomal extracts from rat liver; model for a role of lysosomes in hormon degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 3;70(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K. The fate of insulin bound to adipocytes. Evidence for compartmentalization and processing. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4900–4906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin-receptor interaction in the obese-hyperglycemic mouse. A model of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Effect of catecholamines on amino acid transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Endocrinology. 1978 Feb;102(2):379–385. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-2-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Effect of glucocorticoids on amino acid transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1977 Dec;9(2):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(77)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Effect of insulin on amino acid transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Diabetologia. 1978 Aug;15(2):117–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00422256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Glucagon stimulates the A system for neutral amino acid transport in isolated hepatocytes of adult rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 4;72(3):893–901. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P., Lenoir P. Degradation of insulin by isolated rat liver cells. Diabetes. 1975 Jun;24(6):566–573. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.6.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Guillouzo A., Freychet P. Ultrastructual and biochemical studies of isolated adult rat hepatocytes prepared under hypoxic conditions. Cryopreservation of hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Mar 15;98(2):382–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90448-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTIMORE G. E., TIETZE F. Studies on the mechanism of capture and degradation of insulin-1131 by the cyclically perfused rat liver. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler N. J. The interpretation of grain counts in electron microscope radioautography. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):877–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Carpentier J. L., Perrelet A., Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Occurrence of low density lipoprotein receptors within large pits on the surface of human fibroblasts as demonstrated by freeze-etching. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Apr;113(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Direct visualization of binding, aggregation, and internalization of insulin and epidermal growth factor on living fibroblastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:29–83. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stäubli W., Schweizer W., Suter J., Weibel E. R. The proliferative response of hepatic peroxidomes of neonatal rats to treatment with SU-13 437 (nafenopin). J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):665–689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Binding and degradation of 125I-insulin by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8389–8398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Retention and degradation of 125I-insulin by perfused livers from diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):885–896. doi: 10.1172/JCI108365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R. Stereological principles for morphometry in electron microscopic cytology. Int Rev Cytol. 1969;26:235–302. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61637-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Stäubli W., Gnägi H. R., Hess F. A. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. I. Morphometric model, stereologic methods, and normal morphometric data for rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):68–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Alberico L., Avruch J. Insulin regulation of glycogen synthase in the isolated rat hepatocyte. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 19;69(4):997–1003. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90471-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]