Abstract
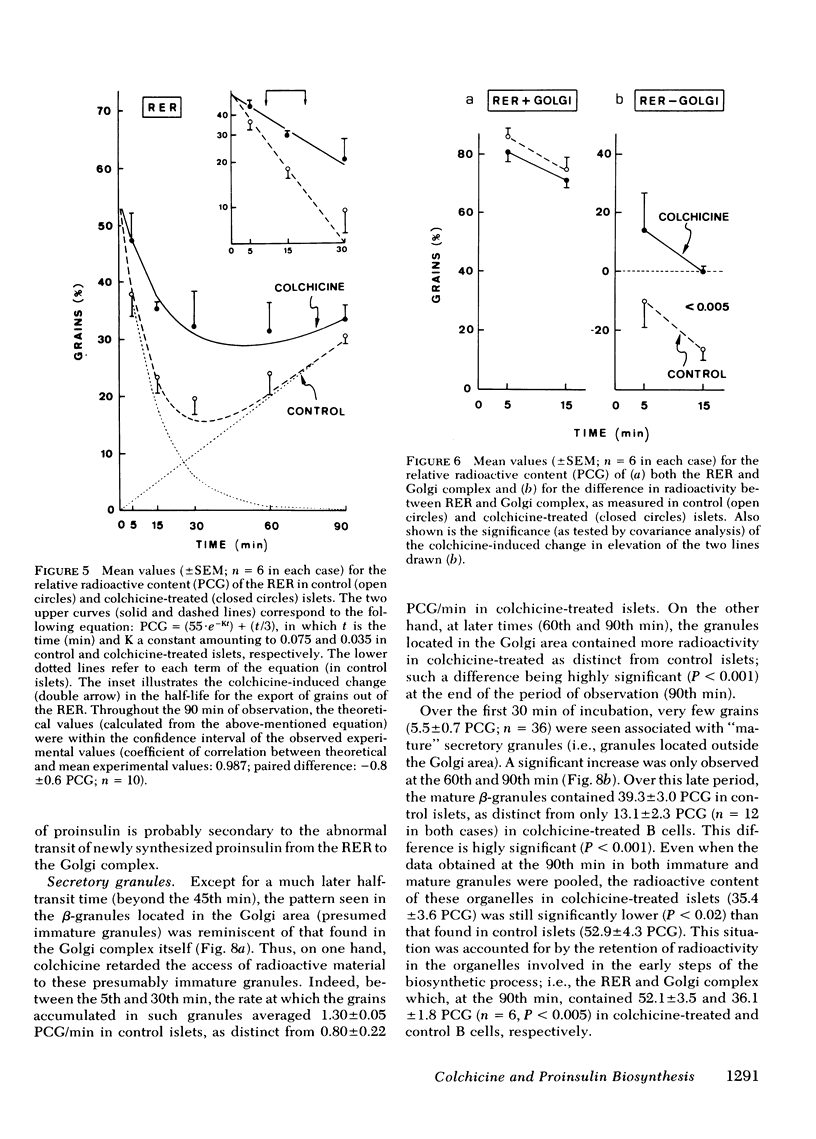
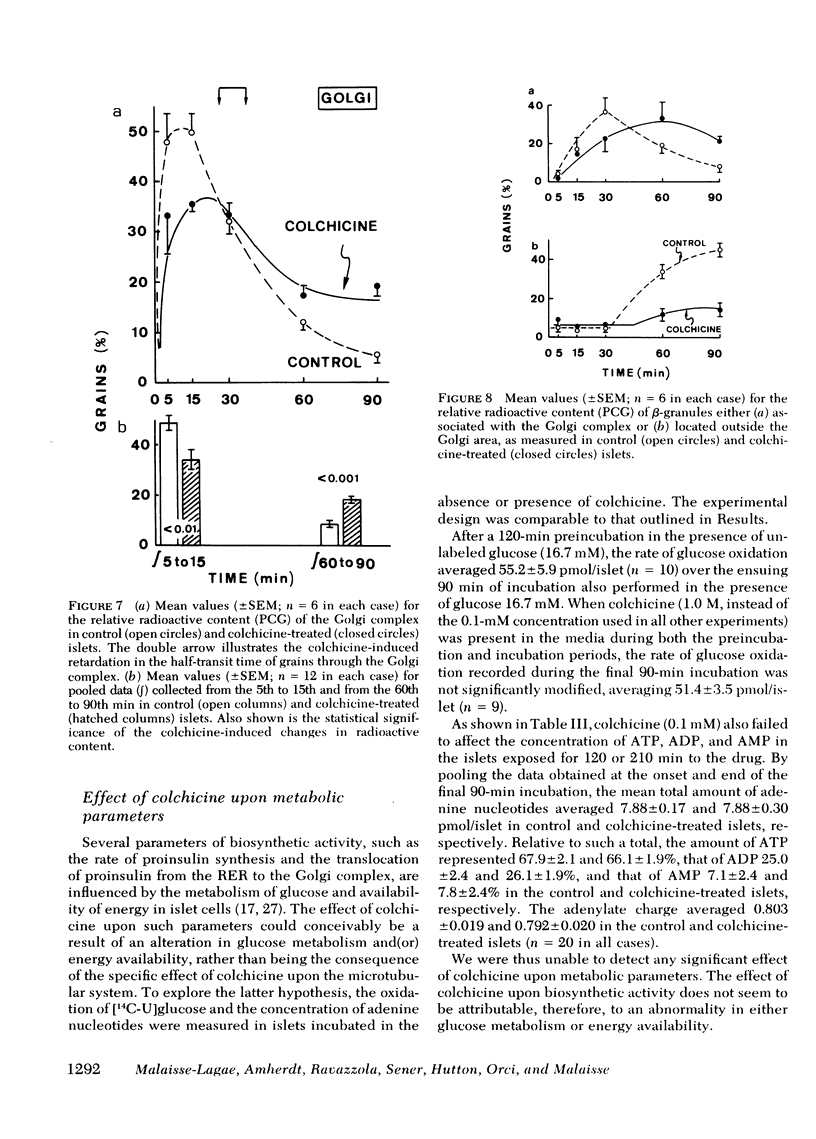
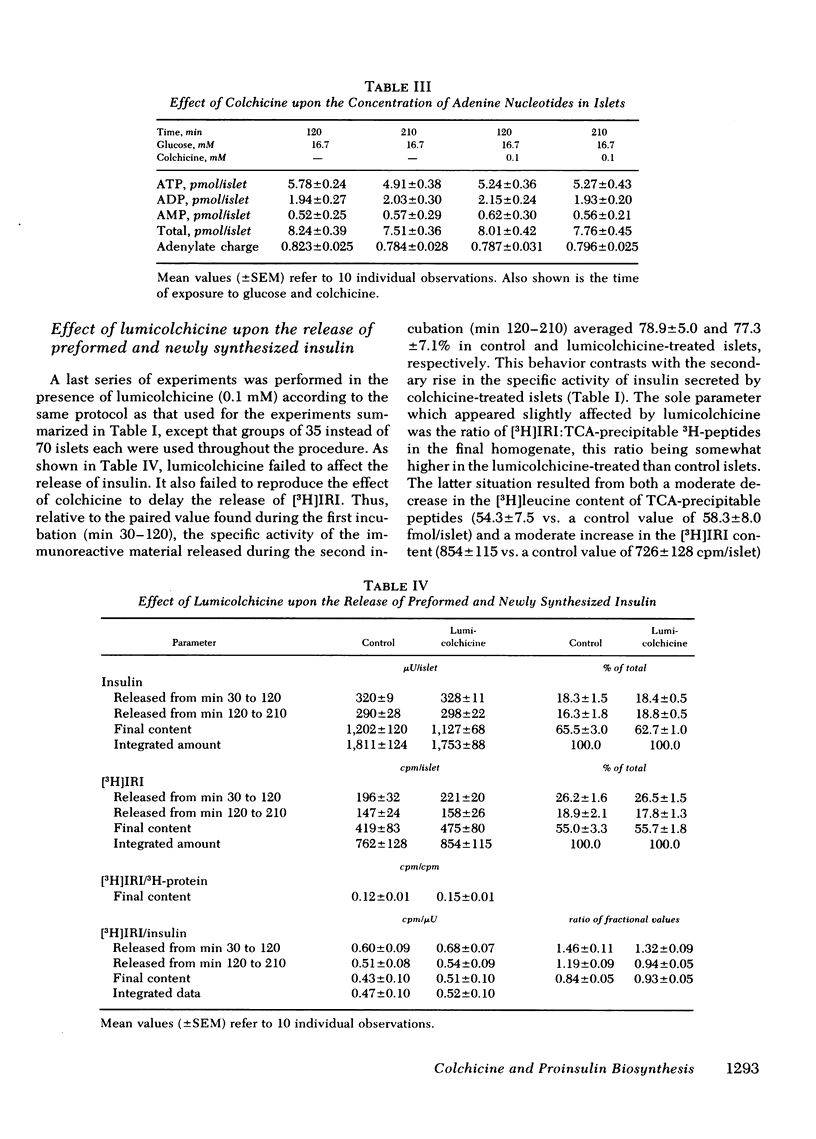
In the pancreatic B cell, microtubules are thought to be involved in the process of insulin release. Their possible participation in the sequence of events leading from the biosynthesis and conversion of proinsulin to the release of newly synthesized insulin was investigated in rat isolated islets exposed to colchicine (0.1 mM). When the islets were preincubated for 30 min with colchicine and [3H]-leucine and, thereafter, incubated for two successive periods of 90 min each, still in the presence of colchicine, the release of preformed insulin was progressively inhibited and that of newly synthesized hormone delayed. When the islets were preincubated for 120 min with colchicine, subsequently pulse-labeled with [3H]leucine, and eventually examined by ultrastructural autoradiography, the export of newly synthesized proinsulin out of the rough endoplasmic reticulum, its transit through the Golgi complex, and its eventual packaging in secretory granules were all retarded. This situation was associated with a delayed conversion of proinsulin to insulin. Under the same experimental conditions, colchicine failed to affect the oxidation of glucose and adenylate charge in the islets. The effect of colchicine upon the release of preformed and newly synthesized insulin was not reproduced by lumicolchicine. It is concluded that colchicine interferes with the system controlling the intracellular transfer of secretory material from site of synthesis to site of release. This interference is likely to be linked to the effect of colchicine on microtubules.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CARO L. G., VAN TUBERGEN R. P., KOLB J. A. High-resolution autoradiography. I. Methods. J Cell Biol. 1962 Nov;15:173–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu L. L., MacGregor R. R., Cohn D. V. Energy-dependent intracellular translocation of proparathormone. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jan;72(1):1–10. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. L., Steiner D. F. Insulin biosynthesis in the rat: demonstration of two proinsulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):278–285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe M. J., Loftfield S., Goldman I. D. A reduction in energy-dependent amino acid transport by microtubular inhibitors in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Oct;86(2 Pt 1):201–211. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040860203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L. Role of ATP in the intracellular translocation of proinsulin and insulin in the rat pancreatic B cell. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 19;235(55):85–86. doi: 10.1038/newbio235085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Habener J. F., Rich A., Potts J. T., Jr Microtubules and the intracellular conversion of proparathyroid hormone to parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1975 Apr;96(4):903–912. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-4-903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Howell S. L., Young D. A., Fink C. J. New hypothesis of insulin secretion. Nature. 1968 Sep 14;219(5159):1177–1179. doi: 10.1038/2191177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lettré H., Paweletz N. Probleme der elektronenmikroskopischen Autoradiographie. Naturwissenschaften. 1966 Jun;53(11):268–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00621640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J., Herchuelz A., Sener A., Malaisse-Lagae F., Malaisse W. J. Cytochalasin B-induced impariment of glucose metabolism in islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1976 Feb;98(2):429–437. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-2-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander S., Moskalewski S., Madsen K., Thyberg J., Friberg U. Influence of colchicine on the synthesis and secretion of proteoglycans and collagen by fetal guinea pig chondrocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):333–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90591-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Brisson G., Malaisse-Lagae F. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. I. Interaction of epinephrine and alkaline earth cations. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Dec;76(6):895–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Hager D. L., Orci L. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. IX. The participation of the beta cell web. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):594–604. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Hutton J. C., Kawazu S., Sener A. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Metabolic effects of menadione in isolated islets. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 1;87(1):121–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Van Obberghen E., Somers G., Devis G., Ravazzola M., Orci L. Role of microtubules in the phasic pattern of insulin release. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:630–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Walker M. O., Lacy P. E. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. V. The participation of a microtubular-microfilamentous system. Diabetes. 1971 May;20(5):257–265. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.5.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Mahy M. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Sorbitol metabolism in isolated islets. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 1;47(2):365–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Van Obberghen E., Devis G., Somers G., Ravazzola M. Dynamics of insulin release and microtubular-microfilamentous system. V. A model for the phasic release of insulin. Eur J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;4(5):313–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb00409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskalewski S., Thyberg J., Friberg U. In vitro influence of colchicine on the Golgi complex in A- and B-cells of guinea pig pancreatic islets. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Feb;54(2):304–317. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80159-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L. A portrait of the pancreatic B-cell. The Minkowski Award Lecture delivered on July 19, 1973, during the 8th Congress of the International Diabetes Federation, held in Brussels, Belgium. Diabetologia. 1974 Jun;10(3):163–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00423031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzelt C., Singh A., Marchand Y. L., Orci L., Jeanrenaud B. Colchicine-binding protein of the liver. Its characterization and relation to microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):609–620. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Marichal M., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XIV. Glucose regulation of insular biosynthetic activity. Endocrinology. 1973 Nov;93(5):1001–1011. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-5-1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Pipeleers-Marichal M. A., Kipnis D. M. Microtubule assembly and the intracellular transport of secretory granules in pancreatic islets. Science. 1976 Jan 9;191(4222):88–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1108194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando H., Borg J., Steiner D. F. Studies on the secretion of newly synthesized proinsulin and insulin from isolated rat islets of Langerhans. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1476–1485. doi: 10.1172/JCI106944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando H., Grodsky G. M. Dynamic synthesis and release of insulin and proinsulin from perifused islets. Diabetes. 1973 May;22(5):354–360. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.5.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seybold J., Bieger W., Kern H. F. Studies on intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the rat exocrine pancreas. II. Inhibition of antimicrotubular agents. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1975 Nov 28;368(4):309–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00432309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson R. L., Steffes M. W., Lindall A. W. Subcellular localization of proinsulin to insulin conversion in isolated rat islets. Endocrinology. 1970 Jan;86(1):88–96. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-1-88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese T., Lazarus N. R., Devrim S., Recant L. Synthesis and release of proinsulin and insulin by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jul;49(7):1394–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI106357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L., Friedkin M. The biochemical events of mitosis. I. Synthesis and properties of colchicine labeled with tritium in its acetyl moiety. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2463–2468. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. H., Malaisse W. J., Reynolds I. J. Assay of partially neutralized guinea pig anti-insulin serum. Endocrinology. 1967 Aug;81(2):226–234. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-2-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]