Abstract
To further characterize mechanisms of glucose counterregulation in man, the effects of pharmacologically inducd deficiencies of glucagon, growth hormone, and catecholamines (alone and in combination) on recovery of plasma glucose from insulin-induced hypoglycemia and attendant changes in isotopically ([3-3H]glucose) determined glucose fluxes were studied in 13 normal subjects. In control studies, recovery of plasma glucose from hypoglycemia was primarily due to a compensatory increase in glucose production; the temporal relationship of glucagon, epinephrine, cortisol, and growth hormone responses with the compensatory increase in glucose appearance was compatible with potential participation of all these hormones in acute glucose counterregulation. Infusion of somatostatin (combined deficiency of glucagon and growth hormone) accentuated insulin-induced hypoglycemia (plasma glucose nadir: 36±2 ng/dl during infusion of somatostatin vs. 47±2 mg/dl in control studies, P < 0.01) and impaired restoration of normoglycemia (plasma glucose at min 90: 73±3 mg/dl at end of somatostatin infusion vs. 92±3 mg/dl in control studies, P<0.01). This impaired recovery of plasma glucose was due to blunting of the compensatory increase in glucose appearance since glucose disappearance was not augmented, and was attributable to suppression of glucagon secretion rather than growth hormone secretion since these effects of somatostatin were not observed during simultaneous infusion of somatostatin and glucagon whereas infusion of growth hormone along with somatostatin did not prevent the effect of somatostatin. The attenuated recovery of plasma glucose from hypoglycemia observed during somatostatin-induced glucagon deficiency was associated with plasma epinephrine levels twice those observed in control studies. Infusion of phentolamine plus propranolol (combined α-and β-adrenergic blockade) had no effect on plasma glucose or glucose fluxes after insulin administration. However, infusion of somatostatin along with both phentolamine and propranolol further impaired recovery of plasma glucose from hypoglycemia compared to that observed with somatostatin alone (plasma glucose at end of infusions: 52±6 mg/dl for somatostatin-phentolamine-propranolol vs. 72±5 mg/dl for somatostatin alone, P < 0.01); this was due to further suppression of the compensatory increase in glucose appearance (maximal values: 1.93±0.41 mg/kg per min for somatostatin-phentolamine-propranolol vs. 2.86±0.32 mg/kg per min for somatostatin alone, P < 0.05). These results indicate that in man (a) restoration of normoglycemia after insulin-induced hypoglycemia is primarily due to a compensatory increase in glucose production; (b) intact glucagon secretion, but not growth hormone secretion, is necessary for normal glucose counterregulation, and (c) adrenergic mechanisms do not normally play an essential role in this process but become critical to recovery from hypoglycemia when glucagon secretion is impaired.
Full text
PDF

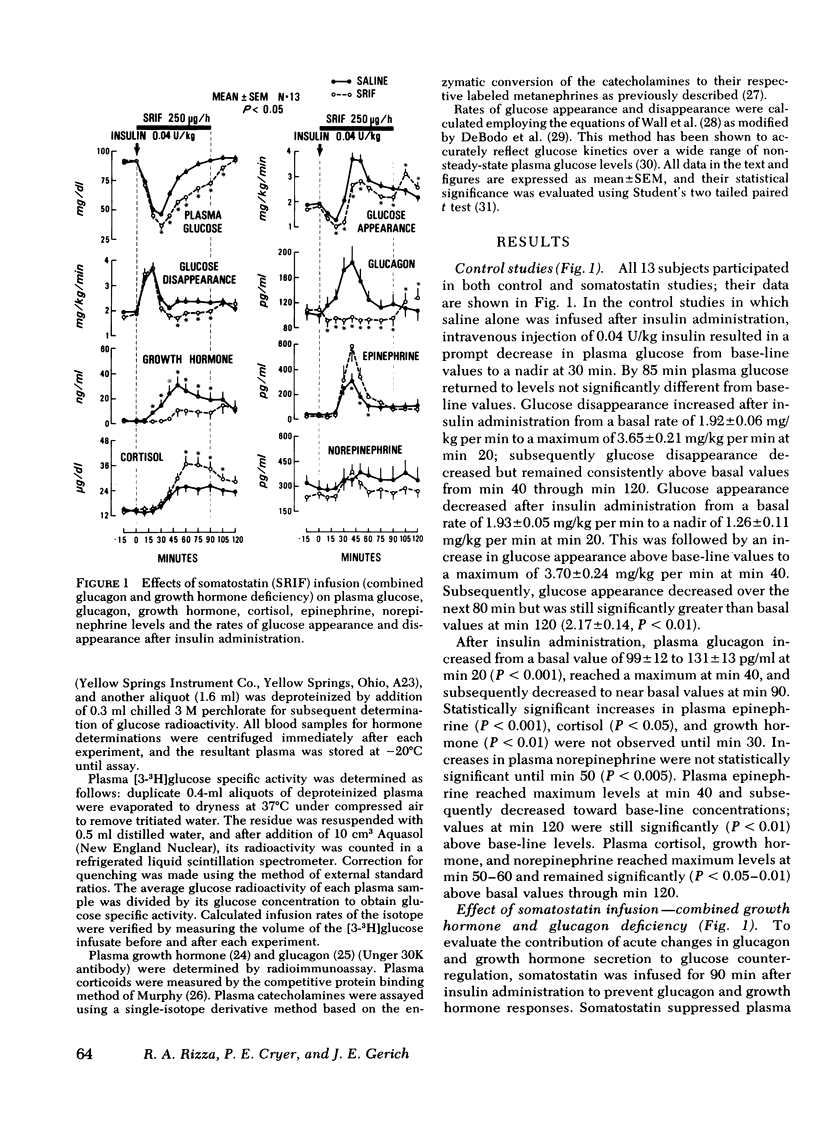
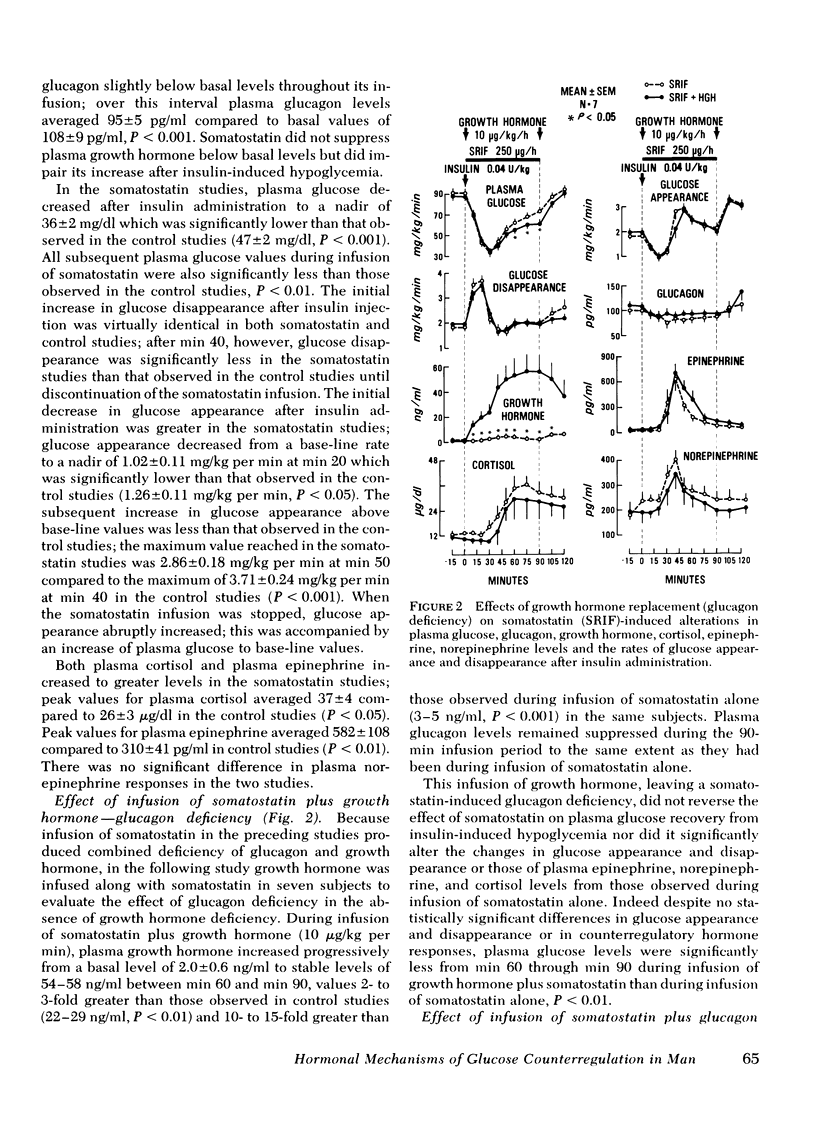
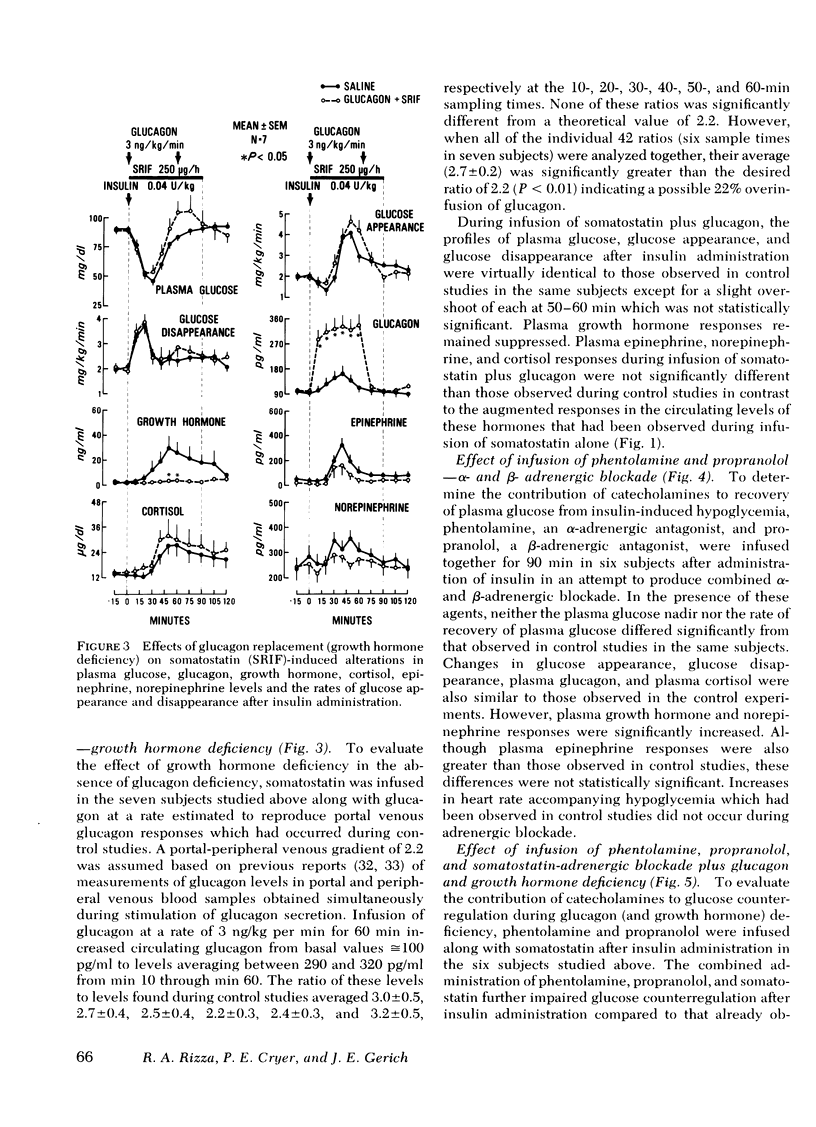
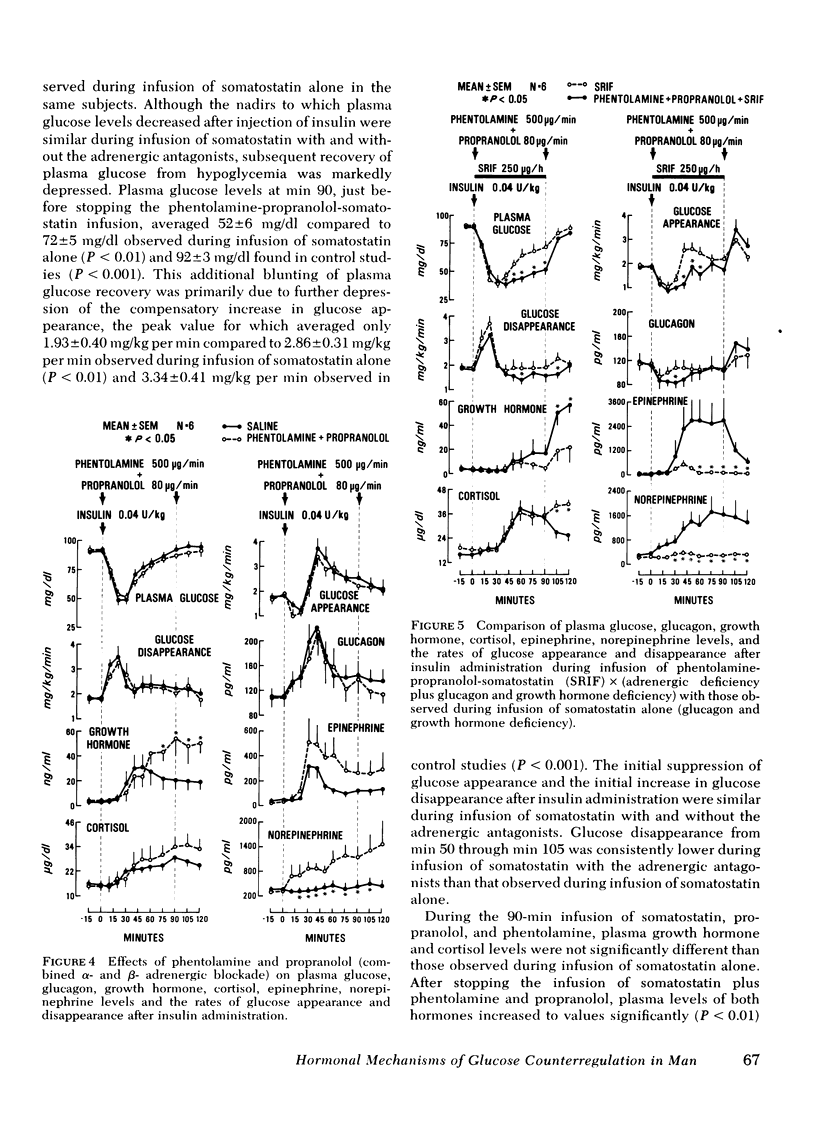




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson E. A., Arky R. A., Woeber K. A. Effects of propranolol on the hormonal and metabolic responses to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Lancet. 1966 Dec 24;2(7478):1386–1388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Forsham P. H. Tissue effects of glucocorticoids. Am J Med. 1972 Nov;53(5):573–589. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Nelson N. C., Andrews S. S. Portal and peripheral vein immunoreactive glucagon concentrations after arginine or glucose infusions. Diabetes. 1974 Mar;23(3):199–202. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.3.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Vaughan N. J. The role of the autonomic innervation in the control of glucagon release during hypoglycaemia in the calf. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):611–623. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodows R. G., Ensinck J. W., Campbell R. G. Mechanism of plasma cyclic AMP response to hypoglycemia in man. Metabolism. 1976 Jun;25(6):659–663. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodows R. G., Pi-Sunyer F. X., Campbell R. G. Neural control of counter-regulatory events during glucopenia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):1841–1844. doi: 10.1172/JCI107366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. S., Kalant N. Effects of insulin and growth hormone on the flux rates of plasma glucose and plasma free fatty acids in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Dec;31(6):647–653. doi: 10.1210/jcem-31-6-647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chideckel E. W., Palmer J., Koerker D. J., Ensinck J., Davidson M. B., Goodner C. J. Somatostatin blockade of acute and chronic stimuli of the endocrine pancreas and the consequences of this blockade on glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):754–762. doi: 10.1172/JCI107986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J., Alberti K. G., Brandsborg O. Plasma catecholamines and blood substrate concentrations: studies in insulin induced hypoglycaemia and after adrenaline infusions. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep 12;5(5):415–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J., Christensen S. E., Hansen A. P., Lundboek K. The effect of somatostatin on plasma noradrenaline and plasma adrenaline concentrations during exercise and hypoglycemia. Metabolism. 1975 Nov;24(11):1267–1272. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke W. L., Santiago J. V., Thomas L., Ben-Galim E., Haymond M. W., Cryer P. E. Adrenergic mechanisms in recovery from hypoglycemia in man: adrenergic blockade. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):E147–E152. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.2.E147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. W., Hetenyi G., Jr The effect of phenoxybenzamine and propranolol and their combination on the restoration of glucose homeostasis after insulin induced hypoglycemia. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1969 Apr;178(2):412–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Santiago J. V., Shah S. Measurement of norepinephrine and epinephrine in small volumes of human plasma by a single isotope derivative method: response to the upright posture. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Dec;39(6):1025–1029. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-6-1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEBODO R. C., STEELE R., ALTSZULER N., DUNN A., BISHOP J. S. ON THE HORMONAL REGULATION OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM; STUDIES WITH C14 GLUCOSE. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1963;19:445–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencker H., Hedner P., Holst J., Tranberg K. G. Pancreatic glucagon response to an ordinary meal. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(5):471–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Silver M. Comparison of the hyperglycaemic and glycogenolytic responses to catecholamines with those to stimulation of the hepatic sympathetic innervation in the dog. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(2):571–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensinck J. W., Walter R. M., Palmer J. P., Brodows R. G., Campbell R. G. Glucagon responses to hypoglycemia in adrenalectomized man. Metabolism. 1976 Feb;25(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Mallette L. E., Jefferson L. S., Wong E. H., Friedmann N., Miller T. B., Jr, Park C. R. The hormonal control of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1970;26:411–461. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571126-5.50014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Robison G. A., Sutherland E. W., Park C. R. Studies on the role of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the hepatic actions of glucagon and catecholamines. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6166–6177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. M., Plonk J. W., Bivens C. H. The role of cortisol and growth hormone in the counter-regulation of insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Horm Metab Res. 1975 Sep;7(5):378–381. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Marliss E. B., Cahill G. F., Jr Metabolic response to human growth hormone during prolonged starvation. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):411–421. doi: 10.1172/JCI106508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG J., PATON A. Effects of insulin after adrenalectomy. Lancet. 1956 Sep 8;271(6941):491–494. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91973-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. J., Cryer P. E., Santiago J. V., Haymond M. W., Pagliara A. S., Kipnis D. M. The role of adrenergic mechanisms in the substrate and hormonal response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):7–15. doi: 10.1172/JCI108460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Tsalikian E., Karam J. H. Studies on the mechanism of epinephrine-induced hyperglycemia in man. Evidence for participation of pancreatic glucagon secretion. Diabetes. 1976 Jan;25(1):65–71. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Schneider V., Dippe S. E., Langlois M., Noacco C., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Characterization of the glucagon response to hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Jan;38(1):77–82. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J., Davis J., Lorenzi M., Rizza R., Bohannon N., Karam J., Lewis S., Kaplan R., Schultz T., Cryer P. Hormonal mechanisms of recovery from insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. Am J Physiol. 1979 Apr;236(4):E380–E385. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.4.E380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood F. C., Landon J. Assessment of hypothalamic pituitary function in endocrine disease. J Clin Pathol. 1966 May;19(3):284–292. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.3.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood F. C., Landon J., Stamp T. C. The plasma sugar, free fatty acid, cortisol, and growth hormone response to insulin. I. In control subjects. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):429–436. doi: 10.1172/JCI105357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G. The control of glycogen metabolism in the liver. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:167–189. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt B., Hansson B. G., Heding L. G., Nilsson K. O. Effect of insulin induced hypoglycaemia on the blood levels of catecholamines, glucagon, growth hormone, cortisol, C-peptide and proinsulin before and during medication with the cardioselective beta-receptor blocking agent metoprolol in man. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1978 Mar;87(3):659–667. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0870659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Goldfine I. D., Neville D. M., Jr, De Meyts P. Alterations in insulin binding induced by changes in vivo in the levels of glucocorticoids and growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1978 Oct;103(4):1054–1066. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-4-1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECOCQ F. R., MEBANE D., MADISON L. L. THE ACUTE EFFECT OF HYDROCORTISONE ON HEPATIC GLUCOSE OUTPUT AND PERIPHERAL GLUCOSE UTILIZATION. J Clin Invest. 1964 Feb;43:237–246. doi: 10.1172/JCI104908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft R., Cerasi E., Hamberger C. A. Studies on the pathogenesis of diabetes in acromegaly. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Dec;56(4):593–607. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0560593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCraw E. F., Peterson M. J., Ashmore J. Autoregulation of glucose metabolism in the isolated perfused rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):232–236. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J., Rabin D. A survey of growth hormone secretion and action. Metabolism. 1973 Sep;22(9):1235–1251. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E., Waid T. H., Joyce M. P. Direct neural inhibition of insulin secretion in response to systemic hypoglycemia. Am J Physiol. 1976 Apr;230(4):1090–1094. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.4.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. E. Some studies of the protein-binding of steroids and their application to the routine micro and ultramicro measurement of various steroids in body fluids by competitive protein-binding radioassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jul;27(7):973–990. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-7-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Henry D. P., Benson J. W., Johnson D. G., Ensinck J. W. Glucagon response to hypoglycemia in sympathectomized man. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):522–525. doi: 10.1172/JCI108305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrilla R., Goodman M. N., Toews C. J. Effect of glucagon: insulin ratios on hepatic metabolism. Diabetes. 1974 Sep;23(9):725–731. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.9.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez G., Trimarco B., Ungaro B., Rengo F., Saccà L. Glucoregulatory response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in Laennec's cirrhosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 May;46(5):778–783. doi: 10.1210/jcem-46-5-778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH J., GLICK S. M., YALOW R. S., BERSONSA Hypoglycemia: a potent stimulus to secretion of growth hormone. Science. 1963 May 31;140(3570):987–988. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3570.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J., Norwich K. H., Vranic M. Measurement and validation of nonsteady turnover rates with applications to the inulin and glucose systems. Fed Proc. 1974 Jul;33(7):1855–1864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Porte D., Jr Adrenergic modulation of basal insulin secretion in man. Diabetes. 1973 Jan;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz T. A., Lewis S. B., Westbie D. K., Gerich J. E., Rushakoff R. J., Wallin J. D. Glucose delivery--a clarification of its role in regulating glucose uptake in rat skeletal muscle. Life Sci. 1977 Feb 15;20(4):733–735. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90479-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimazu T., Ogasawara S. Effects of hypothalamic stimulation on gluconeogenesis and glycolysis in rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1787–1793. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL J. S., STEELE R., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Effect of insulin on utilization and production of circulating glucose. Am J Physiol. 1957 Apr;189(1):43–50. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.189.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R. M., Dudl R. J., Palmer J. P., Ensinck J. W. The effect of adrenergic blockade on the glucagon responses to starvation and hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1214–1220. doi: 10.1172/JCI107864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr Neural control of the endocrine pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1974 Jul;54(3):596–619. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



