Abstract
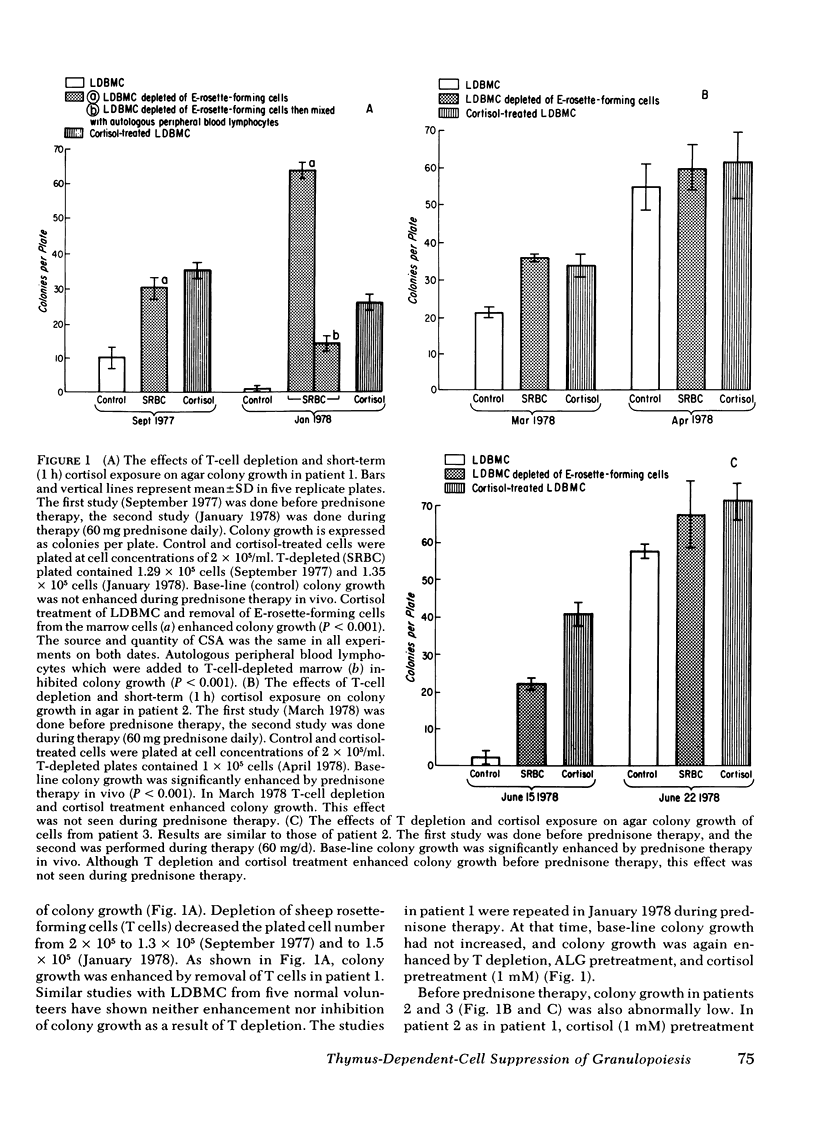
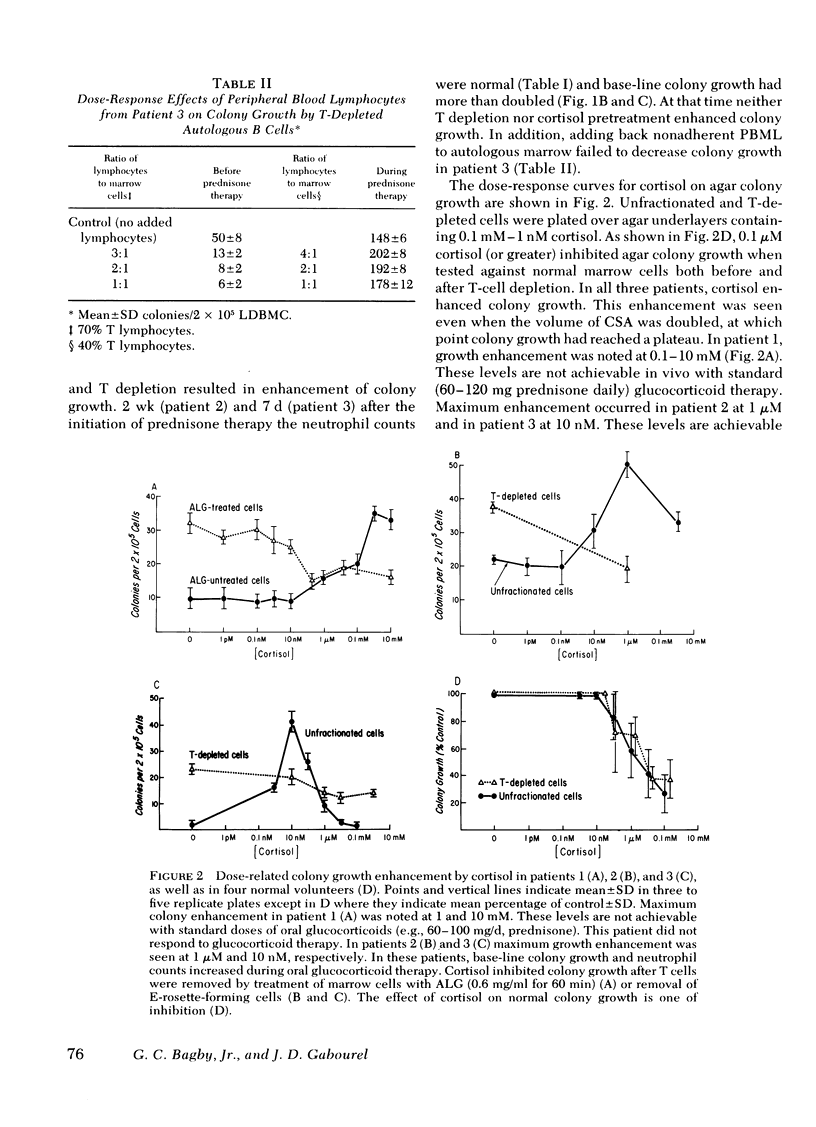
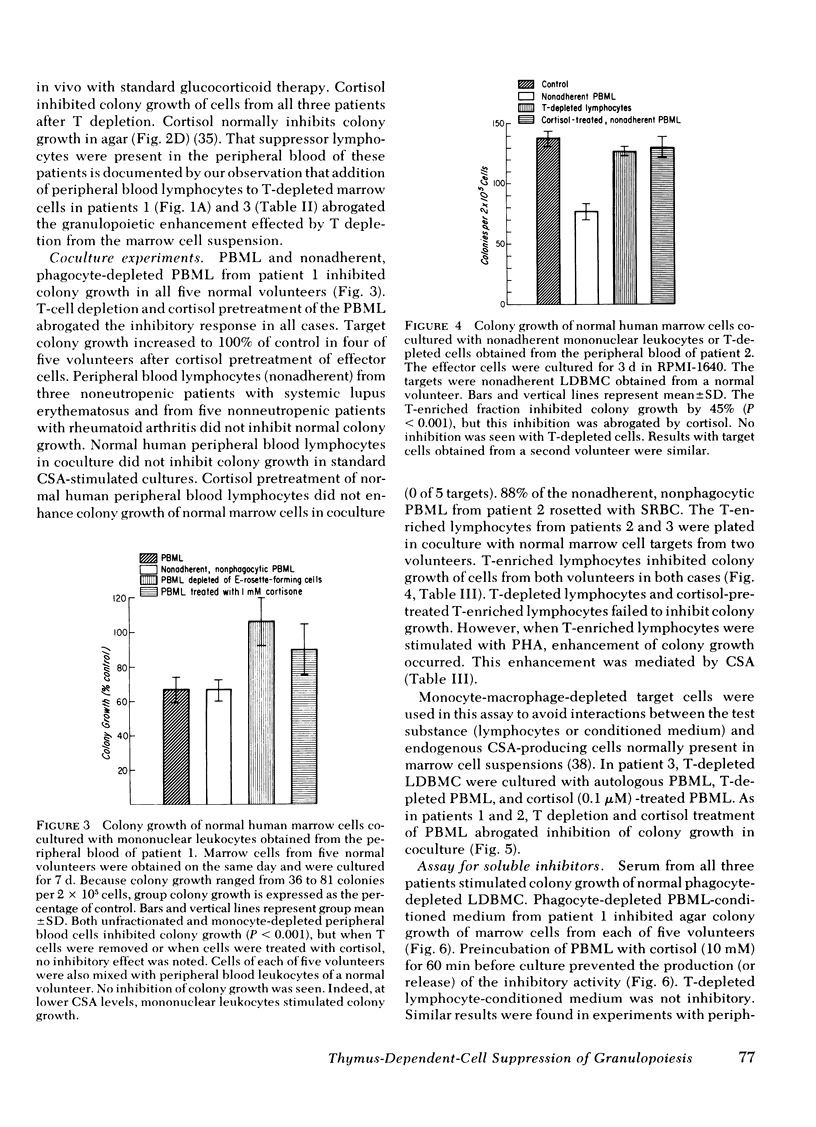
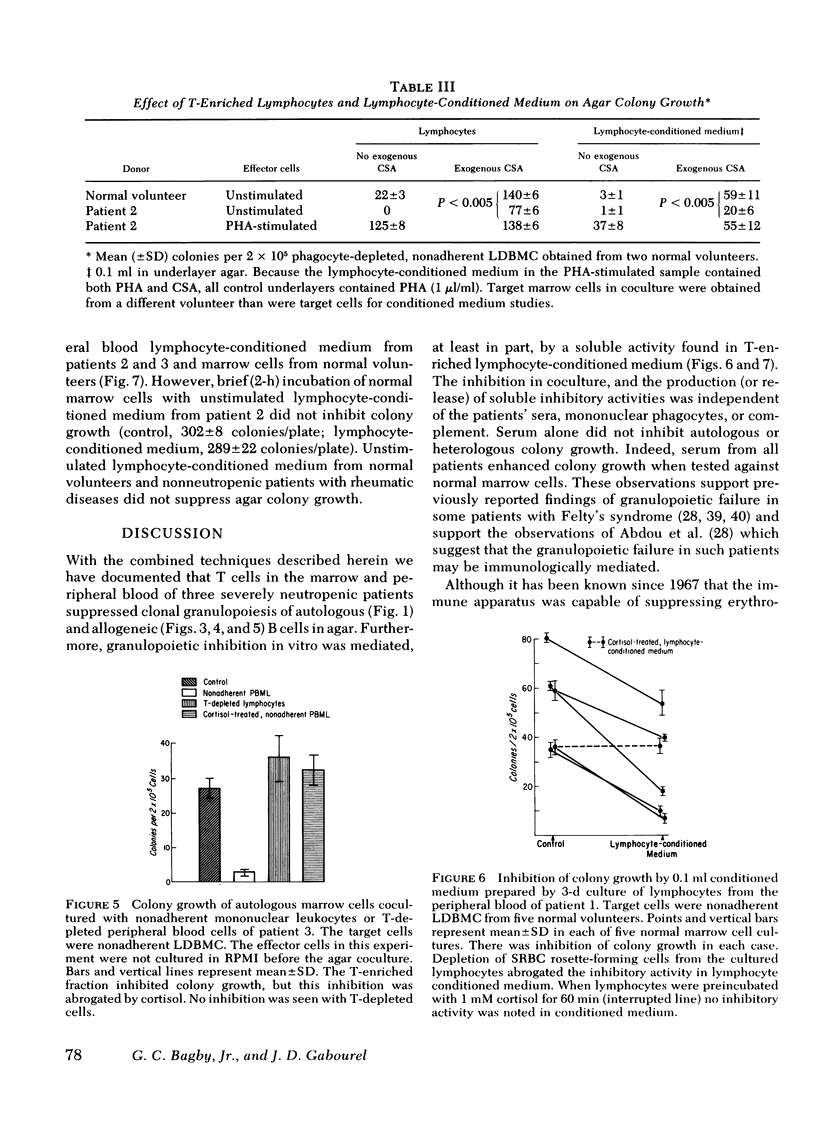
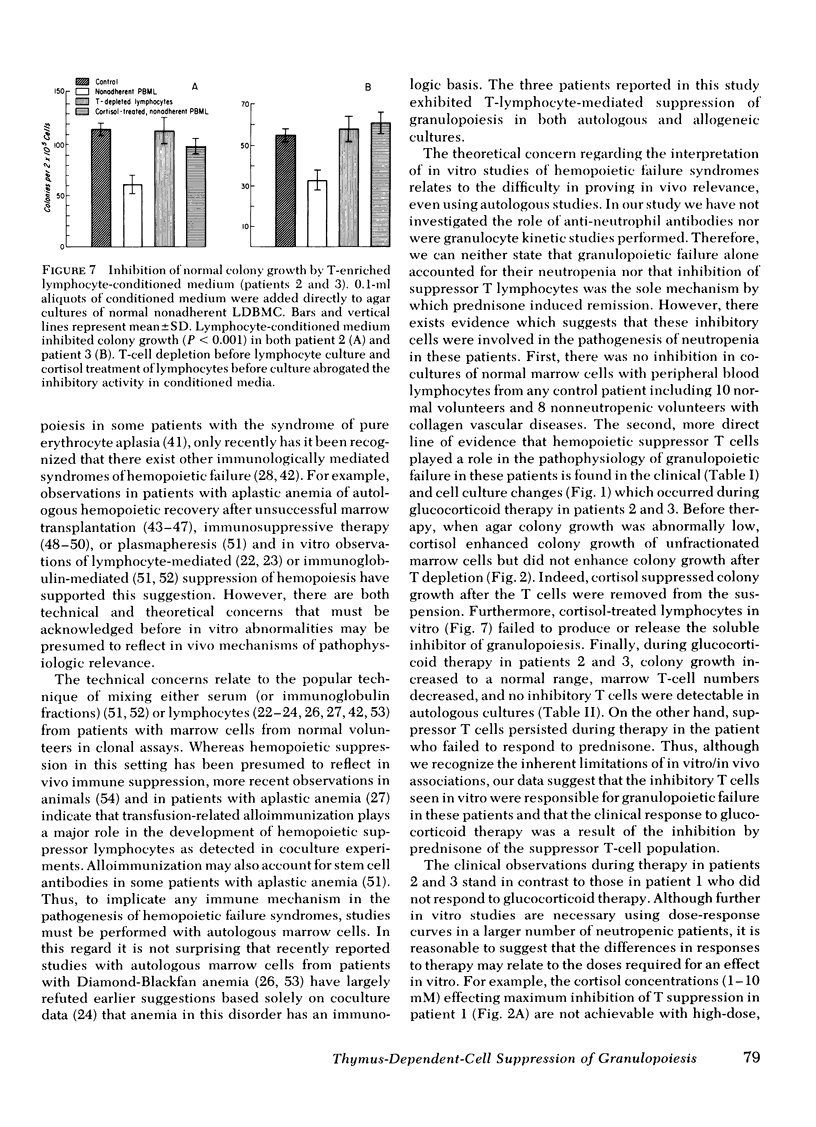
A man with polymyalgia rheumatica (patient 1) and two patients (2 and 3) with Felty's syndrome had neutropenia at the time of diagnosis. Bone marrow samples in each patient were cellular but showed an "arrest" of granulocyte maturation at the myelocyte stage. Agar colony growth of marrow cells from each patient was subnormal but increased after removal of sheep erythrocytes rosette-forming cells (thymus-dependent [T] cells) from marrow cell suspensions before culture. Preincubation of marrow cells with cortisol also enhanced colony growth. Maximum enhancement with cortisol occurred at 1 mM (patient 1), 1 microM (patient 2), and 10 nM (patient 3). Cortisol failed to enhance colony growth after removal of T cells from marrow cell suspensions. Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) and PBL-conditioned medium from all three patients inhibited colony growth of normal human marrow cells. Cortisol treatment of PBL or T depletion from PBL abrogated the inhibition in coculture and with conditioned medium. Prednisone therapy resulted in the disappearance of suppressor T-cell function concomitant with hematologic improvement in patients 2 and 3, but suppressor T cells persisted in patient 1, who did not respond to prednisone. We conclude that cortisol-sensitive T lymphocytes inhibited granulopoiesis in vitro probably by elaboration of a soluble factor or factors. Our results suggest (a) that neutropenia in these patients resulted, at least in part, from T-cell suppression of granulopoiesis, (b) that the effectiveness of prednisone therapy was a result of its inhibition of suppressor T cells, and (c) that responses to glucocorticoid therapy may be predicted in such patients with the agar culture technique and cortisol dose response in vitro.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., NaPombejara C., Balentine L., Abdou N. L. Suppressor cell-mediated neutropenia in Felty's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):738–743. doi: 10.1172/JCI108987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascensão J., Pahwa R., Kagan W., Hansen J., Moore M., Good R. Aplastic anaemia: Evidence for an immunological mechanism. Lancet. 1976 Mar 27;1(7961):669–671. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92780-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby G. C., Jr Stem cell (CFU-C) proliferation and emergence in a case of chronic granulocytic leukaemia: the role of the spleen. Scand J Haematol. 1978 Mar;20(3):193–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1978.tb02447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baran D. T., Griner P. F., Klemperer M. R. Recovery from aplastic anemia after treatment with cyclophosphamide. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 30;295(27):1522–1523. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612302952708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Poplack D., Whang-Peng J., Durm M., Goldman C., Muul L., Waldmann T. A. Characterization of a suppressor-cell leukemia. Evidence for the requirement of an interaction of two T cells in the development of human suppressor effector cells. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 12;298(2):66–72. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801122980202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burek V., Plavljanić D., Slamberger S., Vitale B. Studies on the mechanism of allogeneic disease in mice. I. The influence of bone marrow T lymphocytes on the differentiation and proliferation of hemopoietic stem cells. Exp Hematol. 1977 Nov;5(6):465–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Golde D. W. Immune suppression of hematopoiesis. Am J Med. 1978 Feb;64(2):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Opelz G., Saxon A., Fahey J. L., Golde D. W. Autoimmune panleukopenia. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 30;295(27):1489–1493. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612302952701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dao C., Metcalf D., Zittoun R., Bilski-Pasquier G. Normal human bone marrow cultures in vitro: cellular composition and maturation of the granulocytic colonies. Br J Haematol. 1977 Sep;37(1):127–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton R. W. Inhibitory and stimulatory effects of concanavalin A on the response of mouse spleen cell suspensions to antigen. I. Characterization of the inhibitory cell activity. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1445–1460. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitchen J. J., Cline M. J., Saxon A., Golde D. W. Serum inhibitors of hematopoiesis in a patient with aplastic anemia and systemic lupus erythematosus. Recovery after exchange plasmapheresis. Am J Med. 1979 Mar;66(3):537–542. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)91097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Schneeberger E., Rosen F. S., Merler E. Interaction of human thymus-derived and non-thymus-derived lymphocytes in vitro. Induction of proliferation and antibody synthesis in B lymphocytes by a soluble factor released from antigen-stimulated T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1230–1247. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. W., Burch K. T., Basford N. L. Graft-vs.-Host activity of thymocytes: relationship to the role of thymocytes in hemopoiesis. Blood. 1972 Jun;39(6):850–861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg P. L., Schrier S. L. Granulopoiesis in neutropenic disorders. Blood. 1973 Jun;41(6):753–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Good R. A. Subpopulations of human T lymphocytes. II. Effect of thymopoietin, corticosteroids, and irradiation. Cell Immunol. 1977 Nov;34(1):10–18. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwell L., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Suppressor T-cell inactivation of a helper T-cell factor. Nature. 1977 Jan 6;265(5589):57–59. doi: 10.1038/265057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R., Zanjani E. D., Lutton J. D., Zalusky R., Wasserman L. R. Suppression of erythroid-colony formation by lymphocytes from patients with aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jan 6;296(1):10–13. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197701062960103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R., Zanjani E. D., Vila J., Zalusky R., Lutton J. D., Wasserman L. R. Diamond-Blackfan syndrome: lymphocyte-mediated suppression of erythropoiesis. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):899–900. doi: 10.1126/science.986086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeannet M., Rubinstein A., Pelet B., Kummer H. Prolonged remission of severe aplastic anemia after ALG pretreatment and HL-A-semi-incompatible bone-marrow cell transfusion. Transplant Proc. 1974 Dec;6(4):359–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. R., Metcalf D. Pure and mixed erythroid colony formation in vitro stimulated by spleen conditioned medium with no detectable erythropoietin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3879–3882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. IV. Distribution of surface markers on resting and blast-transformed lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(6):739–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan W. A., Ascensão J. A., Pahwa R. N., Hansen J. A., Goldstein G., Valera E. B., Incefy G. S., Moore M. A., Good R. A. Aplastic anemia: presence in human bone marrow of cells that suppress myelopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2890–2894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Benacerraf B. The regulatory influence of activated T cells on B cell responses to antigen. Adv Immunol. 1972;15:1–94. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60683-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz S. B., Kao V. Studies on red cell aplasia. I. Demonstration of a plasma inhibitor to heme synthesis and an antibody to erythroblast nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):493–500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., Ginsburg W. W., Finkelman F. D., Ziff M. Control of human B lymphocyte responsiveness: enhanced suppressor T cell activity after in vitro incubation. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):902–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner H. A., McCulloch E. A. Interacting cell populations affecting granulopoietic colony formation by normal and leukemic human marrow cells. Blood. 1973 Nov;42(5):701–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. G., Chess L., Hillman D. G., Clarke B., Breard J., Merler E., Housman D. E. Human erythroid burst-forming unit: T-cell requirement for proliferation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):324–339. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. G., Clarke B. J., Hillman D. G., Alter B. P., Housman D. E. Erythroid precursors in congenital hypoplastic (Diamond-Blackfan) anemia. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):489–498. doi: 10.1172/JCI108960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. G., Hillman D. G., Chess L., Alter B. P., Clarke B. J., Breard J., Housman D. E. Normal erythropoietic helper T cells in congenital hypoplastic (Diamond-Blackfan) anemia. N Engl J Med. 1978 May 11;298(19):1049–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197805112981903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. W., Metcalf D. Production of colony-stimulating factor in mitogen-stimulated lymphocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike B. L., Robinson W. A. Human bone marrow colony growth in agar-gel. J Cell Physiol. 1970 Aug;76(1):77–84. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040760111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich R. R., Rich S. S., Truitt G. A. Suppressor T cells in the regulation of immune responses to allogeneic tissues. Transplant Proc. 1978 Mar;10(1):19–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti F. W., Chervenick P. A. Release of colony-stimulating activity from thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):520–527. doi: 10.1172/JCI107958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Stevens R. H., Ramer S. J., Clements P. J., Yu D. T. Glucocorticoids administered in vivo inhibit human suppressor T lymphocyte function and diminish B lymphocyte responsiveness in in vitro immunoglobulin synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):922–930. doi: 10.1172/JCI109017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sensenbrenner L. L., Steele A. A., Santos G. W. Recovery of hematologic competence without engraftment following attempted bone marrow transplantation for aplastic anemia: Report of a case with diffusion chamber studies. Exp Hematol. 1977 Jan;5(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibbitt W. L., Jr, Bankhurst A. D., Williams R. C., Jr Studies of cell subpopulations mediating mitogen hyporesponsiveness in patients with Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):55–63. doi: 10.1172/JCI108925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J. W., Brown J. E., James M. C., Doney K., Warren R. P., Storb R., Thomas E. D. Effect of peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with aplastic anemia on granulocytic colony growth from HLA-matched and -mismatched marrows: effect of transfusion sensitization. Blood. 1978 Jul;52(1):37–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck B., Cornu P., Jeannet M., Nissen C., Burri H. P., Groff P., Nagel G. A., Buckner C. D. Autologous marrow recovery following allogeneic marrow transplantation in a patient with severe aplastic anemia. Exp Hematol. 1976 May;4(3):131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck B., Cornu P., Sartorius J., Nissen C., Groff P., Burri H. P., Jeannet M. Immunologic aspects of aplasia. Transplant Proc. 1978 Mar;10(1):131–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck B., Cornu P., Sartorius J., Nissen C., Groff P., Burri H. P., Jeannet M. Immunologic aspects of aplasia. Transplant Proc. 1978 Mar;10(1):131–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavy L., Cohen I. R., Feldman M. The effect of hydrocortisone on lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis. Cell Immunol. 1973 May;7(2):302–312. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90252-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J. Demonstration of suppressor T cells in a population of 'educated' T cells. Nature. 1974 Mar 15;248(445):236–238. doi: 10.1038/248236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J. T cell factor which can replace T cells in vivo. Nature. 1974 Mar 15;248(445):234–236. doi: 10.1038/248234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Territo M. C. Autologous bone marrow repopulation following high dose cyclophosphamide and allogeneic marrow transplantation in aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1977 Jul;36(3):305–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. D., Storb R., Giblett E. R., Longpre B., Weiden P. L., Fefer A., Witherspoon R., Clift R. A., Buckner C. D. Recovery from aplastic anemia following attempted marrow transplantation. Exp Hematol. 1976 Mar;4(2):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent P. C., Levi J. A., Macqueen A. The mechanism of neutropenia in Felty's syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1974 Jul;27(3):463–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagshal A. B., Jegasothy B. V., Waksman B. H. Regulatory substances produced by lymphocytes. VI. Cell cycle specificity of inhibitor of DNA synthesis action in L cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):171–181. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Blaese R. M., Broder S., Krakauer R. S. Disorders of suppressor immunoregulatory cells in the pathogenesis of immunodeficiency and autoimmunity. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Feb;88(2):226–238. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-2-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Broder S. Suppressor cells in the regulation of the immune response. Prog Clin Immunol. 1977;3:155–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor-Jedrzejczak W., Sharkie S., Ahmed A., Sell K. W., Santos G. W. Theta-sensitive cell and erythropoiesis: identification of a defect in W/Wv anemic mice. Science. 1977 Apr 15;196(4287):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.322288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipori D., Trainin N. The role of a thymus humoral factor in the proliferation of bone marrow CFU-S from thymectomized mice. Exp Hematol. 1975 Nov;3(6):389–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



