Abstract
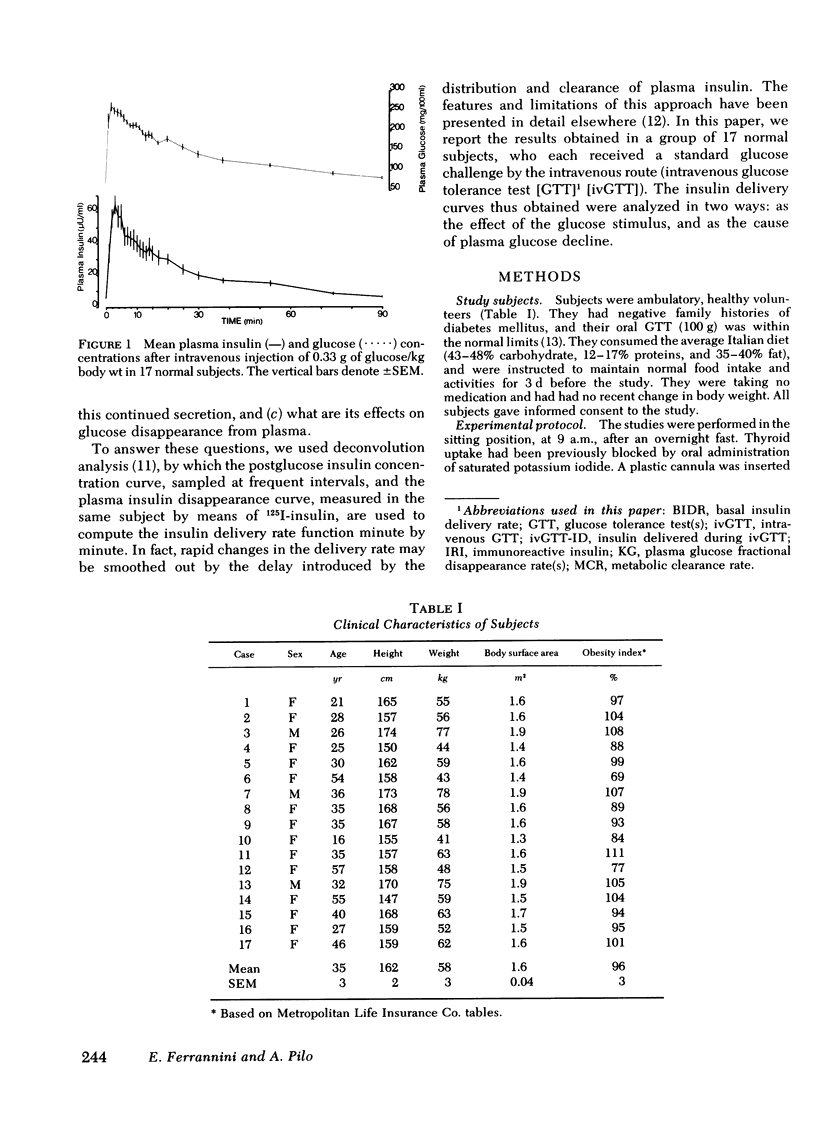
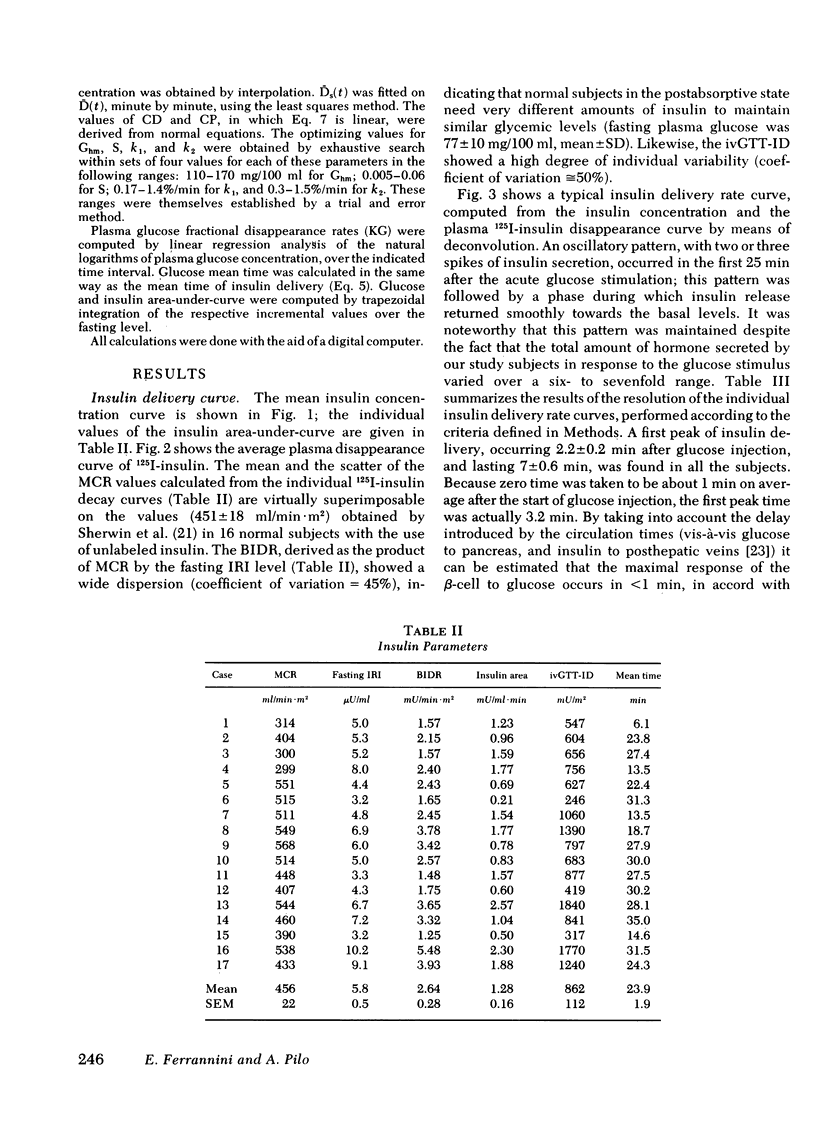
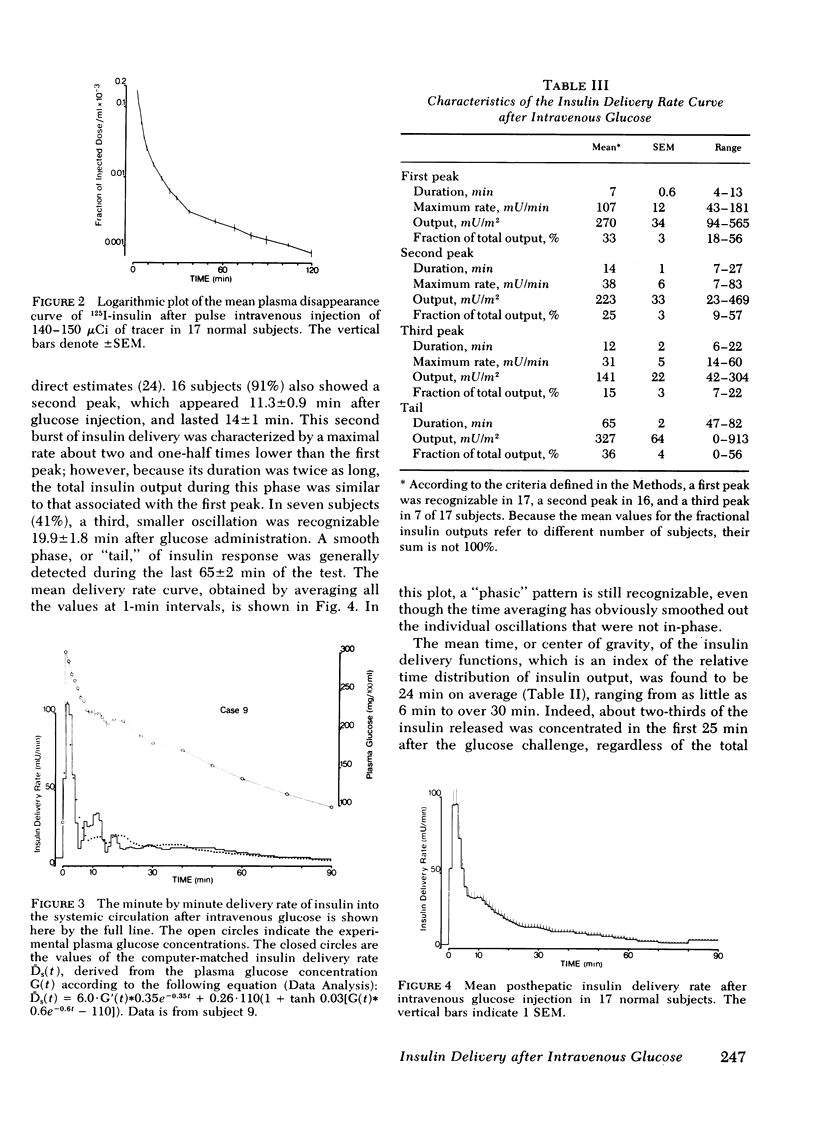
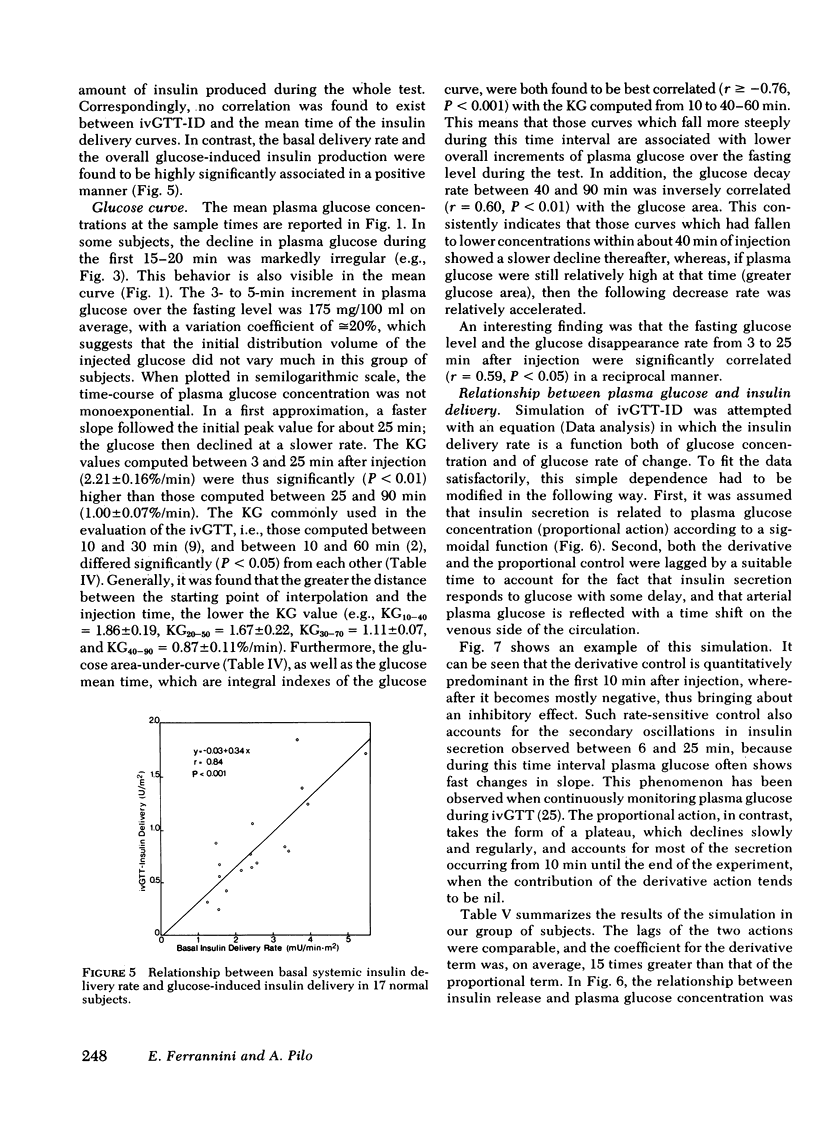
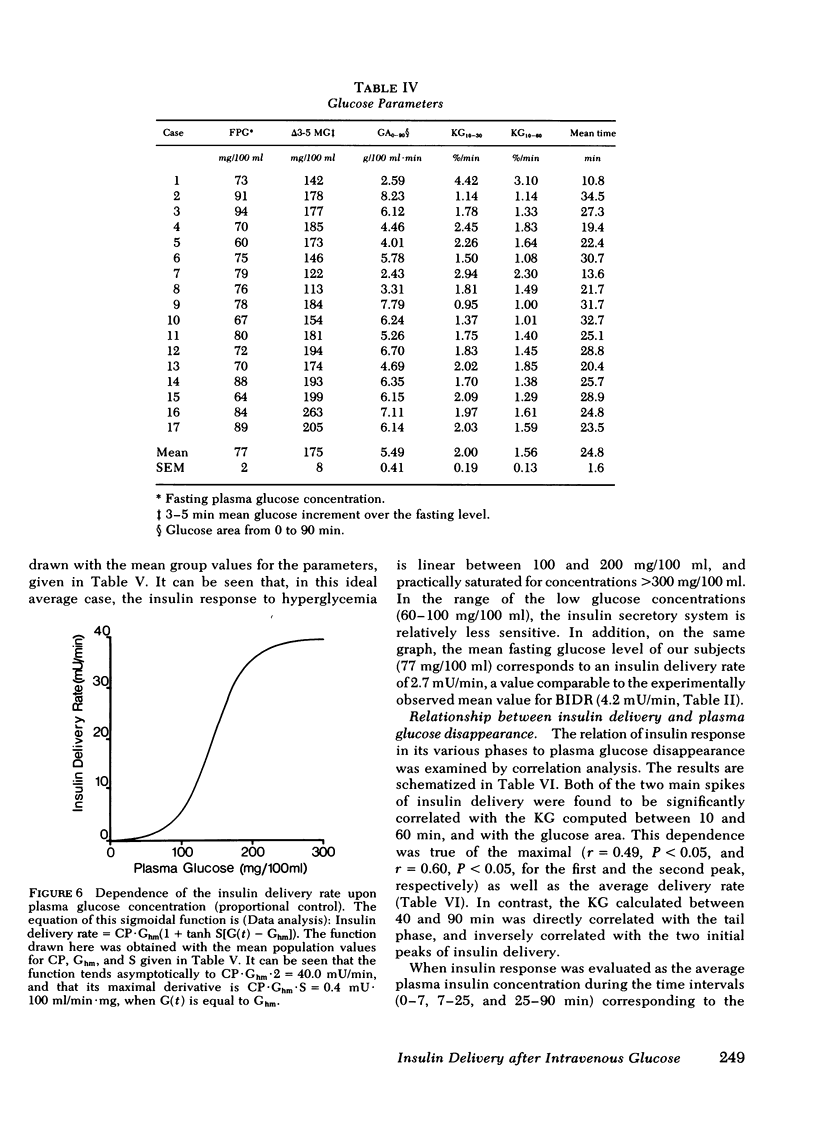
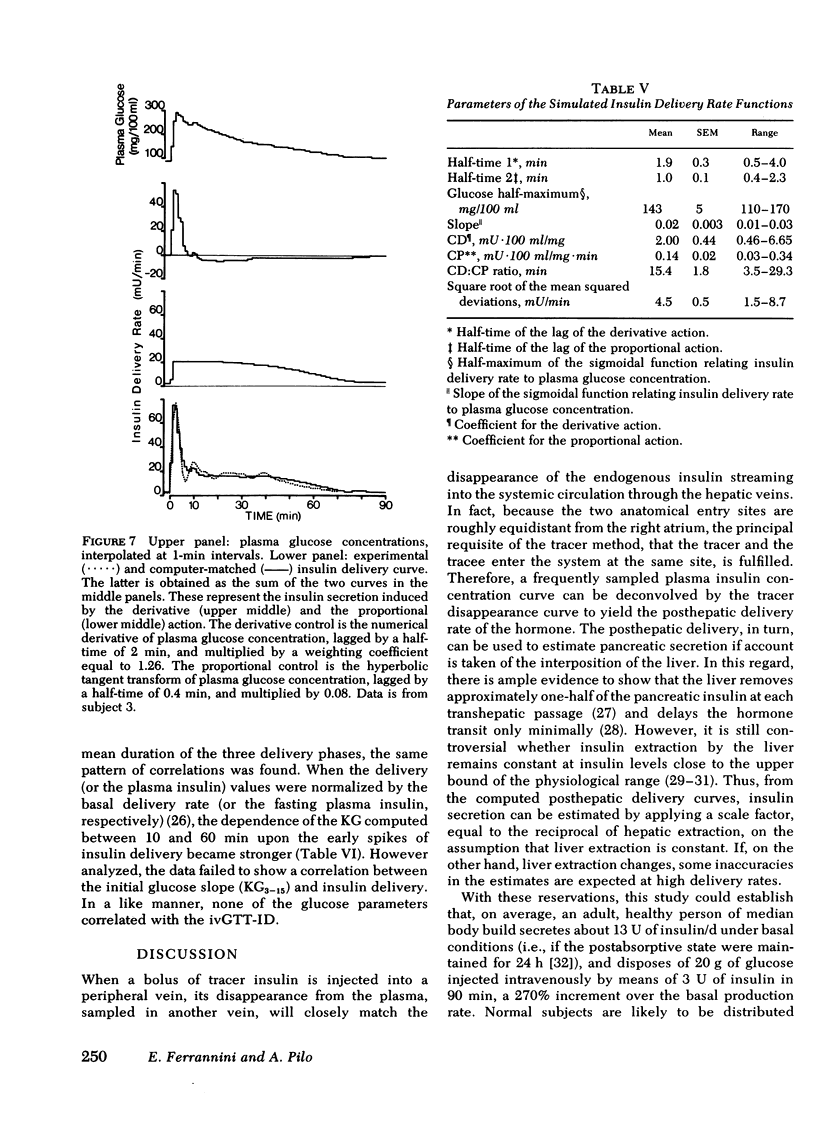
Plasma insulin concentrations after pulse intravenous injection of glucose show an early rise, which declines towards the prestimulation level smoothly. This pattern is the effect of both continuing secretion and hormone disappearance from the plasma. To reconstruct the time-course of the acutal secretory response, we measured insulin disappearance from the plasma of 17 healthy volunteers by means of a bolus intravenous injection of 125I-insulin, and then performed an intravenous glucose tolerance test with frequent blood sampling. The data were analyzed by deconvolution, which made it possible to compute the glucose-induced posthepatic insulin delivery rate minute by minute. Under basal conditions, 2.64 +/- 0.28 (mean +/-SEM) mU/min.m2 reaches the systemic circulation. In the 90 min that follow acute glucose stimulation, 0.86 +/- 0.11 U/m2, a 270% increment over the basal production rate, is made available to the periphery. A wide individual variability was found to exist in both the basal and the glucose-stimulated delivery. They were strongly (P less than 0.001) related to each other in a direct fashion. A first spike of insulin release (107 +/- 12 mU/min) occurred in all the subjects at 2.2 +/- 0.2 min followed, in 16 subjects, by a second spike (38 +/- 6 mU/min), at 11.3 +/- 0.9 min. Two-thirds of the total postglucose insulin output were associated with the initial, oscillatory phase (from 0 to 25 min, on average), and one-third with the "tail" phase (from 25 to 90 min), during which the average delivery rate was 5.0 +/- 0.9 mU/min.m2. The delivery curves were closely (mean squared deviation of 4.5 +/- 0.5 mU/min) reproduced by computer stimulation upon assuming that insulin secretion is a function of both glucose concentration and glucose rate of change. Both the first and the second spike of insulin delivery, but not the total insulin output during the test, showed a significant, positive correlation with the plasma glucose disappearance rate computed between 10 and 60 min. Furthermore, with a time shift of approximately equal to 15 min, a significant relationship between the phases of insulin secretion and the glucose decay rates, computed over corresponding time intervals, was evident throughout the test.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albisser A. M., Leibel B. S., Ewart T. G., Davidovac Z., Botz C. K., Zingg W. An artificial endocrine pancreas. Diabetes. 1974 May;23(5):389–396. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.5.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade J. D., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr The significance of basal insulin levels in the evaluation of the insulin response to glucose in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1549–1557. doi: 10.1172/JCI105646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. N., Urquhart J. The pilot gland approach to the study of insulin secretory dynamics. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1971;27:583–passim. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571127-2.50039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. S., Larner J. Rapid activation-inactivation of liver uridine diphosphate glucose-glycogen transferase and phosphorylase by insulin and glucagon in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 25;242(6):1354–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Nelson N. C. Portal and peripheral vein immunoreactive insulin concentrations before and after glucose infusion. Diabetes. 1970 May;19(5):302–306. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.5.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunzell J. D., Robertson R. P., Lerner R. L., Hazzard W. R., Ensinck J. W., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr Relationships between fasting plasma glucose levels and insulin secretion during intravenous glucose tolerance tests. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Feb;42(2):222–229. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-2-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERASI E., LUFT R. PLASMA-INSULIN RESPONSE TO SUSTAINED HYPERGLYCEMIA INDUCED BY GLUCOSE INFUSION IN HUMAN SUBJECTS. Lancet. 1963 Dec 28;2(7322):1359–1361. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90740-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Fick G., Rudemo M. A mathematical model for the glucose induced insulin release in man. Eur J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;4(4):267–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb00403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Porte D., Jr The effect of rate and dose of glucose infusion on the acute insulin response in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Jun;42(6):1168–1175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-6-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citti L., Battini L., Cecchetti P., Navalesi R. Monoiodoinsulin specifically substituted on A19 tyrosine: preparation, c. J Nucl Med Allied Sci. 1977 Oct-Dec;21(4):152–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citti L., Ferrannini E., Battini L., Navalesi R. Radioimmunoassay of labeled and unlabeled insulin mixtures. J Nucl Biol Med. 1976 Apr-Jun;20(2):75–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Dynamics of insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1968 Sep;83(3):572–584. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Andres R., Bedsoe T. A., Boden G., Faloona G. A., Tobin J. D. A test of the hypothesis that the rate of fall in glucose concentration triggers counterregulatory hormonal responses in man. Diabetes. 1977 May;26(5):445–452. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.5.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Hendler R., Wahren J., Felig P. Influence of hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and the route of glucose administration on splanchnic glucose exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAJANS S. S., CONN J. W. The early recognition of diabetes mellitus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:208–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould M. K., Chaudry I. H. The action of insulin on glucose uptake by isolated rat soleus muscle. II. Dissociation of a priming effect of insulin from its stimulatory effect. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 14;215(2):258–263. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grill V., Adamson U., Cerasi E. Immediate and time-dependent effects of glucose on insulin release from rat pancreatic tissue. Evidence for different mechanisms of action. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1034–1043. doi: 10.1172/JCI109002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M. A threshold distribution hypothesis for packet storage of insulin and its mathematical modeling. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2047–2059. doi: 10.1172/JCI107011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyton J. R., Foster R. O., Soeldner J. S., Tan M. H., Kahn C. B., Koncz L., Gleason R. E. A model of glucose-insulin homeostasis in man that incorporates the heterogeneous fast pool theory of pancreatic insulin release. Diabetes. 1978 Oct;27(10):1027–1042. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.10.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding P. E., Bloom G., Field J. B. Effect of infusion of insulin into portal vein on hepatic extraction of insulin in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1975 May;228(5):1580–1588. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.5.1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Kramer K. J., Sherwin R. S., Liljenquist J. E., Tobin J. D., Andres R., Berman M. Modeling the insulin-glucose system in man. Fed Proc. 1974 Jul;33(7):1865–1868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaden M., Harding P., Field J. B. Effect of intraduodenal glucose administration on hepatic extraction of insulin in the anesthetized dog. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):2016–2028. doi: 10.1172/JCI107386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamori R., Shichiri M., Goriya Y., Yamasaki Y., Shigeta Y., Abe H. Importance of insulin secretion based on the rate of change in blood glucose concentration in glucose tolerance, assessed by the artificial beta cell. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1978 Feb;87(2):339–351. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0870339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerner W., Thum C., Tamás G., Beischer W., Clemens A. H., Pfeiffer E. F. Attempts at perfect normalization of glucose tolerance test of severe diabetics by artificial beta cell. Horm Metab Res. 1976 Jul;8(4):256–261. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBAEK K. Intravenous glucose tolerance as a tool in definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1962 Jun 2;1(5291):1507–1513. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5291.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. L., Porte D., Jr Relationship between intravenous glucose loads, insulin responses and glucose disappearance rate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Sep;33(3):409–417. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire E. A., Helderman J. H., Tobin J. D., Andres R., Berman M. Effects of arterial versus venous sampling on analysis of glucose kinetics in man. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Oct;41(4):565–573. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.4.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirouze J., Collard F., Selam J. L., Pham J. Continuous blood glucose monitoring in insulin-treated diabetes. Horm Metab Res. 1977;Suppl 7:77–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirouze J., Selam J. L., Pham T. C., Cavadore D. Evaluation of exogenous insulin homoeostasis by the artificial pancreas in insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetologia. 1977 May;13(3):273–278. doi: 10.1007/BF01219712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navalesi R., Pilo A., Ferrannini E. Insulin kinetics after portal and peripheral injection of [125I] insulin: II. Experiments in the intact dog. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jun;230(6):1630–1636. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.6.1630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navalesi R., Pilo A., Ferrannini E. Kinetic analysis of plasma insulin disappearance in nonketotic diabetic patients and in normal subjects. A tracer study with 125I-insulin. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):197–208. doi: 10.1172/JCI108918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor M. D., Landahl H. D., Grodsky G. M. Role of rate of change of glucose concentration as a signal for insulin release. Endocrinology. 1977 Jul;101(1):85–88. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilo A., Ferrannini E., Navalesi R. Measurement of glucose-induced insulin delivery rate in man by deconvolution analysis. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):E500–E508. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.6.E500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilo A., Zucchelli G. C. Automatic treatment of radioimmunoassay data: an experimental validation of the results. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Oct 1;64(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Bagdade J. D. Human insulin secretion: as integrated approach. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:219–240. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Pupo A. A. Insulin responses to glucose: evidence for a two pool system in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2309–2319. doi: 10.1172/JCI106197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Olefsky J. M. Relationship between insulin response during the intravenous glucose tolerance test, rate of fractional glucose removal and the degree of insulin resistance in normal adults. Diabetes. 1974 May;23(5):454–459. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.5.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robin M., Saifer A. Determination of glucose in biologic fluids with an automated enzymatic procedure. Clin Chem. 1965 Sep;11(9):840–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röjdmark S., Bloom G., Chou M. C., Jaspan J. B., Field J. B. Hepatic insulin and glucagon extraction after their augmented secretion in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jul;235(1):E88–E96. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.1.E88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodoyez J. C., Sodoyez-Goffaux F., Goff M. M., Zimmerman A. E., Arquilla E. R. [127-I]- or carrier-free [125-I]monoiodoinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4268–4277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Nosslin B., Sterky G. Estimation of the early insulin response to intravenous glucose injection. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Jul;82(1):101–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. C., Grayburn J. A., Newman G. B., Nabarro J. D. Measurement of the insulin delivery rate in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):279–286. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vagnucci A. H., McDonald R. H., Jr, Drash A. L., Wong A. K. Intradiem changes of plasma aldosterone, cortisol, corticosterone and growth hormone in sodium restriction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 May;38(5):761–776. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-5-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


