Abstract
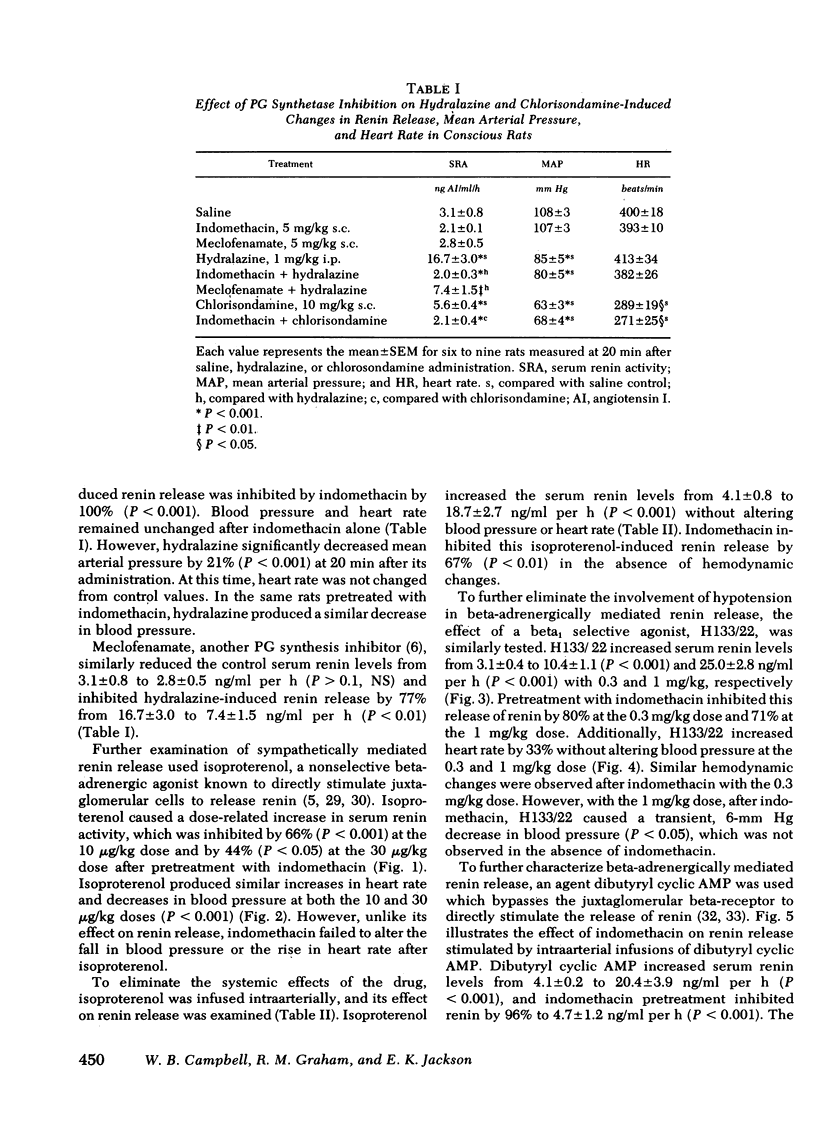
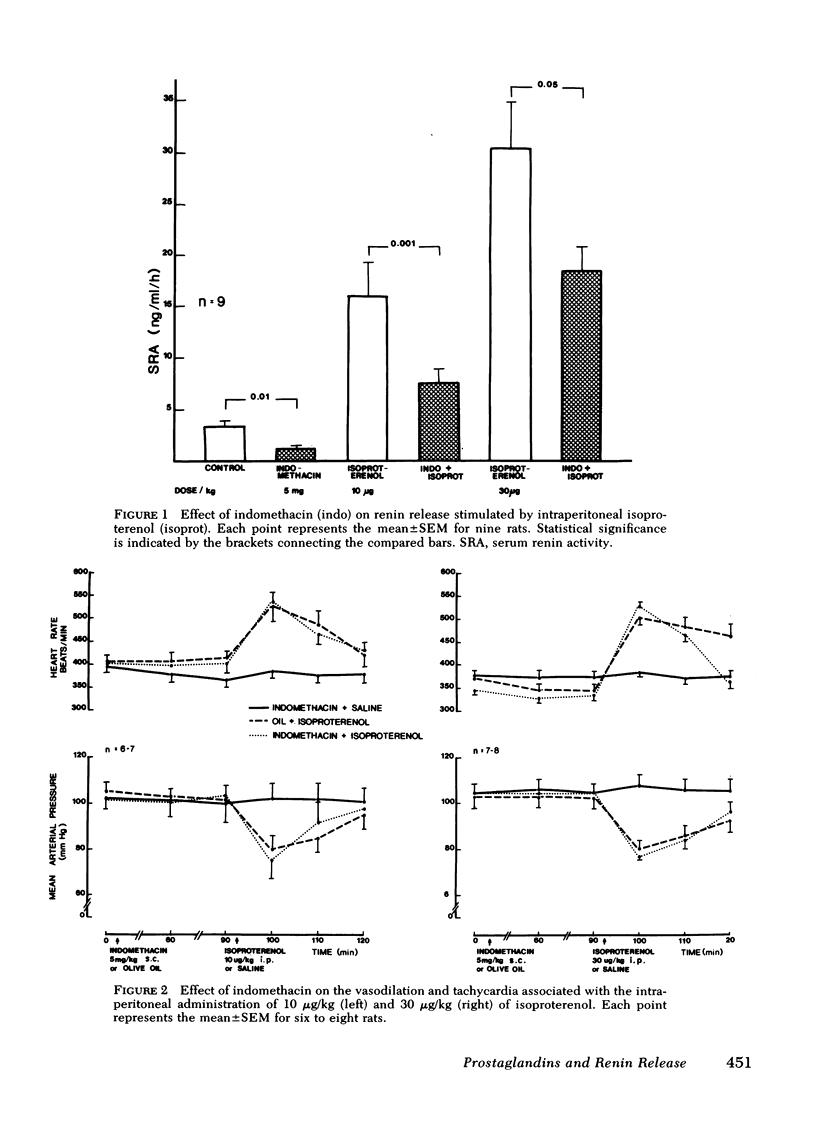
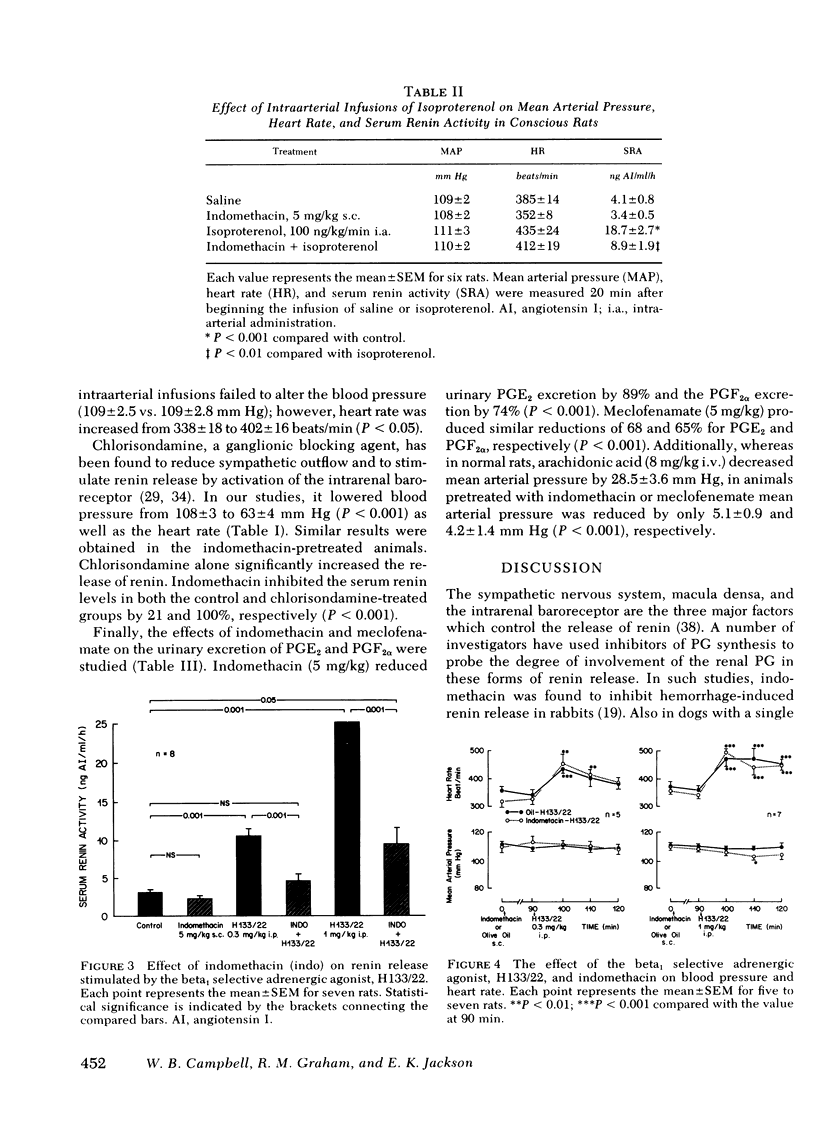
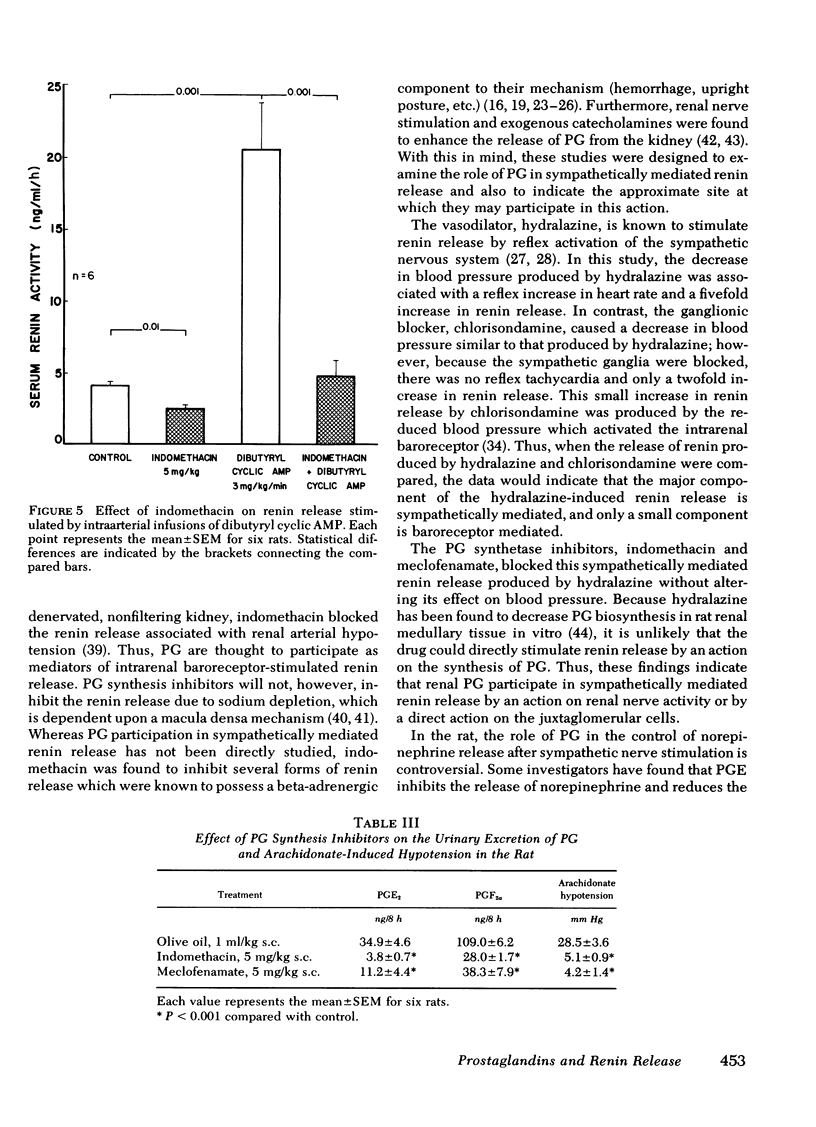
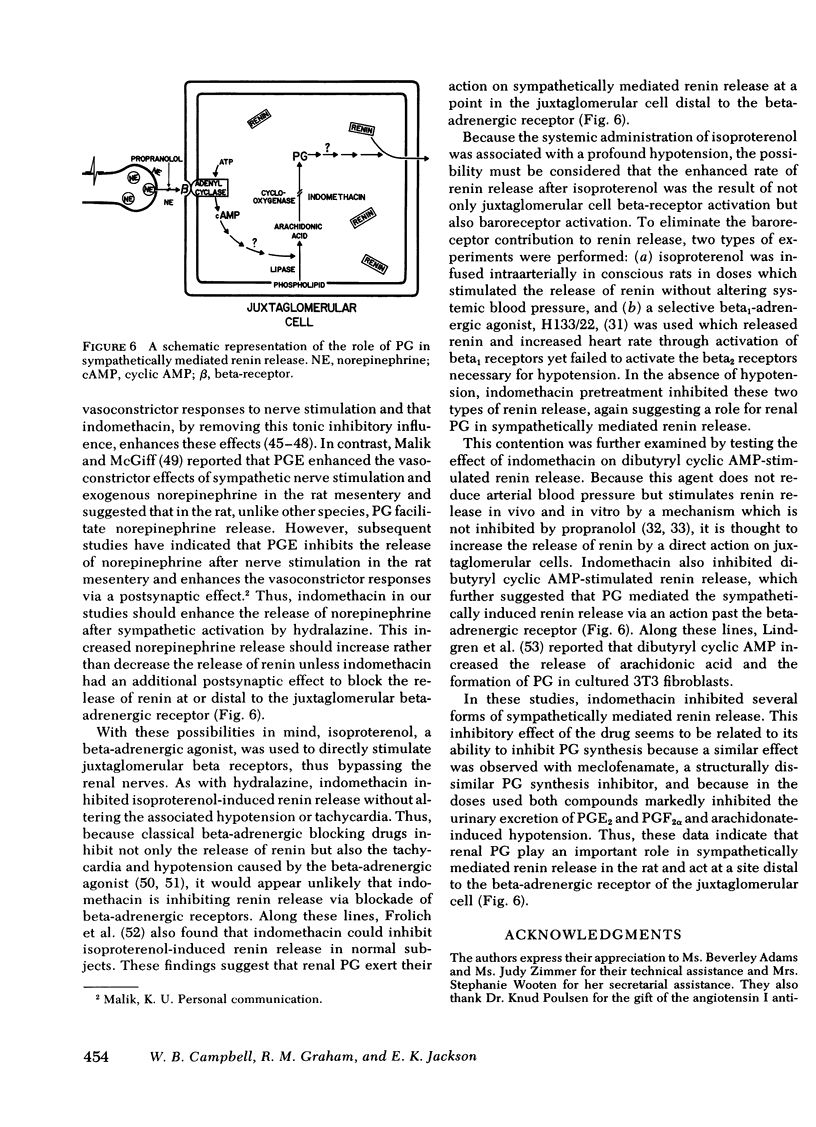
Renal prostaglandins (PG) appear to mediate renin release due to stimulation of the intrarenal baroreceptor, but not that due to activation of the macula densa. However, as the role of PG in sympathetically mediated renin release remains unclear, a possible interrelationship between these factors was examined in conscious rats. Hydralazine increased the serum renin levels from 3.1±0.8 to 16.7±3.0 ng/ml per h at a dose of 1 mg/kg. Indomethacin (5 mg/kg) suppressed urinary PGE2 and PGF2α excretion by 89 and 74%, respectively, arachidonate hypotension by 82%, and inhibited the elevated renin levels from hydralazine by 100% without altering the hypotensive effect of the drug. Another PG synthetase inhibitor, meclofenamate, was also effective in attenuating hydralazine-induced renin release, urinary PGE2 and PGF2α excretion, and arachidonate hypotension. Isoproterenol, a nonselective beta-adrenergic agonist, increased heart rate, lowered blood pressure, and also stimulated the release of renin when administered intraperitoneally. However, intrarenal infusion of the drug only resulted in increased renin release. Indomethacin inhibited isoproterenol-induced renin release by 66 and 67%, respectively, without altering the hemodynamic effects associated with the intraperitoneal administration of the drug. The selective beta1 agonist, H133/22, increased the release of renin and heart rate in a dose-related manner without altering blood pressure. H133/22-induced renin release was inhibited by 80% by indomethacin pretreatment. Finally, intrarenal infusions of dibutyryl cyclic AMP (3 mg/kg per min) increased the serum activity from 4.1±0.2 to 20.4±3.9 ng/ml per h without altering mean arterial pressure. Indomethacin inhibited this renin response to dibutyryl cyclic AMP by 96%. Thus, renal PG appear to be important mediators of sympathetically stimulated renin release acting as a site distal to the beta-adrenergic receptor.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergström S., Farnebo L. O., Fuxe K. Effect of prostaglandin E 2 on central and peripheral catecholamine neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;21(3):362–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger P. M., Eisner G. M., Ramwell P. W., Slotkoff L. M. Effect of prostaglandin synthesis on renal function and renin in the dog. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):244–245. doi: 10.1038/259244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger P. M., Eisner G. M., Ramwell P. W., Slotkoff L. M. Renal actions of prostacyclin. Nature. 1978 Feb 2;271(5644):467–469. doi: 10.1038/271467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger P. M., Eisner G. M., Shea P. T., Ramwell P. W., Slotkoff L. M. Effects of PGD2 on canine renal function. Nature. 1977 Jun 16;267(5612):628–630. doi: 10.1038/267628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson E., Dahlöf C. G., Hedberg A., Persson H., Tångstrand B. Differentiation of cardiac chronotropic and inotropic effects of beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Nov;300(2):101–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00505039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Data J. L., Gerber J. G., Crump W. J., Frölich J. C., Hollifield J. W., Nies A. S. The prostaglandin system. A role in canine baroreceptor control of renin release. Circ Res. 1978 Apr;42(4):454–458. doi: 10.1161/01.res.42.4.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. O., Freeman R. H. Mechanisms regulating renin release. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):1–56. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray F., Charbonnel B., Maclouf J. Radioimmunoassay of prostaglandins Falpha, E1 and E2 in human plasma. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul 29;5(4):311–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham E. W., Zimmerman B. G. Release of prostaglandin-like material from dog kidney during nerve stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1279–1285. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichman M. P., Telfer N., Zia P., Speckart P., Golub M., Rude R. Role of prostaglandins in the pathogenesis of Bartter's syndrome. Am J Med. 1976 May 31;60(6):785–797. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90892-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Mar;26(1):33–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Hedqvist P. Indomethacin-induced increase in noradrenaline turnover in some rat organs. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Jul;54(3):295–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frölich J. C., Hollifield J. W., Dormois J. C., Frölich B. L., Seyberth H., Michelakis A. M., Oates J. A. Suppression of plasma renin activity by indomethacin in man. Circ Res. 1976 Sep;39(3):447–452. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber J. G., Branch R. A., Nies A. S., Gerkens J. F., Shand D. G., Hollifield J., Oates J. A. Prostaglandins and renin release: II. Assessment of renin secretion following infusion of PGI2,E2 and D2 into the renal artery of anesthetized dogs. Prostaglandins. 1978 Jan;15(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(78)80006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. R., Jr, Frölich J. C., Bowden R. E., Taylor A. A., Keiser H. R., Seyberth H. W., Oates J. A., Bartter F. C. Bartter's syndrome: a disorder characterized by high urinary prostaglandins and a dependence of hyperreninemia on prostaglandin synthesis. Am J Med. 1976 Jul;61(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub M. S., Speckart P. F., Zia P. K., Horton R. The effect of prostaglandin A1 on renin and aldosterone in man. Circ Res. 1976 Oct;39(4):574–579. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.4.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms H. H., Gooren L., Spoelstra A. J., Hesse C., Verschoor L. Blockade of isoprenaline-induced changes in plasma free fatty acids, immunoreactive insulin levels and plasma renin activity in healthy human subjects, by propranolol, pindolol, practolol, atenolol, metoprolol and acebutolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;5(1):19–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeton T. K., Pettinger W. A. The dominance of adrenergic mechanisms in mediating hypotensive drug-induced renin release in the conscious rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Feb;208(2):303–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakoff L. R., De Guia D., Vlachakis N., Stricker J., Goldstein M. Effect of sodium balance on arterial blood pressure and renal responses to prostaglandin A1 in man. Circ Res. 1973 Nov;33(5):539–546. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.5.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson C., Weber P., Anggård E. Arachidonic acid increases and indomethacin decreases plasma renin activity in the rabbit. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Oct;28(2):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren J. A., Claesson H. E., Hammarström S. Stimulation of arachidonic acid release and prostaglandin production in 3T3 fibroblasts by adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1978;3:167–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik K. U., McGiff J. C. Modulation by prostaglandins of adrenergic transmission in the isolated perfused rabbit and rat kidney. Circ Res. 1975 May;36(5):599–609. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.5.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., Caudle J., Liddle G. W. In vitro stimulation of renin production by epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cyclic AMP. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Mar;130(3):748–753. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., McAllister R. G. The effect of chronic adrenergic receptor blockade on plasma renin activity in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Feb;34(2):386–394. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-2-386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Douglas J. R., Jr, Jakschik B., Stoecklein P. B., Johnson E. M., Jr Release of renal prostaglandin by catecholamines: relationship to renal endocrine function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Feb;188(2):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Marshall G. R., Johnson E. M., Jr Determinants and modification of adrenergic and vascular resistance in the kidney. Am J Physiol. 1974 Sep;227(3):665–669. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.3.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbiato G., Bevilacqua M., Raggi U., Micossi P., Moroni C., Fasoli A. Effect of prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors on renin and aldosterone in man on a normal or low sodium diet. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1978 Mar;87(3):577–588. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0870577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okahara T., Abe Y., Yamamoto K. Effects of dibutyryl cyclic AMP and propranolol on renin secretion in dogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Nov;156(2):213–218. doi: 10.3181/00379727-156-39909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patak R. V., Mookerjee B. K., Bentzel C. J., Hysert P. E., Babej M., Lee J. B. Antagonism of the effects of furosemide by indomethacin in normal and hypertensive man. Prostaglandins. 1975 Oct;10(4):649–659. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(75)80012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Campbell W. B., Keeton K. Adrenergic component of renin release induced by vasodilating antihypertensive drugs in the rat. Circ Res. 1973 Jul;33(1):82–86. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Keeton K. Altered renin release and propranolol potentiation of vasodilatory drug hypotension. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):236–243. doi: 10.1172/JCI107927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K., Jorgensen J. An easy radioimmunological microassay of renin activity, concentration and substrate in human and animal plasma and tissues based on angiotensin I trapping by antibody. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Nov;39(5):816–825. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-5-816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero J. C., Dunlap C. L., Strong C. G. The effect of indomethacin and other anti-inflammatory drugs on the renin-angiotensin system. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):282–288. doi: 10.1172/JCI108470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero J. C., Strong C. G. The effect of indomethacin blockade of prostaglandin synthesis on blood pressure of normal rabbits and rabbits with renovascular hypertension. Circ Res. 1977 Jan;40(1):35–41. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumpf K. W., Frenzel S., Lowitz H. D., Scheler F. The effect of indomethacin on plasma renin activity in man under normal conditions and after stimulation of the renin angiotensin system. Prostaglandins. 1975 Oct;10(4):641–648. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(75)80011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobert J. A., Slater J. D., Fogelman F., Lightman S. L., Kurtz A. B., Payne N. N. The effect in man of (+)-propranolol and racemic propranolol on renin secretion stimulated by orthostatic stress. Clin Sci. 1973 Mar;44(3):291–295. doi: 10.1042/cs0440291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres V. E., Strong C. G., Romero J. C., Wilson D. M. Indomethacin enhancement of glycerol-induced acute renal failure in rabbits. Kidney Int. 1975 Mar;7(3):170–178. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber P. C., Larsson C., Anggard E., Hamberg M., Corey E. J., Nicolaou K. C., Samuelsson B. Stimulation of renin release from rabbit renal cortex by arachidonic acid and prostaglandin endoperoxides. Circ Res. 1976 Dec;39(6):868–874. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.6.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. A., Thornell I. R., Stokes G. S. Effects of beta adrenergic blocking agents on plasma renin activity in the conscious rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Jan;188(1):234–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P., Holzgreve H., Stephan R., Herbst R. Plasma renin activity and renal sodium and water excretion following infusion of arachidonic acid in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;34(2):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90255-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger M. H., Aoi W., Henry D. P. Direct effect of beta-adrenergic stimulation on renin release by the rat kidney slice in vitro. Circ Res. 1975 Sep;37(3):318–324. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werning C., Vetter W., Weidmann P., Schweikert H. U., Stiel D., Siegenthaler W. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on renin in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):852–856. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whorton A. R., Misono K., Hollifield J., Frolich J. C., Inagami T., Oates J. A. Prostaglandins and renin release: I. Stimulation of renin release from rabbit renal cortical slices by PGI2. Prostaglandins. 1977;14(6):1095–1104. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whorton A. R., Smigel M., Oates J. A., Frölich J. C. Regional differences in prostacyclin formation by the kidney. Prostacyclin is a major prostaglandin of renal cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 28;529(1):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun J., Kelly G., Bartter F. C., Smith H., Jr Role of prostaglandins in the control of renin secretion in the dog. Circ Res. 1977 May;40(5):459–464. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.5.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenser T. V., Herman C. A., Gorman R. R., Davis B. B. Metabolism and action of the prostaglandin endoperoxide PGH2 in rat kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Nov 21;79(2):357–363. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


