Abstract
In view of the potent influences of the central nervous system on glucose metabolism and on its hormonal regulators, and our recent finding of insulin and insulin receptors throughout the central nervous systsem, we have examined extreme conditions of hyperinsulinemia (obese mice) and hypoinsulinemia (streptozotocin-treated rats) with respect to changes in brain insulin and receptor content. Sprague-Dawley rats given streptozotocin (100 mg/kg body wt) developed severe diabetes and by 48 h showed no change in brain insulin. Rats given 65 mg/kg streptozotocin also had severe diabetes, but survived longer. Both at 7 d and at 30 d after streptozotocin treatment there was no significant change in brain insulin or in brain content of insulin receptors, despite the fact that peripheral hepatic receptors were elevated and pancreatic insulin was markedly depleted.
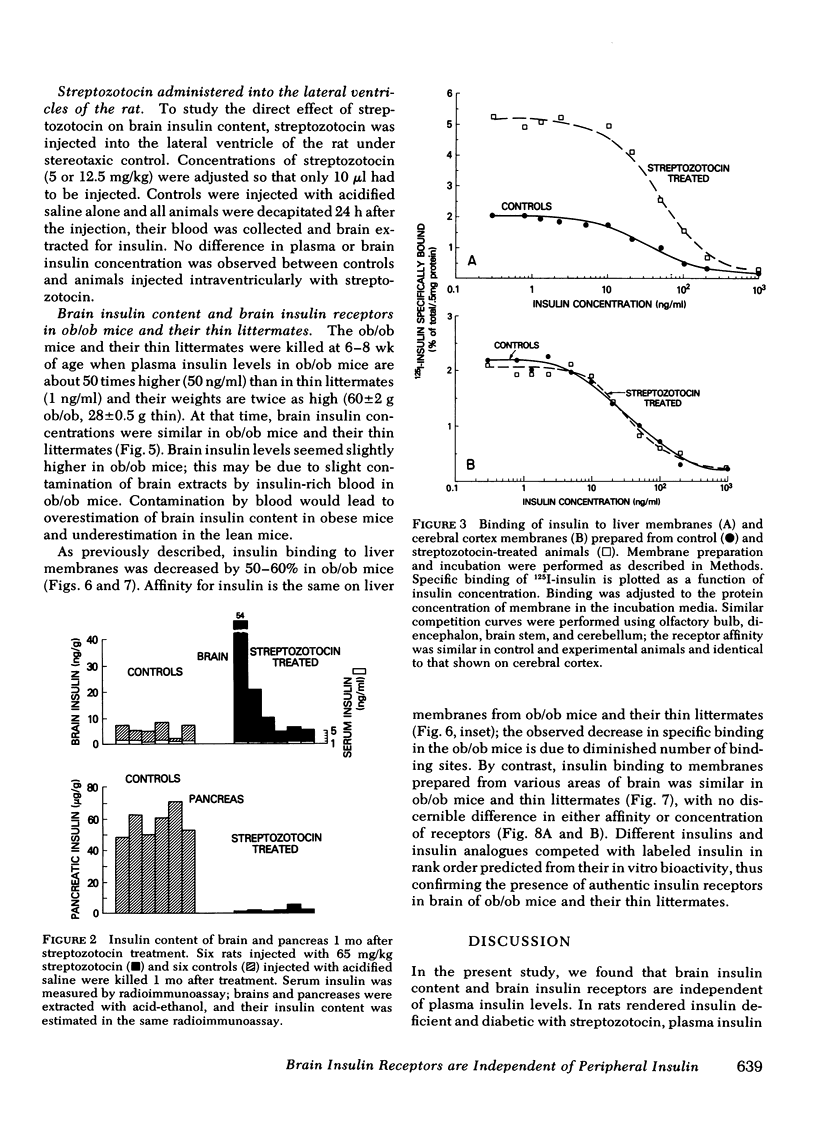
The obese mice were studied at 8-10 wk when peripheral plasma insulin concentrations were 50-fold elevated and receptors on peripheral target cells were reduced to ≅40-50% of normal; brain insulin concentrations and receptor content were indistinguishable from those of thin littermates. Thus, brain insulin, which is typically 10 times higher than plasma insulin concentrations, and brain receptor content, which is equivalent to receptor content on peripheral tissues, appears to be regulated entirely independently of hormone and receptor in the periphery. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that insulin in the central nervous system is synthesized by the neural elements, and plays a role in the central nervous system which is unrelated to peripheral glucose metabolism.
Full text
PDF


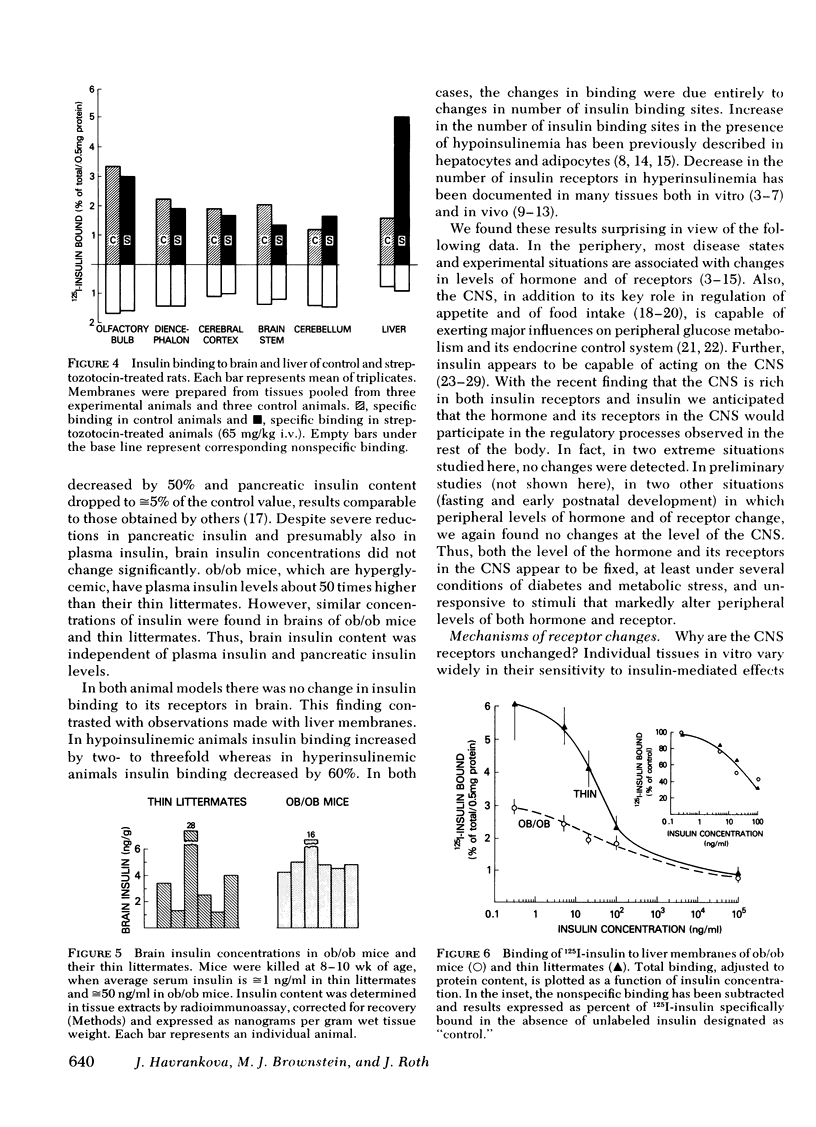

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
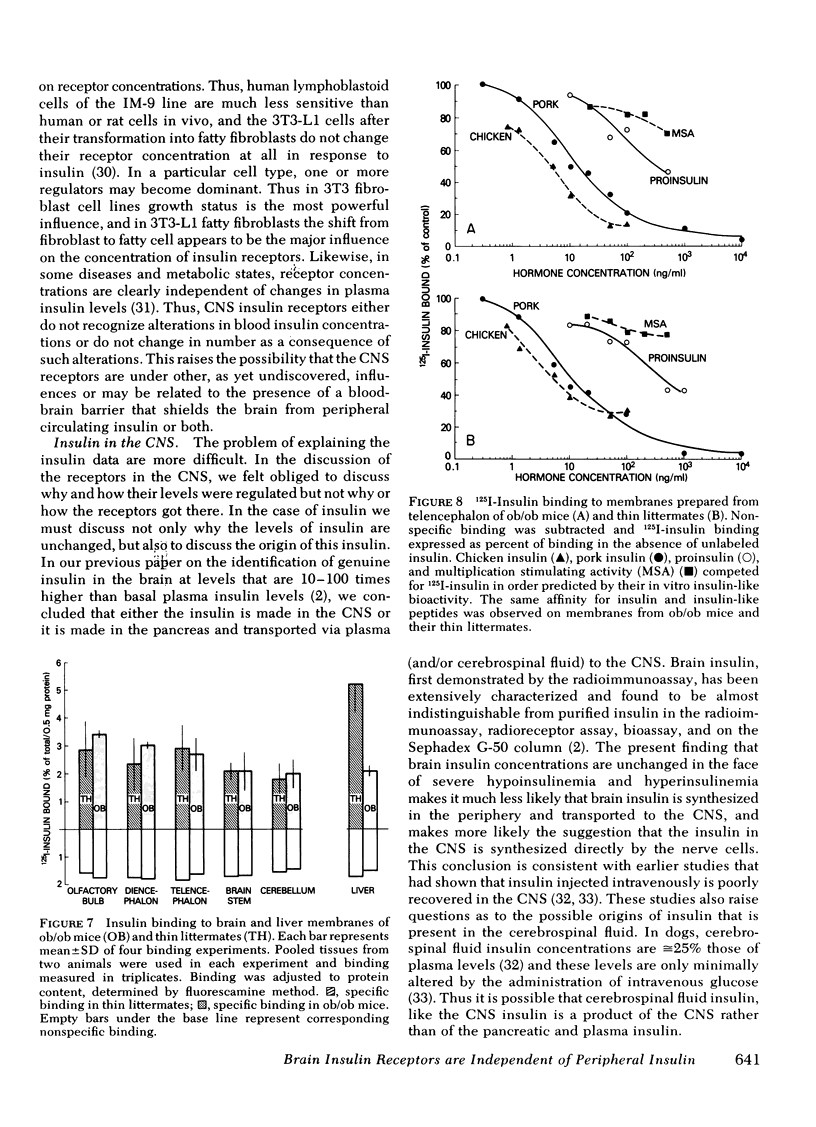
- Archer J. A., Gorden P., Roth J. Defect in insulin binding to receptors in obese man. Amelioration with calorie restriction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):166–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI107907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Gorden P., Roth J., Kahn C. R., De Meyts P. Fluctuations in the affinity and concentration of insulin receptors on circulating monocytes of obese patients: effects of starvation, refeeding, and dieting. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1123–1135. doi: 10.1172/JCI108565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B., Kaplan S. A. Increased insulin binding by hepatic plasma membranes from diabetic rats: normalization by insulin therapy. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):22–30. doi: 10.1172/JCI108618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debons A. F., Krimsky I., From A., Cloutier R. J. Rapid effects of insulin on the hypothalamic satiety center. Am J Physiol. 1969 Oct;217(4):1114–1118. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.4.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgue M. E., Freychet P. Insulin receptors in the heart muscle. Demonstration of specific binding sites and impairment of insulin binding in the plasma membrane of the obese hyperglycemic mouse. Diabetes. 1975 Aug;24(8):715–723. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.8.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Laudat M. H., Laudat P., Rosselin G., Kahn C. R., Gorden P., Roth J. Impairment of insulin binding to the fat cell plasma membrane in the obese hyperglycemic mouse. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Bernardis L. L. Effect of hypothalamic stimulation on plasma glucose, insulin, and glucagon levels. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1596–1603. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Martin F. I., Melick R. A. Correlation between insulin receptor binding in isolated fat cells and insulin sensitivity in obese human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1435–1441. doi: 10.1172/JCI108599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havrankova J., Roth J., Brownstein M. Insulin receptors are widely distributed in the central nervous system of the rat. Nature. 1978 Apr 27;272(5656):827–829. doi: 10.1038/272827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havrankova J., Schmechel D., Roth J., Brownstein M. Identification of insulin in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5737–5741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junod A., Lambert A. E., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Diabetogenic action of streptozotocin: relationship of dose to metabolic response. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2129–2139. doi: 10.1172/JCI106180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Gorden P., Freychet P., Roth J. Insulin receptor defect in insulin resistance: studies in the obese-hyperglycimic mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson F. A., Grunfeld C., Kahn C. R., Roth J. Regulation of insulin receptors and insulin responsiveness in 3T3-L1 fatty fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1979 May;104(5):1383–1392. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-5-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. U., Altszuler N. Insulin in the cerebrospinal fluid. Nature. 1967 Sep 23;215(5108):1375–1376. doi: 10.1038/2151375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer J., Thomas D. W. Regulation of food intake and obesity. Science. 1967 Apr 21;156(3773):328–337. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3773.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Decreased insulin binding to adipocytes and circulating monocytes from obese subjects. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1165–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI108384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Beck-Nielsen H., Heding L. Insulin receptors on monocytes from patients with ketosis-prone diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1978 Nov;27(11):1098–1104. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.11.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr Sympathetic regulation of insulin secretion. Its relation to diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Mar;123(3):252–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafaelsen O. J. Insulin action on the central nervous system. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1967;476:75–84. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1967.tb12686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soli A. H., Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin receptor deficiency in genetic and acquired obesity. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):769–780. doi: 10.1172/JCI108155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll A. H., Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin binding to liver plasm membranes in the obese hyperglycemic (ob/ob) mouse. Demonstration of a decreased number of functionally normal receptors. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4702–4707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo O., Szabo A. J. Evidence for an insulin-sensitive receptor in the central nervous system. Am J Physiol. 1972 Dec;223(6):1349–1353. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.6.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo O., Szabo A. J. Studies on the nature and mode of action of the insulin-sensitive glucoregulator receptor in the central nervous system. Diabetes. 1975 Apr;24(4):328–336. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.4.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr Effect of intracisternal insulin on plasma glucose and insulin in the dog. Diabetes. 1975 Oct;24(10):905–909. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.10.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr Neural control of the endocrine pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1974 Jul;54(3):596–619. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



