Abstract
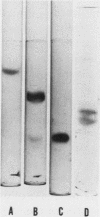
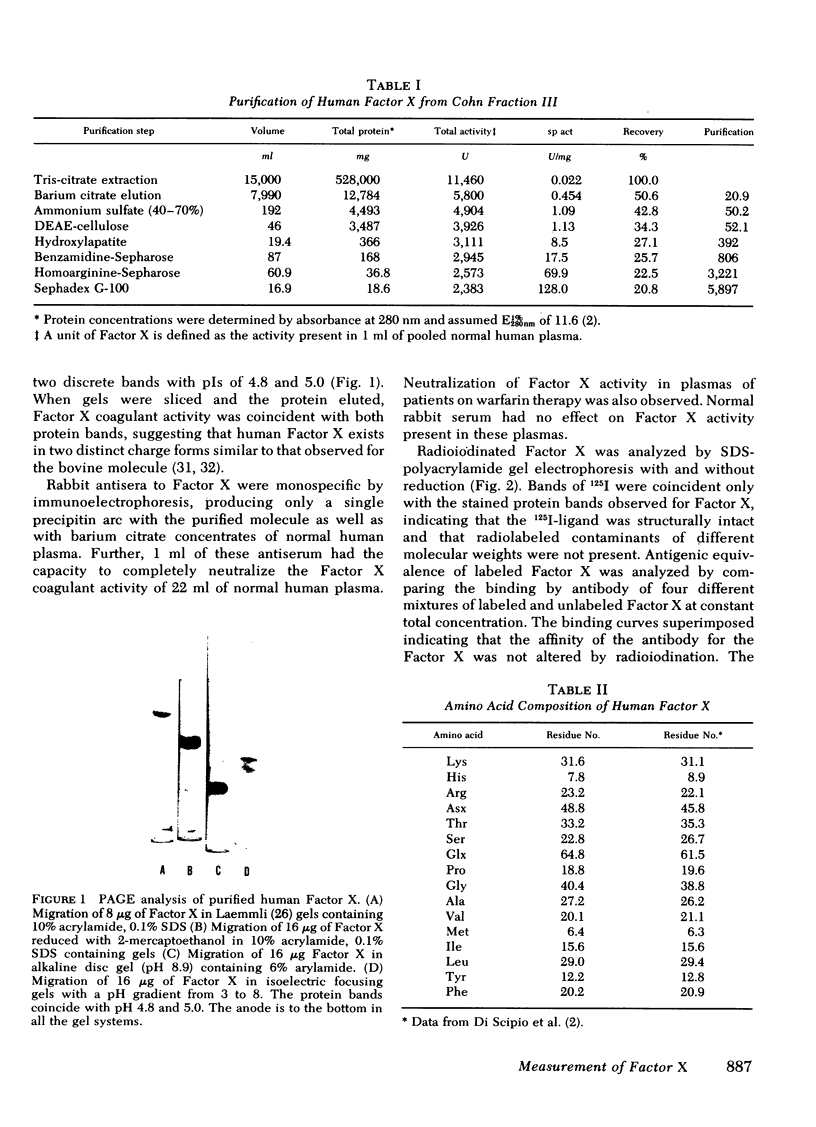
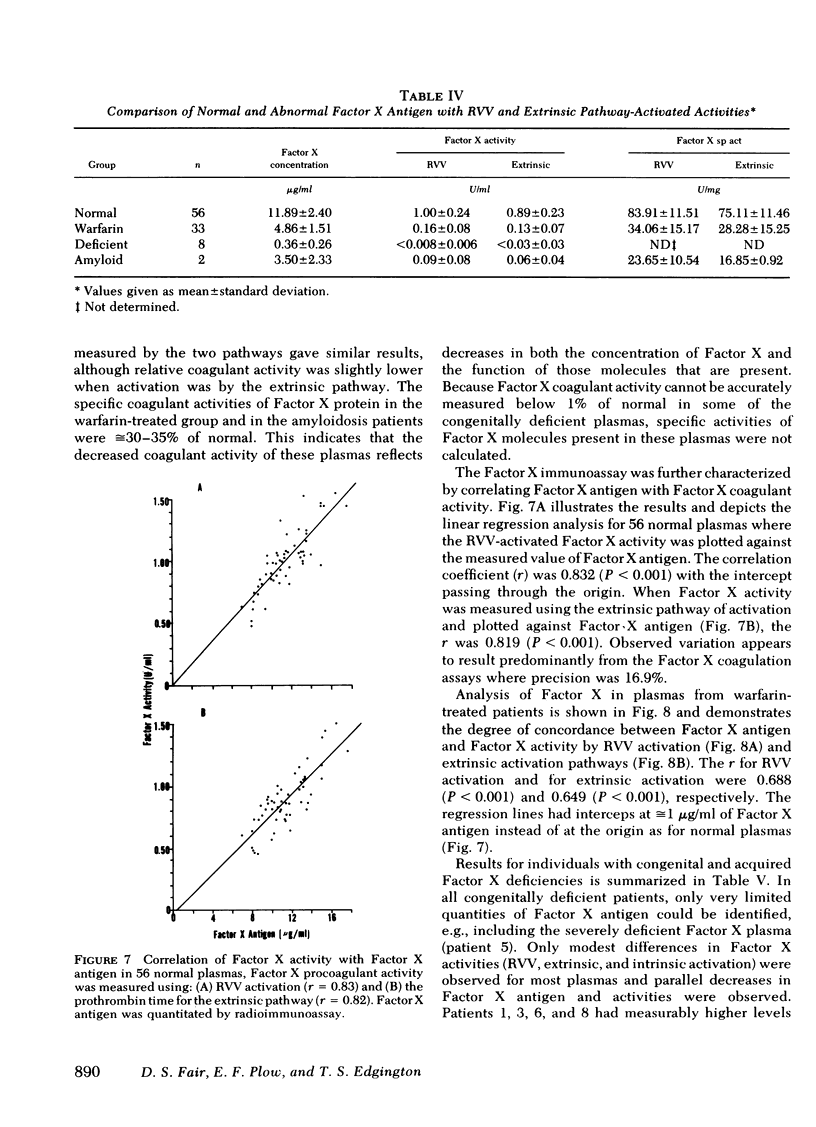
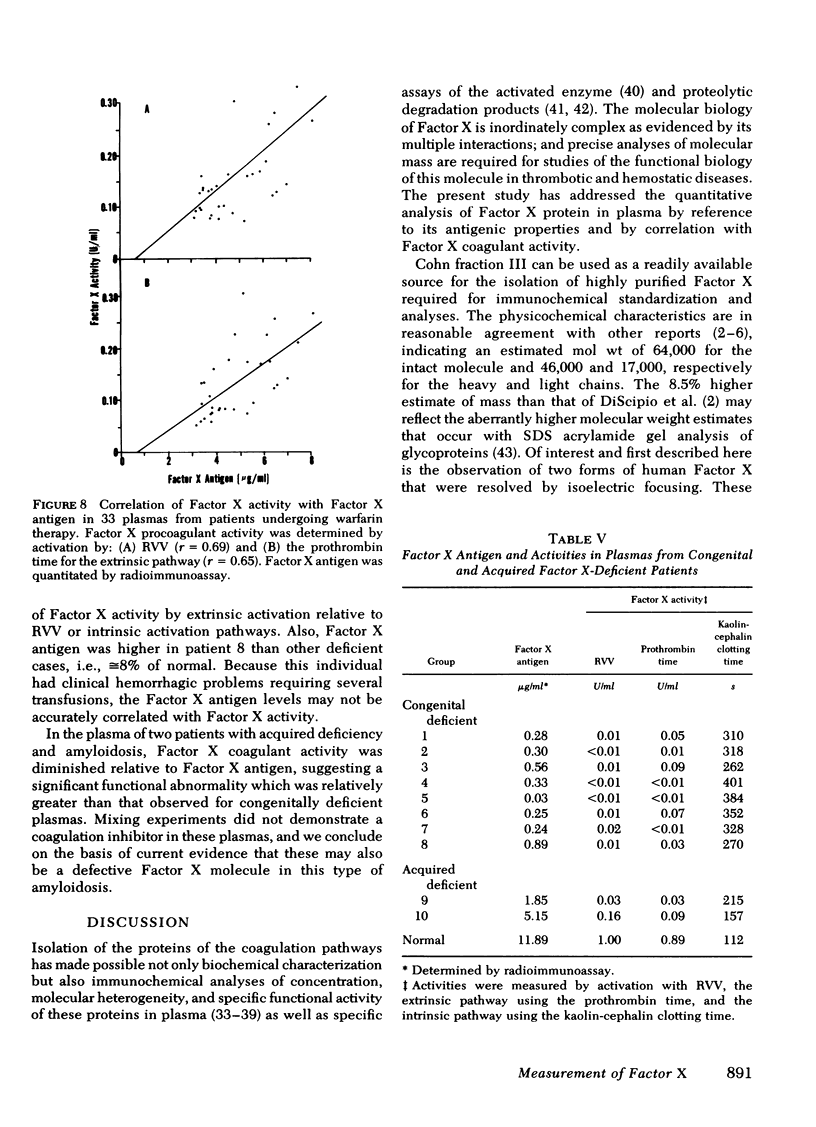
Human Factor X was isolated from Cohn fraction III and characterized by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, amino acid composition, and isoelectric focusing. Two molecular forms with biological activity were observed at isoelectric points of 4.8 and 5.0. Antisera generated to Factor X was monospecific and used to establish an equilibrium competitive inhibition radioimmunoassay. This assay was specific for human Factor X and did not cross-react with human prothrombin or bovine Factor X within the sensitivity range of 6-300 ng Factor X antigen/ml. The mean concentration of Factor X based on the antigen was 11.9 μg/ml, whereas concentration values based on coagulant activity was 7.8 μg/ml. This 30% difference in measurement appears to result from the presence of a subpopulation of Factor X molecules devoid of coagulant activity. The radioimmunoassay was used to qualitatively and quantitatively compare purified Factor X to plasmic Factor X obtained from normal, warfarintreated, acquired Factor X-deficient, and congenitaldeficient patients. In all but one case, the Factor X present in these plasmas was immunochemically identical to the purified Factor X and permitted precise quantitation of these abnormal Factor X molecules. Factor X procoagulant activity was analyzed relative to Factor X antigen and the specific activities were used to characterize normal and abnormal Factor X molecules. Reduced Factor X activity in plasmas from warfarin-treated and acquired Factor X-deficient patients was attributed to both decreases in Factor X antigen and decreased function of the Factor X molecules. Congenitally deficient patients, in general, showed a reduction in Factor X antigen in parallel with Factor X procoagulant activities resulting from comparable decreases in specific biological activity of the molecules.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai H., Takeda Y. Properties and radioimmunoassay of canine factor X. Thromb Res. 1977 Jul;11(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson D. L., Mustafa A. J., Mushinski J. F. Purification of human factor X and comparison of peptide maps of human factor X and prothrombin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 12;188(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHMANN F., DUCKERT F., KOLLER F. The Stuart-Prower factor assay and its clinical significance. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1958 May 1;2(1-2):24–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denson K. W., Lurie A., De Cataldo F., Mannucci P. M. The factor-X defect: recognition of abnormal forms of factor X. Br J Haematol. 1970 Mar;18(3):317–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denson K. W. The levels of factors II, VII, IX and X by antibody neutralization techniques in the plasma of patients receiving phenindione therapy. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jun;20(6):643–648. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb00803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Yates S. G., Davie E. W. A comparison of human prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), factor X (Stuart factor), and protein S. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):698–706. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. Bovine factors X 1 and X 2 (Stuart factor). Isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4882–4891. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Greene E., Furie B. C. Syndrome of acquired factor X deficiency and systemic amyloidosis in vivo studies of the metabolic fate of factor X. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jul 14;297(2):81–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197707142970203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAM J. B., BARROW E. M., HOUGIE C. Stuart clotting defect. II. Genetic aspects of a new hemorrhagic state. J Clin Invest. 1957 Mar;36(3):497–503. doi: 10.1172/JCI103447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudernack G., Berre A. G., Osterud B., Prydz H. Immunological studies on the blood coagulation Factor X and its warfarin-induced precursor. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1974 Mar 15;31(1):40–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolami A., Brunetti A., Bareggi G., Cella G. Abnormal factor X (factor X Friuli) coagulation disorder. The heterozygote population. A study of 57 subjects. Acta Haematol. 1974;51(1):40–50. doi: 10.1159/000208273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemker H. C., Muller A. D. Kinetic aspects of the interaction of blood-clotting enzymes. VI. Localization of the site of blood-coagulation inhibition by the protein induced by vitamin K absence (PIVKA). Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Nov 15;20(1):78–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Hanahan D. J. Studies on bovine factor X. II. Characterization of purified factor X. Observations on some alterations in zone electrophoretic and chromatographic behavior occurring during purification. Biochemistry. 1968 Dec;7(12):4506–4517. doi: 10.1021/bi00852a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Suttie J. W. Recent developments in understanding the mechanism of vitamin K and vitamin K-antagonist drug action and the consequences of vitamin K action in blood coagulation. Prog Hematol. 1977;10:333–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosow D. P. Purification and activation of human factor X: cooperative effect of Ca++ on the activation reaction. Thromb Res. 1976 Dec;9(6):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90104-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause J. R. Acquired factor X deficiency and amyloidosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Feb;67(2):170–173. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/67.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarchick J., Hoyer L. W. Immunoradiometric measurement of the factor VIII procoagulant antigen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1048–1052. doi: 10.1172/JCI109209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindhout M. J., Kop-Klaassen B. H., Kop J. M., Hemker H. C. Purification and properties of the phenprocoumon-induced decarboxyfactor X from bovine plasma. A comparison to normal factor X. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 26;533(2):302–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lox G. D., Strohm G. H., Corrigan J. J., Jr Radioimmunoassay of human prothrombin--the quantitation of plasma factor II antigen. Am J Hematol. 1978;4(3):261–267. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830040308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Properties of the factor Xa binding site on human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6908–6916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik K. H., Laake K. Factor IX in warfarin treated patients. Thromb Res. 1978 Aug;13(2):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peake I. R., Bloom A. L. Immunoradiometric assay of procoagulant factor-VIII antigen in plasma and serum and its reduction in haemophilia. Preliminary studies on adult and fetal blood. Lancet. 1978 Mar 4;1(8062):473–475. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Hougie C., Edgington T. S. Neoantigenic expressions engendered by plasmin cleavage of fibrinogen. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1496–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E., Edgington T. S. Immunobiology of fibrinogen. Emergence of neoantigenic expressions during physiologic cleavage in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):273–282. doi: 10.1172/JCI107183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prydz H., Gladhaug A. Factor X. Immunological studies. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971;25(1):157–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner A. H., Nemes P., Bucholtz C. The use of Coomassie Brilliant Blue G250 perchloric acid solution for staining in electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing on polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 Apr;64(2):509–516. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90461-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D. Statistical quality control and routine data processing for radioimmunoassays and immunoradiometric assays. Clin Chem. 1974 Oct;20(10):1255–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Mannucci P. M., Jeffcoate S. L., Ingram G. I. Immunoradiometric assay of factor VIII related antigen, with observations in 32 patients with von Willebrand's disease. Br J Haematol. 1976 Jun;33(2):221–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb03533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmer G. The prufication of bovine thrombin by affinity chromatography on benzamidine-agarose. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 May;353(5):810–814. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.1.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman M. A., Majerus P. W. The measurement of thrombin in clotting blood by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1249–1258. doi: 10.1172/JCI108579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Jackson C. M. Prothrombin structure, activation, and biosynthesis. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):1–70. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. R. Factor IX antigen by radioimmunoassay. Abnormal factor IX protein in patients on warfarin therapy and with hemophilia B. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):900–910. doi: 10.1172/JCI108712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vician L., Tishkoff G. H. Purification of human blood clotting factor X by Blue Dextran agarose affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 20;434(1):199–208. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. C. Immunologic studies of factor IX (Christmas factor). II. Immunoradiometric assay of factor IX antigen. Br J Haematol. 1978 Jun;39(2):215–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb01091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Roberts J., Edgington T. S. Factor-VIII-related antigen: multiple molecular forms in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5121–5125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]