Abstract
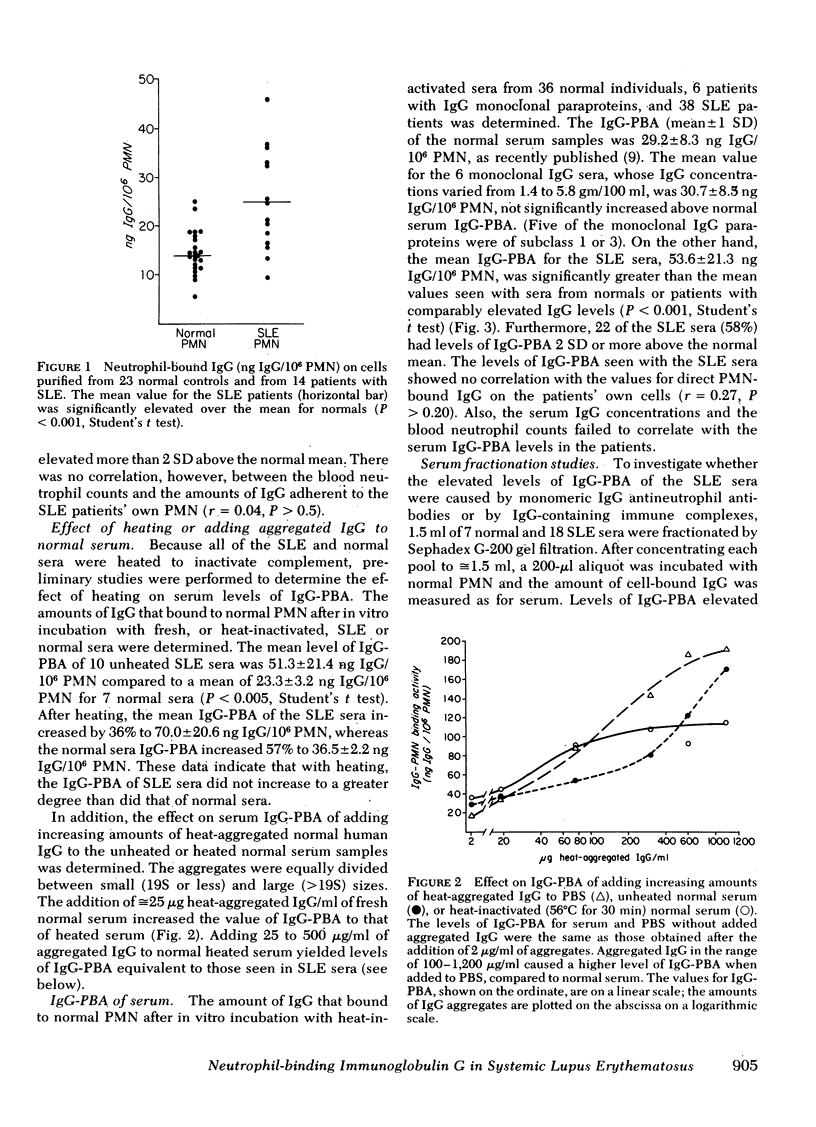
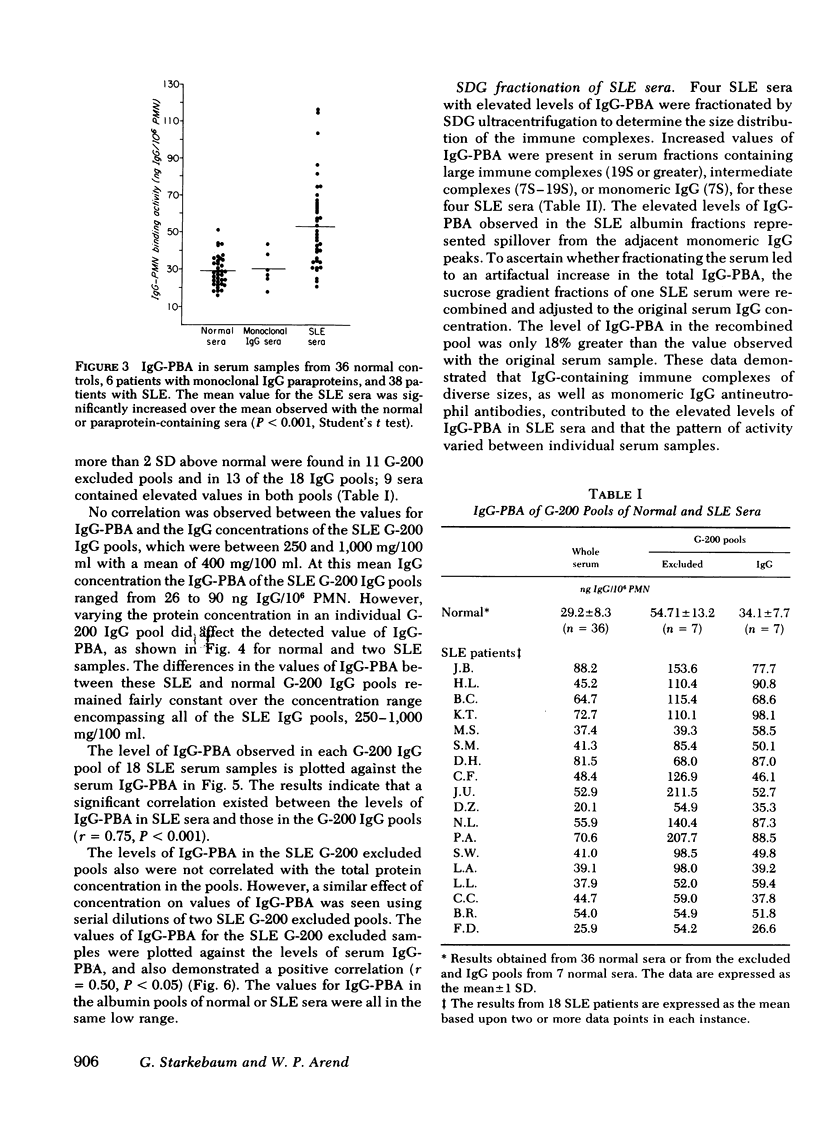
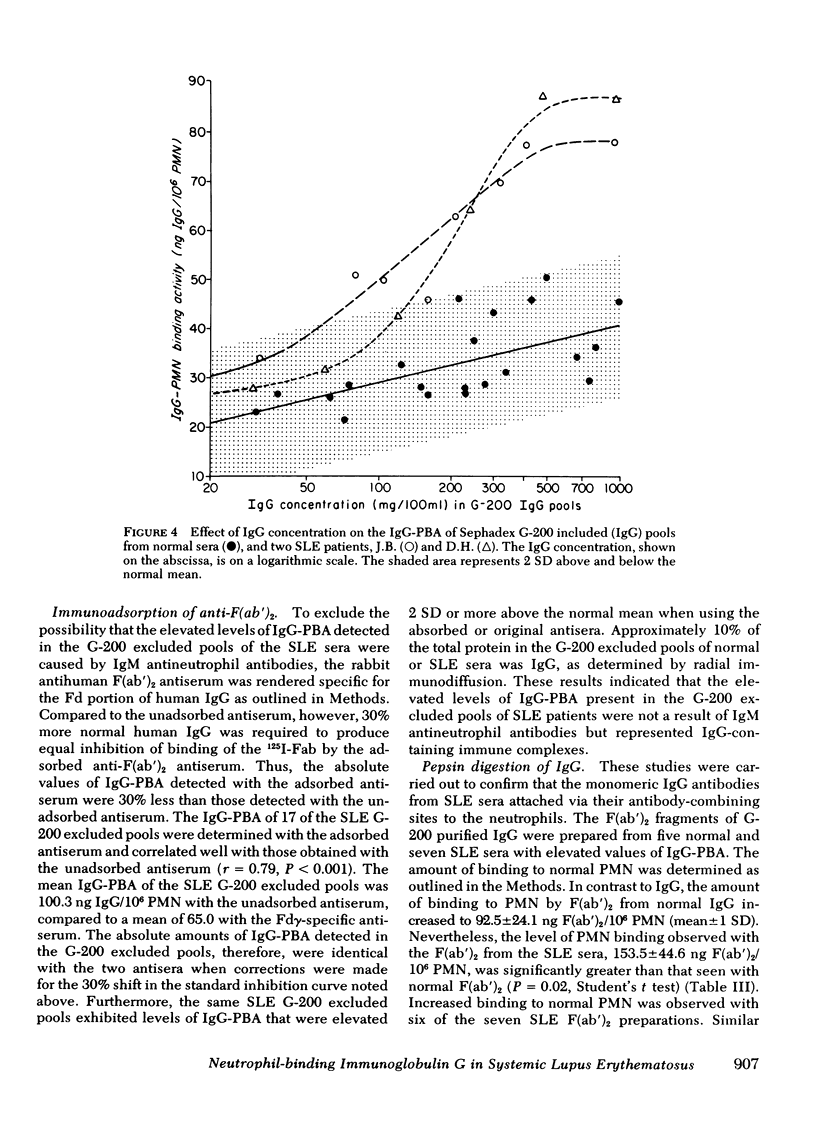
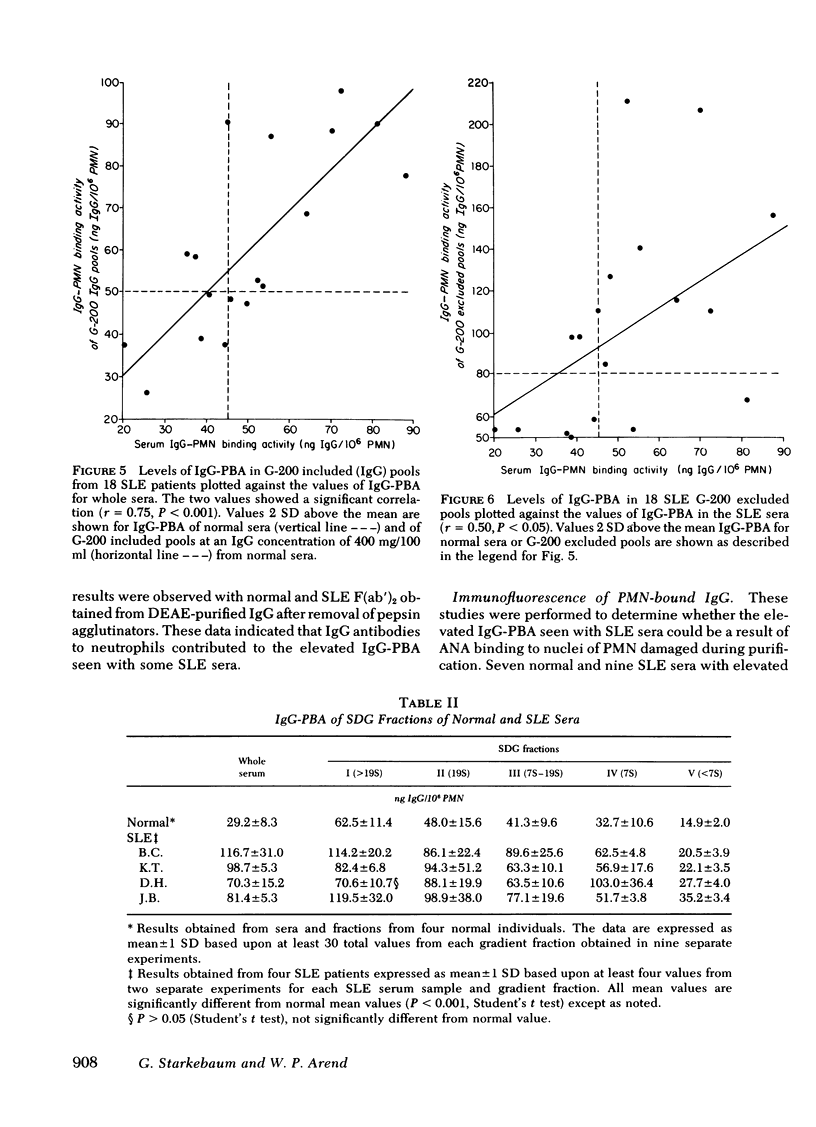
The objectives of these studies were to quantify the amounts of immunoglobulin (Ig)G bound to peripheral blood neutrophils from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and to determine the contributions of soluble immune complexes or anticell antibodies to the levels of IgG neutrophil-binding activity in SLE sera. Neutrophil-bound IgG, determined by a sensitive antiglobulin inhibition assay, was elevated in 7 out of 14 SLE patients compared with values obtained in 23 normal controls. The levels of IgG neutrophil-binding activity in sera were elevated in 22 of 38 patients with SLE over the values seen with 36 normal sera. No correlation was found between the peripheral blood neutrophil counts in the SLE patients and the values for IgG adherent to the cells or serum cell-binding activity. The sera from 18 patients with SLE were fractionated by gel filtration. Elevated levels of IgG neutrophil-binding activity were found in 11 of the 18 G-200 excluded pools and in 13 of the G-200 IgG pools. In nine sera elevated levels were observed in both pools. F(ab')2 fragments of IgG from SLE sera bound to normal polymorphonuclear leukocytes in greater amounts than F(ab')2 fragments of IgG from normal sera. A significant correlation existed between the values of IgG neutrophil-binding activity found in SLE sera and those obtained with both the G-200 excluded and IgG pools. Sucrose density gradient fractionation of four sera from SLE patients confirmed the presence of both large (greater than 19S) and intermediate-sized (7S-19S) cell-binding immune complexes as well as of monomeric IgG antibodies to neutrophils. The levels of IgG neutrophil-binding activity in the SLE sera correlated well with the results obtained with the Raji cell assay for immune complexes as well as with the titer of antibodies to nuclear antigens. These data indicate that circulating neutrophils from patients with SLE commonly have increased amounts of cell-bound IGG. The elevated levels of IgG neutrophil-binding activity in the sera of these patients are caused by both soluble immune complexes and antibodies reactive with neutrophils.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Mannik M. In vitro adherence of soluble immune complexes to macrophages. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):514–531. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale W. F., Helmkamp R. W., Davis T. P., Izzo M. J., Goodland R. L., Contreras M. A., Spar I. L. High specific activity labeling of protein with I-131 by the iodine monochloride method. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jun;122(2):407–414. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers T. K., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Acquired granulocyte abnormality during drug allergic reactions: possible role of complement activation. Blood. 1977 Jan;49(1):3–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Stossel T. P. Effects of anti-human neutrophil antibodies in vitro. Quantitative studies. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1534–1545. doi: 10.1172/JCI107704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cats A., Lafeber G. J., Klein F. Immunoglobulin phagocytosis by granulocytes from sera and synovial fluids in various rheumatoid and nonrheumatoid diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Apr;34(2):146–155. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.2.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curd J. G., Sundsmo J. S., Kolb W. P., Bluestein H. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Neoantigen of the membrane attack complex of human complement: Occurrence on peripheral blood leukocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Mar;21(2):177–182. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAUSSET J., COLOMBANI J., COLOMBANI M. Study of leukopenias and thrombocytopenias by the direct antiglobulin consumption test on leukocytes and/or platelets. Blood. 1961 Dec;18:672–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew S. I., Carter B. M., Guidera D. P., Terasaki P. I. Autoimmune cytotoxic granulocyte antibodies in health and disease. Transplant Proc. 1977 Dec;9(4):1887–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C. Structural units of human 7S gamma globulin. J Clin Invest. 1960 Dec;39:1933–1941. doi: 10.1172/JCI104218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr J., Jacob H. S. In vitro granulocyte adherence and in vivo margination: two associated complement-dependent functions. Studies based on the acute neutropenia of filtration leukophoresis. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):641–652. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr K., LoSpalluto J. Exposure of hidden antigenic determinants in human IgG by digestion with spleen proteases. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):814–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Kubo R. T., Colon S. M., Poulik M. D., Cresswell P., Springer T., Turner M., Strominger J. L. The small subunit of HL-A antigens is beta 2-microglobulin. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1608–1612. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurd E. R., Dowdle W., Casey H., Ziff M. Virus antibody levels in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 May-Jun;15(3):267–274. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E., Ziff M. Immunoglobulin synthesis by peripheral blood cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):219–228. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpatkin S., Garg S. K., Siskind G. W. Autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura and the compensated thrombocytolytic state. Am J Med. 1971 Jul;51(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90317-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightsey A. L., Chapman R. M., McMillan R., Mushovic J., Yelenosky R., Longmire R. L. Immune neutropenia. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jan;86(1):60–62. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-1-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logue G. Felty's syndrome: granulocyte-bound immunoglobulin G and splenectomy. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Oct;85(4):437–442. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL S. R., VURAL I. L., BASSEN F. A., SCHAEFER L. The hematologic aspects of disseminated (systemic) lupus erythematosus. Blood. 1951 Nov;6(11):1059–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Stage D. E. Antibody-agarose immunoadsorbents: complete removal of classes of immunoglobulins from serum. J Immunol. 1971 Jun;106(6):1670–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Jelinek J. Receptors for human gamma G globulin on human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2165–2171. doi: 10.1172/JCI106435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michl J., Ohlbaum D. J., Silverstein S. C. 2-Deoxyglucose selectively inhibits Fc and complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in mouse peritoneal macrophages. I. Description of the inhibitory effect. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1465–1483. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. S., Terasaki P. I., Bernoco D. Autoantibody against B lymphocytes. Lancet. 1977 Sep 3;2(8036):465–467. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91598-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekvig O. P., Hannestad K. Certain polyclonal antinuclear antibodies cross-react with the surface membrane of human lymphocytes and granulocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(10):1041–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revillard J. P., Vincent C., Rivera S. Anti-beta2-microglobulin lymphocytotoxic autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):614–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Hurwitz E. Binding of affinity cross-linked oligomers of IgG to cells bearing Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1338–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson D. M., Ross R. Effects of heterologous antineutrophil serum in guinea pigs. Hematologic and ultrastructural observations. Am J Pathol. 1971 Oct;65(1):79–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Longmire R. L., Reid R. T., Farr R. S. An analysis of the immunological specificity of antiserum against human IgG F(ab)2. Immunochemistry. 1970 Jul;7(7):661–671. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Longmire R. L., Reid R. T., Farr R. S. The measurement of immunoglobulin associated with human peripheral lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Feb;104(2):367–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkebaum G., Price T. H., Lee M. Y., Arend W. P. Autoimmune neutropenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jun;21(5):504–512. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Reinertsen J. L. Lupus in New Zealand mice and in dogs. Bull Rheum Dis. 1977;28(4-5):940–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. The Raji cell radioimmune assay for detecting immune complexes in human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):169–182. doi: 10.1172/JCI108257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]