Abstract
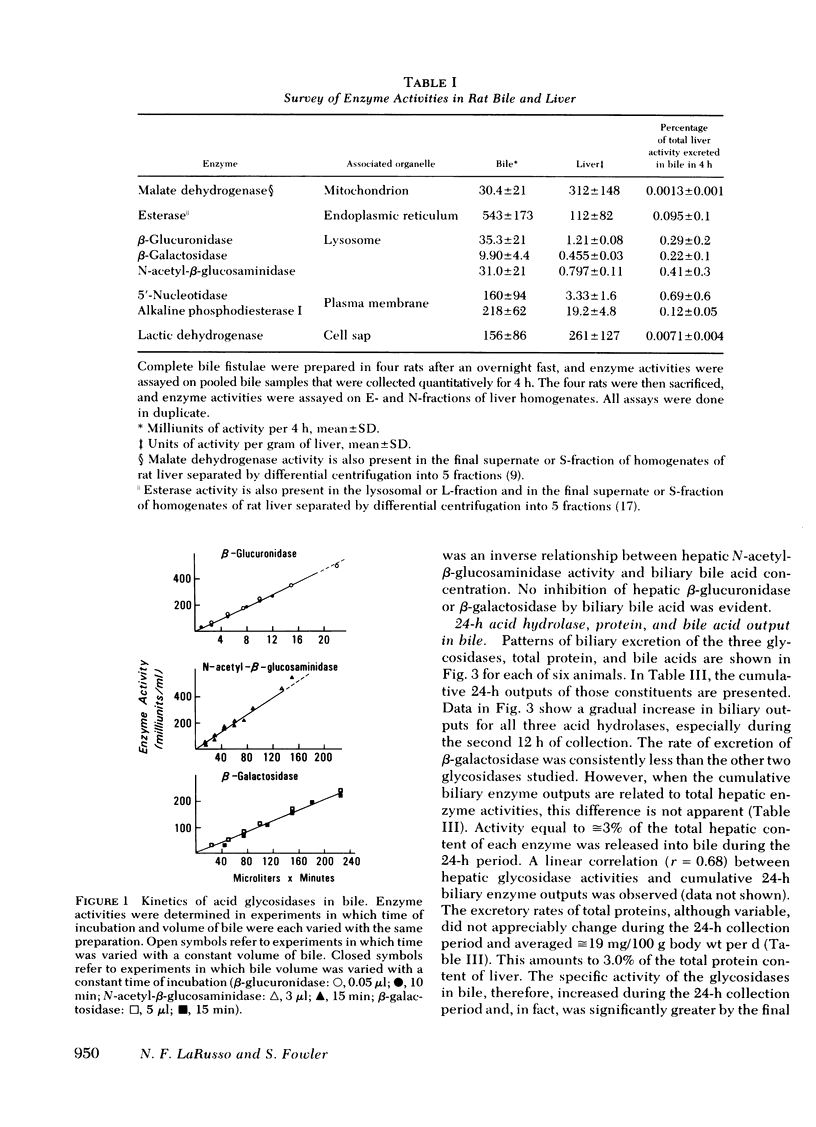
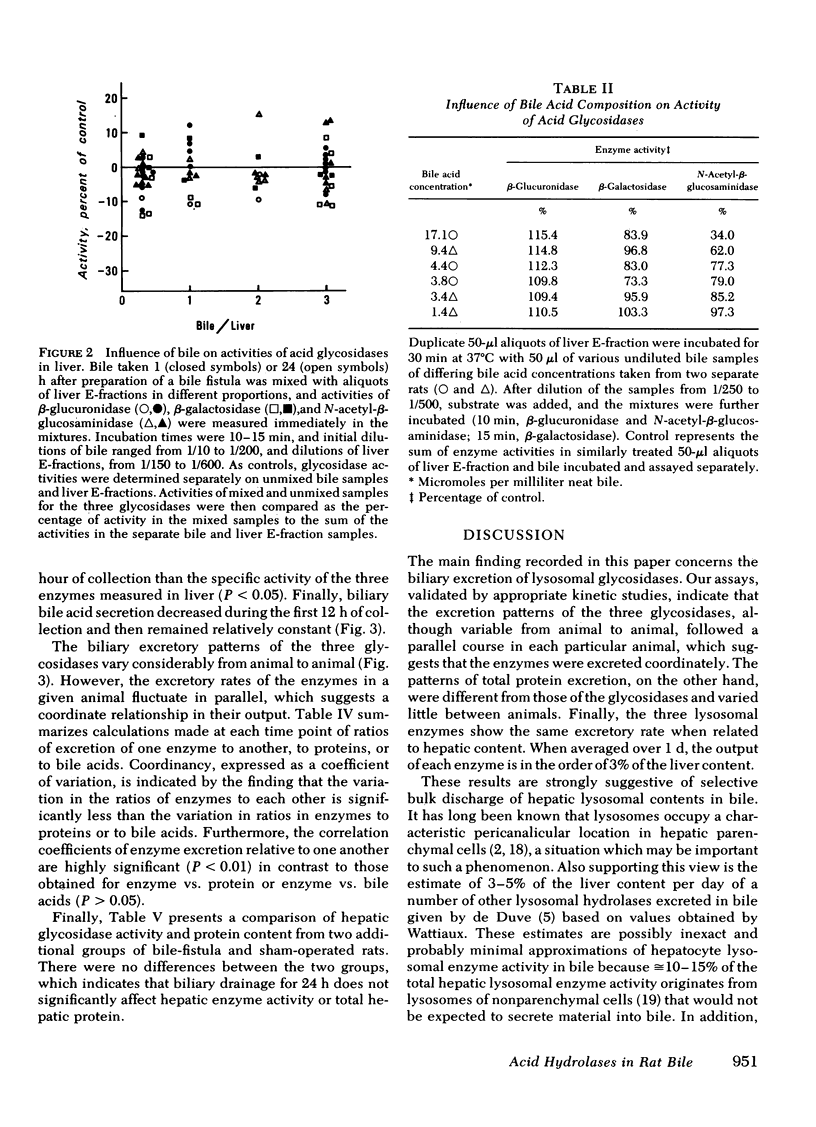
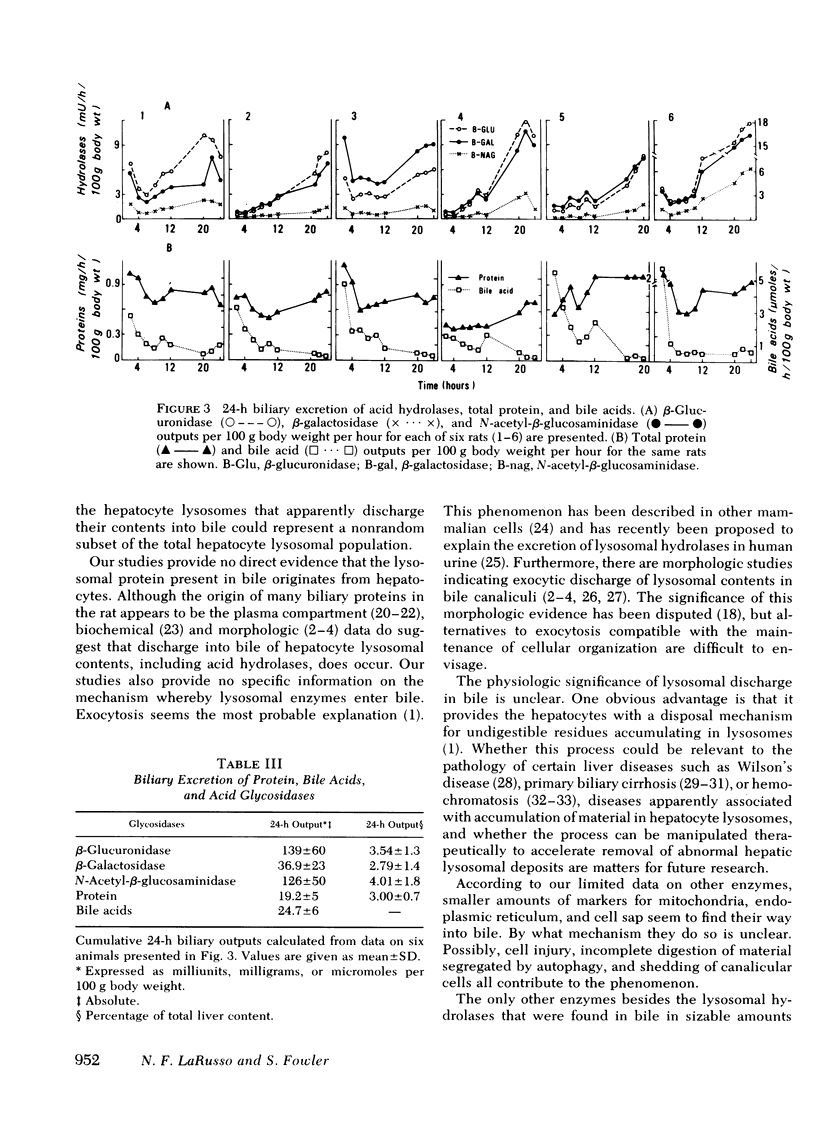
Three lysosomal glycosidases, β-glucuronidase (EC 3.2.1.31), β-galactosidase (EC 3.2.1.23), and N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase (EC 3.2.1.30) have been investigated in bile that was freshly collected from rats through a complete bile fistula. Assay conditions have been established on the basis of appropriate kinetic studies. The biliary excretion patterns for these enzymes were found to vary considerably from rat to rat during the 24-h collection period. In a given animal, however, the three hydrolases were excreted in parallel and showed a gradual increase in activity with time, most marked after 10- 12 h of collection. 24-h biliary outputs of the three hydrolases averaged ≅3% of their respective contents in total liver, and bile diversion had no effect on hepatic glycosidase activity or total protein content. Other enzymes known to be associated primarily with mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and cell sap were also detected in bile, generally in smaller amounts. The biliary excretion of the plasma membrane markers, alkaline phosphodiesterase I and 5′-nucleotidase, however, was comparable to that of the lysosomal hydrolases. Biliary excretion of total protein was relatively constant and corresponded to 3.0% of the total hepatic protein content per day, whereas biliary bile acid secretion decreased during the first 12 h and then remained constant. Exocytic bulk discharge of hepatocyte lysosomes is proposed as the most likely mechanism for the biliary excretion of lysosomal enzymes. These results call attention to the possible pathophysiologic significance of biliary excretion of hepatic lysosomal contents as a means of residue disposal.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry M. Iron and the liver. Gut. 1974 Apr;15(4):324–334. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.4.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaufay H., Amar-Costesec A., Feytmans E., Thinès-Sempoux D., Wibo M., Robbi M., Berthet J. Analytical study of microsomes and isolated subcellular membranes from rat liver. I. Biochemical methods. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):188–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford W. D., Elchlepp J. G., Arstila A. U., Trump B. F., Kinney T. D. Iron metabolism and cell membranes. I. Relation between ferritin and hemosiderin in bile and biliary excretion of lysosome contents. Am J Pathol. 1969 Aug;56(2):201–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni C., Porter K. R. The Fine Structure of the Parenchymal Cell of the Normal Rat Liver: I. General Observations. Am J Pathol. 1965 May;46(5):691–755. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Duve C., Wattiaux R. Functions of lysosomes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1966;28:435–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.28.030166.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Klaassen C. D. Effects of acute administration of taurocholic and taurochenodeoxycholic acid on biliary lipid excretion in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Jan;151(1):198–202. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H., Kremmmer T., Culvenor J. G. Role of membranes in bile formation. Comparison of the composition of bile and a liver bile-canalicular plasma-membrane subfraction. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):589–595. doi: 10.1042/bj1540589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming C. R., Dickson E. R., Baggenstoss A. H., McCall J. T. Copper and primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1974 Dec;67(6):1182–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinsmann W. H., Ericsson J. L. Observations on the subcellular organization of hepatic parenchymal cells. II. Evolution of reversible alterations induced by hypoxia. Lab Invest. 1966 Apr;15(4):762–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth G., Coleman R. Enzyme profiles of mammalian bile. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 21;389(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IWATA T., YAMASAKI K. ENZYMATIC DETERMINATION AND THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS IN BLOOD. J Biochem. 1964 Nov;56:424–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F. Liver cell defaecation: an electron-microscope study of the discharge of lysosomal residual bodies into the intercellular space. J Pathol. 1970 Feb;100(2):99–103. doi: 10.1002/path.1711000204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Lindmark D. G., Müller M. Biliary and renal excretion, hepatic metabolism, and hepatic subcellular distribution of metronidazole in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(18):2247–2254. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton F., Poole B., Beaufay H., Baudhuin P., Coffey J. W., Fowler S., De Duve C. The large-scale separation of peroxisomes, mitochondria, and lysosomes from the livers of rats injected with triton WR-1339. Improved isolation procedures, automated analysis, biochemical and morphological properties of fractions. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):482–513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaître-Coelho I., Jackson G. D., Vaerman J. P. Rat bile as a convenient source of secretory IgA and free secretory component. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Aug;7(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullock B. M., Dobrota M., Hinton R. H. Sources of the proteins of rat bile. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 1;543(4):497–507. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90304-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullock B. M., Hinton R. H. The relation of bile proteins to serum and liver plasma membrane [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(1):274–276. doi: 10.1042/bst0060274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe-Kaas A. C., Berg T., Seljelid R. Distribution of lysosomal enzymes in different types of rat liver cells. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Apr;99(1):146–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90689-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen C. A., Jr, Dickson E. R., Goldstein N. P., Baggenstoss A. H., McCall J. T. Hepatic subcellular distribution of copper in primary biliary cirrhosis. Comparison with other hyperhepatocupric states and review of the literature. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 Feb;52(2):73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen K., Peterson J. Coordinacy of lysosomal enzyme excretion in human urine. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):751–762. doi: 10.1172/JCI108989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Müller M., De Duve C. Lysosomes of the arterial wall. I. Isolation and subcellular fractionation of cells from normal rabbit aorta. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1117–1139. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Seymour C. A. Acid hydrolase activities and lysosomal integrity in liver biopsies from patients with iron overload. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Jan;50(1):75–78. doi: 10.1042/cs0500075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEINBERG I. H., STERNLIEB I. WILSON'S DISEASE. Annu Rev Med. 1965;16:119–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.16.020165.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipponen P. Orcein positive hepatocellular material in long-standing biliary diseases. II. Ultrastructural studies. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1976;11(6):553–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda S., Eto Y., Aoki K. Bile lysosomal enzymes: characteristics and pathological significance for various hepatobiliary disorders. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Sep 1;79(2):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



