Abstract
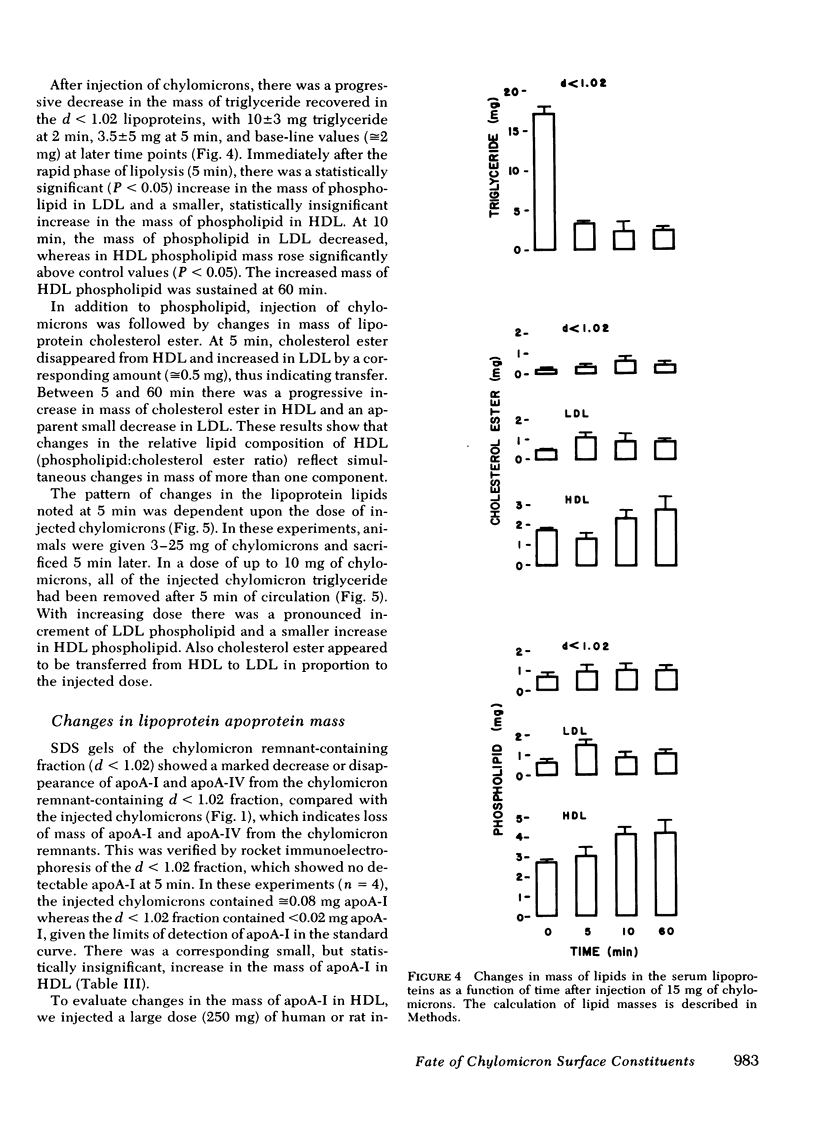
To study the metabolic fate of chylomicron phospholipid and apoproteins, 15 mg of doubly labeled ([3H]leu, [32P]phospholipid) rat mesenteric lymph chylomicrons were injected as an intravenous bolus into conscious rats. The specific radioactivity, composition, pool size, and morphology of the plasma lipoproteins were determined after 2-60 min. After injection of chylomicrons, there was a rapid transfer of radioactivity into high density lipoproteins (HDL). At peak specific activity in HDL (2-5 min), 35% of injected apoprotein and 25% of phospholipid radioactivity were recovered in HDL (d 1.063-1.21 g/ml), with smaller recoveries in other lipoproteins and liver. There was an initial rapid rise of 32P specific activity in HDL and d 1.02-1.063 lipoproteins (low density lipoproteins [LDL]), but whereas LDL specific activity subsequently converged with that of d < 1.02 lipoproteins, HDL specific activity decayed more rapidly than LDL or d < 1.02 lipoproteins.
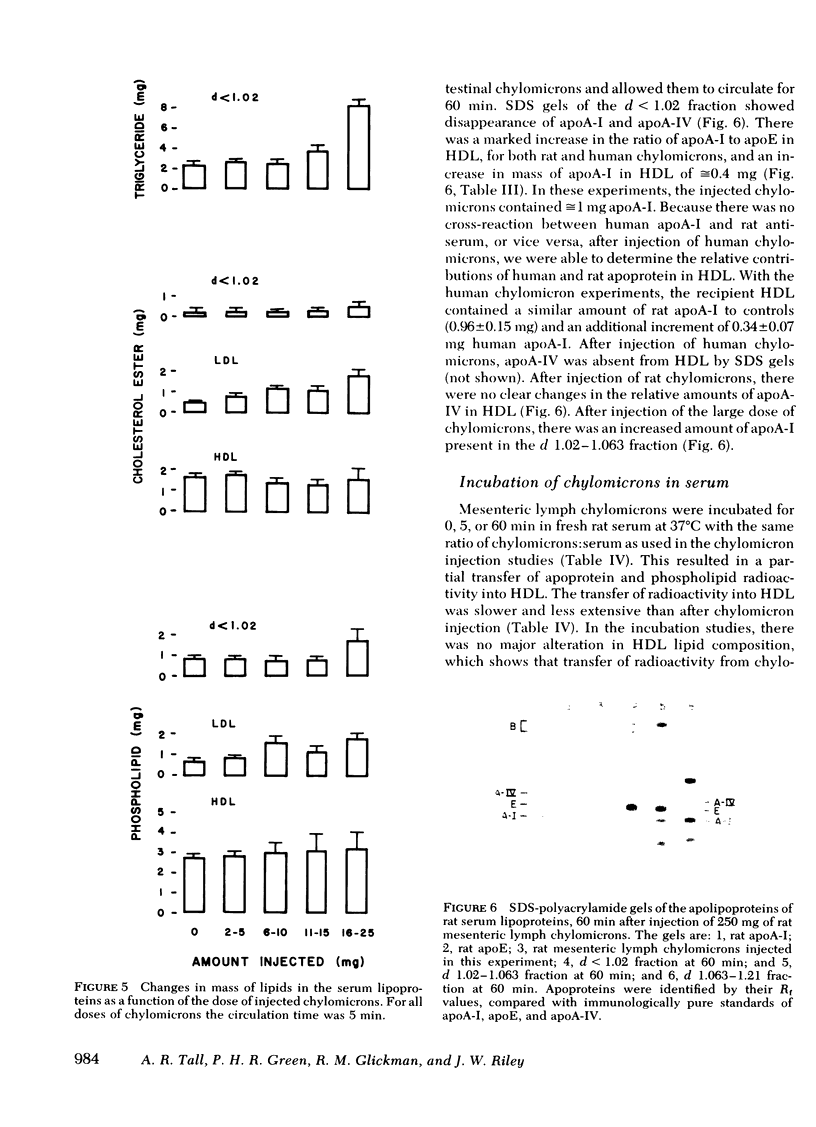
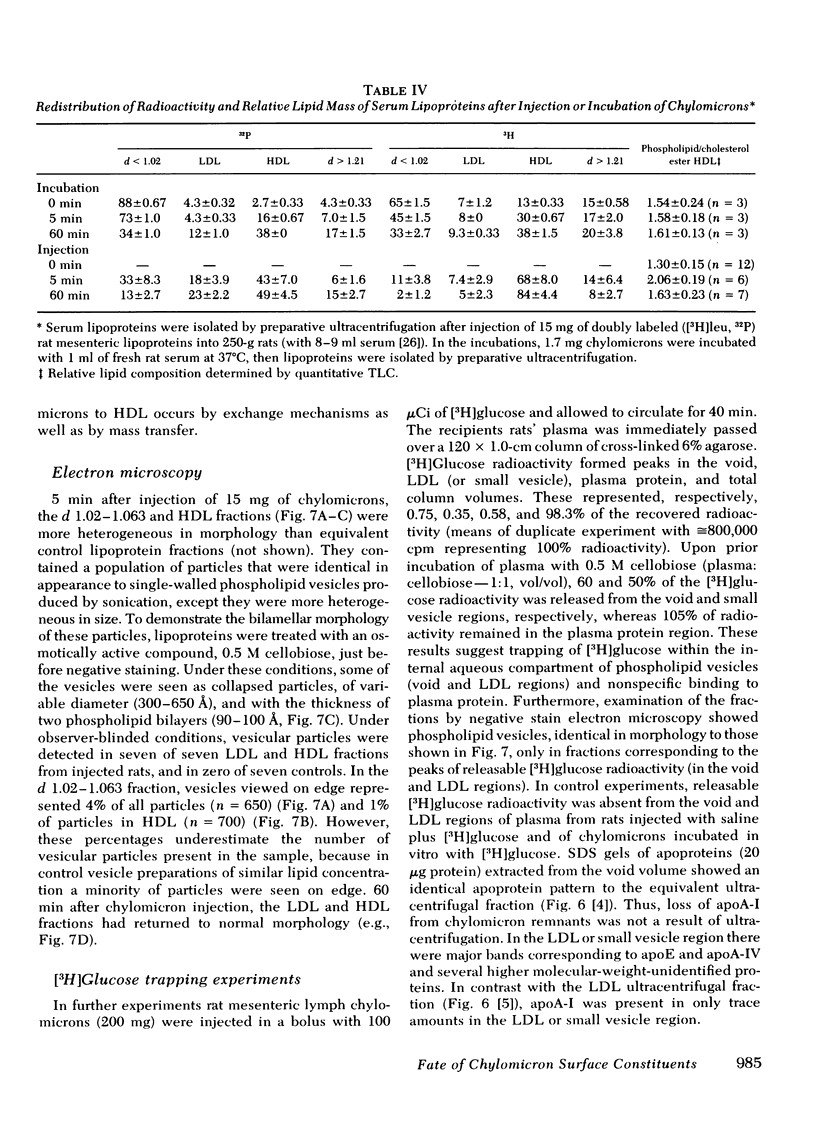
Lipolysis of chylomicrons was associated with a transfer of phospholipid mass into LDL and HDL. At 5 min, 80% of injected triglyceride had been lipolyzed and there was a significant increase in phospholipid mass in LDL and a smaller increase in HDL. At 10 min, the mass of phospholipid in LDL had returned towards control values, and there was a further increase in phospholipid mass in HDL, which suggested phospholipid transfer from LDL to HDL.
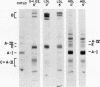
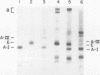
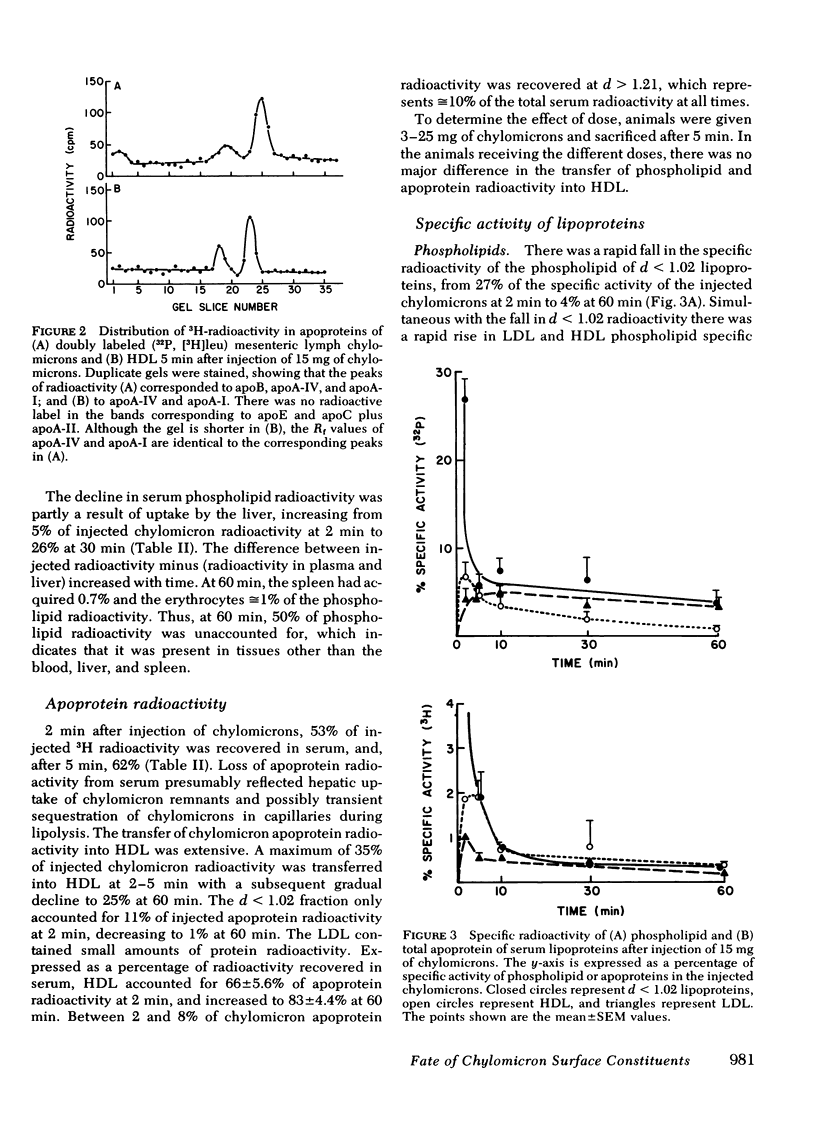
In donor lymph chylomicrons 3H-radioactivity was present in apoprotein (apo)B, apoA-I, and apoA-IV, but only radioactivity of apoA-I and apoA-IV were transferred to HDL. Transfer of radioactivity was associated with loss of mass of apoA-I and apoA-IV from the fraction that contained the chylomicron remnants (d < 1.02). With injection of 15 mg chylomicron, there was a small but insignificant increase in the relatively large pool of HDL apoA-I. However, 60 min after injection of 250 mg of human or rat intestinal chylomicrons into the rat, there was a significant increase in HDL apoA-I that resulted from acquisition of a major fraction of the chylomicron apoA-I.
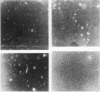
After injection of chylomicrons, phospholipid vesicles were observed by negative stain electron microscopy in the LDL and HDL ultracentrifugal fractions, especially in the LDL. Upon addition of an osmotically active compound, cellobiose, vesicles were observed as flattened particles with a double lipid bilayer thickness (≅ 100 Å). To validate further the identity of these particles, chylomicrons were injected into rats with [3H]glucose, and the recipient rats' plasma was fractionated by chromatography on 6% agarose. Trapping of [3H]glucose occurred in the void and LDL regions of the column, and vesicular particles were identified in these column fractions by negative stain electron microscopy.
Catabolism of chylomicrons is associated with a rapid transfer of phospholipid, apoA-I, and possibly apoA-IV into HDL. Chylomicron phospholipid appears to give rise to vesicles which are probably incorporated into preexisting HDL. Chylomicron surface components may be an important source of plasma HDL.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARR D. P., RUSS E. M., EDER H. A. Protein-lipid relationships in human plasma. II. In atherosclerosis and related conditions. Am J Med. 1951 Oct;11(4):480–493. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(51)90183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Scow R. O. Effects of lipoprotein lipase on the structure of chylomicrons. J Cell Biol. 1973 Sep;58(3):689–708. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Scow R. O. Retention of lipolytic products in chylomicrons incubated with lipoprotein lipase: electron microscope study. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jan;17(1):57–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum C. B., Levy R. I., Eisenberg S., Hall M., 3rd, Goebel R. H., Berman M. High density lipoprotein metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;60(4):795–807. doi: 10.1172/JCI108833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge W. C., Little J. A., Steiner G., Chow A., Poapst M. Hypertriglyceridemia associated with deficiency of apolipoprotein C-II. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 8;298(23):1265–1273. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806082982301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Olsson G., Ballantyne D. On the rise in low density and high density lipoproteins in response to the treatment of hypertriglyceridaemias in type IV and type V hyperlipoproteinaemias. Atherosclerosis. 1977 Apr;26(4):603–609. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(77)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Eisenberg S. Very low density lipoprotein. Metabolism of phospholipids, cholesterol, and apolipoprotein C in the isolated perfused rat heart. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1654–1665. doi: 10.1172/JCI109086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chobanian J. V., Tall A. R., Brecher P. I. Interaction between unilamellar egg yolk lecithin vesicles and human high density lipoprotein. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):180–187. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing D. T. Photodensitometry in the thin-layer chromatographic analysis of neutral lipids. J Chromatogr. 1968 Nov 5;38(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(68)85011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Stein Y., Stein O. The role of lysolecithin in phospholipid metabolism of human umbilical and dog carotid arteries. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 4;137(2):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T. M., Nichols A. V., Gong E. L., Levy R. I., Lux S. Electron microscopic study on reassembly of plasma high density apoprotein with various lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 5;248(2):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Green P. H., Lees R. S., Tall A. Apoprotein A-I synthesis in normal intestinal mucosa and in Tangier disease. N Engl J Med. 1978 Dec 28;299(26):1424–1427. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197812282992602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Green P. H. The intestine as a source of apolipoprotein A1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2569–2573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Kirsch K. Lymph chylomicron formation during the inhibition of protein synthesis. Studies of chylomicron apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2910–2920. doi: 10.1172/JCI107487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Norum K. R. The metabolic role of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase: perspectives form pathology. Adv Lipid Res. 1973;11:1–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon T., Castelli W. P., Hjortland M. C., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Am J Med. 1977 May;62(5):707–714. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90874-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. H., Glickman R. M., Saudek C. D., Blum C. B., Tall A. R. Human intestinal lipoproteins. Studies in chyluric subjects. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):233–242. doi: 10.1172/JCI109444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. H., Tall A. R., Glickman R. M. Rat intestine secretes discoid high density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):528–534. doi: 10.1172/JCI108963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J. Early effects of fat ingestion on lipids and lipoproteins of serum in man. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jun;36(6 Pt 1):848–854. doi: 10.1172/JCI103491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Blaurock A. E., Sata T. Cholestasis: lamellar structure of the abnormal human serum lipoprotein. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):475–478. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Williams M. C., Fielding C. J., Havel R. J. Discoidal bilayer structure of nascent high density lipoproteins from perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):667–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI108513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert P. N., Forte T., Heinen R. J., Fredrickson D. S. Tangier disease: one explanation of lipid storage. N Engl J Med. 1978 Sep 7;299(10):519–521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197809072991005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. S., Shipley G. G., Small D. M. Physical chemistry of the lipids of human atherosclerotic lesions. Demonstration of a lesion intermediate between fatty streaks and advanced plaques. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):200–211. doi: 10.1172/JCI108450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp L., Chobanian A. V., Brecher P. I. The in vivo transformation of phospholipid vesicles to a particle resembling HDL in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1251–1258. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80149-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. I., Lees R. S., Fredrickson D. S. The nature of pre beta (very low density) lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):63–77. doi: 10.1172/JCI105324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. J., Miller N. E. Plasma-high-density-lipoprotein concentration and development of ischaemic heart-disease. Lancet. 1975 Jan 4;1(7897):16–19. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordasini R., Frey F., Flury W., Klose G., Greten H. Selective deficiency of hepatic triglyceride lipase in uremic patients. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 22;297(25):1362–1366. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712222972502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESTEL P. J., HAVEL R. J., BEZMAN A. METABOLISM OF CONSTITUENT LIPIDS OF DOG CHYLOMICRONS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Aug;42:1313–1321. doi: 10.1172/JCI104815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel P. J., Havel R. J., Bezman A. SITES OF INITIAL REMOVAL OF CHYLOMICRON TRIGLYCERIDE FATTY ACIDS FROM THE BLOOD. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41(10):1915–1921. doi: 10.1172/JCI104648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Formation of cholesteryl ester-rich particulate lipid during metabolism of chylomicrons. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):465–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads G. G., Gulbrandsen C. L., Kagan A. Serum lipoproteins and coronary heart disease in a population study of Hawaii Japanese men. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 5;294(6):293–298. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602052940601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabesin S. M., Hawkins H. L., Kuiken L., Ragland J. B. Abnormal plasma lipoproteins and lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):510–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. Lipoprotein apoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1978 Aug;19(6):667–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Jenkins L. L., Brewer H. B., Jr Human chylomicron apolipoprotein metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 30;80(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90691-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Bell E., Alpers D. H. Intestinal apoproteins during fat absorption. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1539–1550. doi: 10.1172/JCI109074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. G., Atkinson D., Scanu A. M. Small-angle x-ray scattering of human serum high-density lipoproteins. J Supramol Struct. 1972;1(2):98–104. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein Y., Stein O. Metabolism of labeled lysolecithin, lysophosphatidyl ethanolamine and lecithin in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 1;116(1):95–107. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strisower E. H., Adamson G., Strisower B. Treatment of hyperlipidemias. Am J Med. 1968 Oct;45(4):488–501. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R., Hogan V., Askinazi L., Small D. M. Interaction of plasma high density lipoproteins with dimyristoyllecithin multilamellar liposomes. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):322–326. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R., Small D. M. Solubilisation of phospholipid membranes by human plasma high density lipoproteins. Nature. 1977 Jan 13;265(5590):163–164. doi: 10.1038/265163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. E., Lees R. S. Metabolic relationships among the plasma lipoproteins. Reciprocal changes in the concentrations of very low and low density lipoproteins in man. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1051–1057. doi: 10.1172/JCI106896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. D., Haskell W., Klein H., Lewis S., Stern M. P., Farquhar J. W. The distribution of plasma lipoproteins in middle-aged male runners. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11):1249–1257. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Windmueller H. G. Identification of circulating apolipoproteins synthesized by rat small intestine in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2525–2528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]