Abstract
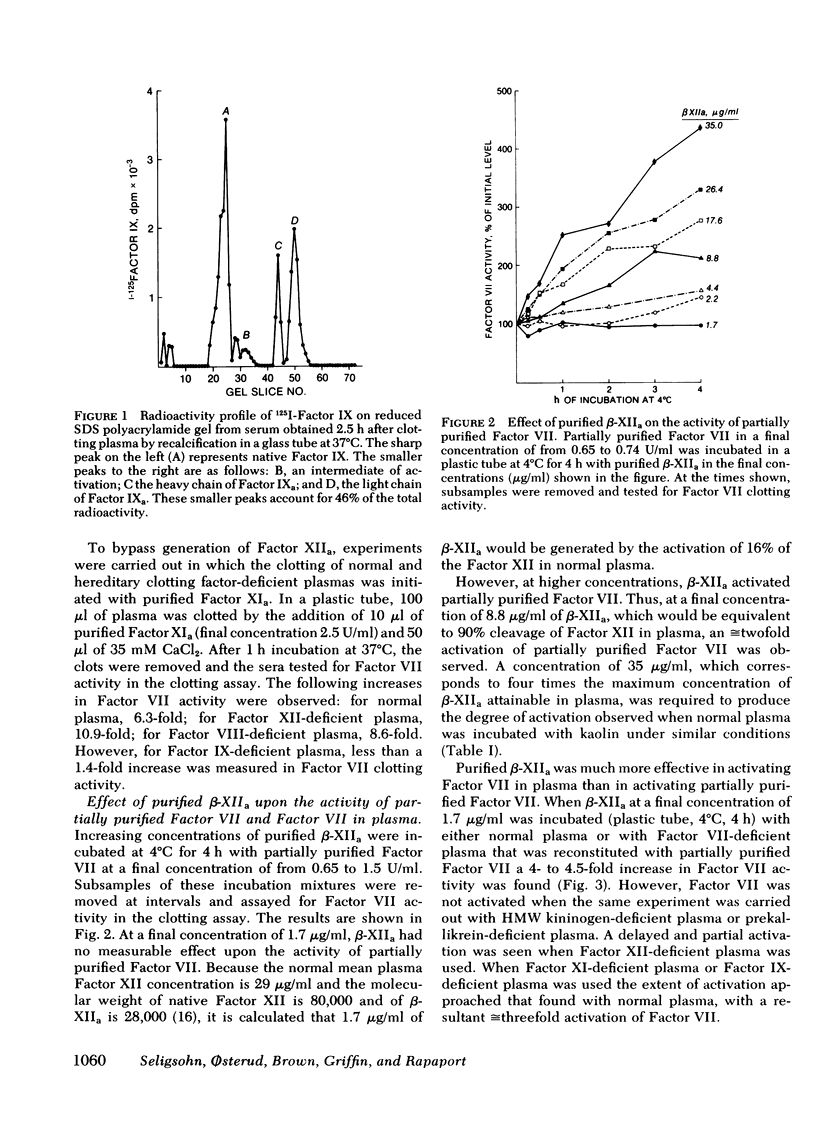
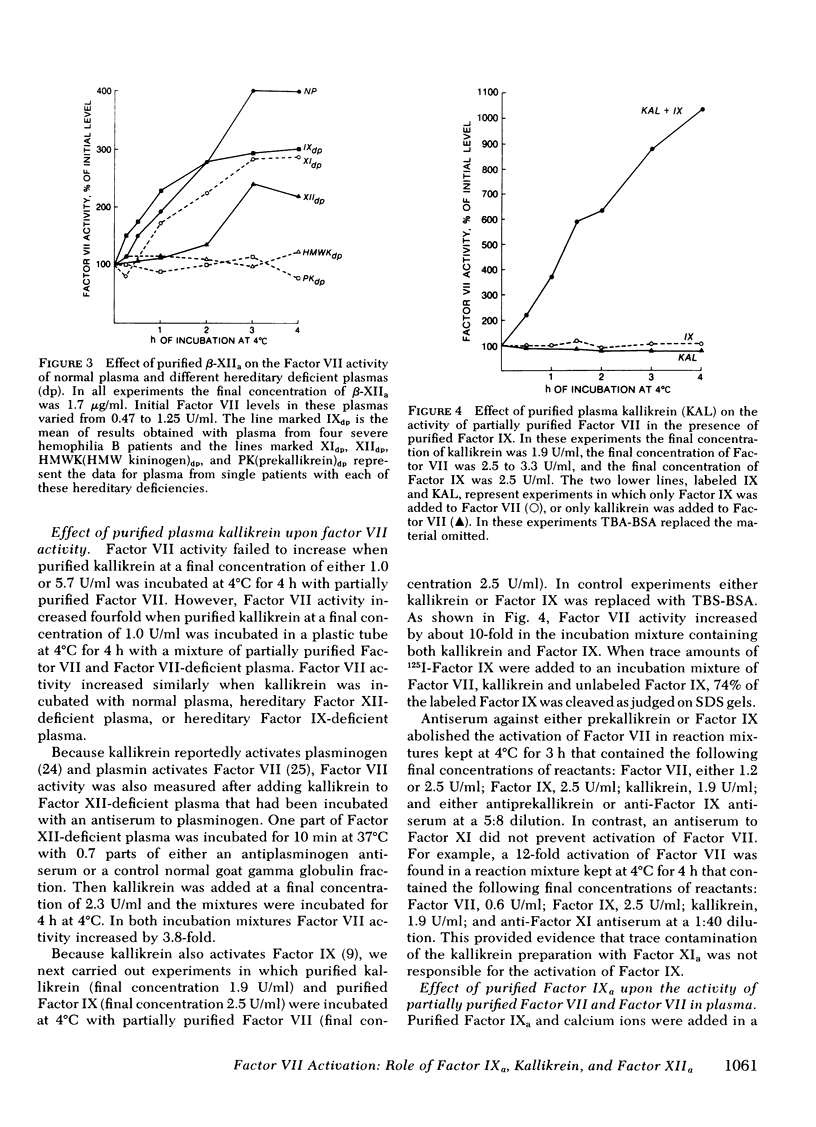
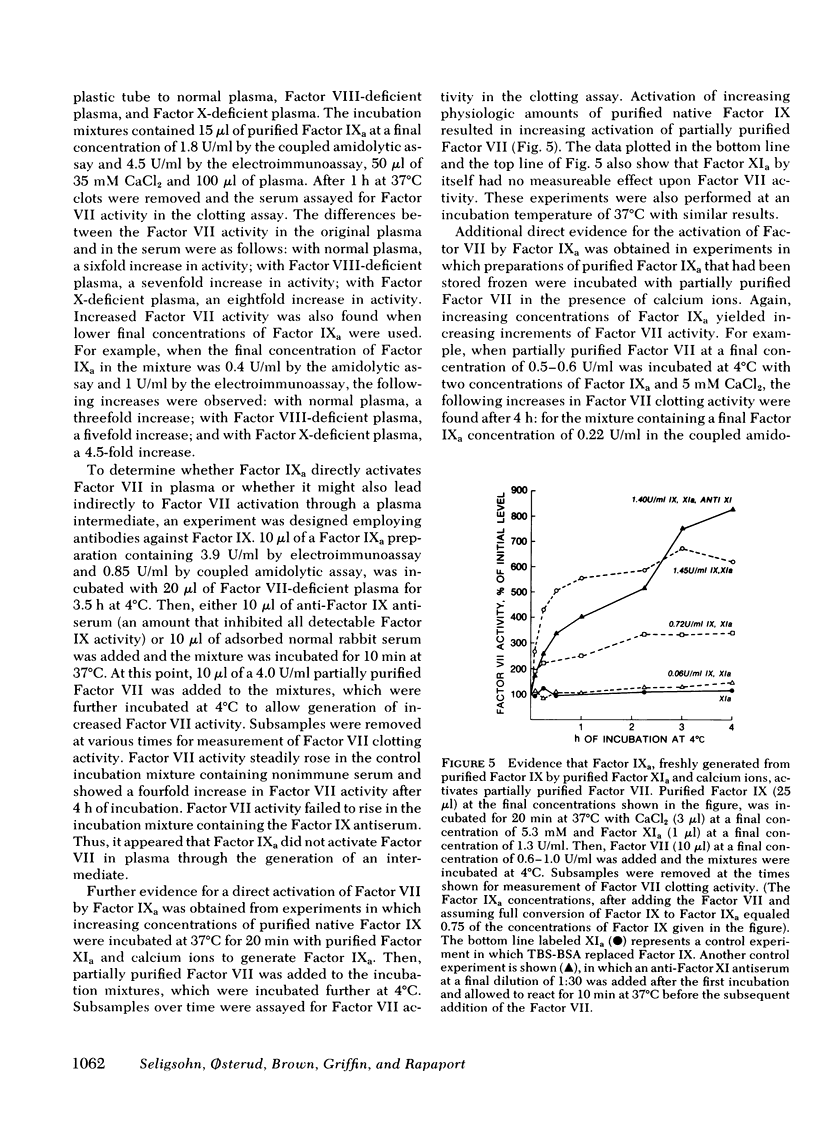
Factor VII can be activated, to a molecule giving shorter clotting times with tissue factor, by incubating plasma with kaolin or by clotting plasma. The mechanisms of activation differ. With kaolin, activated Factor XII (XIIa) was the apparent principal activator. Thus, Factor VII was not activated in Factor XII-deficient plasma, was partially activated in prekallikrein and high-molecular weight kininogen (HMW kininogen)-deficient plasmas, but was activated in other deficient plasmas. After clotting, activated Factor IX (IXa) was the apparent principal activator. Thus, Factor VII was not activated in Factor XII-,HMW kininogen-, XI-, and IX-deficient plasmas, but was activated in Factor VIII-, X-, and V-deficient plasmas. In further studies, purified small-fragment Factor XIIa (β-XIIa), kallikrein, and Factor IXa were added to partially purified Factor VII and to plasma. High concentrations of β-XIIa activated Factor VII in a purified system; much lower concentrations of β-XIIa activated Factor VII in normal plasma but not in prekallikrein or HWM kininogen-deficient plasmas. Kallikrein alone failed to activate partially purified Factor VII but did so when purified Factor IX was added. Kallikrein also activated Factor VII in normal, Factor XII-, and Factor IX-deficient plasmas. Purified Factor IXa activated partially purified Factor VII and had no additional indirect activating effect in the presence of plasma. These results demonstrate that both Factor XIIa and Factor IXa directly activate human Factor VII, whereas kallikrein, through generation of Factor XIIa and Factor IXa, functions as an indirect activator of Factor VII.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Deficiency of factor XII-dependent plasminogen proactivator in prekallikrein-deficient plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jan;91(1):148–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Human blood coagulation factor XI. Purification, properties, and mechanism of activation by activated factor XII. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6432–6437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Characterization of bovine factor XIIa (activated Hageman factor). Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4182–4188. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjonnaess H. Cold promoted activation of factor VII. 3. Relation to the kallikrein system. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Oct 31;28(2):182–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjonnaess H. Cold promoted activation of factor VII. I. Evidence for the existence of an activator. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Oct 31;28(2):155–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Cochrane C. G. Human factor XII (Hageman factor). Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:56–65. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H. Role of surface in surface-dependent activation of Hageman factor (blood coagulation factor XII). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1998–2002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJORT P., RAPAPORT S. I., OWREN P. A. A simple, specific one-stage prothrombin assay using Russell's viper venom in cephalin suspension. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Jul;46(1):89–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUGIE C. A simple assay method for factor X (Stuart-Prower factor). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Mar;109:754–756. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUGIE C. Studies on the fate of coagulation factors during the clotting of normal and pathological blood. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1959 Sep 1;3:578–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTON C. L., Jr, HJORT P. F. Development of increased factor VII activity during the spontaneous coagulation of blood. J Clin Invest. 1961 Apr;40:743–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI104308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. A pre-albumin activator of prekallikrein. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):802–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W. Activation of bovine factor VII (proconvertin) by factor XIIa (activated Hageman factor). Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4189–4194. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laake K., Osterud B. Activation of purified plasma factor VII by human plasmin, plasma kallikrein, and activated components of the human intrinsic blood coagulation system. Thromb Res. 1974 Dec;5(6):759–772. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik K. H., Osterud B., Prydz H., Berg K. Electroimmunoassay of factor IX in hemophilia B. Thromb Res. 1975 Sep;7(3):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Human blood coagulation factor IX. Purification, properties, and mechanism of activation by activated factor XI. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5946–5951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Flengsrud R. Purification and some characteristics of the coagulation factor IX from human plasma. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):469–474. doi: 10.1042/bj1450469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Activation of factor IX by the reaction product of tissue factor and factor VII: additional pathway for initiating blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5260–5264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPAPORT S. I., AAS K., OWREN P. A. The effect of glass upon the activity of the various plasma clotting factors. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jan;34(1):9–19. doi: 10.1172/JCI103067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe R., Bagdasarian A., Colman R., Nemerson Y. Activation of bovine factor VII by hageman factor fragments. Blood. 1977 Oct;50(4):611–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe R., Nemerson Y. Activation and control of factor VII by activated factor X and thrombin. Isolation and characterization of a single chain form of factor VII. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):388–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport S. I., Hjort P. F., Patch M. J., Jeremic M. Consumption of serum factors and prothrombin during intravascular clotting in rabbits. Scand J Haematol. 1966;3(1):59–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1966.tb00626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Surface and fluid phase activities of two forms of activated Hageman factor produced during contact activation of plasma. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):719–729. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Griffin J. H. The binding and cleavage characteristics of human Hageman factor during contact activation. A comparison of normal plasma with plasmas deficient in factor XI, prekallikrein, or high molecular weight kininogen. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1167–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI108741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Ratnoff O. D. Alteration of factor VII activity by activated Fletcher factor (a plasma kallikrein): a potential link between the intrinsic and extrinsic blood-clotting systems. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Mar;85(3):405–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Osterud B., Griffin J. H., Rapaport S. I. Evidence for the participation of both activated factor XII and activated factor IX in cold-promoted activation of factor VII. Thromb Res. 1978 Dec;13(6):1049–1056. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90233-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Coupled amidolytic assay for factor VII: its use with a clotting assay to determine the activity state of factor VII. Blood. 1978 Nov;52(5):978–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanberge J. N., Matsuoka T. Studies regarding the effect of foreign-surface contact on the one-stage prothrombin time determination. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 May 15;15(3):442–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



