Figure 5. Repeated stress shifts the dendritic spine distribution in BA principal neurons, but not LAT.
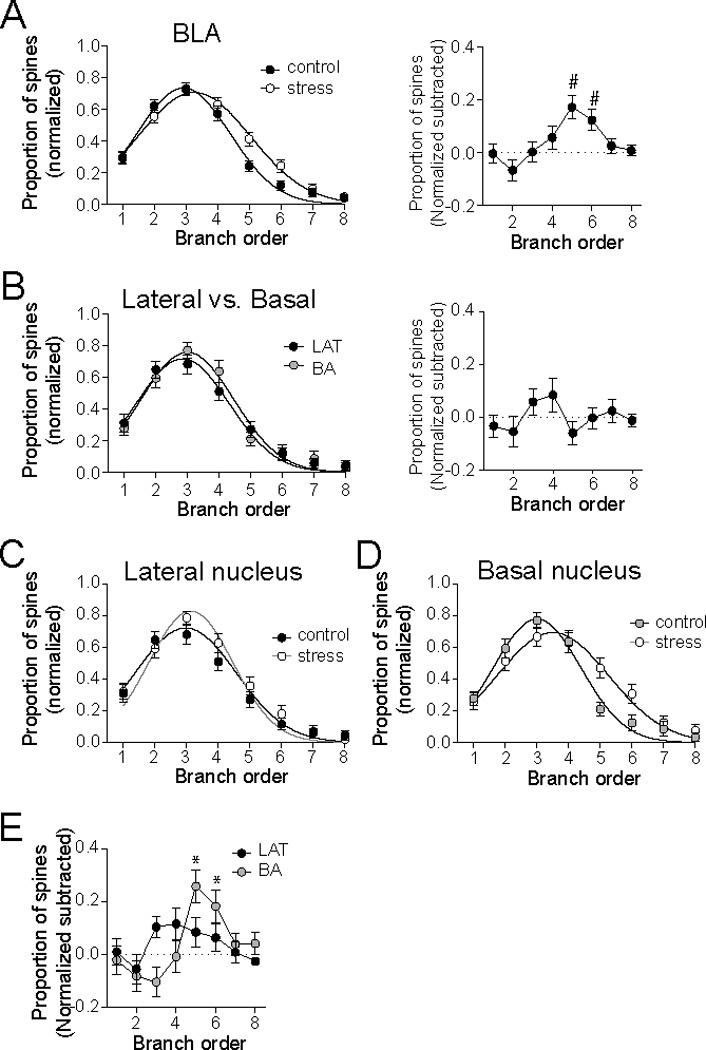
A) There was a significant difference in the normalized distribution of spines across the dendritic tree of BLA principal neurons after repeated stress (left). Subtraction of the average control spine distribution demonstrates that the peak effects of repeated stress lie between the 4th – 6th dendritic branch orders. B) There was no significant difference in the distribution of spines between LAT and BA neurons (left), and no significant difference when LAT and BA spine distribution was subtracted. C) Repeated stress did not significantly change the normalized distribution of spines in LAT principal neurons. D) Repeated stress caused a significant shift in the distribution of spines across the dendritic tree of BA principal neurons. E) Repeated stress did not lead to any significant changes in the subtracted effects of repeated stress in LAT neurons (black), but did significantly change the subtracted effects across branch orders in BA neurons (grey). # indicates BA group significantly different than 0. * indicates BA group significantly different than 0.
