Abstract
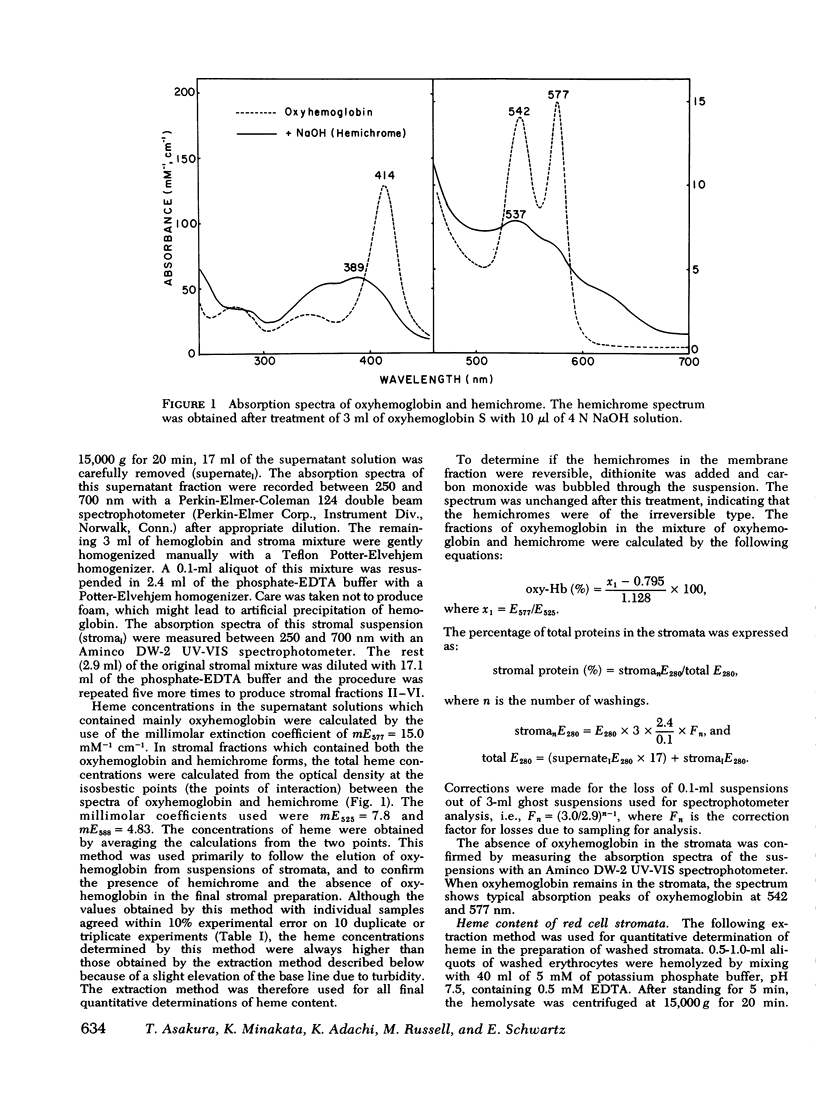
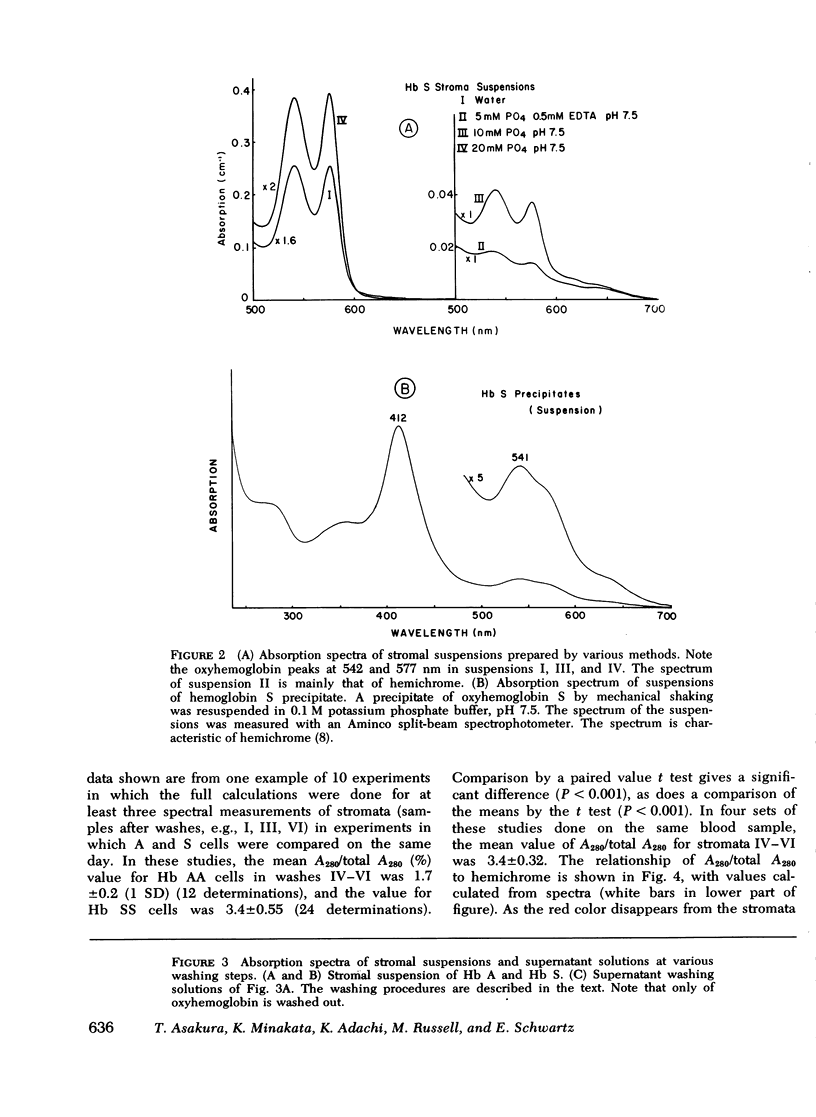
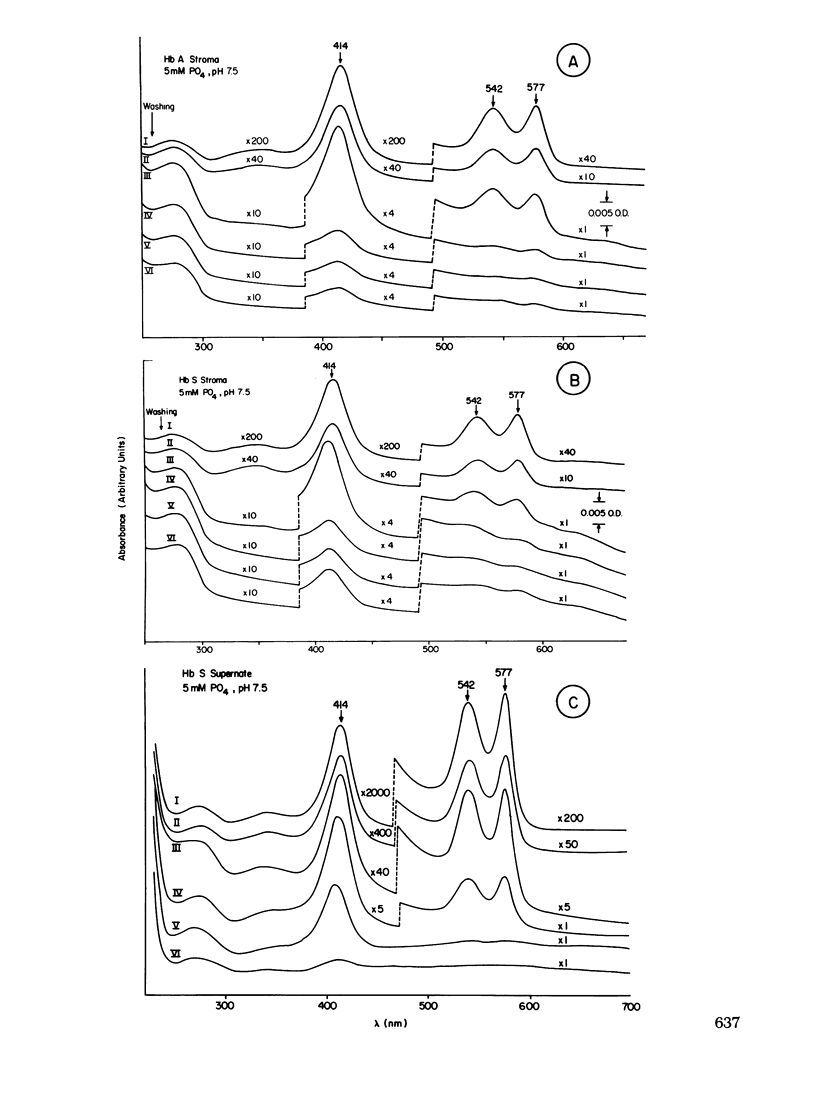
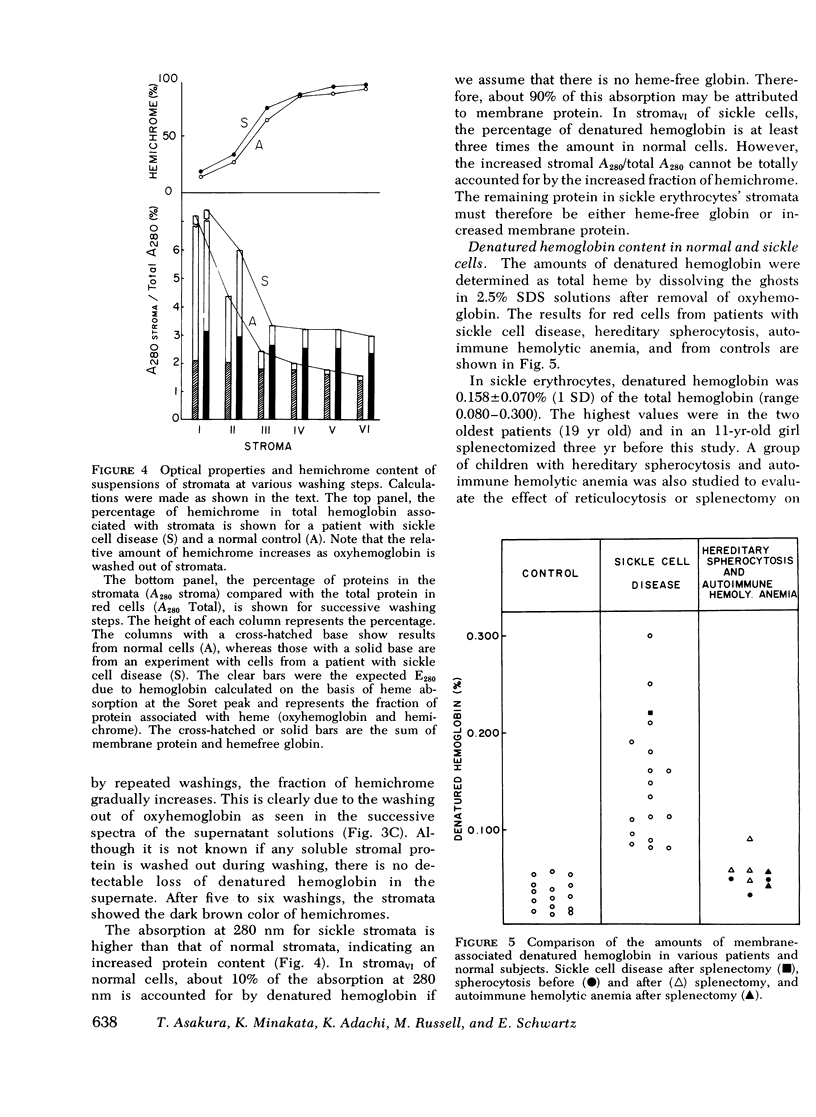
To study the nature of numerous inclusion bodies seen in red cells from patients with sickle cell disease (Hb SS), we have prepared red cell ghosts free of oxyhemoglobin and analyzed them by spectrophotometric and heme extraction methods. The absorption spectrum in the visible region of the ghost suspensions was typical of hemichromes. The spectrum was similar to that of denatured hemoglobin repared by treatment of oxyhemoglobin S with mechanical shaking or heat. Similar treatment of cells containing only normal hemoglobin (Hb AA) showed a very small amount of denatured hemoglobin, approximately one-fifth of the amount in Hb SS cells. The amount of denatured hemoglobin determined after solution of membrane with 2.5% sodium dodecyl sulfate was 0.158+/-0.070% (1 SD) of the total cellular heme in Hb SS patients. In controls, the amount was 0.030+/-0.016%. Persons with Hb AA and reticulocytosis did not have an elevated amount of membrane-associated heme. In patients with hereditary spherocytosis and autoimmune hemolytic anemia, denatured stromal hemoglobin was normal or slightly elevated before and after splenectomy. The increased amount of denatured hemoglobin in Hb SS red cells may be related to the instability of sickle oxyhemoglobin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON H. M., TURNER J. C. Relation of hemoglobin to the red cell membrane. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:1–7. doi: 10.1172/JCI104007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakura T., Agarwal P. L., Relman D. A., McCray J. A., Chance B., Schwartz E., Friedman S., Lubin B. Mechanical instability of the oxy-form of sickle haemoglobin. Nature. 1973 Aug 17;244(5416):437–438. doi: 10.1038/244437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakura T., Onishi T., Friedman S., Schwartz E. Abnormal precipitation of oxyhemoglobin S by mechanical shaking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1594–1598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durocher J. R., Conrad M. E. Erythrocyte membrane proteins in sickle cell anemia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jun;146(2):373–375. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S., Nagel R. L., Bookchin R. M., Roth E. F., Jr, Tellez-Nagel I. The binding of hemoglobin to membranes of normal and sickle erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 14;375(3):422–433. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., ENGLE L. K., ALLEN D. W. Oxidative hemolysis and precipitation of hemoglobin. I. Heinz body anemias as an acceleration of red cell aging. J Clin Invest. 1960 Dec;39:1818–1836. doi: 10.1172/JCI104206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLIPSTEIN F. A., RANNEY H. M. Electrophoretic components of the hemoglobin of red cell membranes. J Clin Invest. 1960 Dec;39:1894–1899. doi: 10.1172/JCI104213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz E. A. Denaturation of the normal and abnormal hemoglobin molecule. Semin Hematol. 1974 Oct;11(4):441–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz E. A., Peisach J., Blumberg W. E. Studies on the stability of oxyhemoglobin A and its constituent chains and their derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3356–3366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz E. A., Peisach J., Bradley T. B., Blumberg W. E. Role of haemichromes in the formation of inclusion bodies in haemoglobin H disease. Nature. 1969 Apr 19;222(5190):248–250. doi: 10.1038/222248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. G., Takeda I., Gustavson L. P., Alperin J. B. Intraerythrocytic precipitations of haemoglobins S and C. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 19;235(55):88–90. doi: 10.1038/newbio235088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C., Carrell R. W. Studies of hemoglobin denaturation and Heinz body formation in the unstable hemoglobins. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):678–689. doi: 10.1172/JCI107806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C., Carrell R. W. The attachment of Heinz bodies to the red cell membrane. Br J Haematol. 1973 Nov;25(5):585–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



