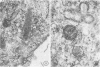
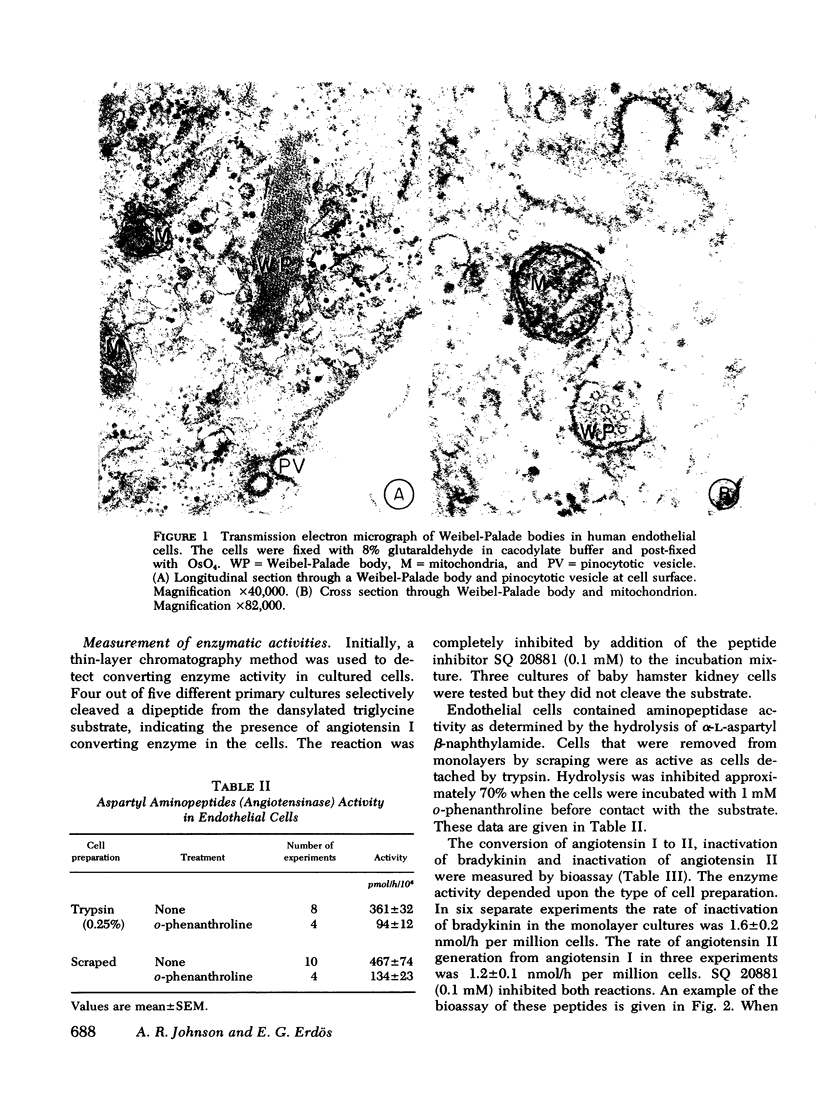
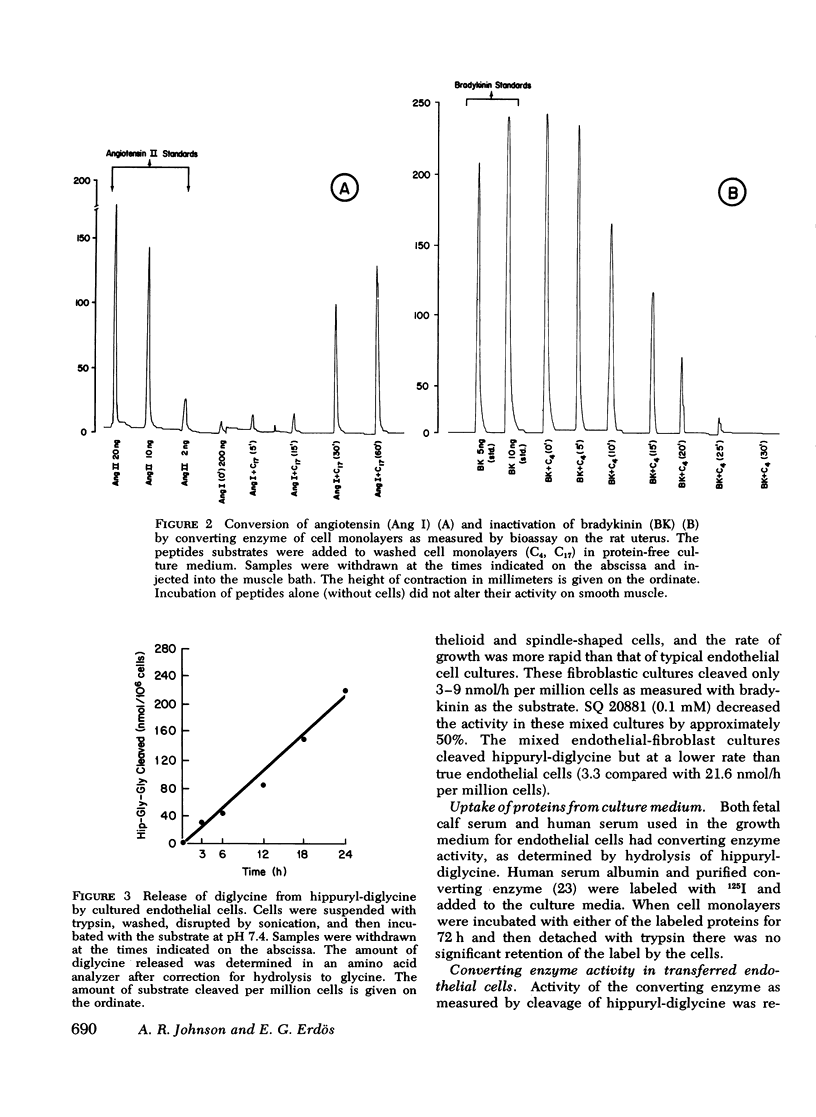
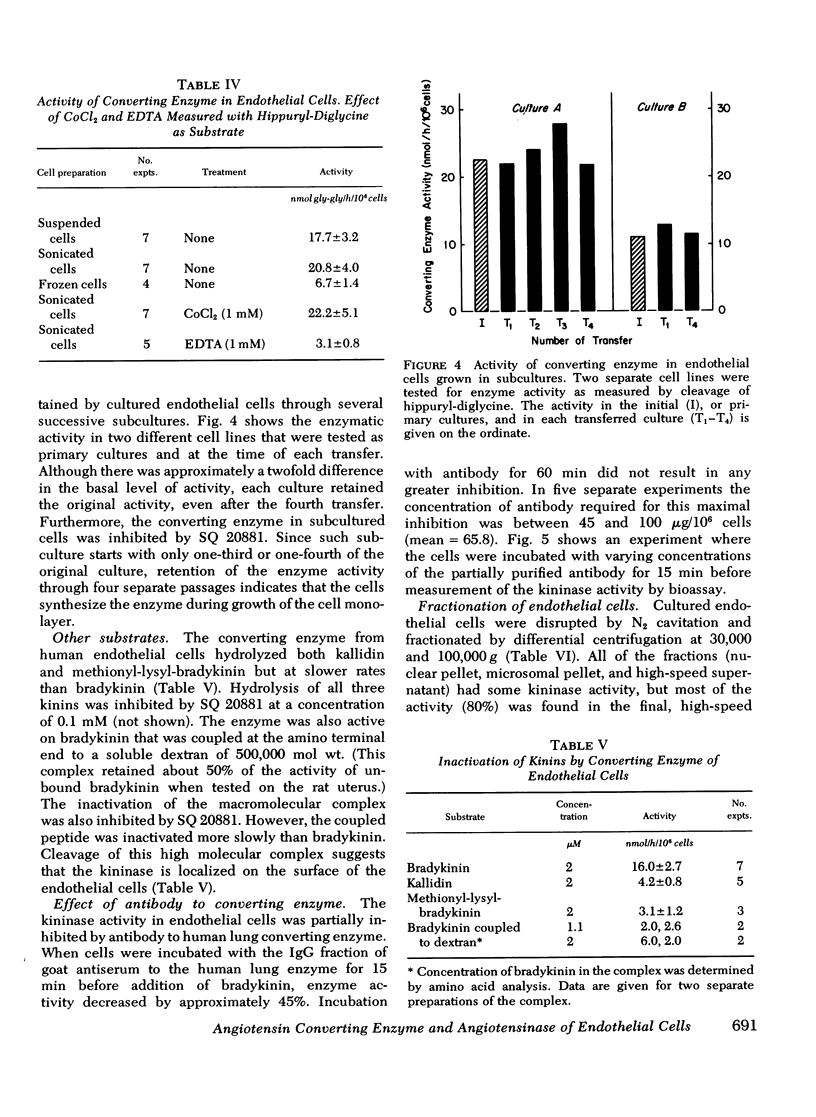
Abstract
Cultured endothelial cells provide a model for the study of interactions of vasoactive peptides with endothelium. Endothelial cell cultured from veins of human umbilical cords contain both angiotensin I converting enzyme (kininase II) and angiotensinase activities. Intact monolayers of cells can both activate angiotensin I and inactivate bradykinin when the peptides are added to culture flasks in protein-free medium. Intact suspended cells or lysed cells convert angiotensin I to angiotensin II, inactivate bradykinin, and hydrolyze hippuryldiglycine to hippuric acid and diglycine. These actions are inhibited by SQ 20881, the specific inhibitor of converting enzyme. The kininase activity of endothelial cells was partially inhibited by antibody to human lung converting enzyme. Endothelial cells also inactivate longer analogs of bradykinin, such as kallidin, methionyl-lysyl bradykinin, and bradykinin coupled covalently to 500,000 mol wt dextran. The endothelial cells retained converting enzyme activity through four successive subcultures, indicating that the enzyme is synthesized by the cells surface, and it is apparently a marker for endothelial cells, since cultured human fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and baby hamster kidney cells do not have it. Endothelial cells also contain an aminopheptidase which hydrolyzes both angiotensin II and the synthetic substrate, alpha-L-aspartyl beta-naphthylamide. The angiotensinase activity increased when the cells were lysed, which suggests that the enzyme is localized within the cells, Hydrolysis of both alpha-L-aspartyl beta-naphthylamide and angiotensin II was inhibited by omicron-phenanthroline, indicating that the enzyme is an A-tipe anigotensinase.
Full text
PDF




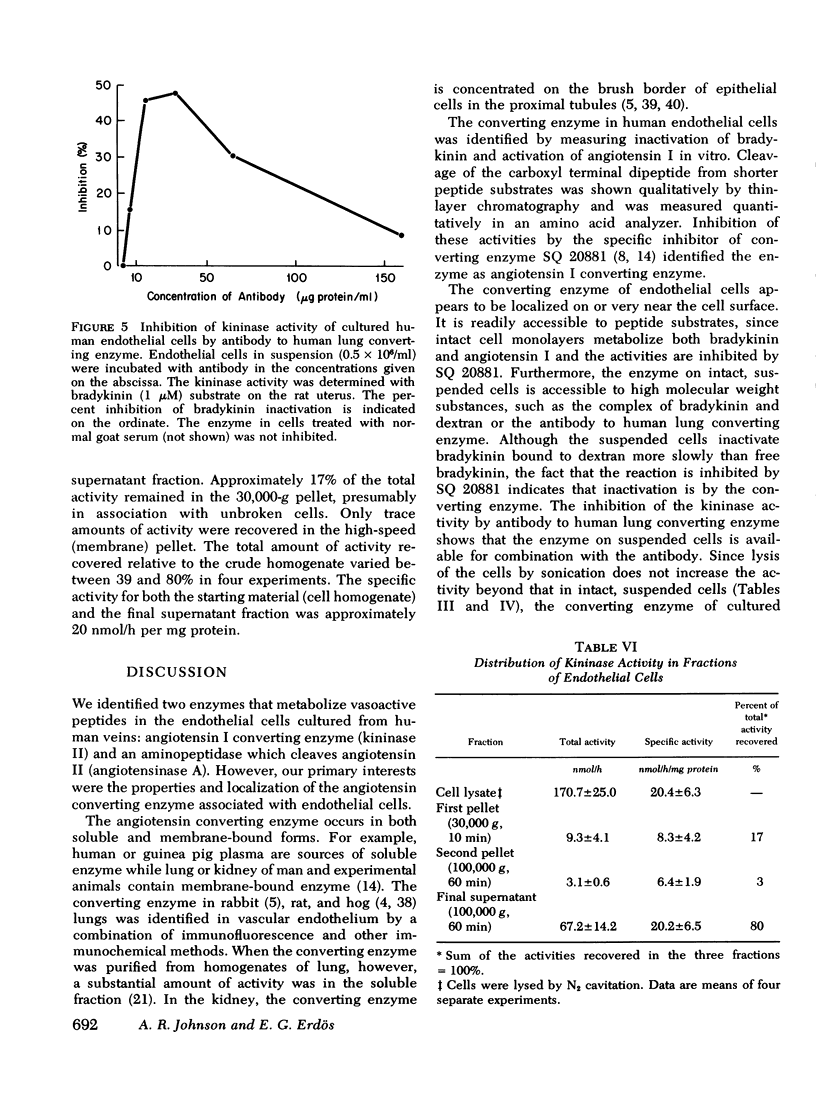



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiken J. W., Vane J. R. Inhibition of converting enzyme of the renin-angiotensin system in kidneys and hindlegs of dogs. Circ Res. 1972 Mar;30(3):263–273. doi: 10.1161/01.res.30.3.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhle Y. S., Reynard A. M., Vane J. R. Metabolism of the angiotensins in isolated perfused tissues. Nature. 1969 Jun 7;222(5197):956–959. doi: 10.1038/222956a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhle Y. S., Vane J. R. Pharmacokinetic function of the pulmonary circulation. Physiol Rev. 1974 Oct;54(4):1007–1045. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.4.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. D., Sambhi M. P. Simultaneous assay of angiotensin I and II and determination of converting enzyme activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Dec;170(2):326–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron P., Campeau L., David P. Fate of angiotensin I and II in the human pulmonary circulation. Am J Cardiol. 1969 Oct;24(4):544–547. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(69)90498-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron P., Huggins C. G. Pulmonary activation of synthetic angiotensin I. Life Sci. 1968 Sep 1;7(17):965–970. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(68)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell P. R., Seegal B. C., Hsu K. C., Das M., Soffer R. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme: vascular endothelial localization. Science. 1976 Mar 12;191(4231):1050–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.175444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier J. G., Robinson B. F. Comparison of effects of locally infused angiotensin I and II on hand veins and forearm arteries in man: evidence for converting enzyme activity in limb vessels. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Aug;47(2):189–192. doi: 10.1042/cs0470189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorer F., Ryan J. W., Stewart J. M. Hydrolysis of bradykinin and its higher homologues by angiotensin-converting enzyme. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):915–917. doi: 10.1042/bj1410915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdos E. G., Yang H. Y. An enzyme in microsomal fraction of kidney that inactivates bradykinin. Life Sci. 1967 Mar 15;6(6):569–574. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G. Conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Am J Med. 1976 May 31;60(6):749–759. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90889-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G. Hypotensive peptides: bradykinin, kallidin, and eledoisin. Adv Pharmacol. 1966;4:1–90. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Folkman J. Human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Growth and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):673–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S. Human vascular smooth muscle in culture. Growth and ultrastructure. Lab Invest. 1975 Jul;33(1):16–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall E. R., Kato J., Erdös E. G., Robinson C. J., Oshima G. Angiotensin i-converting enzyme in the nephron. Life Sci. 1976 Jun 1;18(11):1299–1303. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haudenschild C. C., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Folkman J. Fine structure of vascular endothelium in culture. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Jan;50(1):22–32. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igic R., Erdös E. G., Yeh H. S., Sorrells K., Nakajima T. Angiotensin I converting enzyme of the lung. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(9 Suppl):51–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of von Willebrand factor by cultured human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1906–1909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary W. P., Ledingham J. G. Removal of angiotensin by isolated perfused organs of the rat. Nature. 1969 Jun 7;222(5197):959–960. doi: 10.1038/222959a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis L. J., Hoak J. C., Maca R. D., Fry G. L. Replication of human endothelial cells in culture. Science. 1973 Aug 3;181(4098):453–454. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4098.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik K. U., Nasjletti A. Facilitation of adrenergic transmission by locally generated angiotensin II in rat mesenteric arteries. Circ Res. 1976 Jan;38(1):26–30. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatsu I., Gillespie L., George J. M., Folk J. E., Glenner G. G. Serum aminopeptidases, "angiotensinase," and hypertension. II. Amino acid beta-napthylamide hydrolysis by normal and hypertensive serum. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 May;14(5):853–861. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima G., Gecse A., Erdös E. G. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme of the kidney cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 20;350(1):26–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peach M. J., Sarstedt C. A., Vaughan E. D., Jr Changes in cardiovascular and adrenal cortical responses to angiotensin III induced by sodium deprivation in the rat. Circ Res. 1976 Jun;38(6 Suppl 2):117–121. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.6.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. W., Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Whitaker C., Chung A. Subcellular localization of pulmonary antiotensin-converting enzyme (kininase II). Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):497–499. doi: 10.1042/bj1460497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Ryan J. W., Whitaker C., Chiu A. Localization of angiotensin converting enzyme (kininase II). II. Immunocytochemistry and immunofluorescence. Tissue Cell. 1976;8(1):125–145. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(76)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I. The lung in relation to vasoactive hormones. Fed Proc. 1973 Sep;32(9):1972–1976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H. A., Thomas G. H., Miller C. S., Kelly T. E., Siggers D. Mucolipidosis 3 (pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy): cytological and ultrastructural observations of cultured fibroblast cells. Clin Genet. 1973;4(5):388–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1973.tb01165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. The release and fate of vaso-active hormones in the circulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Feb;35(2):209–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R., PALADE G. E. NEW CYTOPLASMIC COMPONENTS IN ARTERIAL ENDOTHELIA. J Cell Biol. 1964 Oct;23:101–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Gedney C. D., Dowben R. M., Erdös E. G. Isolation of membrane-bound renal kallikrein and kininase. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):755–758. doi: 10.1042/bj1510755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Erdös E. G., Levin Y. Characterization of a dipeptide hydrolase (kininase II: angiotensin I converting enzyme). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):291–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Hoyer L. W., Dickson L., Edgington T. S. Determination of the von Willebrand's disease antigen (factor VIII-related antigen) in plasma by quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jul;86(1):152–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]