Abstract
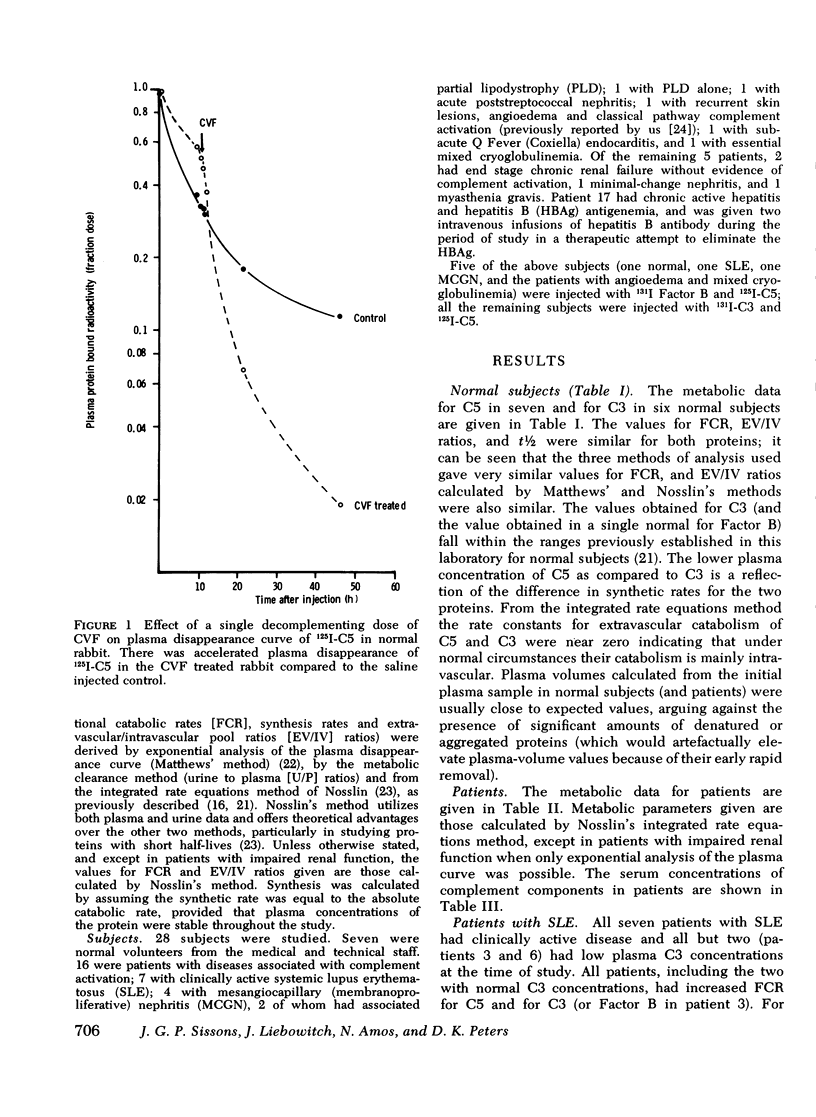
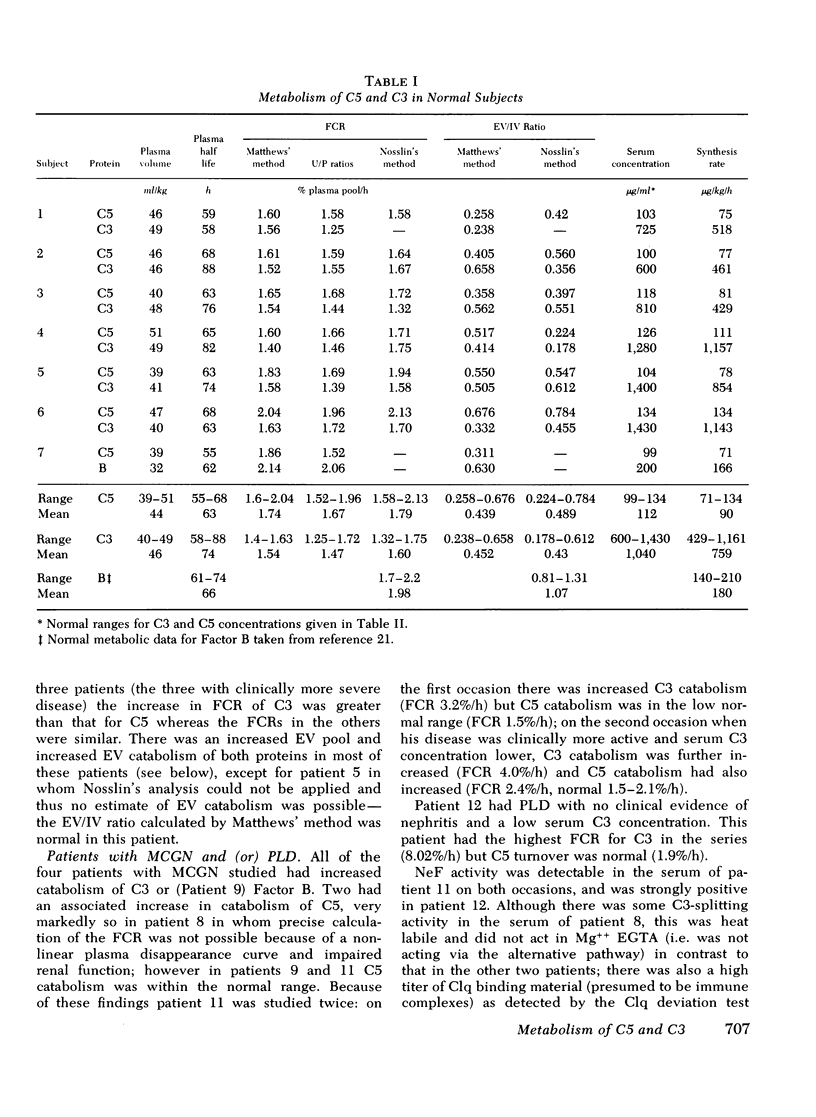
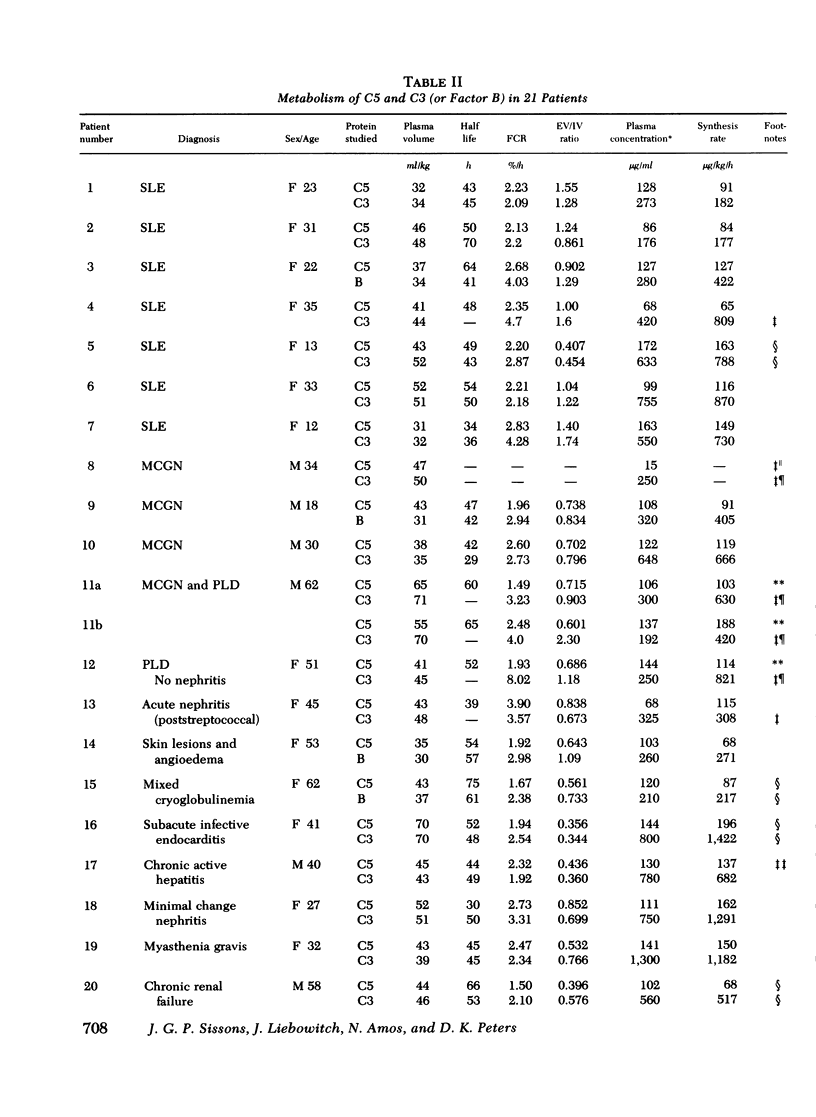
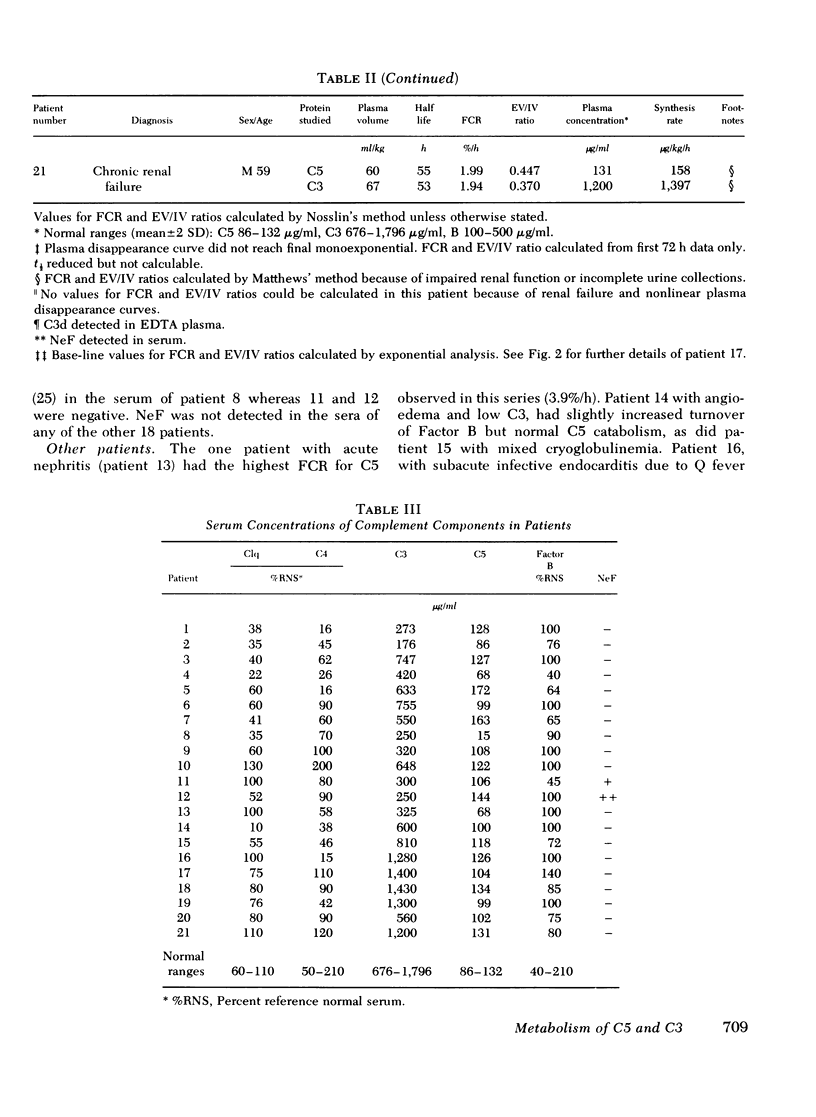
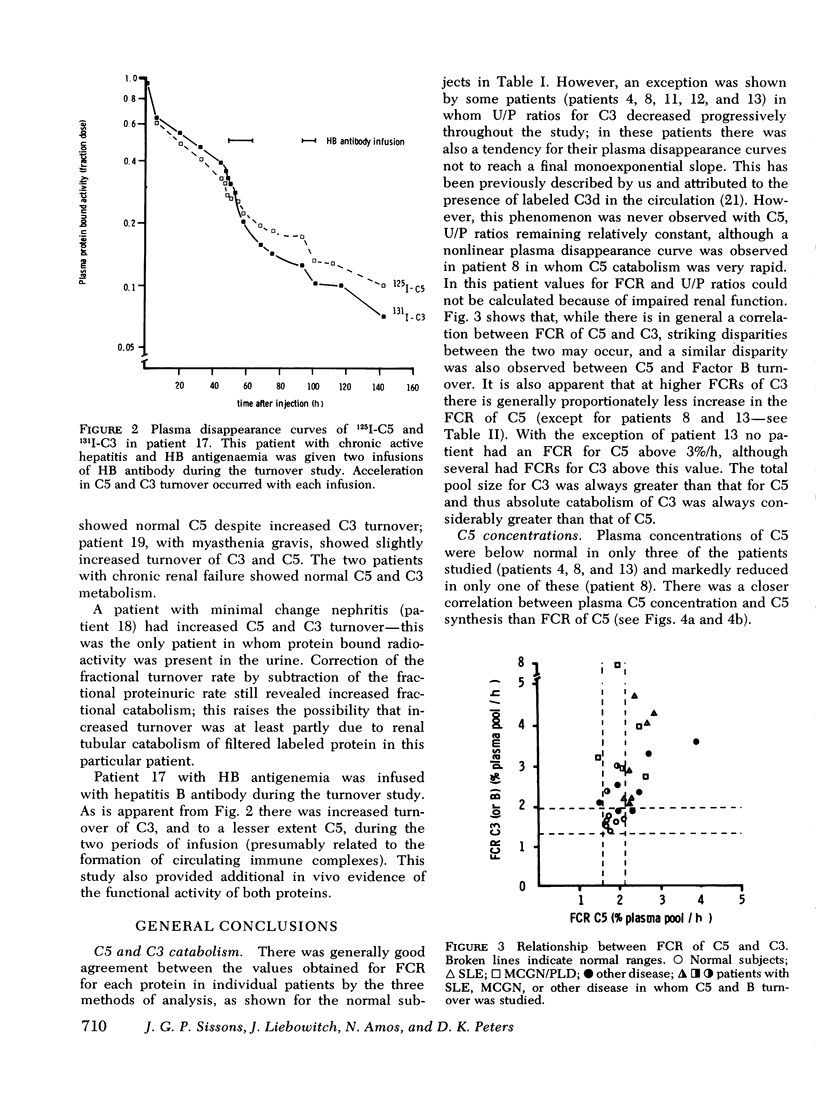
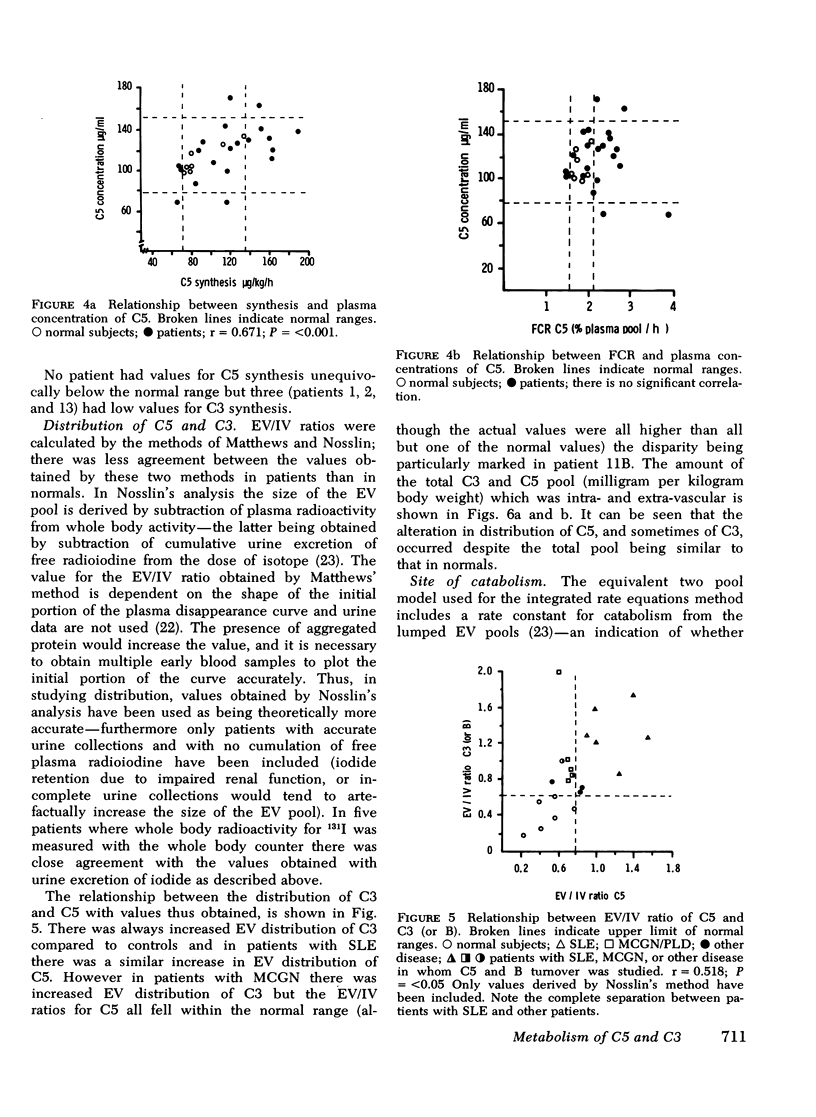
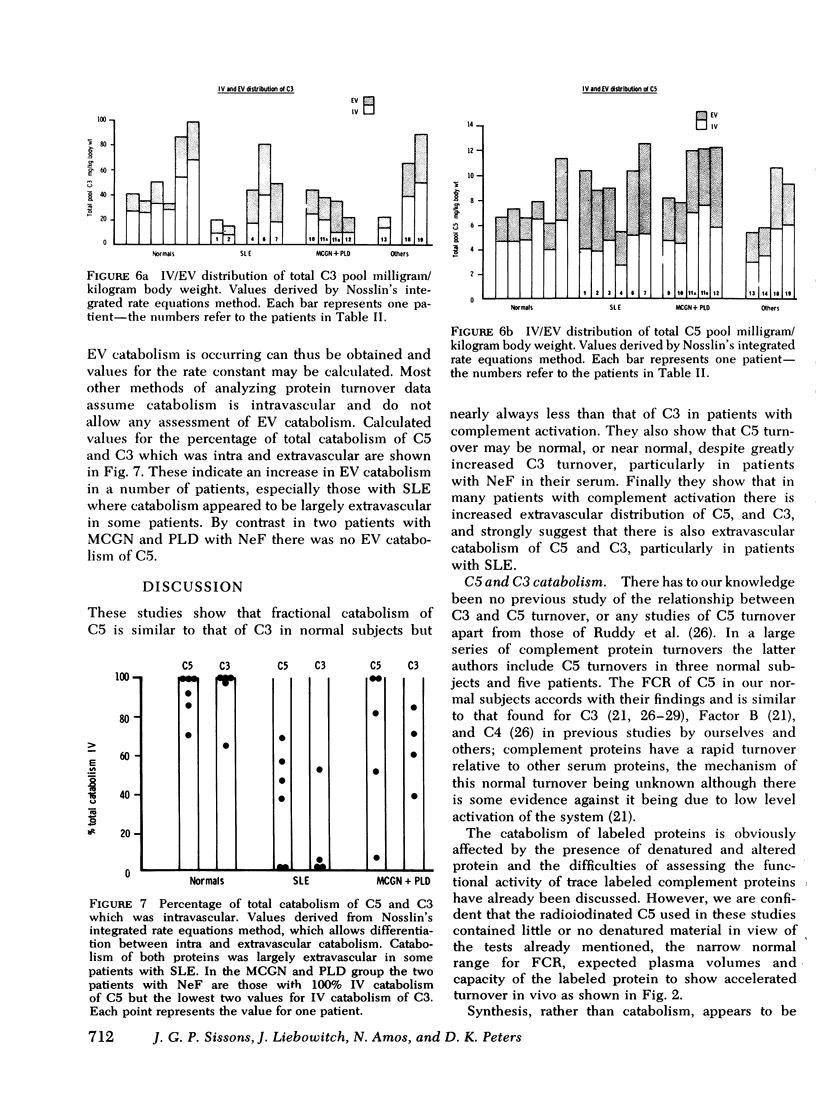
The metabolism of the fifth component of complement (C5), and its relatonship to metabolism of the third component of complement (C3), has been studied in normal subjects and patients by simultaneous administration of radioiodine labeled C5 and C3. In seven normal subjects the fractional catabolic rate of C5 ranged from 1.5 to 2.1% of the plasma pool/h and extravascular/intravascular distribution ratio from 0.22 to 0.78, these values being similar to those obtained for C3, and synthesis rate from 71 to 134 mug/kg per h, In patients with complement activation the increase in fractional catabolic rate of C5 was nearly always less than that of C3. The data also showed that there was increased extravascular distribution of C3 and C5 in most patients and considerable extravascular catabolism of both proteins in some. However, there were differences in metabolic parameters between patients with different types of complement activation. In patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, fractional catabolism and extravascular distribution of C3 and C5 were both increased, and there was marked extravascular catabolism of both proteins. There was increased fractional catabolism and extravascular distribution of C3 in patients with mesangiocapillary nephritis and (or) partial lipodystrophy, and fractional catabolism of C5 was also increased in three of six studies although distribution of C5 was always within the normal range; however, in two patients with nephritic factor in their serum fractional catabolism of C5 was normal despite markedly increased C3 turnover, suggesting that in patients with alternative pathway activation by nephritic factor little or no C5 convertase is generated.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Alper CA, Rosen FS: Studies of the in vivo behavior of human C'3 in normal subjects and patients. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):2021–2034. doi: 10.1172/JCI105691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amos N., Sissons J. G., Girard J. F., Lachmann P. J., Peters D. K. The cofactors required by C3 nephritic factor to generate a C3 convertase in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):474–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth J. A., Williams D. G., Naish P., Lachmann P. J., Peters D. K. Metabolism of radio-labelled C3: effects of in vivo activation in rabbits. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Mar;16(3):445–452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth J. A., Williams D. G., Sherington E., Lachmann P. J., Peters D. K. Metabolic studies of the third component of complement and the glycine-rich beta glycoprotein in patients with hypocomplementemia. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1578–1587. doi: 10.1172/JCI107708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth J. A., Williams D. G., Sherington E., Peters D. K. Metabolism of the third component of complement (C3) in normal human subjects. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Feb;46(2):223–229. doi: 10.1042/cs0460223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. C3 nephritic factor (C3NeF): stabilization of fluid phase and cell-bound alternative pathway convertase. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. C3 requirements for formation of alternative pathway C5 convertase. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):630–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Isolation of alternative pathway C3 convertase containing uncleaved B and formed in the presence of C3 nephritic factor (C3neF). J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):568–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Initiation of C3 cleavage in the alternative complement pathway. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1357–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Properdin: binding to C3b and stabilization of the C3b-dependent C3 convertase. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):856–863. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Ruddy S., Carpenter C. B., Schur P. H., Merrill J. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Austen K. F. Metabolism of third complement component (C3) in nephritis. Involvement of the classic and alternate (properdin) pathways for complement activation. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 26;287(17):835–840. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210262871701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A., Lachmann P. J., Halbwachs L., Hobart M. J. Haemolytic diffusion plate assays for factors B and D of the alternative pathway of complement activation. Immunochemistry. 1976 Apr;13(4):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90341-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medicus R. G., Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Alternative pathway of complement: recruitment of precursor properdin by the labile C3/C5 convertase and the potentiation of the pathway. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1076–1093. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON U. R., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. ISOLATION OF BETA IF-GLOBULIN FROM HUMAN SERUM AND ITS CHARACTERIZATION AS THE FIFTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:277–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson U. R., Mandle R. J., Jr, McConnell-Mapes J. A. Human C3 and C5: subunit structure and modifications by trypsin and C42-C423. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):815–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson U. R., Tomar R. H., Taylor F. B., Jr Additional studies on human C5: development of a modified purification method and characterization of the purified product by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Immunochemistry. 1972 Jul;9(7):709–723. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosslin B. Analysis of disappearance time-curves after single injection of labelled proteins. Ciba Found Symp. 1972;9:113–130. doi: 10.1002/9780470719923.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters D. K., Martin A., Weinstein A., Cameron J. S., Barratt T. M., Ogg C. S., Lachmann P. J. Complement studies in membrano-proliferative glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Jul;11(3):311–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Alternative pathway of complement: demonstration and characterization of initiating factor and its properdin-independent function. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1062–1075. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Medicus R. G., Gïtze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Properdin- and nephritic factor-dependent C3 convertases: requirement of native C3 for enzyme formation and the function of bound C3b as properdin receptor. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):760–772. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sissons J. G., Peters D. K., Williams D. G., Boulton-Jones J. M., Goldsmith H. J. Skin lesions, angio-oedema, and hypocomplementaemia. Lancet. 1974 Dec 7;2(7893):1350–1352. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92216-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sissons J. G., West R. J., Fallows J., Williams D. G., Boucher B. J., Amos N., Peters D. K. The complement abnormalities of lipodystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 26;294(9):461–465. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602262940902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliwinski A. J., Zvaifler N. J. Decreased synthesis of the third component of complement (C3) in hypocomplementemic systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 May;11(1):21–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A. T., Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C1q deviation test for the detection of immune complexes, aggregates of IgG, and bacterial products in human serum. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):139–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler J. M., Daha M. R., Austen K. F., Fearon D. T. Control of the amplification convertase of complement by the plasma protein beta1H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3268–3272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K., Ruddy S. Modulation of C3b hemolytic activity by a plasma protein distinct from C3b inactivator. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1011–1013. doi: 10.1126/science.948757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K., Ruddy S. Modulation of the alternative complement pathways by beta 1 H globulin. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1147–1163. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Peters D. K., Fallows J., Petrie A., Kourilsky O., Morel-Maroger L., Cameron J. S. Studies of serum complement in the hypocomplementaemic nephritides. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):391–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



