Abstract
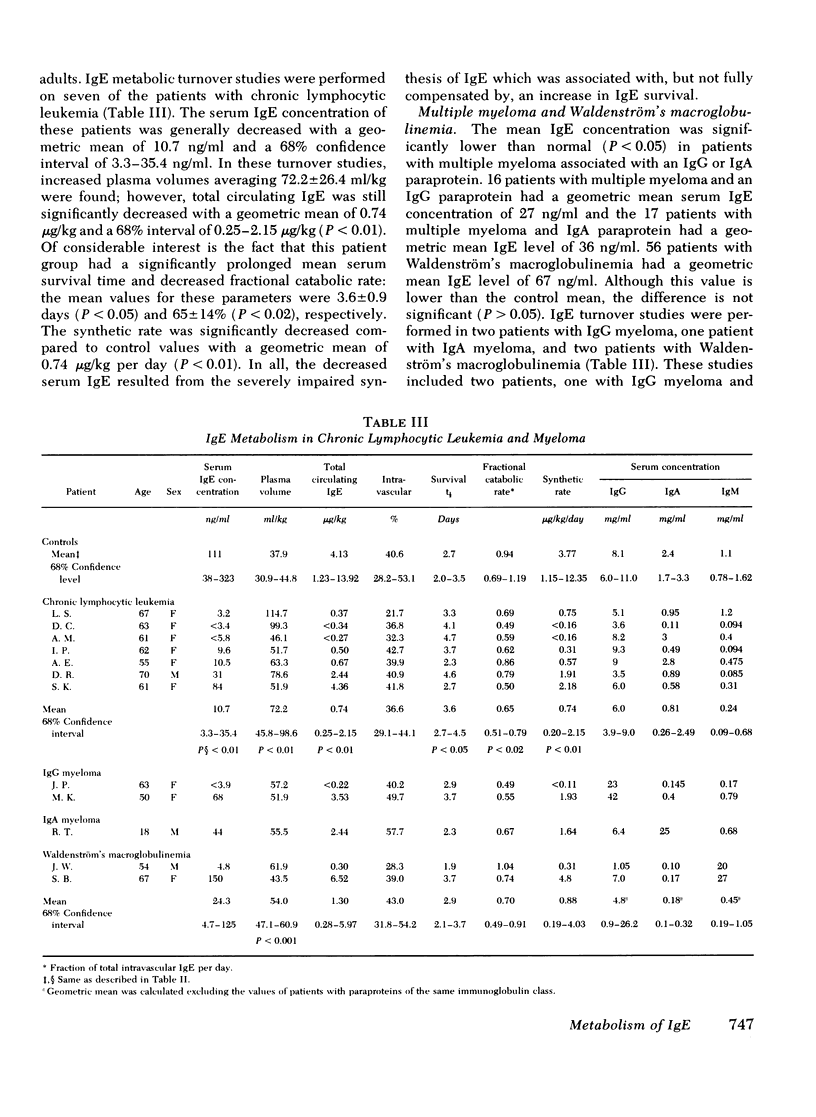
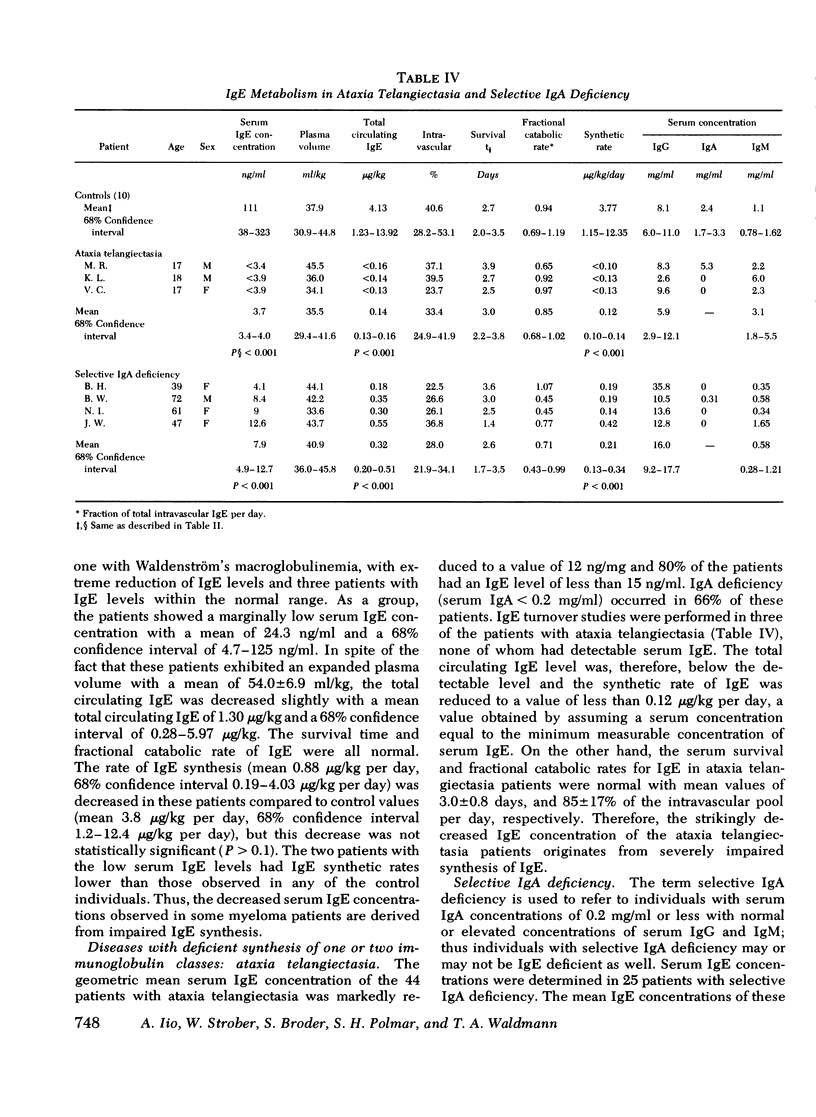
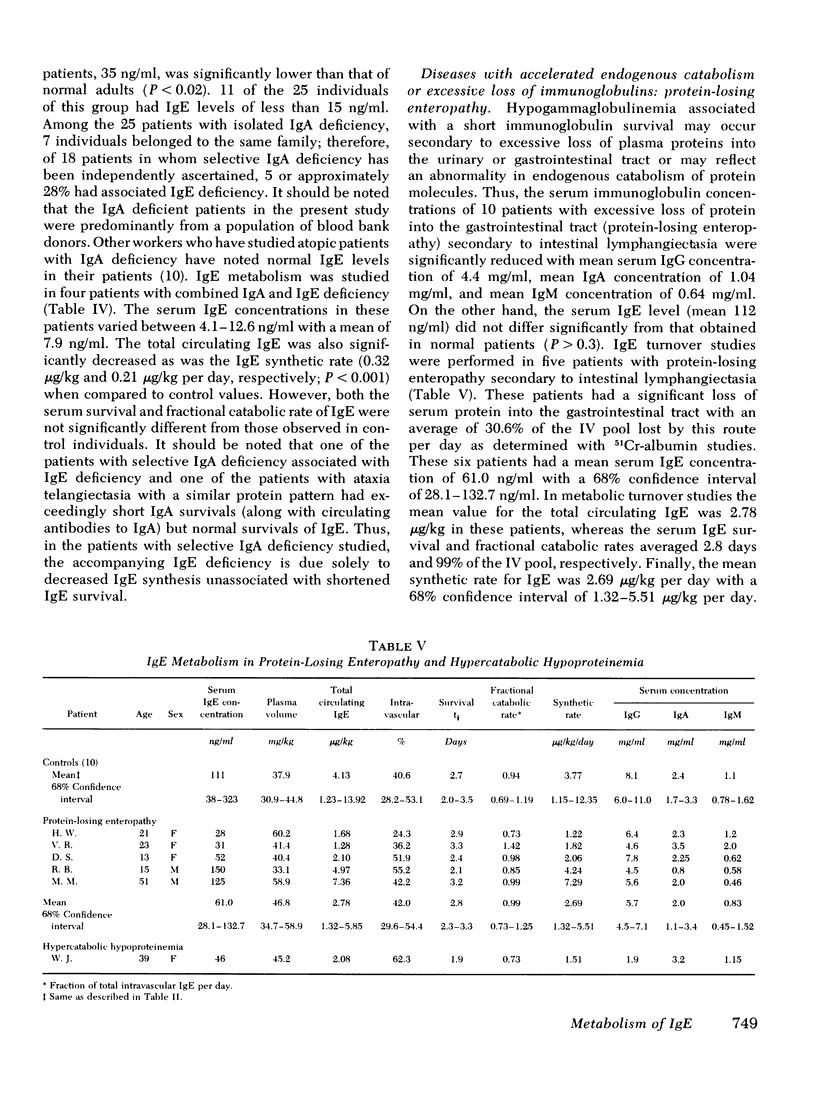
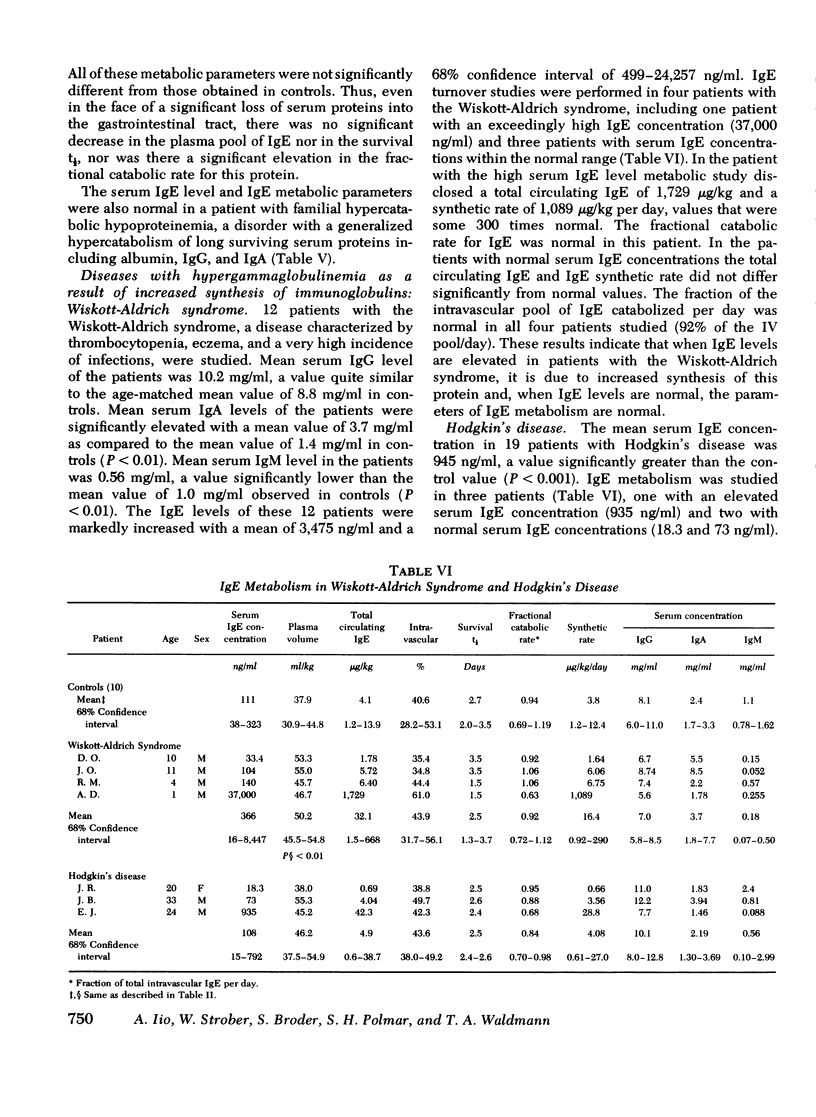
Serum IgE concentrations were determined and IgE turnover studies were performed in control individuals as well as in patients with several disease states. Patients with common variable hypogammaglobulinemia, thymoma and hypogammaglobulinemia, ataxia telangiectasia, and selective IgA deficiency had significantly decreased mean serum IgE concentrations. In turnover studies, this was found to be due to decreased IgE synthesis. In spite of these depressed mean values, some patients with common variable hypogammaglobulinemia had normal serum IgE concentrations and synthetic rates. Patients with the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome had a significantly elevated mean serum IgE concentration. In one of four patients studied with the turnover technique, a strikingly high IgE concentration was present and was associated with an elevated IgE synthetic rate. Three other patients had both normal serum IgE concentrations and synthetic rates. Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia had significantly decreased mean serum concentrations and synthetic rates for IgE. The depressed IgE synthesis was associated with a significantly prolonged IgE half-life. Patients with Hodgkin's disease had significantly increased serum IgE concentrations. One of three patients studied had a high serum IgE concentration and synthetic rate of IgE. The two other patients had normal serum IgE concentrations associated with normal synthetic rates. Finally patients with protein-losing enteropathy or familial hypercatabolic hypoproteinemia had normal IgE concentrations associated with normal IgE metabolic parameters. In these cases, the disorder in the catabolic rate was not severe enough to affect the total amount of circulating IgE because IgE normally has a very high fractional catabolic rate. In general, IgE levels in a variety of disease states were correlated with IgE synthetic rates and abnormalities in the catabolic rate of IgE in disease did not exert an important effect on IgE concentration.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiuti F., Fontana L., Gatti R. A. Membrane-bound immunoglobulin (Ig) and in vitro production of Ig by lymphoid cells from patients with primary immunodeficiencies. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(1):9–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T., Johansson S. G. IgE concentrations in children with atopic diseases. A clinical study. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;36(3):219–232. doi: 10.1159/000230745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaese R. M., Strober W., Brown R. S., Waldmann T. A. The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. A disorder with a possible defect in antigen processing or recognition. Lancet. 1968 May 18;1(7551):1056–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Humphrey R., Durm M., Blackman M., Meade B., Goldman C., Strober W., Waldmann T. Impaired synthesis of polyclonal (non-paraprotein) immunoglobulins by circulating lymphocytes from patients with multiple myeloma Role of suppressor cells. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 30;293(18):887–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510302931801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Fiscus S. A. Serum IgD and IgE concentrations in immunodeficiency diseases. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):157–165. doi: 10.1172/JCI107906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Fisher R. I., Terry W. D. Lymphocytes in patients with variable immunodeficiency and panhypogammaglobulinemia. Evaluation of B and T cell surface markers and a proposed classification. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):834–840. doi: 10.1172/JCI107623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eltringham J. R., Kaplan H. S. Immunodeficiency in Hodgkin disease. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(1):278–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Schneeberger E., Merler E., Rosen F. S. Heterogeneity of "acquired" or common variable agammaglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jul 4;291(1):1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197407042910101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Rabellino E., Pirofsky B. Immunoglobulins on the surface of lymphocytes. IV. Distribution in hypogammaglobulinemia, cellular immune deficiency, and chronic lymphatic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2368–2375. doi: 10.1172/JCI106735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogarth-Scott R. S., Johansson S. G., Bennich H. Antibodies to Toxocara in the sera of visceral larva migrans patients: the significance of raised levels of IgE. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Dec;5(6):619–625. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Hornbrook M. M. Physicochemical properties of reaginic antibody. V. Correlation of reaginic activity wth gamma-E-globulin antibody. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):840–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Identification of gamma-E-antibodies as a carrier of reaginic activity. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1187–1198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S. G., Bennich H. Immunological studies of an atypical (myeloma) immunoglobulin. Immunology. 1967 Oct;13(4):381–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S. G. Raised levels of a new immunoglobulin class (IgND) in asthma. Lancet. 1967 Nov 4;2(7523):951–953. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90792-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlan P., Stanworth D. R., Webster A. D., Asherson G. L. Serum IgE in immune deficiency disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Mar;16(3):375–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. V., Holland P. V., Sugarbaker E., Strober W., Waldmann T. A. Anaphylactic reactions to IgA: a difficult transfusion problem. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Oct;54(4):618–621. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/54.4.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa M., Kochwa S., Smith C., Ishizaka K., McIntyre O. R. Clinical aspects of IgE myeloma. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 27;281(22):1217–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911272812204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura K., Tada T. Regulation of homocytotropic antibody formation in the rat. 3. Effect of thymectomy and splenectomy. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):1019–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polmar S. H., Waldmann T. A., Balestra S. T., Jost M. C., Terry W. D. Immunoglobulin E in immunologic deficiency diseases. I. Relation of IgE and IgA to respiratory tract disease in isolated IgE deficiency, IgA deficiency, and ataxia telangiectasia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Feb;51(2):326–330. doi: 10.1172/JCI106817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polmar S. H., Waldmann T. A., Terry W. D. IgE in immunodeficiency. Am J Pathol. 1972 Dec;69(3):499–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen F. S., Janeway C. A. The gamma globulins. 3. The antibody deficiency syndromes. N Engl J Med. 1966 Sep 29;275(13):709–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196609292751307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon S. E. Immunoglobulin synthesis and tumor kinetics of multiple myeloma. Semin Hematol. 1973 Apr;10(2):135–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff R. I., Buckley R. H., Gilbertsen R. B., Metzgar R. S. Membrane receptors and in vitro responsiveness of lymphocytes in human immunodeficiency. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):376–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober W., Wochner R. D., Barlow M. H., McFarlin D. E., Waldmann T. A. Immunoglobulin metabolism in ataxia telangiectasia. J Clin Invest. 1968 Aug;47(8):1905–1915. doi: 10.1172/JCI105881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober W., Wochner R. D., Carbone P. P., Waldmann T. A. Intestinal lymphangiectasia: a protein-losing enteropathy with hypogammaglobulinemia, lymphocytopenia and impaired homograft rejection. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1643–1656. doi: 10.1172/JCI105656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Taniguchi M., Okumura K. Regulation of homocytotropic antibody formation in the rat. II. Effect of X-irradiation. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):1012–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Perkins H. A., Fudenberg H. H. Anaphylactoid transfusion reactions associated with anti-IgA. Lancet. 1968 Aug 10;2(7563):312–315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90527-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Durm M., Broder S., Blackman M., Blaese R. M., Strober W. Role of suppressor T cells in pathogenesis of common variable hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):609–613. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91940-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Iio A., Ogawa M., McIntyre O. R., Strober W. The metabolism of IgE. Studies in normal individuals and in a patient with IgE myeloma. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1139–1144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Polmar S. H., Balestra S. T., Jost M. C., Bruce R. M., Terry W. D. Immunoglobulin E in immunologic deficiency diseases. II. Serum IgE concentration of patients with acquired hypogammaglobulinemia, thymoma and hypogammaglobulinemia, myotonic dystrophy, intestinal lymphangiectasia and Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. J Immunol. 1972 Aug;109(2):304–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Strober W. Metabolism of immunoglobulins. Prog Allergy. 1969;13:1–110. doi: 10.1159/000385919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zolla S. The effect of plasmacytomas on the immune response of mice. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):1039–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


