Abstract
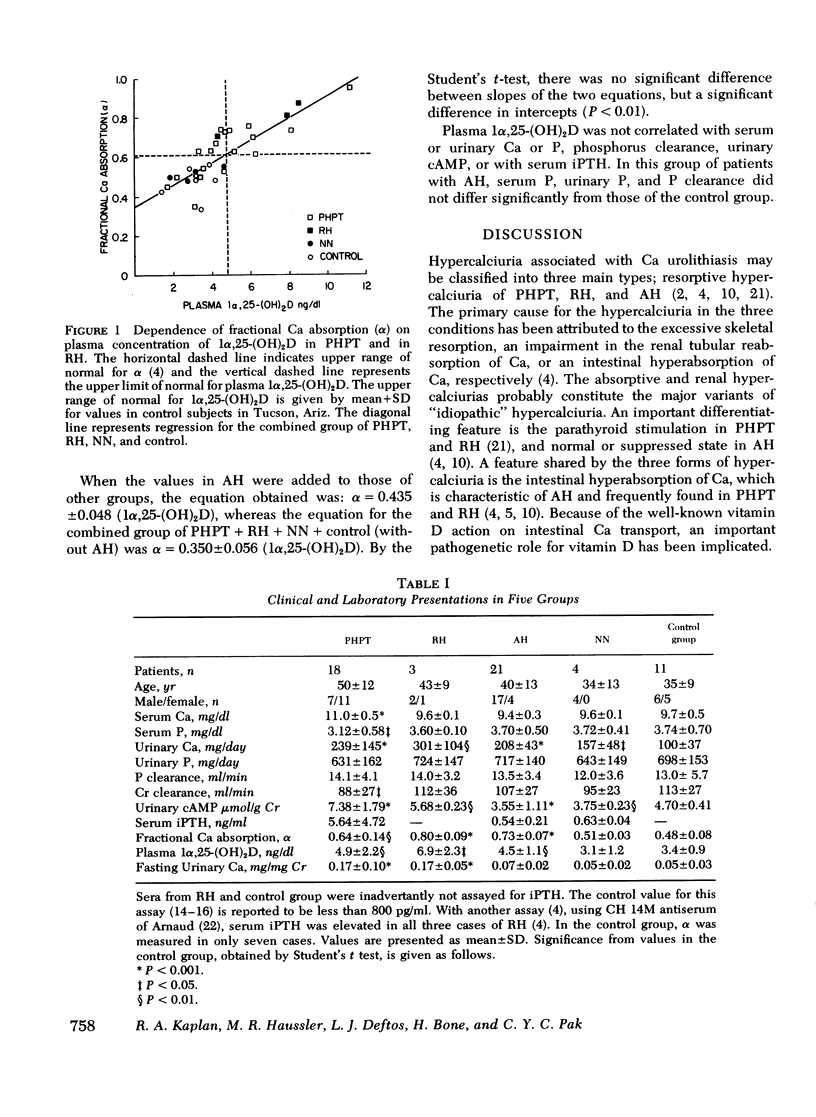
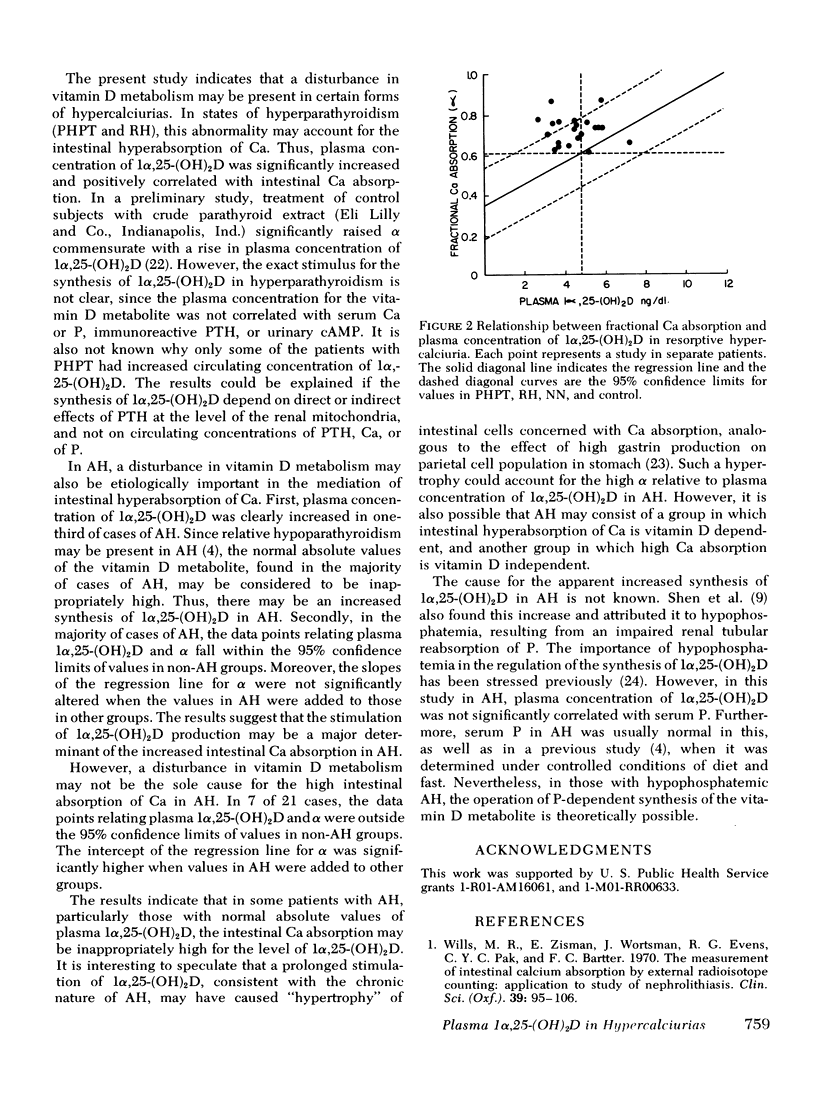
The cuase for the intestinal hyperabsorptionof calcium (Ca) in various forms of hypercalciurias was explored by a careful measurement of plasma 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxycholecalciferol [1 alpha, 25-(OH)I D] and by an assessment of intestinal Ca absorption and of parathyroid function. In 18 cases of primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT), the mean plasma concentration of 1 alpha, 25-(OH)2D was significantly increased (4.9 +/- 2.2 SD ng/dl vs. 3.4 +/- 0.9 ng/dl for the control group), and was significantly correlated with fractional Ca absorption (alpha) (r = 0.80, P less than 0.001). Plasma 1 alpha, 25-(OH)2D was also correlated with urinary Ca (P less than 0.05), but not with serum Ca or phosphorus (P), P clearance, urinary cyclic AMP, or serum immunoreactive parathyroid hormone. In 21 cases of absorptive hypercalciuria (AH), plasma 1 alpha, 25-(OH)2D was elevated in one-third of cases, and the mean value of 4.5 +/- 1.1 ng/dl was significantly higher than that of the control group (P less than 0.01). Since relative hypoparathyroidism may be present, the normal absolute value of plasma 1 alpha, 25-(OH)2D, found in two-thirds of cases of AH, may be considered to be inappropriately high. Moreover, in the majority of cases of AH, the data points relating plasma 1 alpha, 25-(OH)2D and alpha fell within 95% confidence limits of values found in non-AH groups (including PHPT). The results suggest that the intestinal hyperabsorption of Ca in PHPT aw AH may be vitamin D dependent. However, the disturbance in vitamin D metabolism may not be the sole cause for the high Ca absorption in AH, since in some patients with AH, the intestinal Ca absorption appears to be inapp
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brumbaugh P. F., Haussler D. H., Bressler R., Haussler M. R. Radioreceptor assay for 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Science. 1974 Mar 15;183(4129):1089–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4129.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumbaugh P. F., Haussler D. H., Bursac K. M., Haussler M. R. Filter assay for 1alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Utilization of the hormone's target tissue chromatin receptor. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 24;13(20):4091–4097. doi: 10.1021/bi00717a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe F. L., Canterbury J. M., Firpo J. J., Reiss E. Evidence for secondary hyperparathyroidism in idiopathic hypercalciuria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):134–142. doi: 10.1172/JCI107156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deftos L. J., Lorenzi M., Bohanon N., Tsalakian E., Schneider V., Gerich J. E. Somatostatin does not suppress plasma parathyroid hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Jul;43(1):205–207. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deftos L. J., McMillan P. J., Sartiano G. P., Abuid J., Robinson A. G. Simultaneous ectopic production of parathyroid hormone and calcitonin. Metabolism. 1976 May;25(5):543–550. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deftos L. J., Parthemore J. G. Secretion of parathyroid hormone in patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):416–420. doi: 10.1172/JCI107777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M., Holick M. F., Deluca H. F., Boyle I. T. Control of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol metabolism by parathyroid glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1673–1676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN P. H., BENEDICT P. H., FORBES A. P., DUDLEY H. R. Idiopathic hypercaicuria. N Engl J Med. 1958 Oct 23;259(17):802–807. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195810232591702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M. R. Vitamin D: mode of action and biomedical applications. Nutr Rev. 1974 Sep;32(9):257–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1974.tb00970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M. R., Brumbaugh P. F., Hussler M. R., Wergedal J. E., Baylink D. J. Regulation of serum 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 by calcium and phosphate in the rat. Science. 1975 Nov 7;190(4214):578–580. doi: 10.1126/science.1188357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R. A., Snyder W. H., Stewart A., Pak C. Y. Metabolic effects of parathyroidectomy in asymptomatic primary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Mar;42(3):415–426. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-3-415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pak C. Y., East D. A., Sanzenbacher L. J., Delea C. S., Bartter F. C. Gastrointestinal calcium absorption in nephrolithiasis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Aug;35(2):261–270. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pak C. Y., Kaplan R., Bone H., Townsend J., Waters O. A simple test for the diagnosis of absorptive, resorptive and renal hypercalciurias. N Engl J Med. 1975 Mar 6;292(10):497–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197503062921002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pak C. Y., Oata M., Lawrence E. C., Snyder W. The hypercalciurias. Causes, parathyroid functions, and diagnostic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):387–400. doi: 10.1172/JCI107774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems G., Vansteenkiste Y., Limbosch J. M. Stimulating effect of gastrin on cell proliferation kinetics in canine fundic mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1972 Apr;62(4):583–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills M. R., Wortsman J., Pak C. Y., Bartter F. C. The role of parathyroid hormone in the gastro-intestinal absorption of calcium. Clin Sci. 1970 Jul;39(1):89–94. doi: 10.1042/cs0390089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills M. R., Zisman E., Wortsman J., Evens R. G., Pak C. Y., Bartter F. C. The measurement of intestinal calcium absorption by external radioisotope counting: application to study of nephrolithiasis. Clin Sci. 1970 Jul;39(1):95–106. doi: 10.1042/cs0390095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



