Abstract
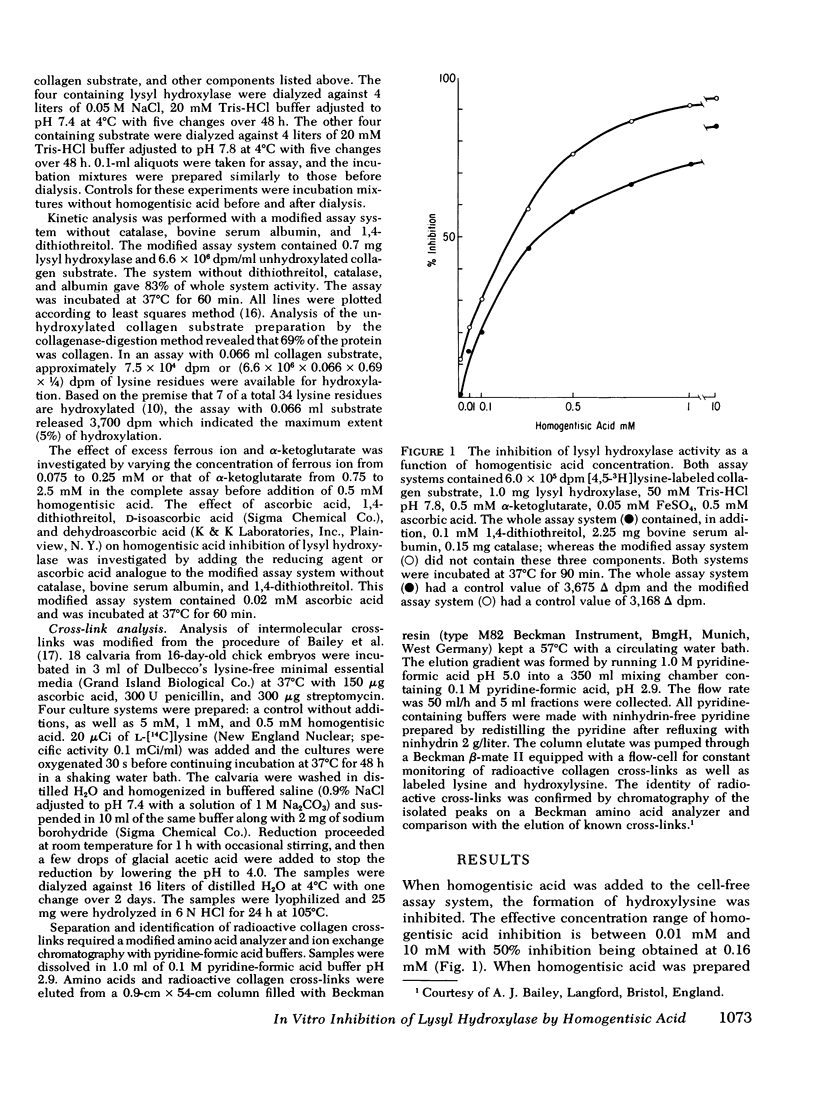
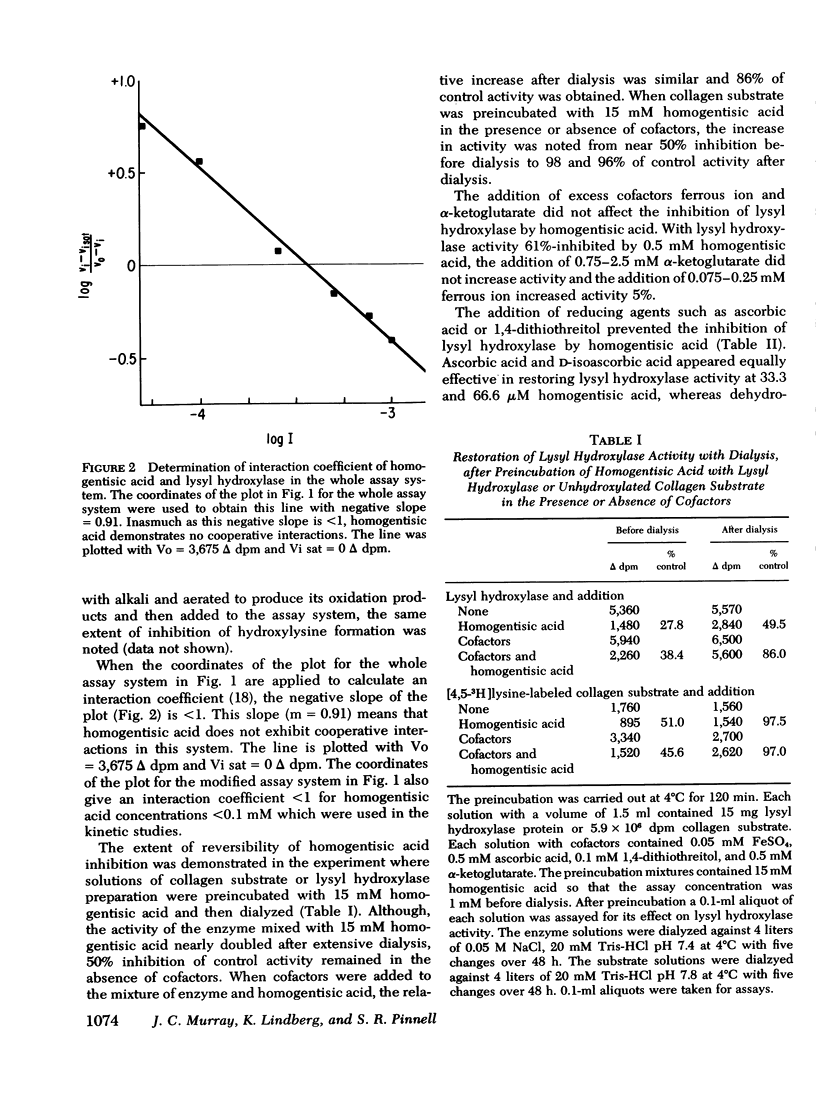
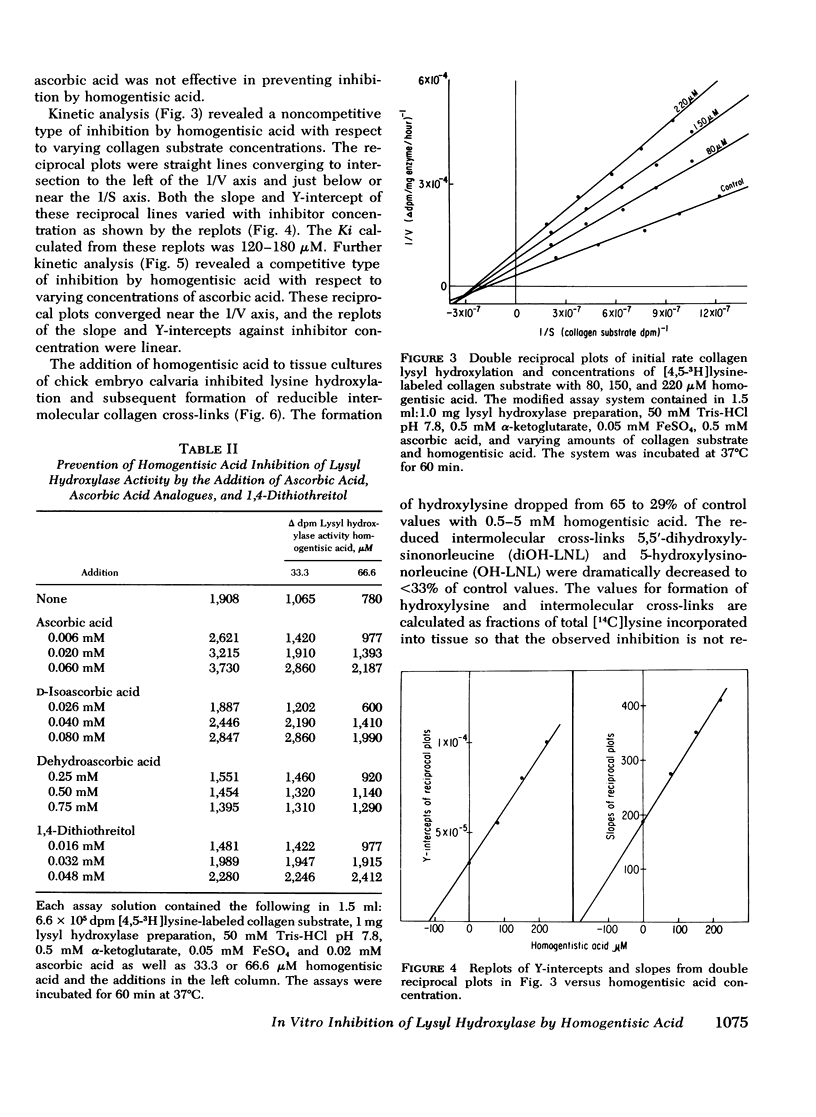
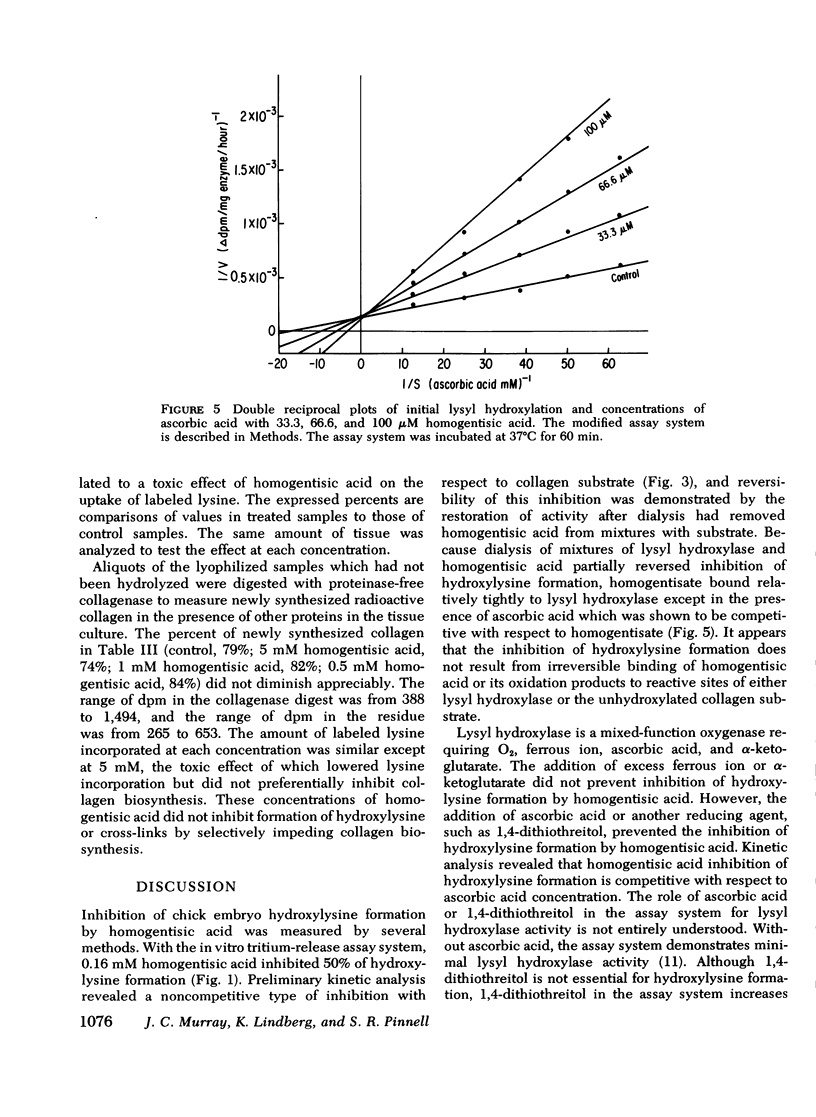
Homogentisic acid inhibits the in vitro activity of chick embryo lysyl hydroxylase, a microsomal enzyme which catalyzes the transformation of certain lysyl residues in collagen to hydroxylysine. Chick embryo lysyl hydroxylase activity was measured as specific tritium release as tritium water from a [4,5-3H]lysine-labeled unhydroxylated collagen substrate prepared from chick calvaria. Kinetic studies revealed a linear, noncompetitive type of inhibition with respect to collagen substrate with a Ki of 120-180 μM. The inhibition by homogentisic acid was reversible in that enzyme activity could be restored after dialysis of preincubated mixtures of homogentisic acid with enzyme or substrate. The inhibition by homogentisic acid was competitive with respect to ascorbic acid, and the addition of reducing agents, such as ascorbic acid or 1,4-dithiothreitol, protected lysyl hydroxylase activity from homogentisic acid inhibition.
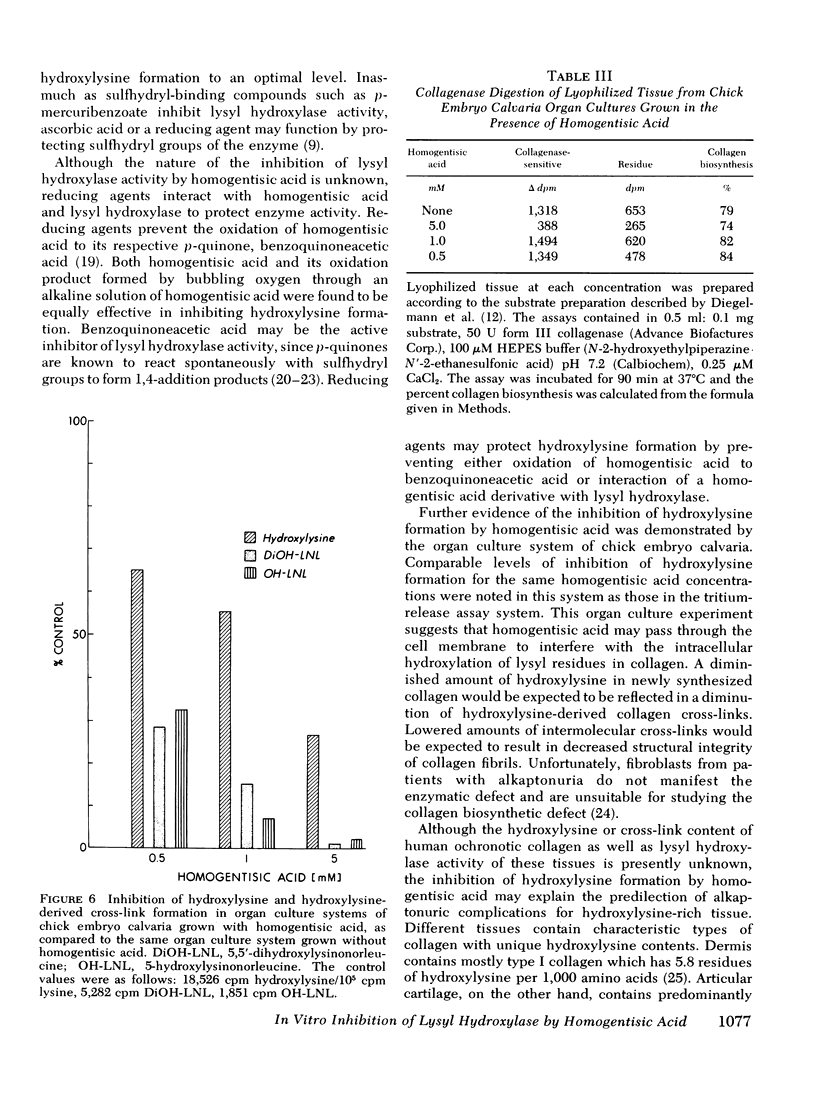
In organ cultures of embryonic chick calvaria, biosynthesis of hydroxylysine-derived intermolecular collagen cross-links was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by 0.5-5 mM homogentisic acid. Because homogentisic acid inhibits the formation of hydroxylysine in a cell-free assay and in organ cultures, this compound must pass into the cells of calvaria to inhibit intracellular hydroxylysine formation and subsequently to diminish the reducible intermolecular cross-links of the newly synthesized collagen. We propose that the inhibition of lysyl hydroxylase and the resulting hydroxylsine-deficient, structurally modified collagen may be clinically significant in the defective connective tissue found in alkaptonuric patients.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORNSTEIN P., PIEZ K. A. A BIOCHEMICAL STUDY OF HUMAN SKIN COLLAGEN AND THE RELATION BETWEEN INTRA- AND INTERMOLECULAR CROSS-LINKING. J Clin Invest. 1964 Sep;43:1813–1823. doi: 10.1172/JCI105055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Peach C. M., Fowler L. J. Chemistry of the collagen cross-links. Isolation and characterization of two intermediate intermolecular cross-links in collagen. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):819–831. doi: 10.1042/bj1170819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Robins S. P., Balian G. Biological significance of the intermolecular crosslinks of collagen. Nature. 1974 Sep 13;251(5471):105–109. doi: 10.1038/251105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. T., Cunningham L. W. Evidence for the linkage of a disaccharide to hydroxylysine in tropocollagen. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 10;241(17):3882–3888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diegelmann R. F., Peterkofsky B. Collagen biosynthesis during connective tissue development in chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1972 Jul;28(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diegelmann R. F., Rothkopf L. C., Cohen I. K. Measurement of collagen biosynthesis during wound healing. J Surg Res. 1975 Oct;19(4):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(75)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Glimcher M. J. Analysis of a crosslinked peptide from calf bone collagen: evidence that hydroxylysyl glycoside participates in the crosslink. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):663–671. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90764-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallop P. M., Blumenfeld O. O., Seifter S. Structure and metabolism of connective 801 tissue proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:617–672. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. A., Nester E. W. Regulatory enzymes of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis. II. The enzymology of feedback inhibition of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 25;241(14):3373–3380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang A. H., Piez K. A., Gross J. Characterization of the alpha-chains of chick skin collagen and the nature of the NH2-terminal cross-link region. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3648–3655. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivirikko K. I., Prockop D. J. Partial purification and characterization of protocollagen lysine hydroxylase from chick embryos. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):366–379. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Collagen cross-linking: identification of two cyanogen bromide peptides containing sites of intermolecular cross-link formation in cartilage collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 15;45(2):444–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90839-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Isolation and characterization of a collagen from chick cartilage containing three identical alpha chains. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1652–1659. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Lunde L. G. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha 1(II) chain of bovine and human cartilage collagen. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3153–3159. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Robertson P. B. The stability of collagen cross-links when derived from hydroxylsyl residues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 5;54(1):432–439. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90940-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L. Rapid assay for lysyl-protocollagen hydroxylase activity. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jan;45(1):202–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P., Bailey A. J. Isolation and characterization of glycosyl derivatives of the reducible cross-links in collagens. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jan 15;38(3):334–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Characterization and quantitative determination of the hydroxylysine-linked carbohydrate units of several collagens. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):602–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZANNONI V. G., MALAWISTA S. E., LA DU B. N. Studies on ochronosis. II. Studies on benzoquinoneacetic acid, a probale intermediate in the connective tissue pigmentation of alcaptonuria. Arthritis Rheum. 1962 Dec;5:547–556. doi: 10.1002/art.1780050603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


