Abstract
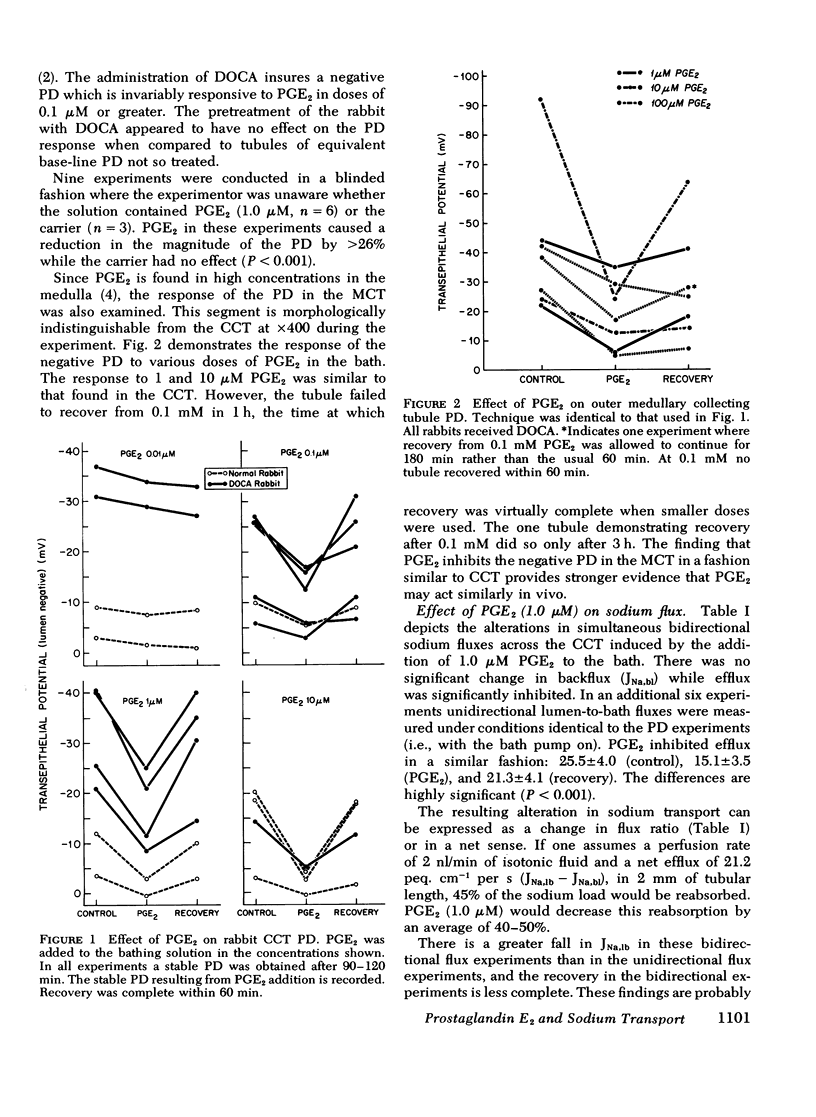
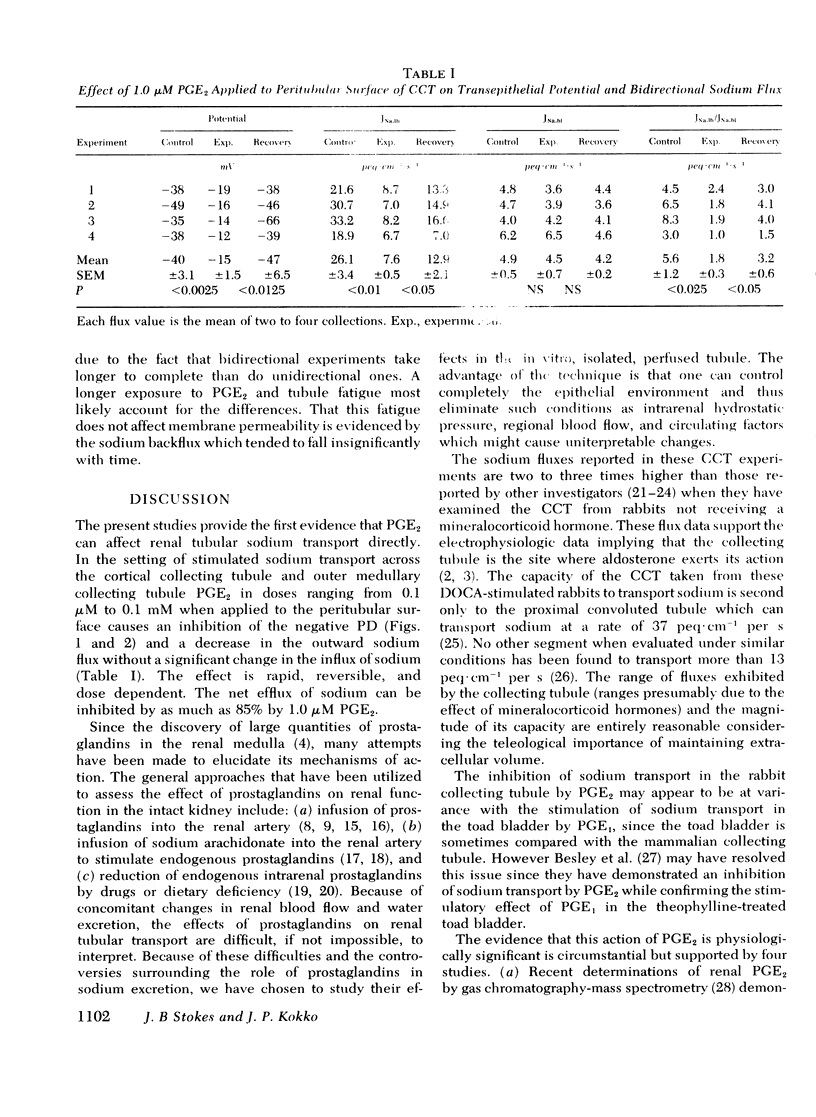
This study was designed to examine whether prostaglandin E2 can directly affect sodium transport across isolated perfused rabbit renal collecting tubules. Changes in transepithelial potential and isotopic sodium fluxes in response to peritubular prostaglandin E2 were measured. In addition, changes in transepithelial potential of the outer medullary collecting tubule in response to prostaglandin E2 were also measured. With few exceptions, all rabbits received 5 mg/day desoxycorticosterone acetate for 4-11 days before experimentation. The results of the experiments show that: (a) prostaglandin E2 inhibits the negative transepithelial potential in the cortical collecting tubule as well as the outer medullary collecting tubule; (b) prostaglandin E2 inhibits net sodium transport out of the lumen by inhibiting efflux while backflux is unaffected; (c) prostaglandin E2 produces this inhibition within 15 min, and the effects are dose dependent and reversible. These results suggest that prostaglandin E2 may modulate sodium transport in vivo and may contribute to the final regulation of sodium excretion.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beitch B. R., Beitch I., Zadunaisky J. A. The stimulation of chloride transport by prostaglandins and their interaction with epinephrine, theophylline, and cyclic AMP in the corneal epithelium. J Membr Biol. 1974;19(4):381–396. doi: 10.1007/BF01869987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besley G. T., Frith D. A., Snart R. S. An inhibitor of the toad bladder cyclic AMP system and theophylline-stimulated Na+ transport. Steroids Lipids Res. 1974;5(5-6):365–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer H. C. Storage life of prostaglandin E 2 in ethanol and saline. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Oct;23(10):804–805. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Green N. Function of the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1973 Mar;224(3):659–668. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.3.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. C., Splawinski J. A., Oates J. A., Nies A. S. Enhanced renal prostaglandin production in the dog. II. Effects on intrarenal hemodynamics. Circ Res. 1975 Jan;36(1):204–207. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.1.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichman M. P., Telfer N., Zia P., Speckart P., Golub M., Rude R. Role of prostaglandins in the pathogenesis of Bartter's syndrome. Am J Med. 1976 May 31;60(6):785–797. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90892-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine L. G., Bourgoignie J. J., Hwang K. H., Bricker N. S. On the influence of the natriuretic factor from patients with chronic uremia on the bioelectric properties and sodium transport of the isolated mammalian collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):590–597. doi: 10.1172/JCI108505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frindt G., Burg M. B. Effect of vasopressin on sodium transport in renal cortical collecting tubules. Kidney Int. 1972 Apr;1(4):224–231. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fülgraff G., Meiforth A. Effects of prostaglandin E 2 on excretion and reabsorption of sodium and fluid in rat kidneys (micropuncture studies). Pflugers Arch. 1971;330(3):243–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00588615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. R., Jr, Frölich J. C., Bowden R. E., Taylor A. A., Keiser H. R., Seyberth H. W., Oates J. A., Bartter F. C. Bartter's syndrome: a disorder characterized by high urinary prostaglandins and a dependence of hyperreninemia on prostaglandin synthesis. Am J Med. 1976 Jul;61(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Kurg M. B., Obloff J. The nature of transtubular Na and K transport in isolated rabbit renal collecting tubules. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1815–1826. doi: 10.1172/JCI106399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Orloff J. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on the permeability response of the isolated collecting tubule to vasopressin, adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, and theophylline. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1154–1161. doi: 10.1172/JCI105804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. B., Barter F. C. Effects of prostaglandins E 1 , A 1 , and F 2 on renal handling of salt and water. Am J Physiol. 1973 Jul;225(1):218–224. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.1.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. B., Imai M., Kokko J. P. A functional comparison of the cortical collecting tubule and the distal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1284–1294. doi: 10.1172/JCI108048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. B., Kokko J. P. Effects of aldosterone and potassium-sparing diuretics on electrical potential differences across the distal nephron. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):82–89. doi: 10.1172/JCI108625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Kokko J. P. Sodium chloride, urea, and water transport in the thin ascending limb of Henle. Generation of osmotic gradients by passive diffusion of solutes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):393–402. doi: 10.1172/JCI107572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschenbaum M. A., Stein J. H. The effect of inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis on urinary sodium excretion in the conscious dog. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):517–521. doi: 10.1172/JCI108304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Characteristics of NaCl and water transport in the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):69–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI106485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P. Proximal tubule potential difference. Dependence on glucose on glucose, HCO 3 , and amino acids. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1362–1367. doi: 10.1172/JCI107308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P. Sodium chloride and water transport in the descending limb of Henle. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1838–1846. doi: 10.1172/JCI106401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson C., Anggård E. Mass spectrometric determination of prostaglandin E2, F2alpha and A2 in the cortex and medulla of the rabbit kidney. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;28(4):326–328. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb04169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. B., Crowshaw K., Takman B. H., Attrep K. A. The identification of prostaglandins E(2), F(2alpha) and A(2) from rabbit kidney medulla. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1251–1260. doi: 10.1042/bj1051251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson L. C., Sharp G. W. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on sodium transport and osmotic water flow in the toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1046–1052. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Maldonado M., Tsaparas N., Eknoyan G., Suki W. N. Renal actions of prostaglandins: comparison with acetylcholine and volume expansion. Am J Physiol. 1972 May;222(5):1147–1152. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.5.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen H. M., Andersen H. On the localization of a prostaglandin-dehydrogenase activity in the kidney. Histochemie. 1968;14(2):189–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00306340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J., Simone P. G., Silbergleit A. Effects of prostaglandin deficiency on natriuresis, diuresis, and blood pressure. Prostaglandins. 1974 Mar 10;5(5):435–440. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. H., Reineck H. J. The role of the collecting duct in the regulation of excretion of sodium and other electrolytes. Kidney Int. 1974 Jul;6(1):1–9. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner L. C., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Ion transport in cortical collecting tubule; effect of amiloride. Am J Physiol. 1974 Aug;227(2):453–459. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandhoy J. W., Ott C. E., Schneider E. G., Willis L. R., Beck N. P., Davis B. B., Knox F. G. Effects of prostaglandins E1 and E2 on renal sodium reabsorption and Starling forces. Am J Physiol. 1974 May;226(5):1015–1021. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.5.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum J., Splawinski J. A., Oates J. A., Nies A. S. Enhanced renal prostaglandin production in the dog. I. Effects on renal function. Circ Res. 1975 Jan;36(1):197–203. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verberckmoes R., van Damme B B., Clement J., Amery A., Michielsen P. Bartter's syndrome with hyperplasia of renomedullary cells: successful treatment with indomethacin. Kidney Int. 1976 Mar;9(3):302–307. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



